Food Cold Chain Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: food-cold-chain
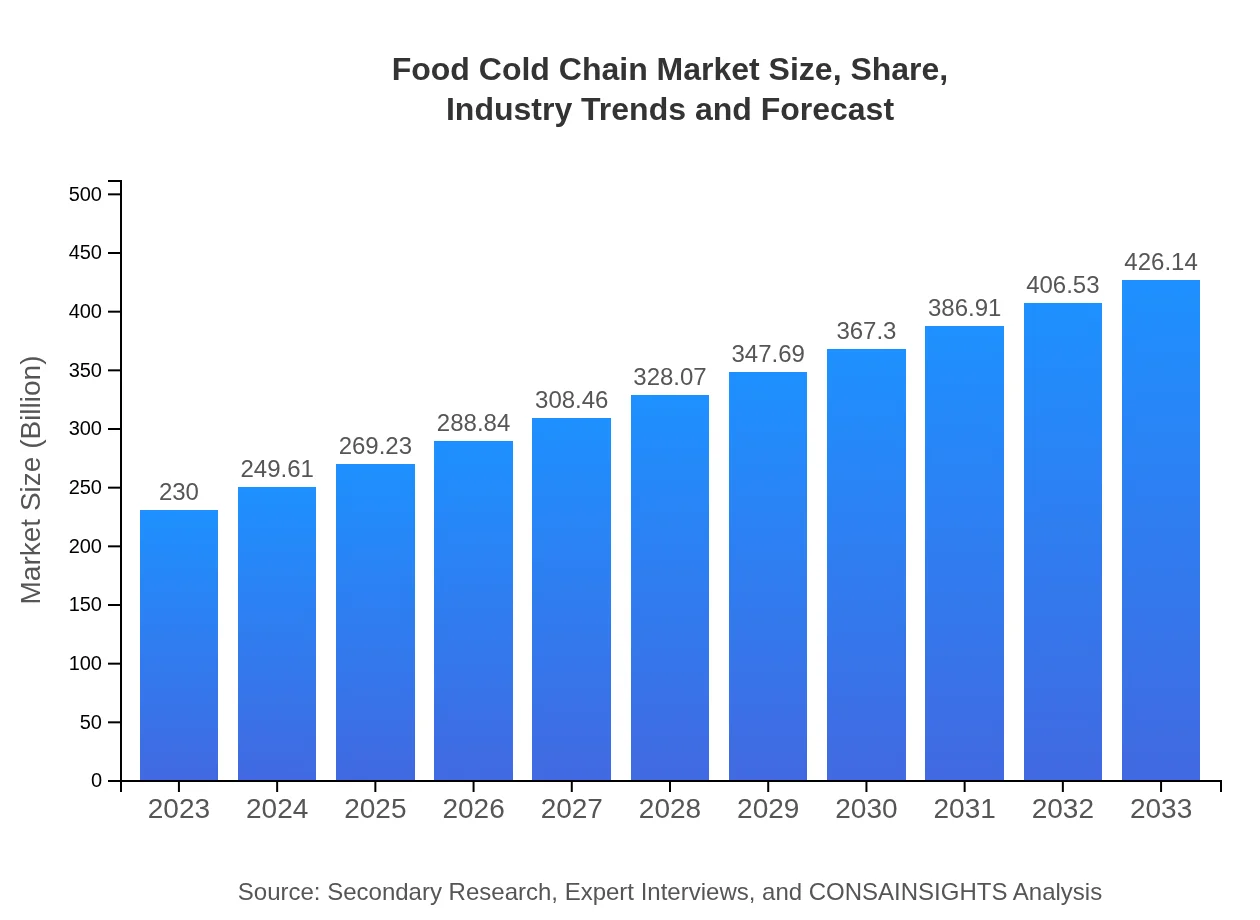
Food Cold Chain Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Food Cold Chain market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market trends, segmentations, and regional insights to guide stakeholders and investors in making informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $230.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $426.14 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cold Chain Technologies, Lineage Logistics, Americold Realty Trust, United Technologies Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Food Cold Chain Market Overview
Customize Food Cold Chain Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Food Cold Chain market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Food Cold Chain's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Food Cold Chain
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Food Cold Chain market in 2023?
Food Cold Chain Industry Analysis
Food Cold Chain Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Food Cold Chain Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Food Cold Chain Market Report:
Europe's market size in 2023 stands at $64.95 billion, predicted to escalate to $120.34 billion by 2033. The region's commitment to sustainability and food waste reduction contributes to the robust cold chain investments.Asia Pacific Food Cold Chain Market Report:
In 2023, the Food Cold Chain market in the Asia Pacific region is valued at $47.33 billion, expected to grow to $87.70 billion by 2033. This growth is supported by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing emphasis on food safety standards.North America Food Cold Chain Market Report:
North America leads the market with an expected size of $77.35 billion in 2023, growing to $143.31 billion by 2033. Here, advanced technology adoption and high food safety standards significantly drive the market growth.South America Food Cold Chain Market Report:
The South American market segment accounts for a valuation of $11.78 billion in 2023, with projections rising to $21.82 billion by 2033. The increase stems from enhanced cold storage infrastructure and rising demand for fresh food products.Middle East & Africa Food Cold Chain Market Report:
The Middle Eastern and African market is poised at $28.59 billion in 2023, expected to reach $52.97 billion by 2033. Key drivers include an expanding retail market and increasing foreign investment in the food sector.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
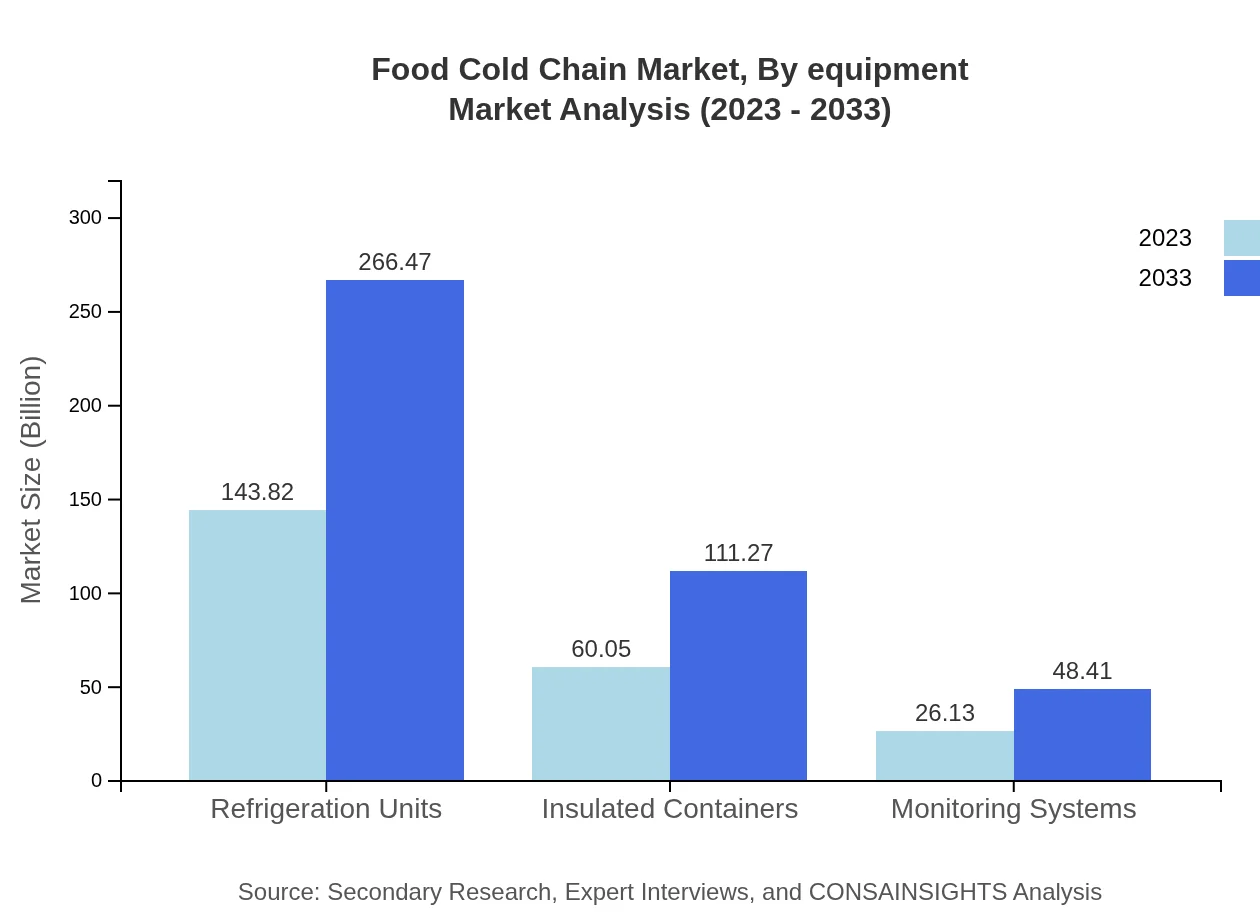
Food Cold Chain Market Analysis By Equipment
In the Food Cold Chain Market, refrigeration units dominate with a market size of $143.82 billion in 2023, projected to rise to $266.47 billion by 2033. Insulated containers, monitoring systems, and distribution centers also play significant roles, addressing diverse cold chain needs across sectors.
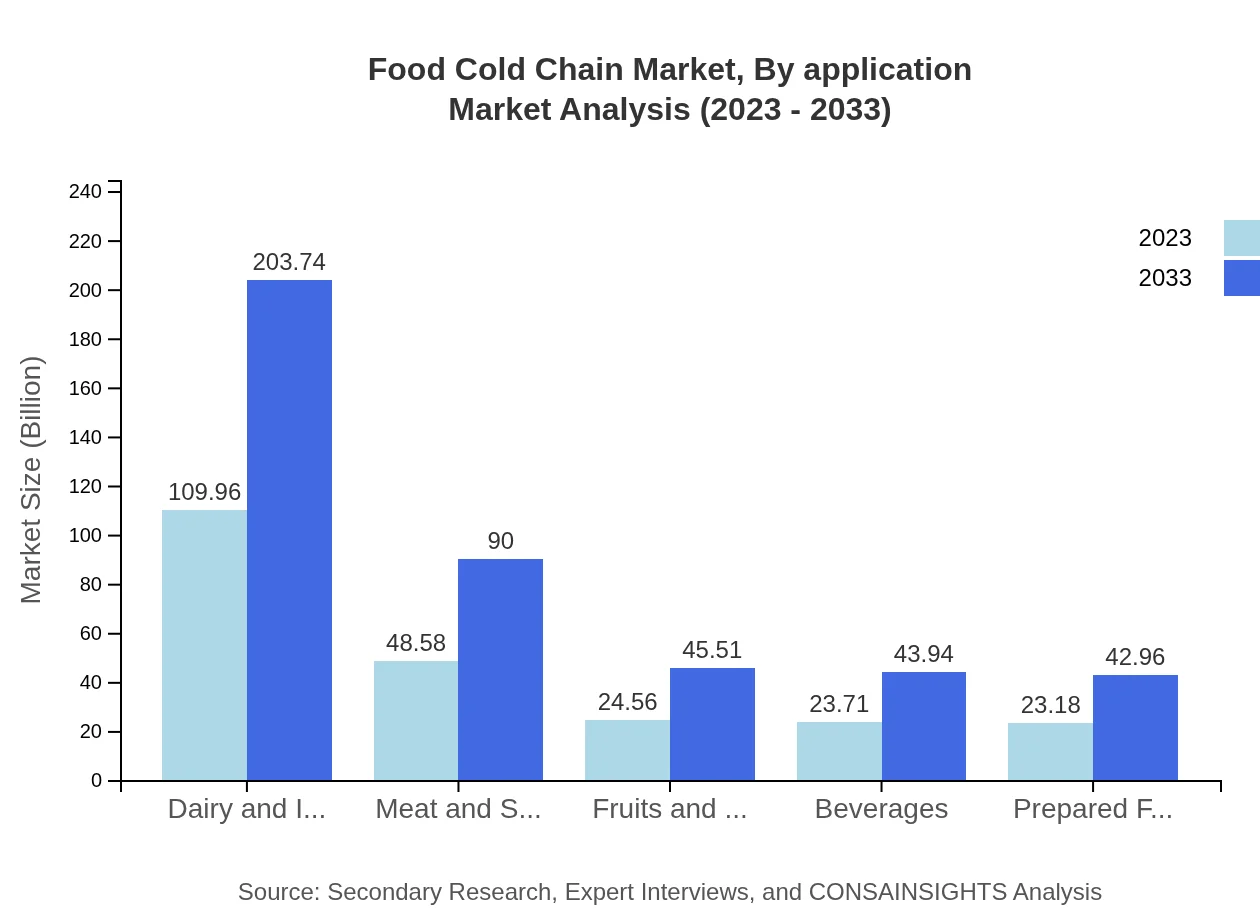
Food Cold Chain Market Analysis By Application
The market segmentation by application includes retail, food service, food manufacturers, and wholesale distributors. Retail holds the largest share, amounting to $118.73 billion in 2023, rising to $219.97 billion in 2033, driven by the growth of supermarkets and online grocery delivery services.
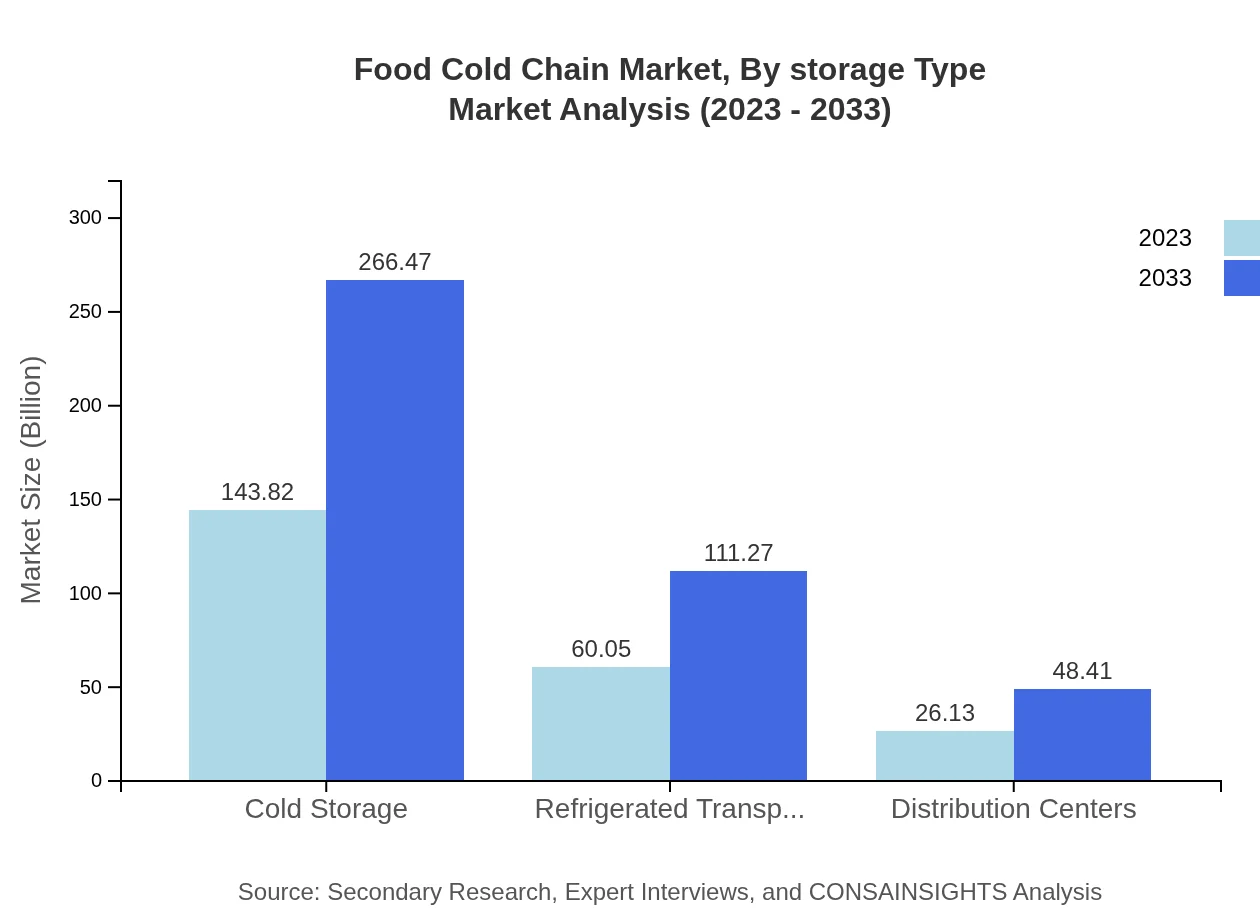
Food Cold Chain Market Analysis By Storage Type
Cold storage facilities account for a significant part of the market, reporting a size of $143.82 billion in 2023, anticipated to double by 2033. The evolution of technology in cold storage solutions is driving enhancements in operational efficiency and energy management.
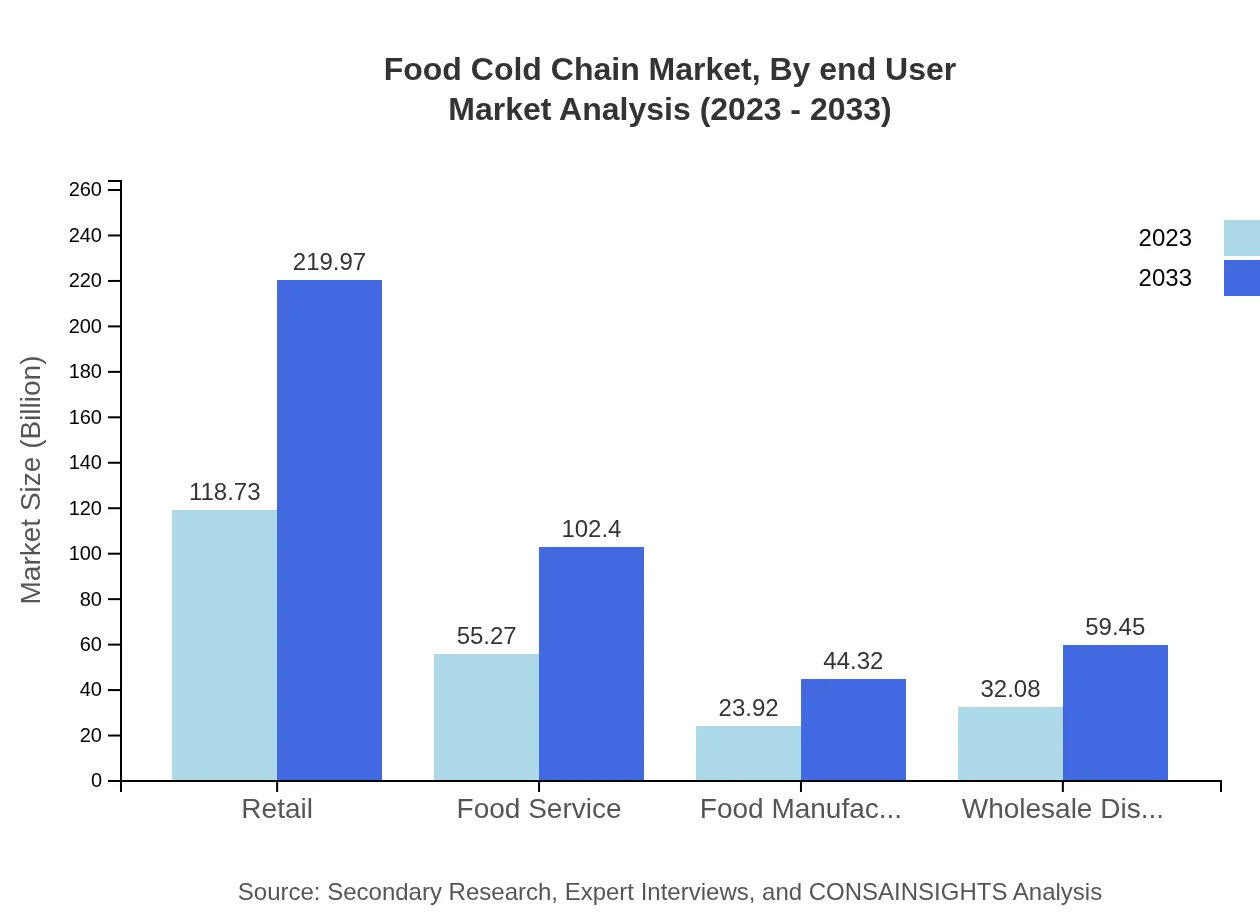
Food Cold Chain Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment analysis indicates retail as a crucial player, reflecting $118.73 billion in market size in 2023, with incremental growth anticipated in the food service and food manufacturing sectors as well.
Food Cold Chain Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Food Cold Chain Industry
Cold Chain Technologies:
Specializes in temperature-controlled packaging solutions and logistics services to ensure food products maintain optimal temperatures throughout the supply chain.Lineage Logistics:
One of the largest temperature-controlled logistics companies worldwide, providing integrated logistics services across various regions.Americold Realty Trust:
Leading cold storage and logistics provider, focusing on food safety and technological innovations in maintaining cold chain efficiency.United Technologies Corporation:
Provides advanced refrigeration and HVAC systems essential for maintaining cold chain integrity across various applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Food Cold Chain?
The global Food Cold Chain market is valued at $230 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2%, projecting substantial growth into the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the Food Cold Chain industry?
Key market players include major logistics companies, refrigeration manufacturers, and food distributors. These companies are pivotal in establishing best practices and driving innovation within the cold chain sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Food Cold Chain industry?
Growth is primarily driven by increasing demand for perishable goods, advancements in refrigeration technology, regulatory compliance for food safety, and rising consumer preferences for fresh food products.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Food Cold Chain?
The Asia Pacific region is identified as the fastest-growing market for Food Cold Chain, with an expected growth from $47.33 billion in 2023 to $87.70 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Food Cold Chain industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the Food Cold Chain industry, providing in-depth insights and analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this Food Cold Chain market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, insights on trends, competitive landscapes, regional market breakdowns, and forecasts for future growth across segments and regions.
What are the market trends of Food Cold Chain?
Current trends include the rise of automation in cold storage, increasing investments in refrigerated transport, sustainability measures in logistics, and the integration of IoT for real-time monitoring.