Enterprise Software Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: enterprise-software
Enterprise Software Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Enterprise Software market, covering market size, growth rates, segmentation, and regional insights from 2023 to 2033, helping stakeholders understand the forecasted landscape and make informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
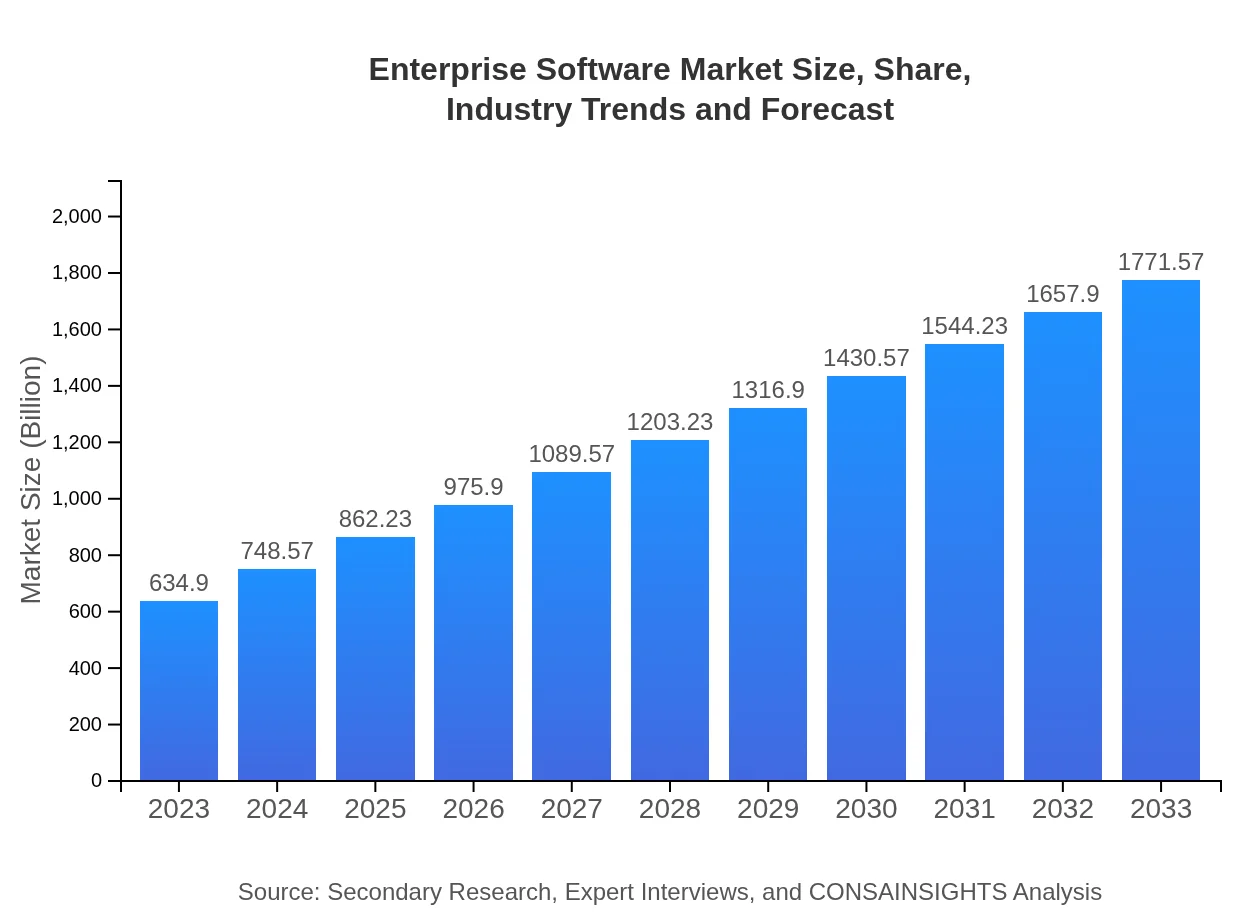
| 2023 Market Size | $634.90 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $1771.57 Billion |
| Top Companies | Salesforce, Microsoft, SAP, Oracle, IBM |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Enterprise Software Market Overview
Customize Enterprise Software Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Enterprise Software market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Enterprise Software's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Enterprise Software
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Enterprise Software market in 2023?
Enterprise Software Industry Analysis
Enterprise Software Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Enterprise Software Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Enterprise Software Market Report:
Europe's market is anticipated to grow from $164.12 billion in 2023 to $457.95 billion by 2033. The European region emphasizes compliance with data protection regulations, which is driving the demand for enterprise software solutions to manage risk and protect customer data effectively.Asia Pacific Enterprise Software Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the enterprise software market is projected to grow from $125.65 billion in 2023 to $350.59 billion by 2033, driven by rapid digitalization initiatives across emerging economies, especially in India and China. Companies are investing heavily in cloud solutions to enhance operational capabilities, improving the efficiency of business processes and scalability.North America Enterprise Software Market Report:
In North America, the enterprise software market, valued at $239.74 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $668.94 billion by 2033. The region is the leading market for enterprise solutions due to a highly competitive business environment where companies prioritize adopting innovative technologies to drive efficiency and growth.South America Enterprise Software Market Report:
The South American market is expected to see growth from $48.44 billion in 2023 to $135.17 billion by 2033. The expansion is fueled by the increasing adoption of cloud computing and mobile solutions across various sectors, enhancing operational performance and customer engagement.Middle East & Africa Enterprise Software Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is forecasted to increase from $56.95 billion in 2023 to $158.91 billion by 2033. The growth is supported by the rising emphasis on digital transformation, investment in infrastructure, and increasing adoption of enterprise applications among various sectors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
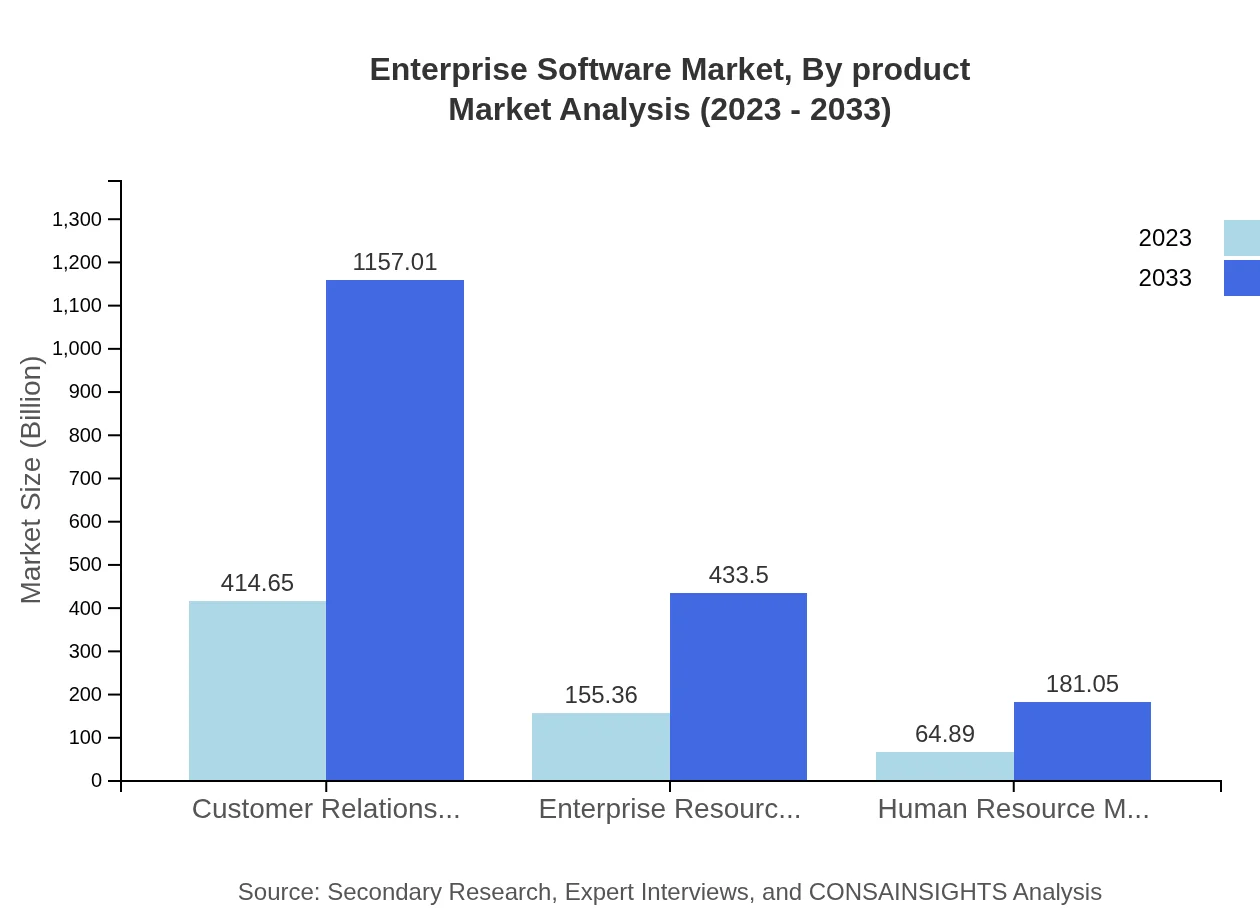
Enterprise Software Market Analysis By Product
The product segmentation indicates that Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is expected to grow from $414.65 billion in 2023 to $1,157.01 billion in 2033. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) stands at $155.36 billion in 2023, with projections of reaching $433.50 billion by 2033. Other significant segments include Financial Services and Business Intelligence, which are anticipated to maintain substantial market shares throughout the forecast period.
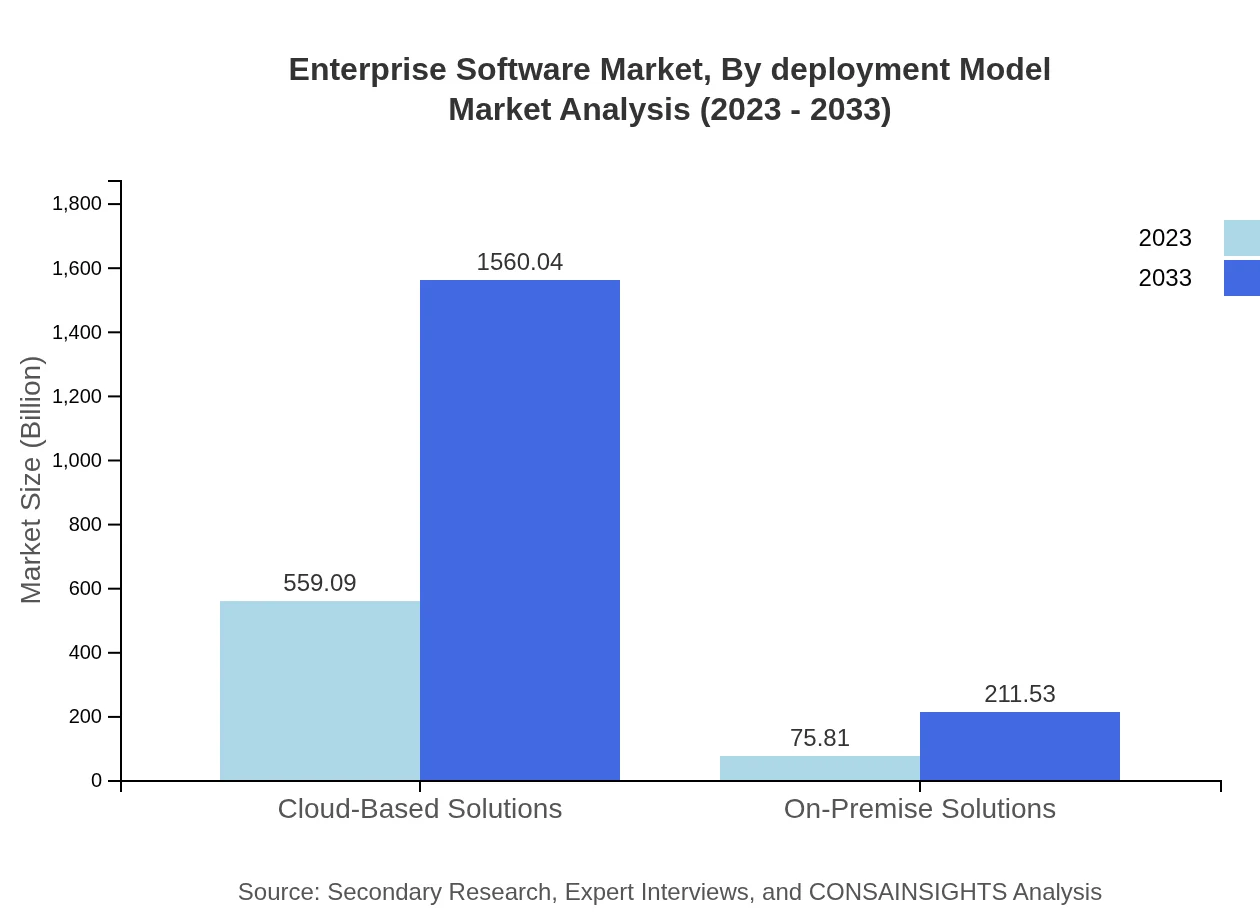
Enterprise Software Market Analysis By Deployment Model
Cloud-based solutions dominate the deployment model segment, expected to rise from $559.09 billion in 2023 to $1,560.04 billion in 2033, while on-premise solutions will grow from $75.81 billion to $211.53 billion. The shift towards cloud environments underscores the growing preference among businesses for scalable and flexible solutions.
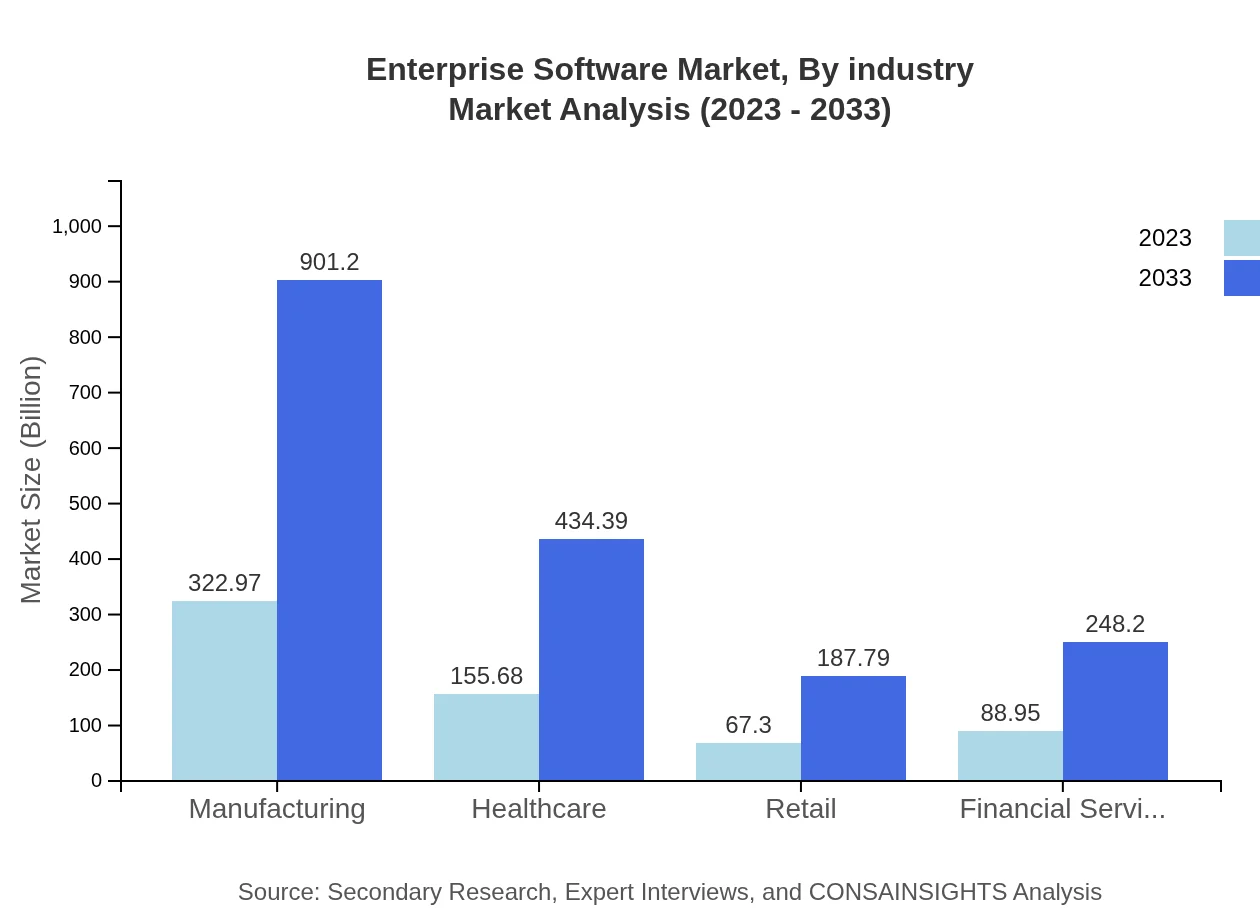
Enterprise Software Market Analysis By Industry
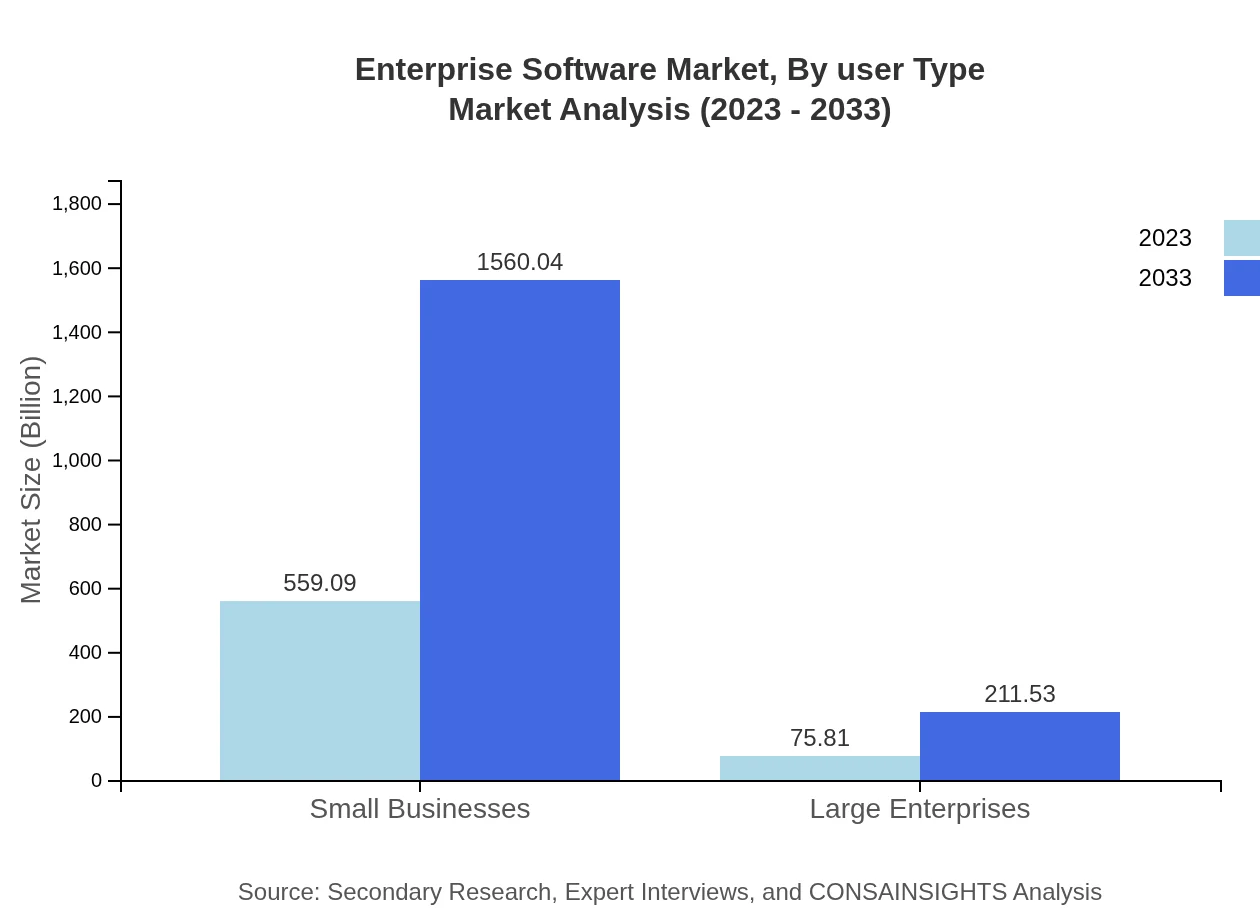
Segment analysis by industry reveals that small businesses will see the most significant growth, forecasted to expand from $559.09 billion in 2023 to $1,560.04 billion by 2033. Large enterprises will grow from $75.81 billion to $211.53 billion in revenue, reflecting sustained demand across sectors like manufacturing and healthcare.
Enterprise Software Market Analysis By User Type
The market for small businesses is expected to dominate user-type segmentation, intended to experience substantial growth, maintaining a strong share in the market. In contrast, large enterprises maintain a steady segment representing evolving needs for integrated and robust enterprise solutions.
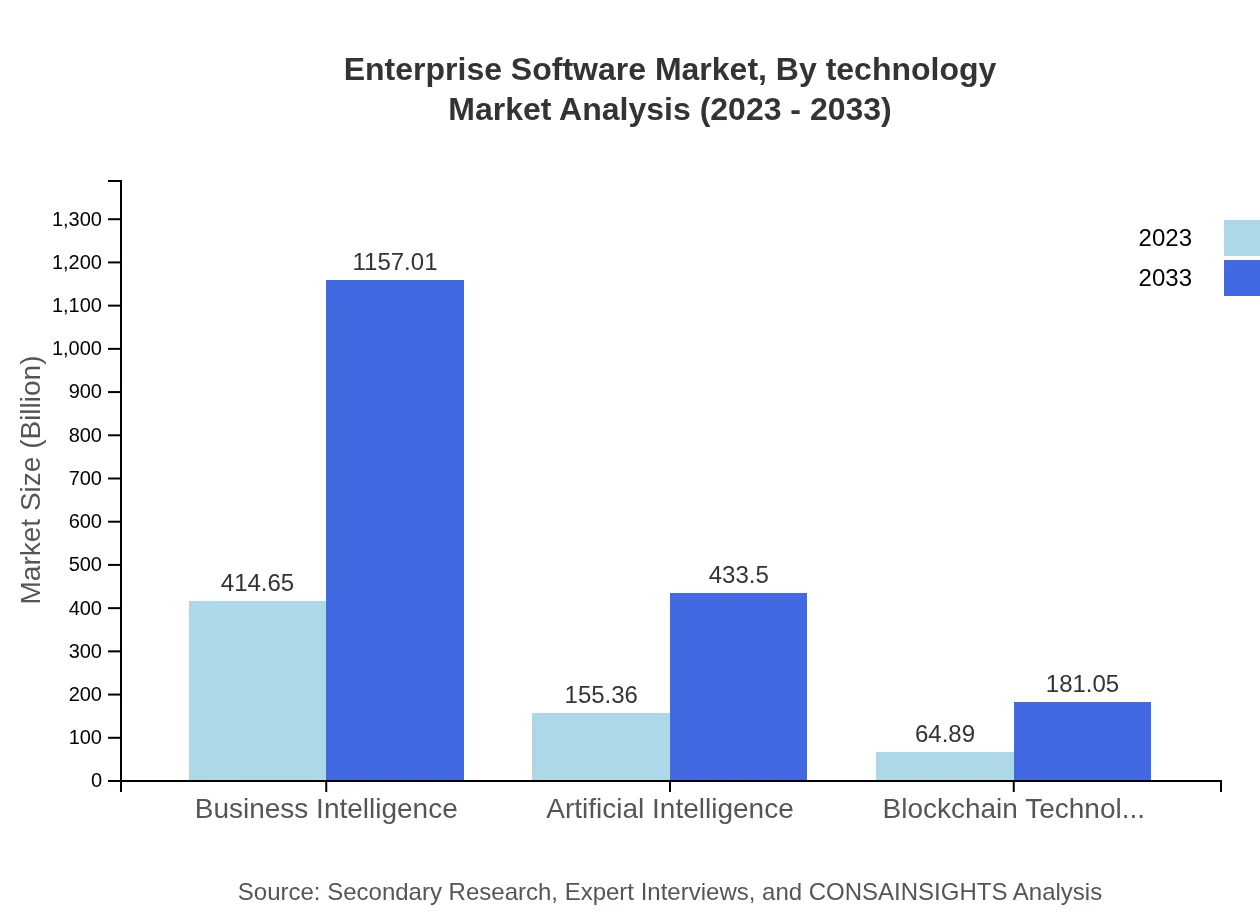
Enterprise Software Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements such as Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain Technology are increasingly becoming essential in the enterprise software landscape. The AI segment is projected to grow from $155.36 billion to $433.50 billion, illustrating AI's pivotal role in data processing and decision-making, whereas blockchain applications are gaining traction, projected to grow to $181.05 billion by 2033.
Enterprise Software Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Enterprise Software Industry
Salesforce:
Salesforce is a leading provider of CRM solutions that empower organizations to improve customer relationships and drive sales through innovative cloud-based technologies.Microsoft:
Microsoft offers a broad spectrum of enterprise software solutions, including Azure, Office 365, and Dynamics 365, enabling businesses to enhance productivity and workflow efficiencies.SAP:
SAP specializes in ERP solutions and has a robust suite of applications that help businesses manage operations effectively, leveraging real-time data analytics.Oracle:
Oracle provides a comprehensive range of enterprise software, from database management systems to cloud applications, recognized for their ability to handle complex business functions.IBM:
IBM's enterprise solutions focus on data management, AI, and analytics, playing an integral role in helping businesses transform and leverage their data assets.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of enterprise software?
The global enterprise software market is valued at approximately $634.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.4%, potentially reaching significant heights by 2033. This growth indicates a strong demand for enterprise solutions across various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the enterprise software industry?
Key players in the enterprise software industry include leading corporations such as Microsoft, Salesforce, Oracle, SAP, and IBM. These companies dominate the market with innovative solutions across various sectors, including customer relationship management and enterprise resource planning.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the enterprise software industry?
Growth in the enterprise software industry is primarily driven by the increasing demand for automation, the rise in cloud computing, and the need for enhanced data analytics. Investment in digital transformation and the integration of advanced technologies further accentuate this growth.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the enterprise software market?
The fastest-growing region in the enterprise software market is Asia Pacific, projected to reach approximately $350.59 billion by 2033, up from $125.65 billion in 2023. North America follows closely, expected to grow to $668.94 billion during the same period.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the enterprise software industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights specializes in providing customized market report data tailored to the enterprise software industry. This includes specific insights and analyses based on client requirements, facilitating informed decision-making for businesses.
What deliverables can I expect from this enterprise software market research project?
From the enterprise software market research project, you can expect detailed market analysis reports, segmentation insights, competitive landscape reviews, and actionable recommendations. These deliverables will aid in strategic planning and market positioning.
What are the market trends of enterprise software?
Current market trends in enterprise software include a shift towards cloud-based solutions, increased integration of AI and machine learning, and growing focus on cybersecurity. Additionally, organizations are prioritizing mobile accessibility and user-friendly interfaces in software development.