Food Service Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: food-service
Food Service Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Food Service market, encompassing market size, growth forecasts, industry trends, segmentation, and regional insights from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
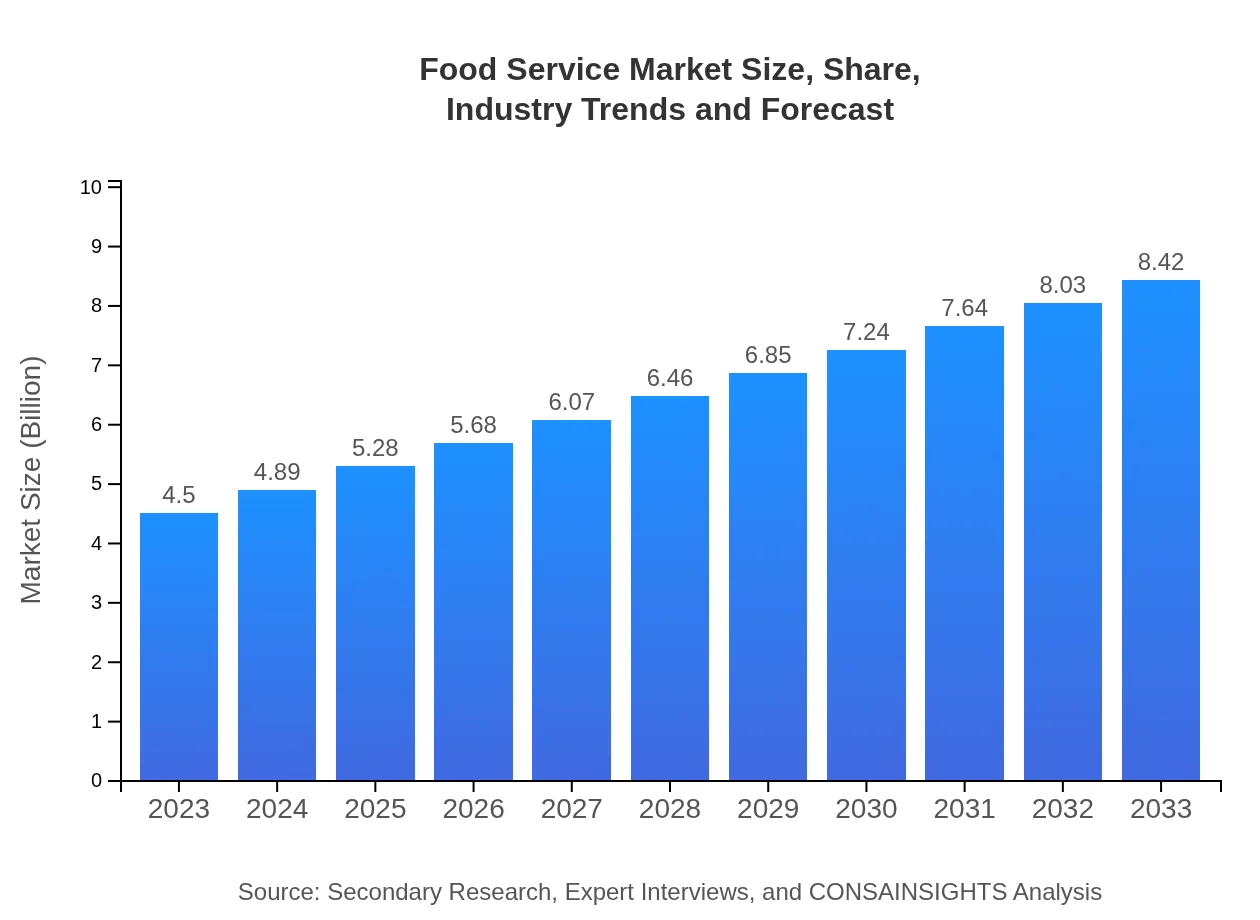
| 2023 Market Size | $4.50 Trillion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $8.42 Trillion |
| Top Companies | McDonald's Corporation, Starbucks Corporation, Restaurant Brands International (RBI), Yum! Brands |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Food Service Market Overview
Customize Food Service Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Food Service market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Food Service's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Food Service
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Food Service Market in 2023?
Food Service Industry Analysis
Food Service Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Food Service Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Food Service Market Report:
The European Food Service market is set to grow from $1.11 trillion in 2023 to $2.08 trillion by 2033. Strong growth is projected due to an increased focus on health and nutrition. European consumers are increasingly demanding transparency in sourcing and preparing food, which is prompting restaurants to adopt local and sustainable practices.Asia Pacific Food Service Market Report:
In 2023, the Food Service market in Asia Pacific is valued at approximately $0.94 trillion and is expected to reach $1.77 trillion by 2033. The region is witnessing a dramatic shift towards online food delivery, driven by urbanization and changing lifestyle patterns. Countries like China and India are leading this surge due to their large, young populations and rising disposable incomes.North America Food Service Market Report:
North America's Food Service market is one of the largest, valued at approximately $1.50 trillion in 2023 and projected to grow to $2.81 trillion by 2033. The market is characterized by a high preference for convenience and digital ordering solutions, with the U.S. leading the charge in the adoption of food technology innovations.South America Food Service Market Report:
The South American Food Service market shows promising growth from $0.33 trillion in 2023 to approximately $0.61 trillion by 2033. The growth is primarily driven by the increasing middle-class population and the expansion of international chains in key urban areas. This trend is complemented by a growing culinary diversity and local cuisine appreciation.Middle East & Africa Food Service Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Food Service market is expected to grow from $0.62 trillion in 2023 to $1.15 trillion by 2033. The rapid urbanization, coupled with a young demographic, is significantly contributing to this growth. The rise in disposable income levels is resulting in increased spending on dining out and food delivery.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
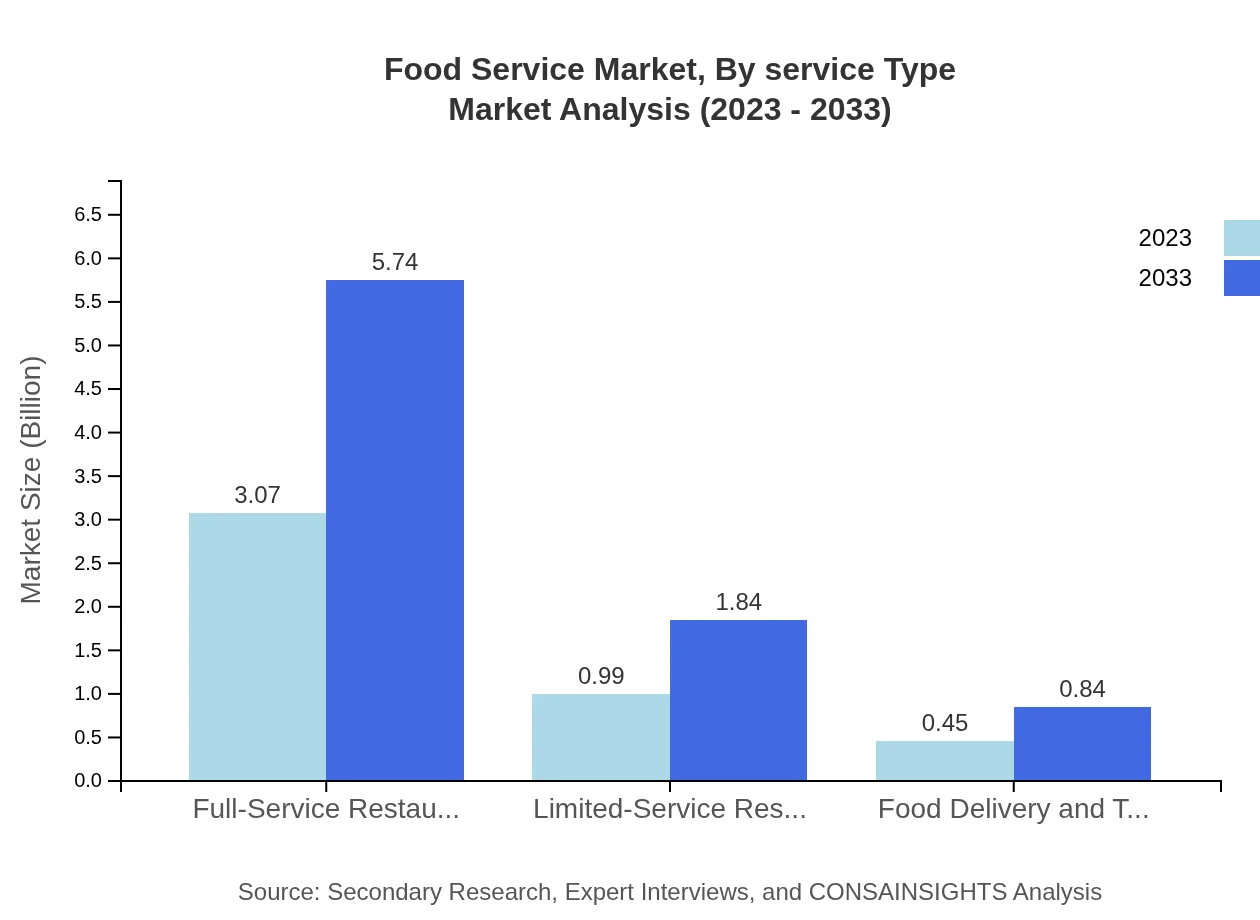
Food Service Market Analysis By Service Type
In the service type segment, Full-Service Restaurants are projected to grow from $3.07 trillion in 2023 to $5.74 trillion by 2033, maintaining a dominant market share of 68.12%. Limited-Service Restaurants are also significant contributors, with market sizes expanding from $0.99 trillion to $1.84 trillion, holding a 21.9% share. Food Delivery and Takeout is a burgeoning segment, anticipated to increase from $0.45 trillion to $0.84 trillion, accounting for 9.98% of the market.
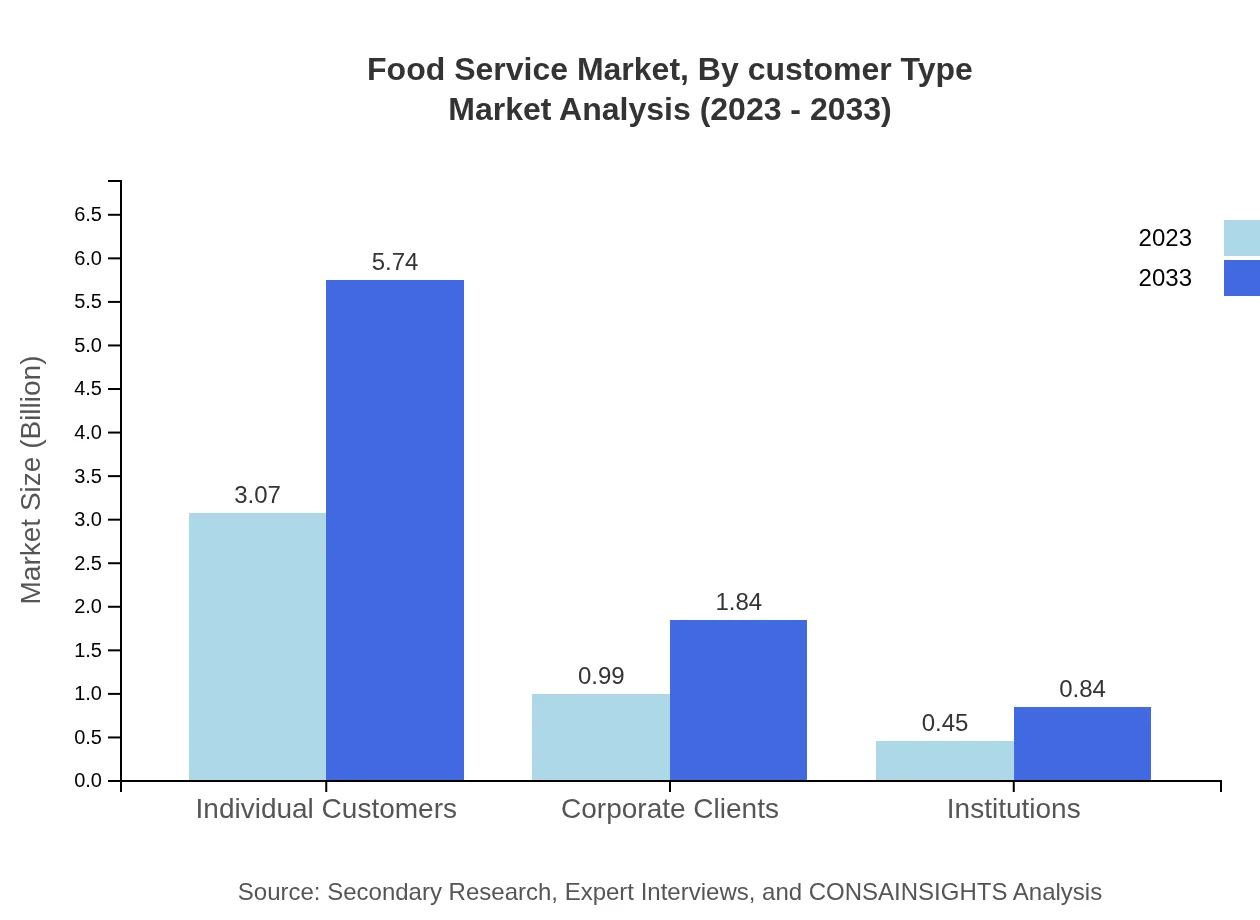
Food Service Market Analysis By Customer Type
The customer type segmentation reveals that Individual Customers dominate the market, contributing $3.07 trillion in 2023 and projected to rise to $5.74 trillion by 2033, reflecting a 68.12% market share. Corporate Clients, while smaller, are expected to grow from $0.99 trillion to $1.84 trillion, maintaining a share of 21.9%. Institutions exhibit potential growth as well, with an increase from $0.45 trillion to $0.84 trillion, keeping a 9.98% share.
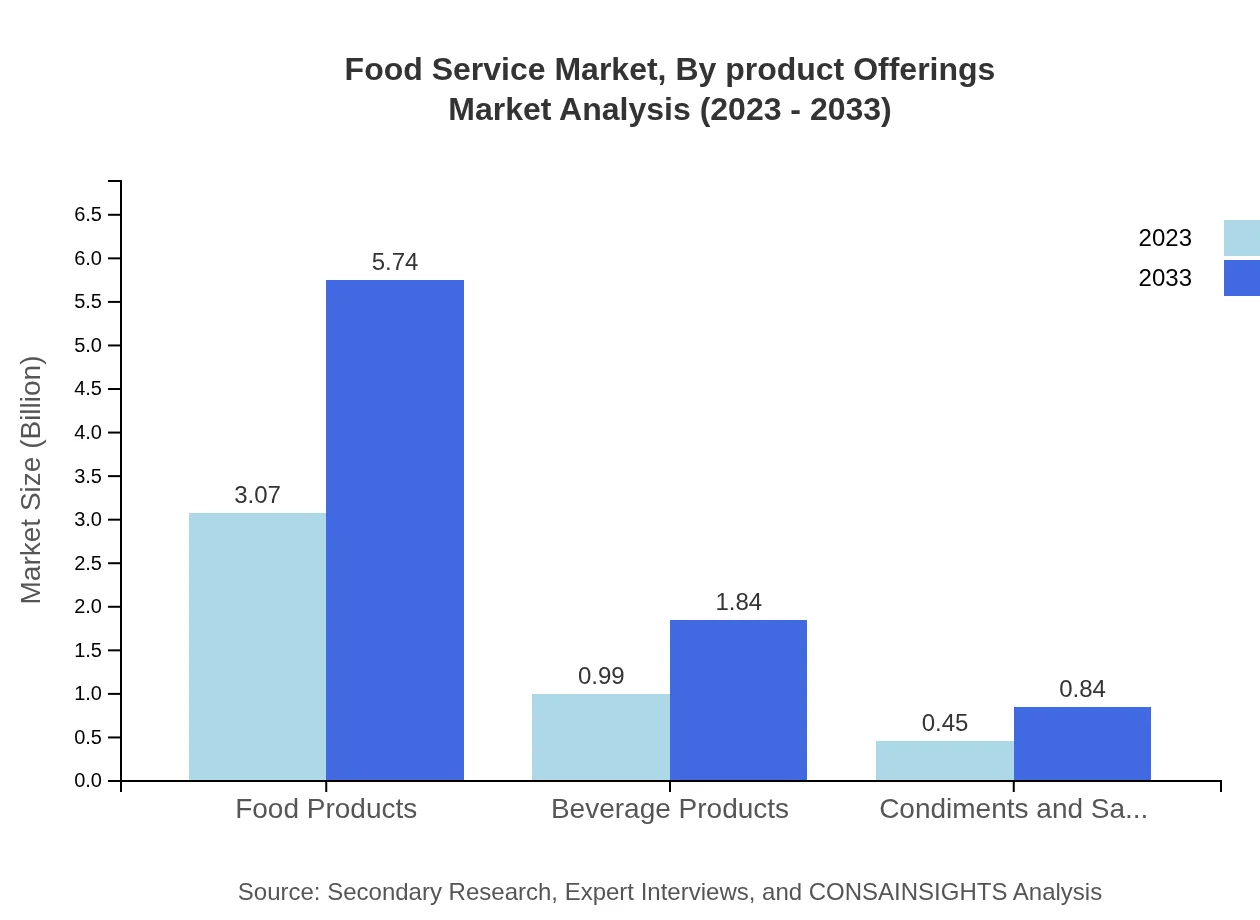
Food Service Market Analysis By Product Offerings
In terms of product offerings, Food Products account for $3.07 trillion, growing to $5.74 trillion by 2033 with a 68.12% share. Beverage Products are also noteworthy, with growth from $0.99 trillion to $1.84 trillion, holding a 21.9% share. Condiments and Sauces contribute to the market's diverse portfolio, increasing from $0.45 trillion to $0.84 trillion, representing 9.98% of total offerings.
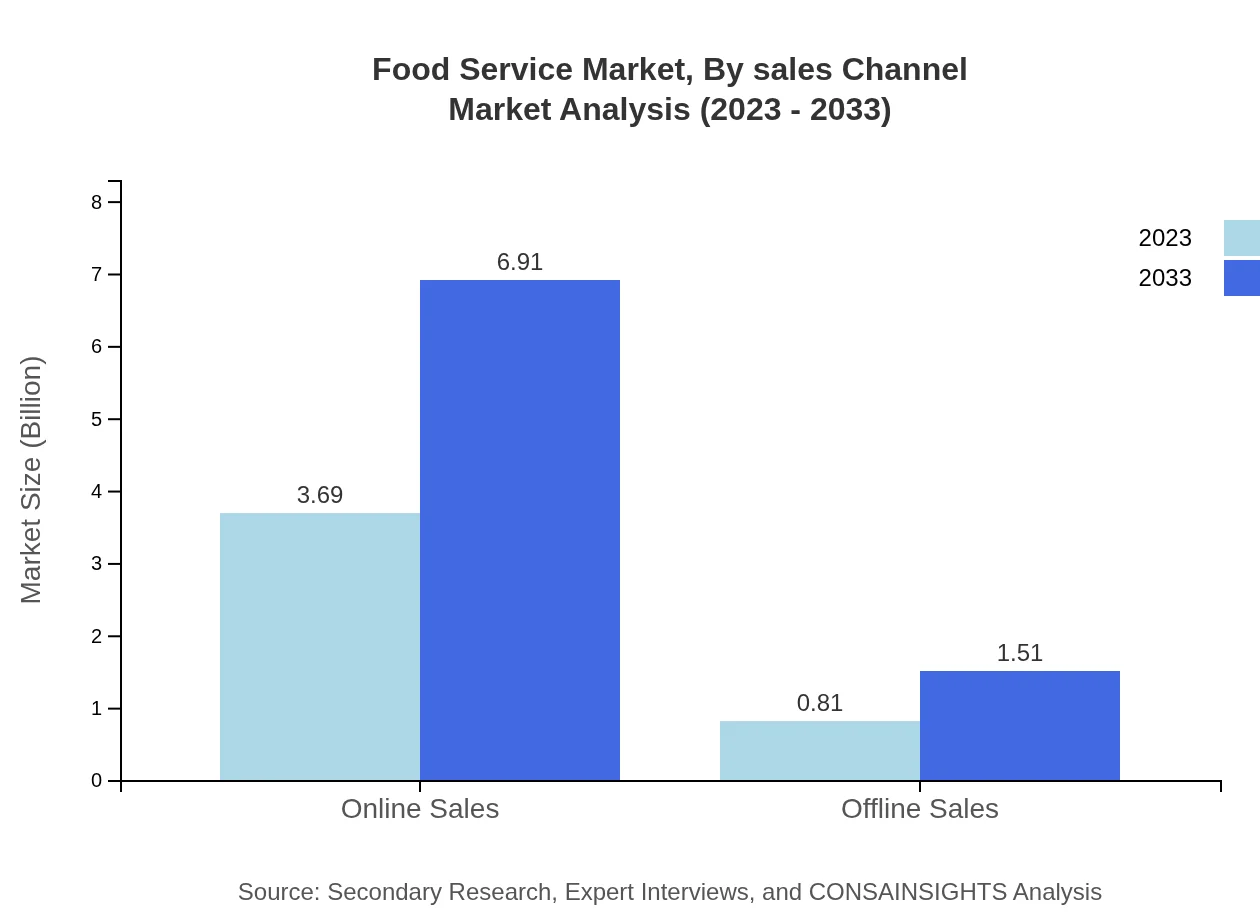
Food Service Market Analysis By Sales Channel
When analyzing sales channels, Online Sales remarkably lead with a size increase from $3.69 trillion in 2023 to $6.91 trillion by 2033, capturing a commanding 82.03% share of the market. Offline Sales, while growing from $0.81 trillion to $1.51 trillion, represent a diminishing share at 17.97% as consumer preferences shift towards digital ordering solutions.
Food Service Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Food Service Industry
McDonald's Corporation:
A leading global food service retailer known for its hamburgers, fries, and breakfast items, McDonald's has pioneered the fast-food industry with its franchising model and continues to innovate with digital menus and delivery services.Starbucks Corporation:
Starbucks is a prominent coffeehouse chain that has changed the landscape of food service by focusing on premium coffee experiences and social responsibility initiatives, along with a robust digital ordering and rewards program.Restaurant Brands International (RBI):
Owner of several international fast-food brands including Burger King and Tim Hortons, RBI leverages a diversified portfolio to drive growth while embracing digital innovations to enhance customer engagement.Yum! Brands:
Yum! Brands oversees popular restaurant chains such as Taco Bell and Pizza Hut, focusing on global expansion and menu diversification to cater to varying consumer tastes.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of food Service?
The global food-service market size is projected to reach $4.5 trillion by 2033, with a robust CAGR of 6.3%. This significant growth reflects a rising demand for diverse dining experiences and food delivery services.
What are the key market players or companies in this food Service industry?
Key players in the food-service industry include major chains like McDonald's, Starbucks, and Yum! Brands. These companies are leading the market by continually innovating menu offerings and enhancing customer engagement through technology.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the food Service industry?
Key drivers for growth in the food-service industry include increased consumer spending on dining out, the rise in food delivery services, and evolving consumer preferences for healthier and diverse meal options.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the food Service?
The fastest-growing region in the food-service market is Asia-Pacific, projected to grow from $0.94 trillion in 2023 to $1.77 trillion by 2033, driven by urbanization and rising disposable incomes in developing countries.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the food Service industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored for specific segments within the food-service industry, helping businesses make informed strategic decisions based on their unique needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this food Service market research project?
From the food-service market research project, you can expect detailed market analysis, segmentation data, growth forecasts, competitive landscape insights, and actionable recommendations tailored to your business objectives.
What are the market trends of food Service?
Trends in the food-service industry include the surge in online ordering, an emphasis on sustainable practices, the growth of plant-based menus, and the integration of technology in service delivery to enhance customer experience.