Food Testing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: food-testing
Food Testing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Food Testing market, covering insights into market trends, segmentation, regional performance, and forecasts for the period 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
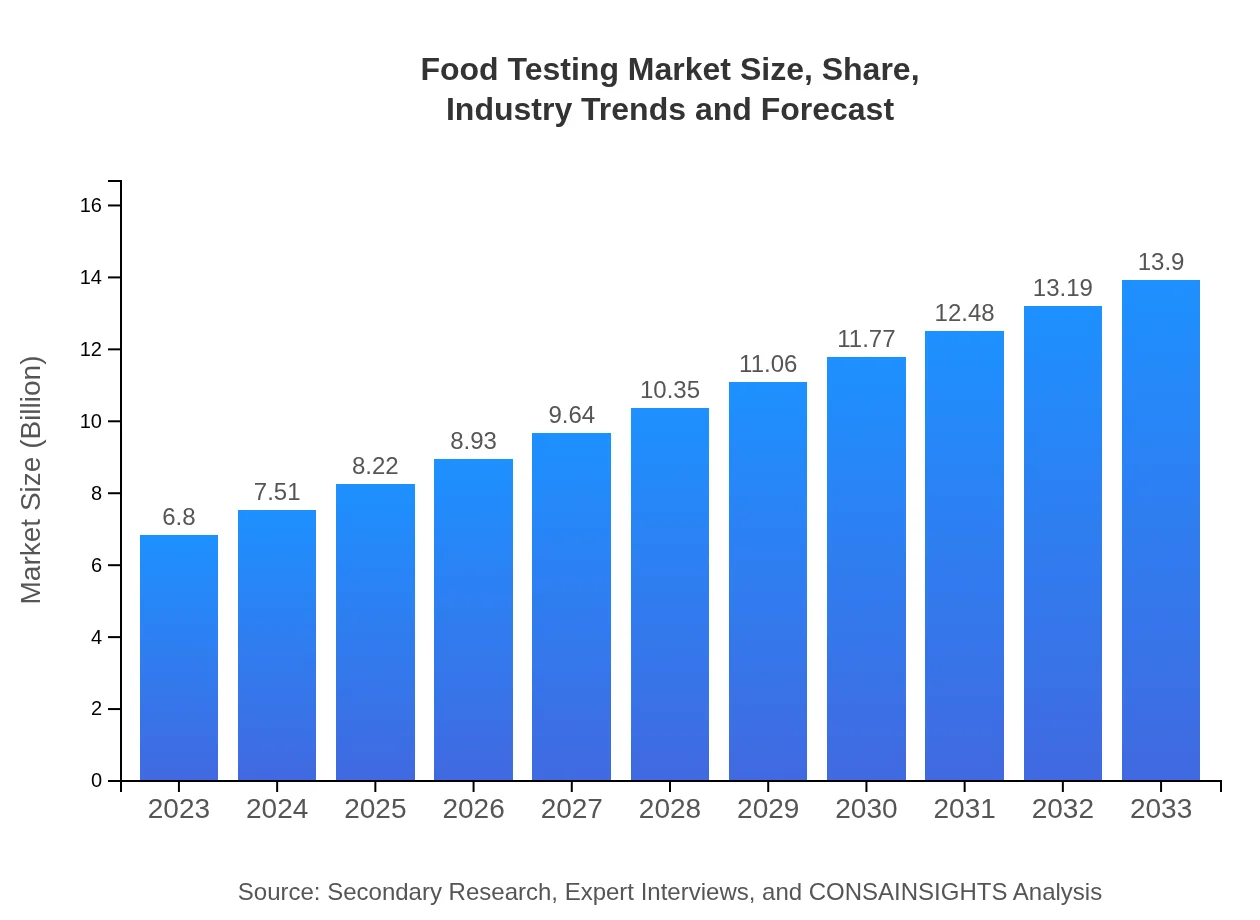
| 2023 Market Size | $6.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13.90 Billion |
| Top Companies | Eurofins Scientific, SGS S.A., Intertek Group plc, TÜV SÜD |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Food Testing Market Overview
Customize Food Testing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Food Testing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Food Testing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Food Testing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Food Testing market in 2023?
Food Testing Industry Analysis
Food Testing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Food Testing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Food Testing Market Report:
The European market is projected to grow from $1.70 billion in 2023 to $3.47 billion by 2033, driven by stringent regulations and high consumer awareness regarding food safety. The competitive landscape includes a focus on technological advancements and sustainability, as well as increasing collaboration between testing laboratories and food manufacturers.Asia Pacific Food Testing Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing significant market growth, projected to expand from $1.34 billion in 2023 to $2.73 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization, changing dietary patterns, and a surge in demand for processed and packaged food. Regulatory authorities in countries like India and China are tightening food safety standards, creating opportunities for testing entities.North America Food Testing Market Report:
North America dominates the Food Testing market with an expected increase from $2.44 billion in 2023 to $4.98 billion by 2033. Stringent food safety regulations by agencies like the FDA and increased imports of food products are major contributing factors. The market is characterized by a high adoption rate of advanced testing technologies that enhance food safety processes.South America Food Testing Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to grow from $0.61 billion in 2023 to $1.24 billion by 2033. Key drivers include increased investment in food safety from both government and private sectors and the rising awareness among consumers about the importance of food quality. Brazil and Argentina are at the forefront of this transformation.Middle East & Africa Food Testing Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is anticipated to grow from $0.72 billion in 2023 to $1.48 billion by 2033. Factors such as increasing investments in food safety infrastructure and rising population density are fostering this growth. There’s also a notable trend towards modernizing food testing processes within the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
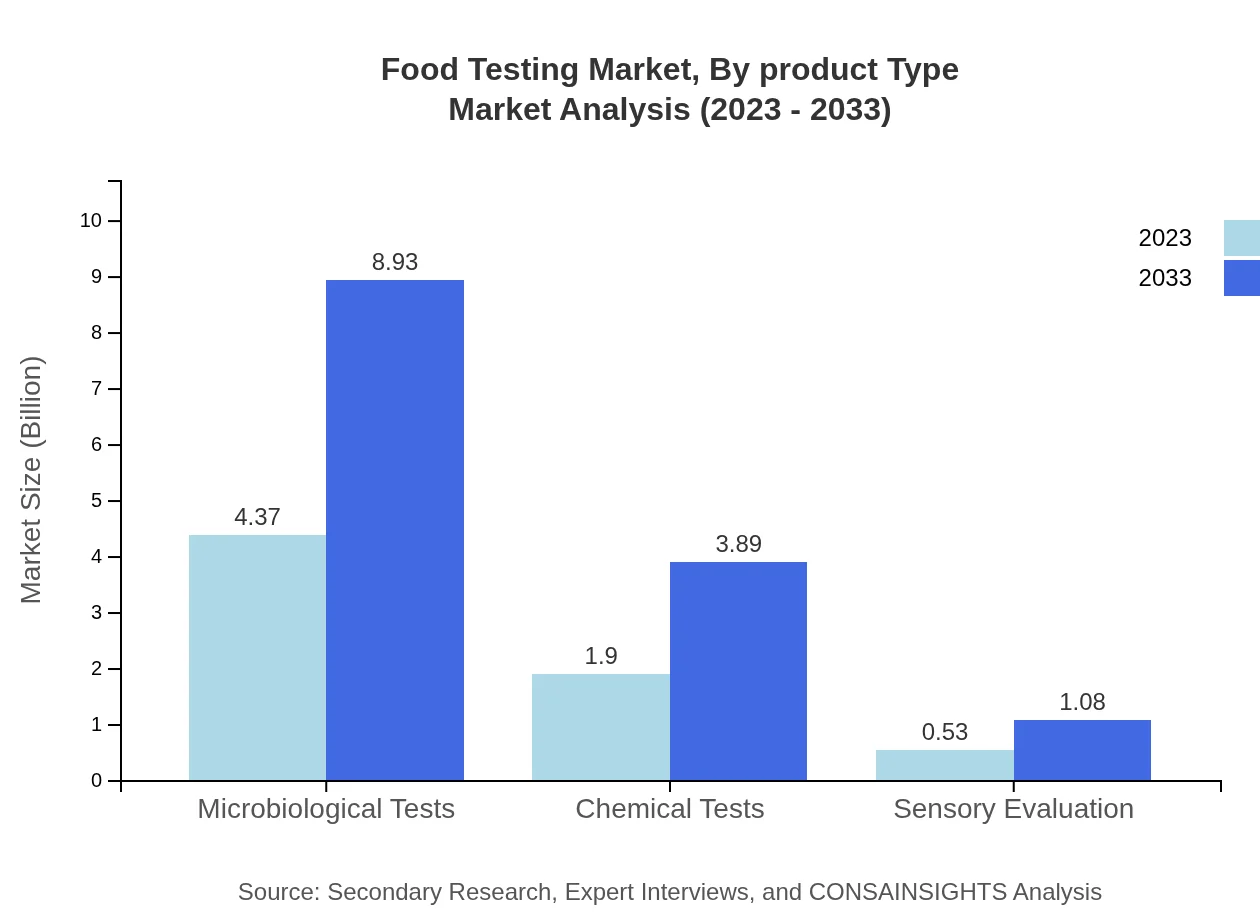
Food Testing Market Analysis By Product Type
In 2023, the Food Testing Market by Product Type was valued at approximately $5.96 billion, with projections reaching $12.18 billion by 2033. The largest segment, Traditional Methods, holds a significant share of 87.66%. Meanwhile, Advanced Technologies, while smaller in share at 12.34%, are gaining ground due to innovation and increased efficiency.
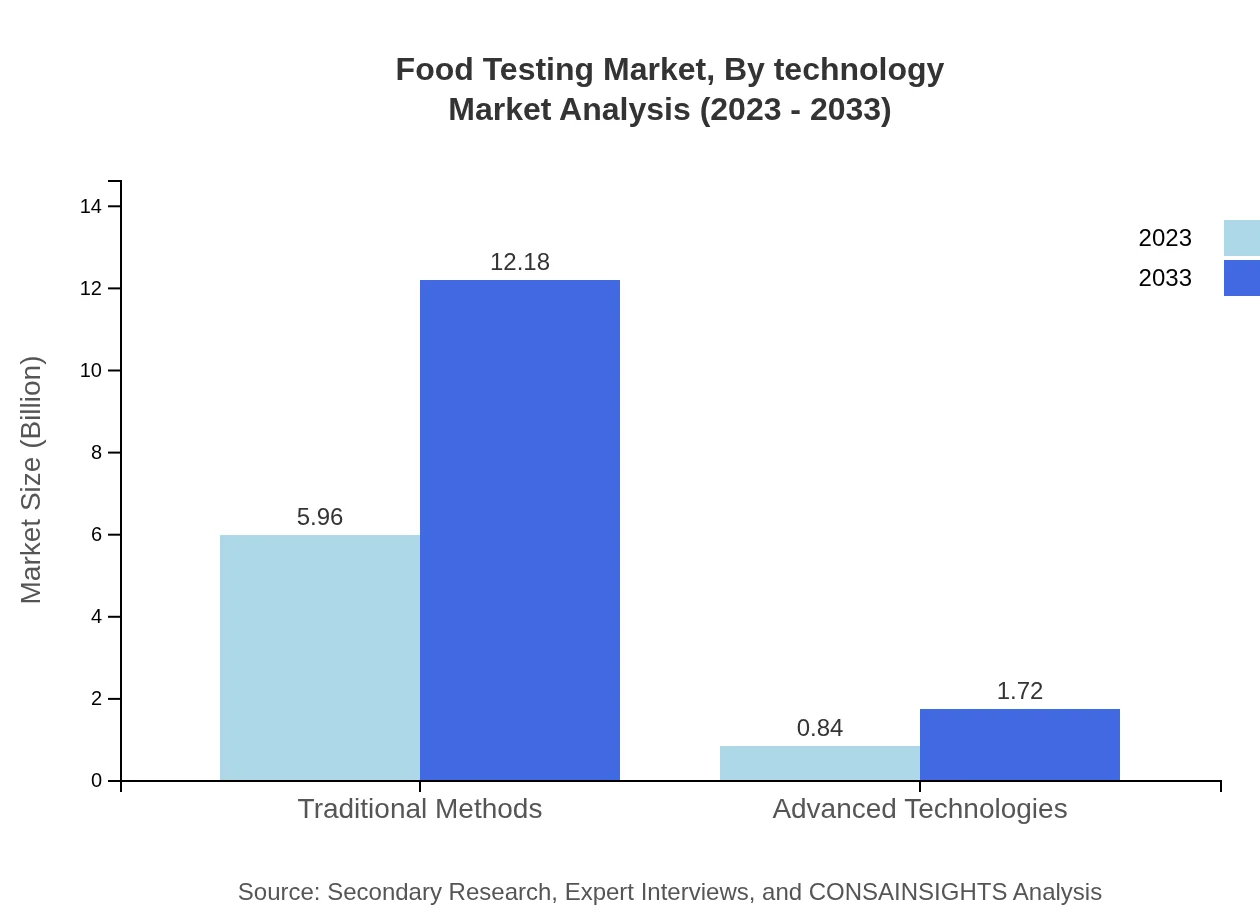
Food Testing Market Analysis By Technology
The Food Testing market, segmented by technology, shows that traditional testing methods dominate with a market size of $5.96 billion in 2023. However, Advanced Technologies, with an initial valuation of $0.84 billion, are expected to grow rapidly as companies seek faster, more reliable testing solutions.
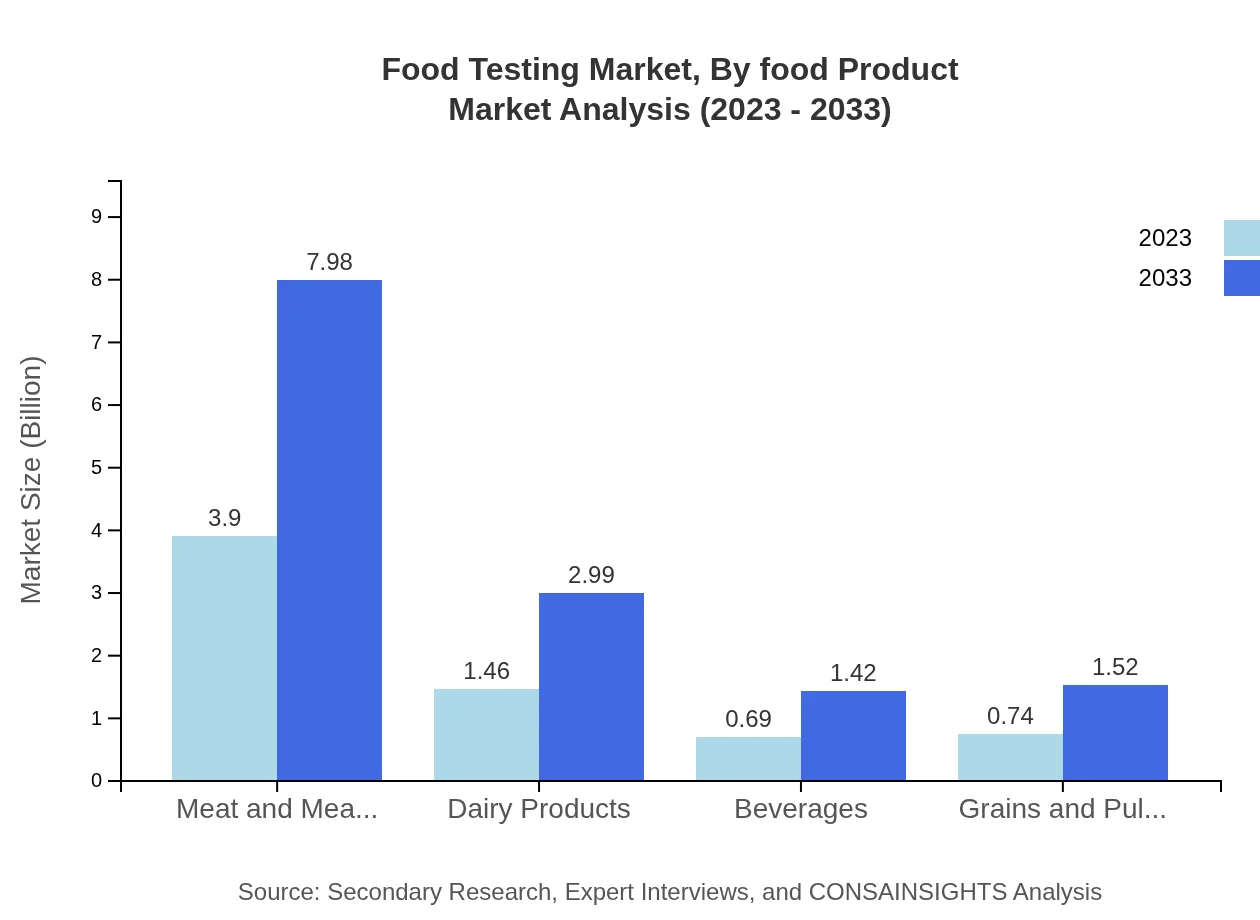
Food Testing Market Analysis By Food Product
In the Food Testing market segmented by food product, meat and meat products dominate the market with a share of 57.39%. In 2023, this segment is valued at $3.90 billion, projected to grow to $7.98 billion by 2033. Dairy and beverages follow, each holding significant shares and are also expected to experience steady growth.
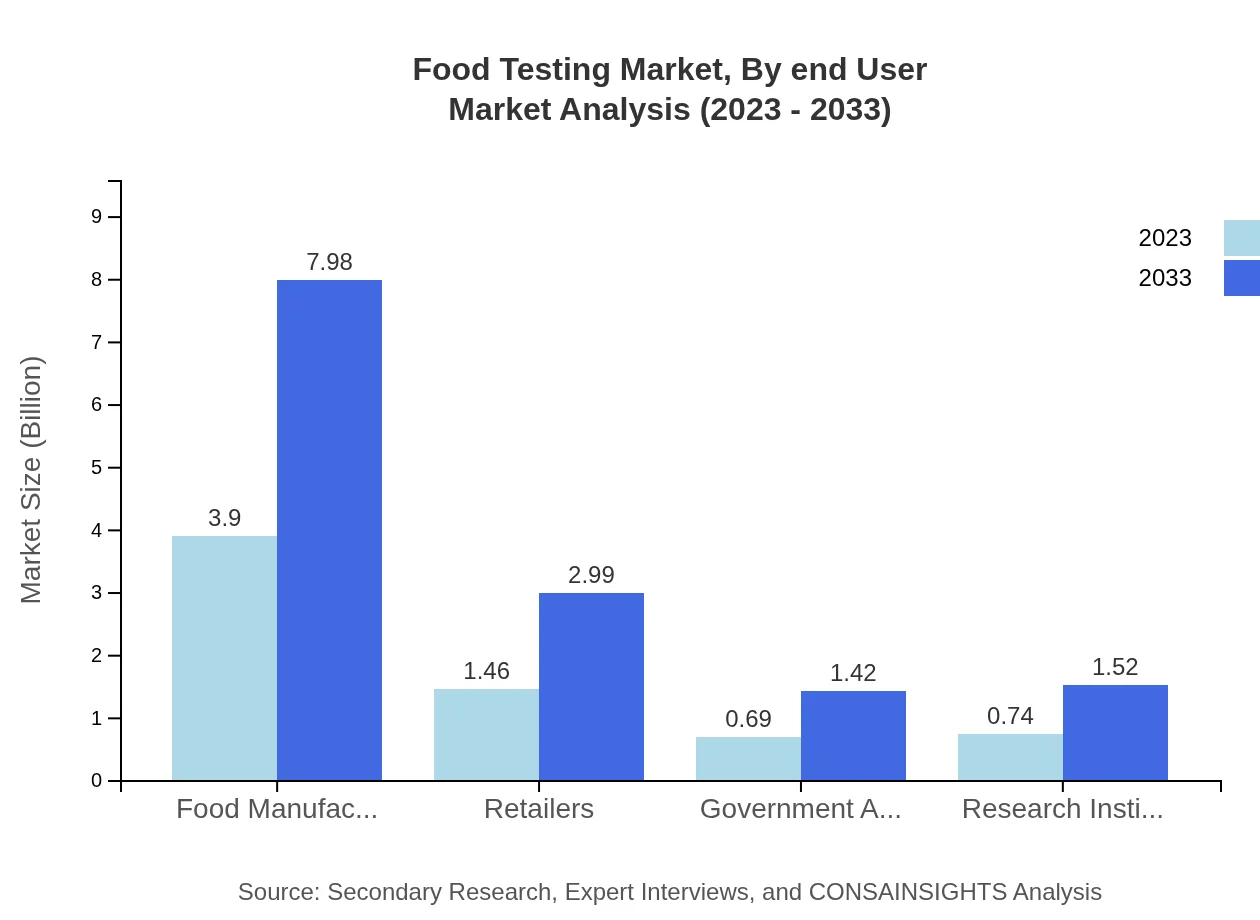
Food Testing Market Analysis By End User
The major end-user segment, Food Manufacturers, comprised 57.39% of market share in 2023 with a total market size of $3.90 billion, forecasted to reach $7.98 billion by 2033. Retailers and Government Agencies also play vital roles, underscoring the importance of integrity and safety from food production to consumption.
Food Testing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Food Testing Industry
Eurofins Scientific:
A global leader in food testing services, Eurofins offers a wide array of analytical services for food quality and safety. Their expertise and extensive laboratory network set industry standards.SGS S.A.:
SGS is recognized as the world's leading inspection, verification, testing, and certification company. They hold a strong position in the food testing market with an extensive portfolio covering various food products.Intertek Group plc:
Intertek provides quality and safety solutions, delivering innovative services and expert consulting across various sectors, including food testing, ensuring consumer confidence.TÜV SÜD:
A global technical services provider, TÜV SÜD focuses on safety and quality assurance, offering specialized services in food testing and compliance.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of food Testing?
The food testing market is projected to reach approximately $6.8 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% from its current valuation. This growth reflects increasing demand for food safety and quality assurance globally.
What are the key market players or companies in the food Testing industry?
Key players in the food testing market include SGS SA, Eurofins Scientific, Intertek Group plc, and Bureau Veritas. These companies dominate the landscape providing comprehensive testing services to food manufacturers, retailers, and government agencies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the food testing industry?
Growth in the food testing industry is driven by rising consumer awareness regarding food safety, regulatory compliance, and technological advancements in testing solutions. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of foodborne diseases fuels demand for reliable testing methodologies.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the food testing market?
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing in the food testing market, with a projected market size increasing from $1.34 billion in 2023 to $2.73 billion by 2033, highlighting the region's rapid industrial growth and increasing food safety standards.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the food testing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients within the food testing industry, ensuring that users receive relevant, actionable insights and metrics suited to their particular interests and requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this food testing market research project?
Clients can expect detailed reports encompassing market trends, growth forecasts, company profiles, segmentation analyses, and comprehensive regional insights, providing a holistic view of the food testing landscape to inform strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of food testing?
Current trends in the food testing market include an increased focus on microbiological and chemical testing, greater utilization of advanced technologies, and shifting consumer preferences toward transparency in food sourcing and production methods.