Failure Analysis Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: failure-analysis
Failure Analysis Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the Failure Analysis market, examining key trends, growth potential, competitive landscape, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
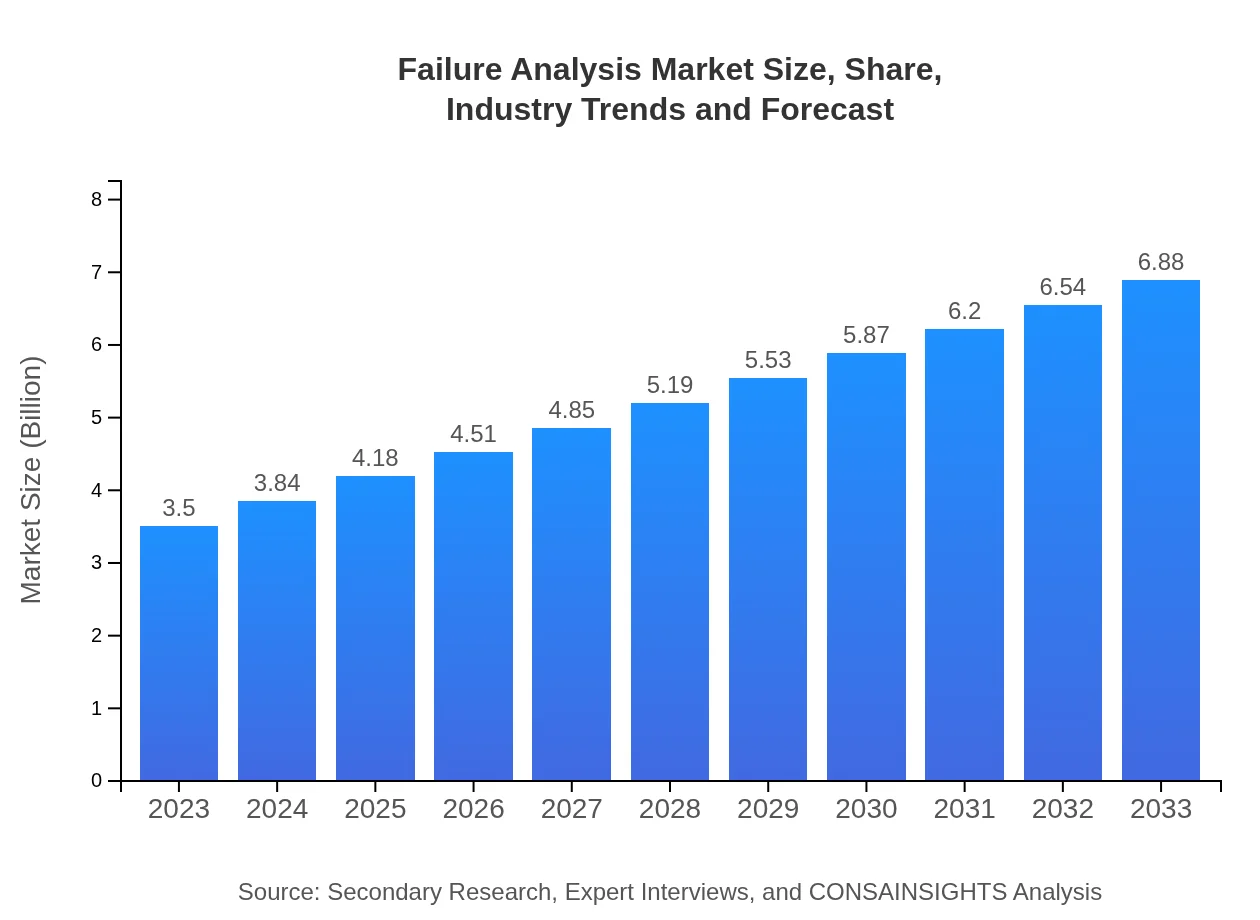
| 2023 Market Size | $3.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $6.88 Billion |
| Top Companies | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carl Zeiss AG, KLA Corporation, Horiba Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Failure Analysis Market Overview
Customize Failure Analysis Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Failure Analysis market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Failure Analysis's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Failure Analysis
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Failure Analysis market in 2023?
Failure Analysis Industry Analysis
Failure Analysis Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Failure Analysis Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Failure Analysis Market Report:
In Europe, the market size is approximately $0.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to increase to $1.72 billion by 2033, driven by strong regulations on product safety and a robust manufacturing sector.Asia Pacific Failure Analysis Market Report:
In 2023, the Failure Analysis market in the Asia Pacific region is valued at $0.70 billion, projected to grow to $1.37 billion by 2033, highlighting a robust CAGR driven by the rapid industrialization and personnel skilled in failure analysis techniques.North America Failure Analysis Market Report:
North America, holding a market share of $1.16 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow to $2.28 billion by 2033, supported by leadership in technological innovation and a high density of manufacturing and automotive industries.South America Failure Analysis Market Report:
The South American market is currently valued at $0.29 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $0.57 billion by 2033, driven by growing technological adoption in manufacturing processes but facing challenges due to economic fluctuations.Middle East & Africa Failure Analysis Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market size stands at $0.48 billion in 2023, expected to reach $0.95 billion by 2033 as industrial growth and increasing focus on quality in manufacturing emerge.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
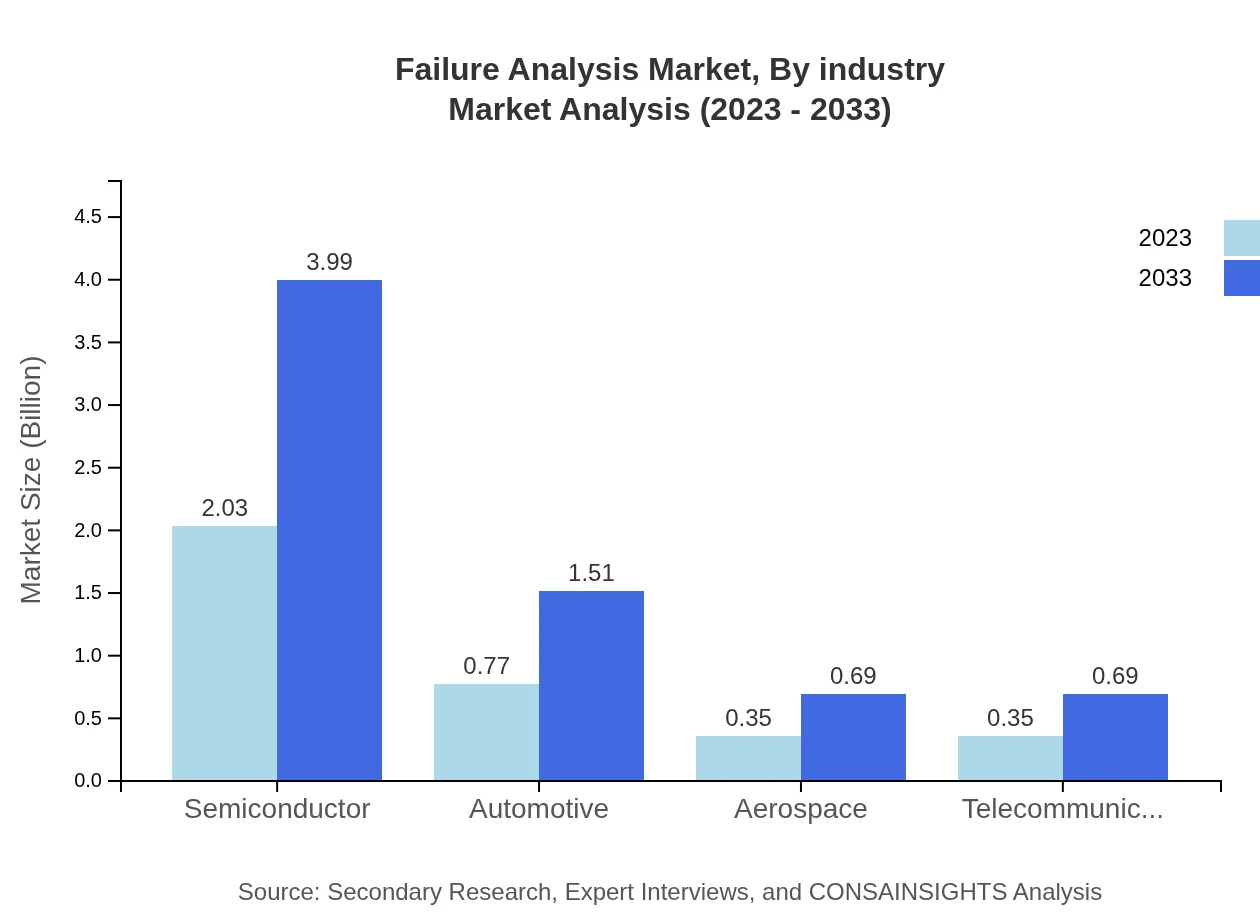
Failure Analysis Market Analysis By Industry
The Failure Analysis market is significantly influenced by the Semiconductor industry, valued at $2.03 billion in 2023, which is projected to grow to $3.99 billion by 2033 due to the complexity of semiconductor devices. The Automotive sector follows closely, with current values at $0.77 billion expected to rise to $1.51 billion, reflecting the importance of safety and reliability in vehicles.
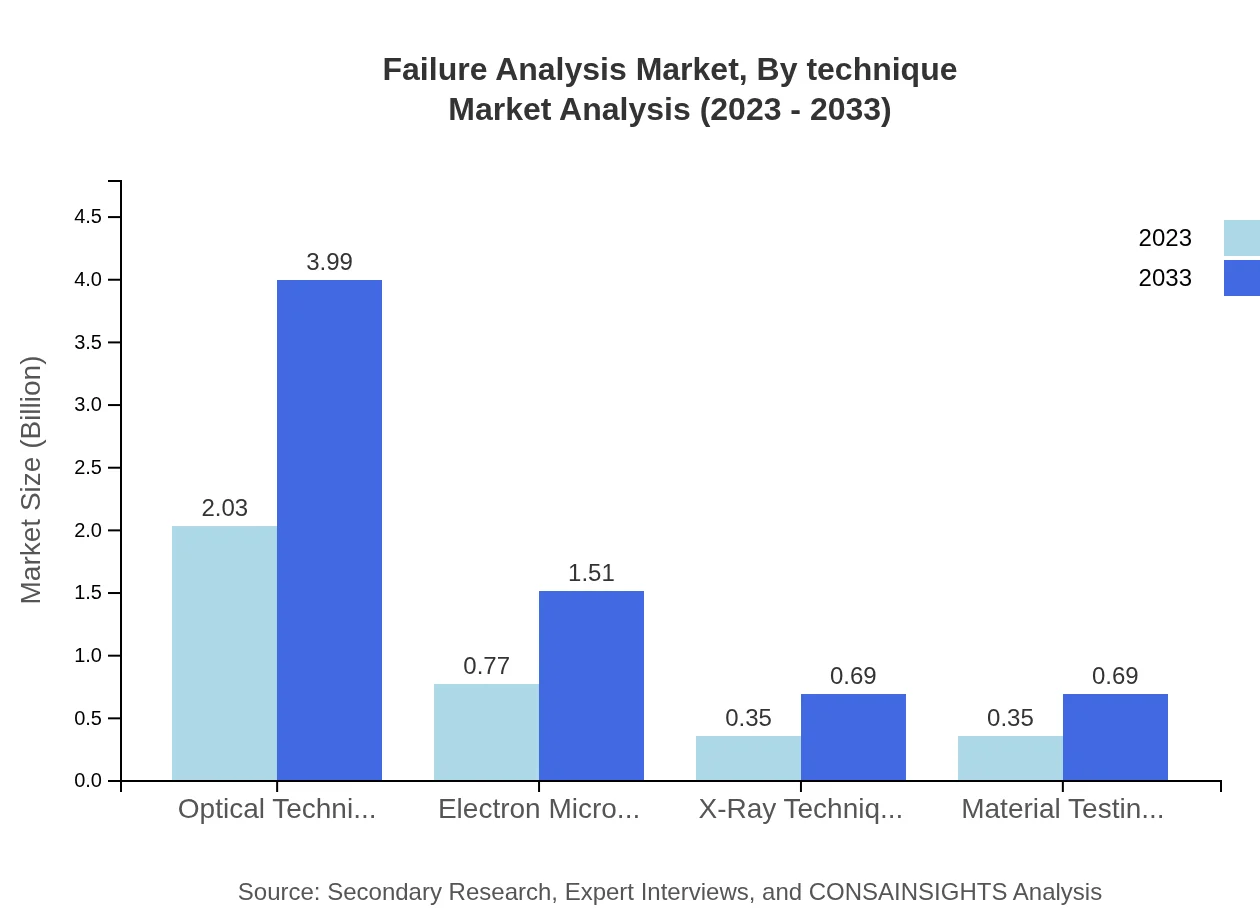
Failure Analysis Market Analysis By Technique
Optical Techniques dominate the market, valued at $2.03 billion in 2023, with expectations of reaching $3.99 billion by 2033. Electron Microscopy Techniques are significant contributors as well, showcasing capacity increases from $0.77 billion to $1.51 billion across the same timeline. Both are crucial for providing detailed insights into materials and component failures.
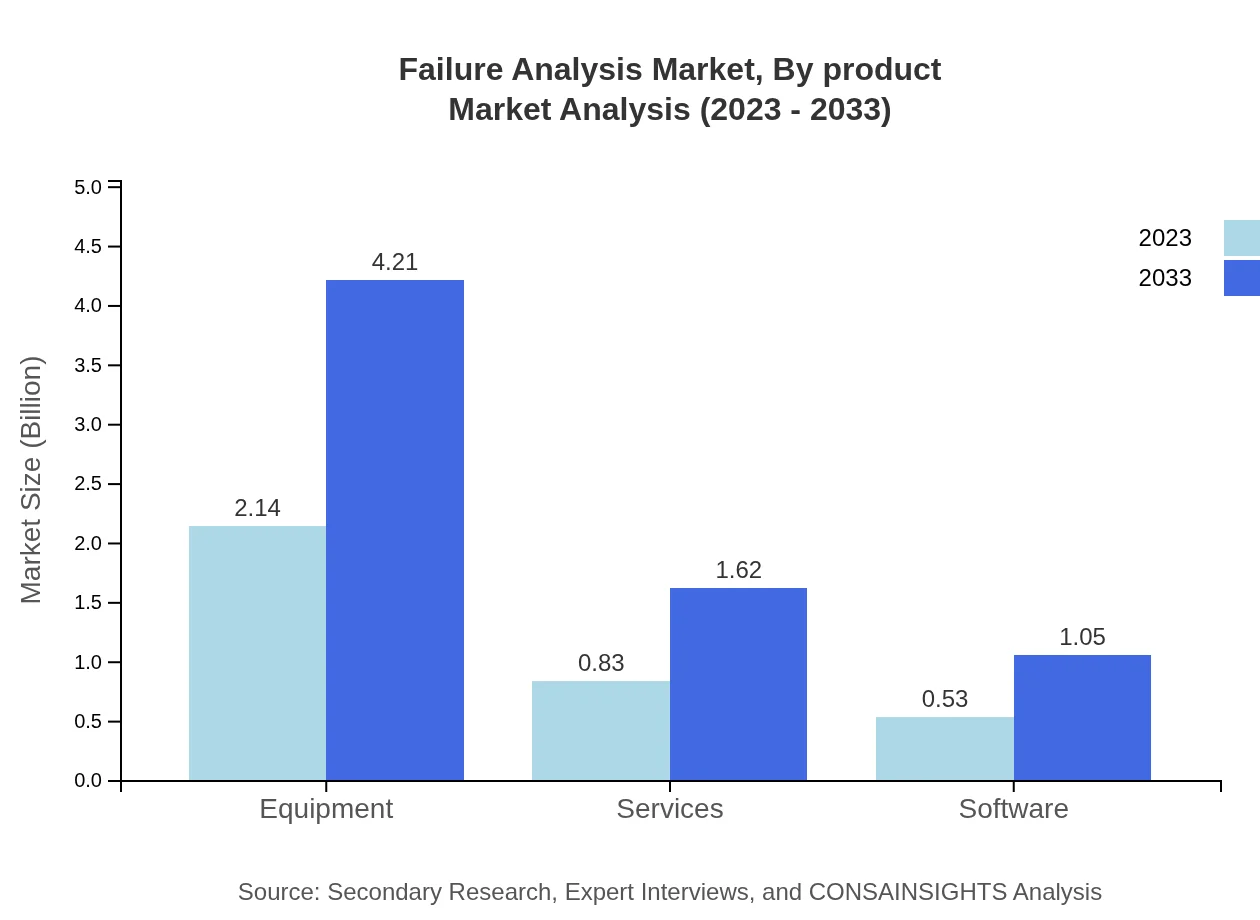
Failure Analysis Market Analysis By Product
Equipment holds a substantial market size of $2.14 billion as of 2023, with growth projected to $4.21 billion by 2033. This is complemented by services at $0.83 billion, forecasted to rise to $1.62 billion, reflecting the flexibility and expertise increasingly demanded from analysis service providers.
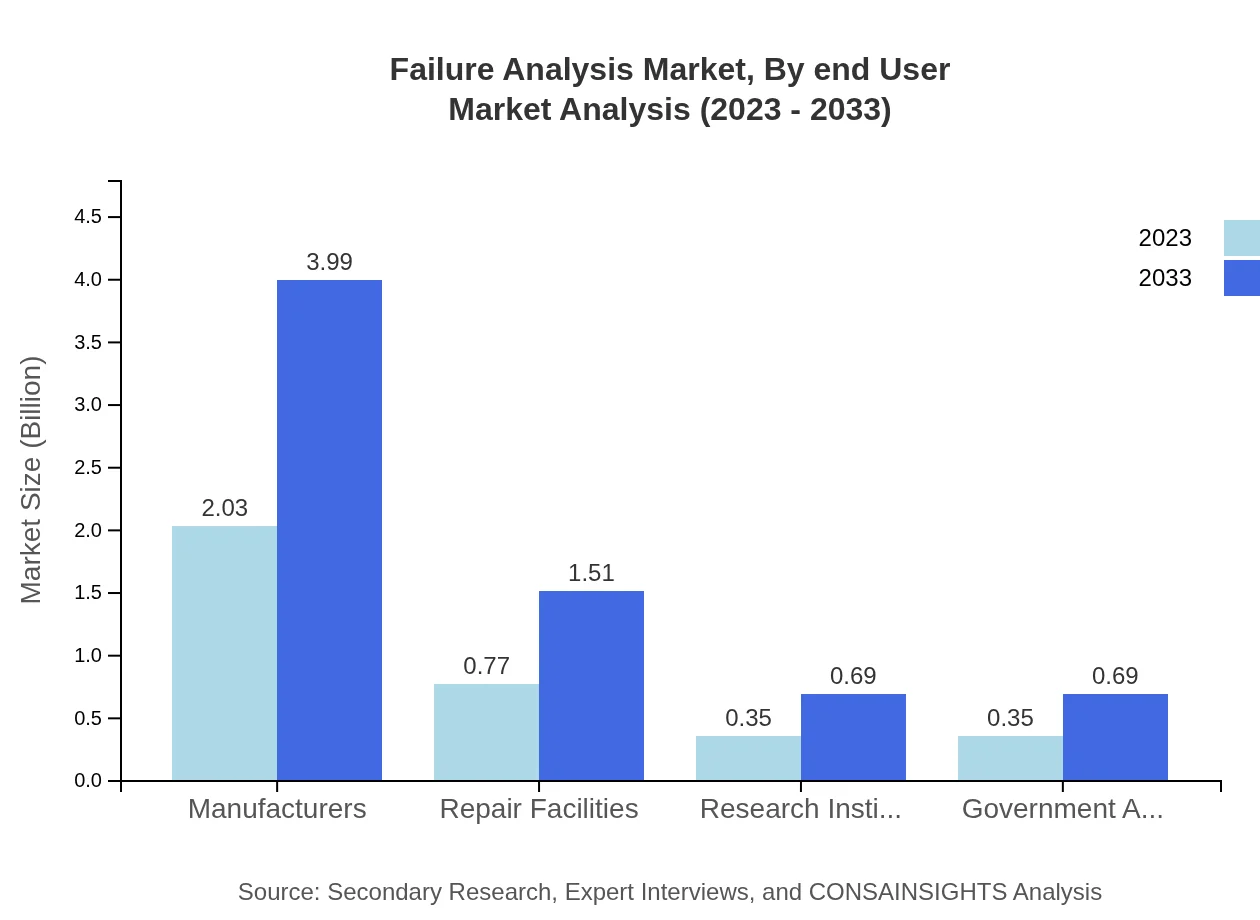
Failure Analysis Market Analysis By End User
Manufacturers show considerable investment in failure analysis, valued at $2.03 billion in 2023, expected to double by 2033. Repair Facilities account for another critical segment, starting at $0.77 billion in 2023 and aiming for $1.51 billion by 2033, illustrating the essential need for ongoing product evaluation and maintenance.
Failure Analysis Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Failure Analysis Industry
Thermo Fisher Scientific:
A leader in electron and optical microscopy technologies, providing advanced instruments for failure analysis across multiple sectors.Carl Zeiss AG:
Known for its high-performance imaging equipment, Zeiss specializes in optical and electron microscopy products crucial for effective failure analysis.KLA Corporation:
A prominent provider of process control and yield management solutions, KLA’s technologies are essential in the semiconductor industry for competitor analysis.Horiba Ltd.:
Offers analytical and measuring equipment, royalty solutions, and advanced technology products for failure diagnosis across various materials.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Failure Analysis?
The Failure Analysis market is projected to grow from $3.5 billion in 2023 to substantial figures by 2033, with a CAGR of 6.8%. This growth reflects increasing investments in quality assurance and operational efficiency across various industries.
What are the key market players or companies in this Failure Analysis industry?
Key players in the Failure Analysis industry include leading technology firms, specialized equipment manufacturers, and service providers focused on quality assurance. These companies leverage advanced technologies to enhance reliability and safety in products across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Failure Analysis industry?
The growth in the Failure Analysis industry is driven by rising demand for quality assurance in manufacturing, advancements in technologies, and stringent regulations governing product safety. Increasing complexities in products and devices also heighten the need for effective failure analysis techniques.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Failure Analysis?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the Failure Analysis market, with expected growth from $0.70 billion in 2023 to $1.37 billion by 2033. North America follows closely, escalating from $1.16 billion to $2.28 billion in the same period, indicating robust demand.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Failure Analysis industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients in the Failure Analysis industry. This includes detailed segment analysis, regional data, and insights that align with organizational goals and market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this Failure Analysis market research project?
Expected deliverables from the Failure Analysis market research project include comprehensive reports on market trends, segmentation data, competitive analysis, and detailed forecasts. Clients will receive actionable insights and strategic recommendations based on thorough data analysis.
What are the market trends of Failure Analysis?
Current market trends in Failure Analysis include a rise in automation and digitalization in testing processes, increased integration of machine learning for predictive maintenance, and growing incorporation of advanced materials analytics. These trends reflect industry shifts towards enhanced safety and operational efficiency.