Food Traceability Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: food-traceability
Food Traceability Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report explores the Food Traceability market, providing comprehensive insights into its size, growth trends, technological advancements, and regional analyses for the forecast period of 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
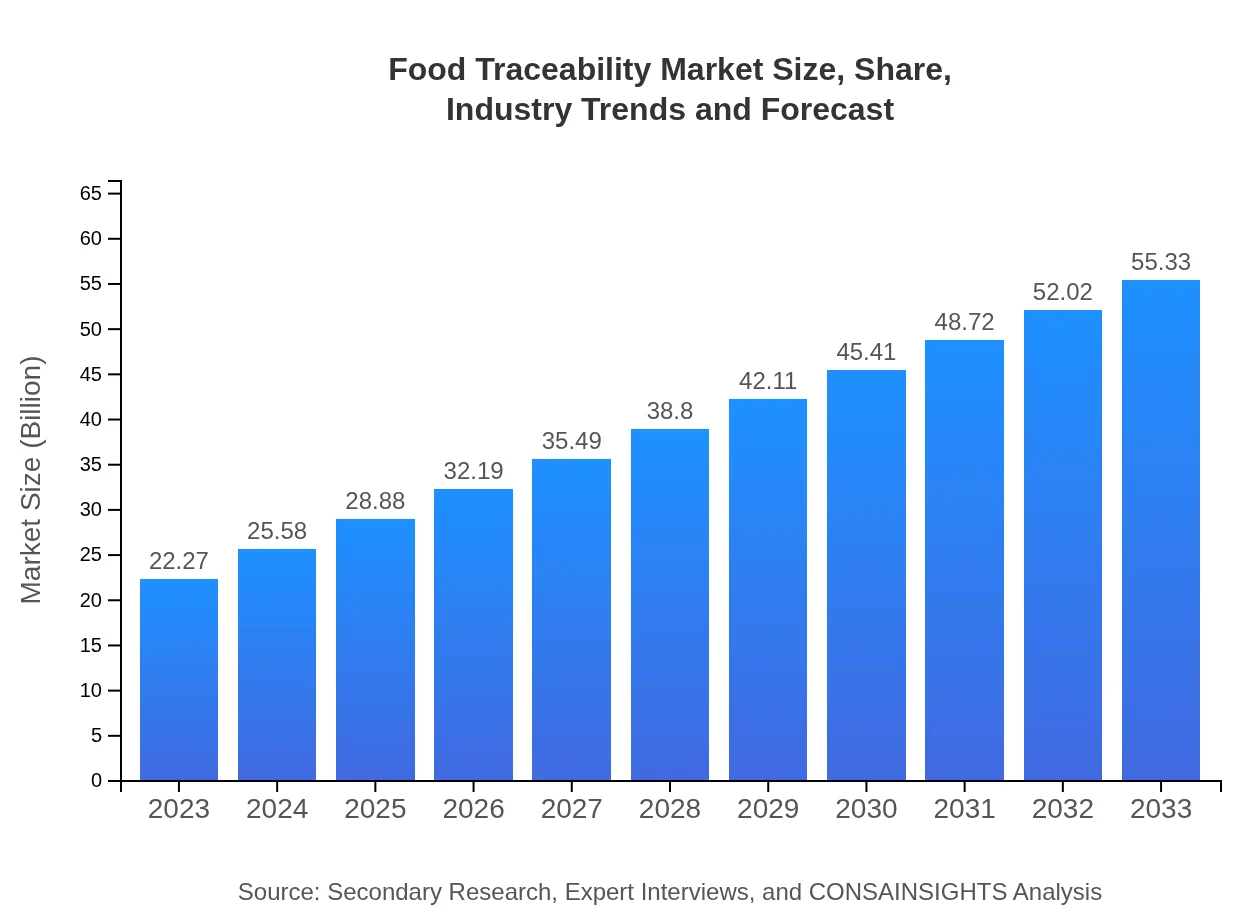
| 2023 Market Size | $22.27 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $55.33 Billion |
| Top Companies | IBM, Zebra Technologies, SAP SE, Pfizer , Sysco Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Food Traceability Market Overview
Customize Food Traceability Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Food Traceability market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Food Traceability's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Food Traceability
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Food Traceability market in 2023 and 2033?
Food Traceability Industry Analysis
Food Traceability Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Food Traceability Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Food Traceability Market Report:
In Europe, the Food Traceability market was valued at $7.58 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $18.84 billion by 2033. The European market is known for its strict food safety regulations and consumer demand for transparency, which drive investments in traceability technologies.Asia Pacific Food Traceability Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Food Traceability market was valued at $3.91 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach $9.72 billion by 2033. The regulatory push for food safety and growing consumer demand for high-quality food products drive this growth. Countries like China and Japan are leading in adopting advanced technologies to enhance traceability.North America Food Traceability Market Report:
North America holds a significant share, with the market size estimated at $7.61 billion in 2023, projected to reach $18.90 billion by 2033. This growth is largely attributed to stringent regulatory requirements and a robust focus on food safety practices across the United States and Canada.South America Food Traceability Market Report:
The South American Food Traceability market is estimated to grow from $2.14 billion in 2023 to $5.32 billion by 2033. Increasing awareness of food safety issues and regulatory compliance is expected to bolster traceability initiatives across the region, particularly in Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Food Traceability Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa Food Traceability market is anticipated to grow from $1.03 billion in 2023 to $2.56 billion by 2033. Growth in this region is rising from an increasing focus on food quality and the adoption of traceability solutions, particularly in sectors like agriculture and fisheries.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Food Traceability Market Analysis By Technology
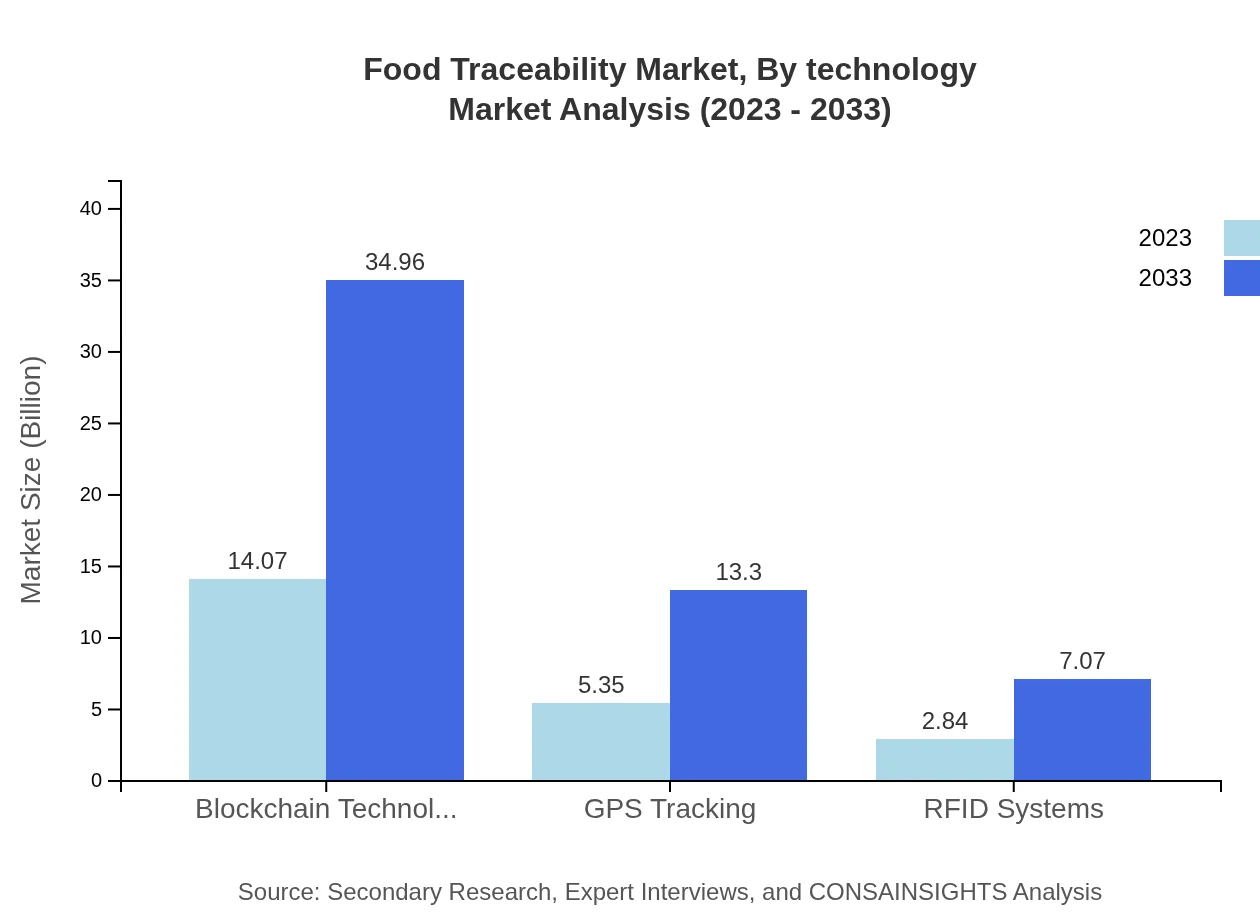
The technology segment of the Food Traceability market showcases a wide array of innovations. Blockchain technology leads with a market size of $14.07 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $34.96 billion by 2033. It facilitates secure and transparent food data exchanges. GPS tracking will see sizeable growth, from $5.35 billion to $13.30 billion over the same period, due to its importance in monitoring food logistics. RFID systems and data management technologies are also crucial for optimizing supply chains and ensuring product integrity.
Food Traceability Market Analysis By Application
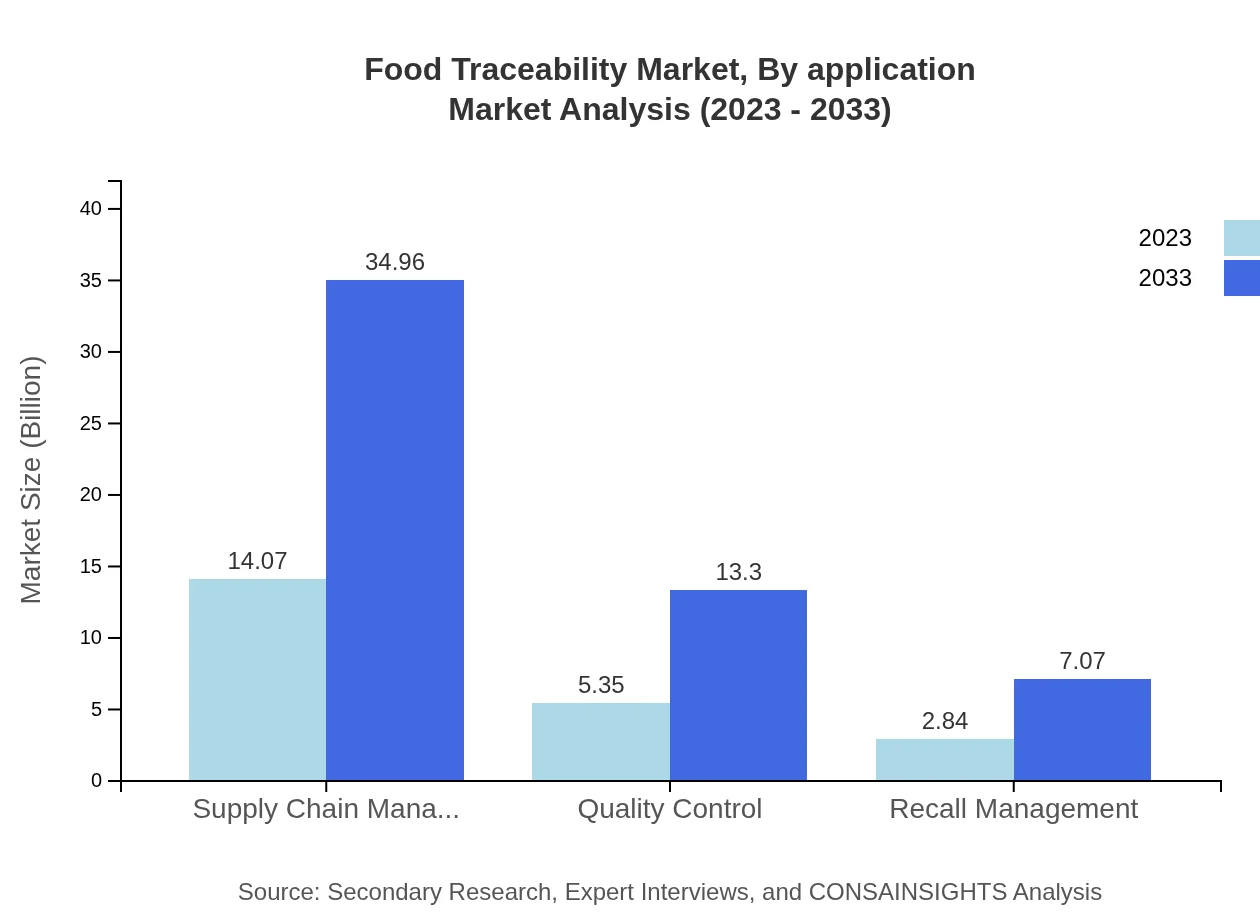
Applications within the Food Traceability market encompass supply chain management (market size $14.07 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $34.96 billion) and quality control (growing from $5.35 billion to $13.30 billion). Traceability is essential for managing recalls efficiently, with this segment estimated to expand from $2.84 billion in 2023 to $7.07 billion by 2033, playing a critical role in enhancing public health safety.
Food Traceability Market Analysis By Industry
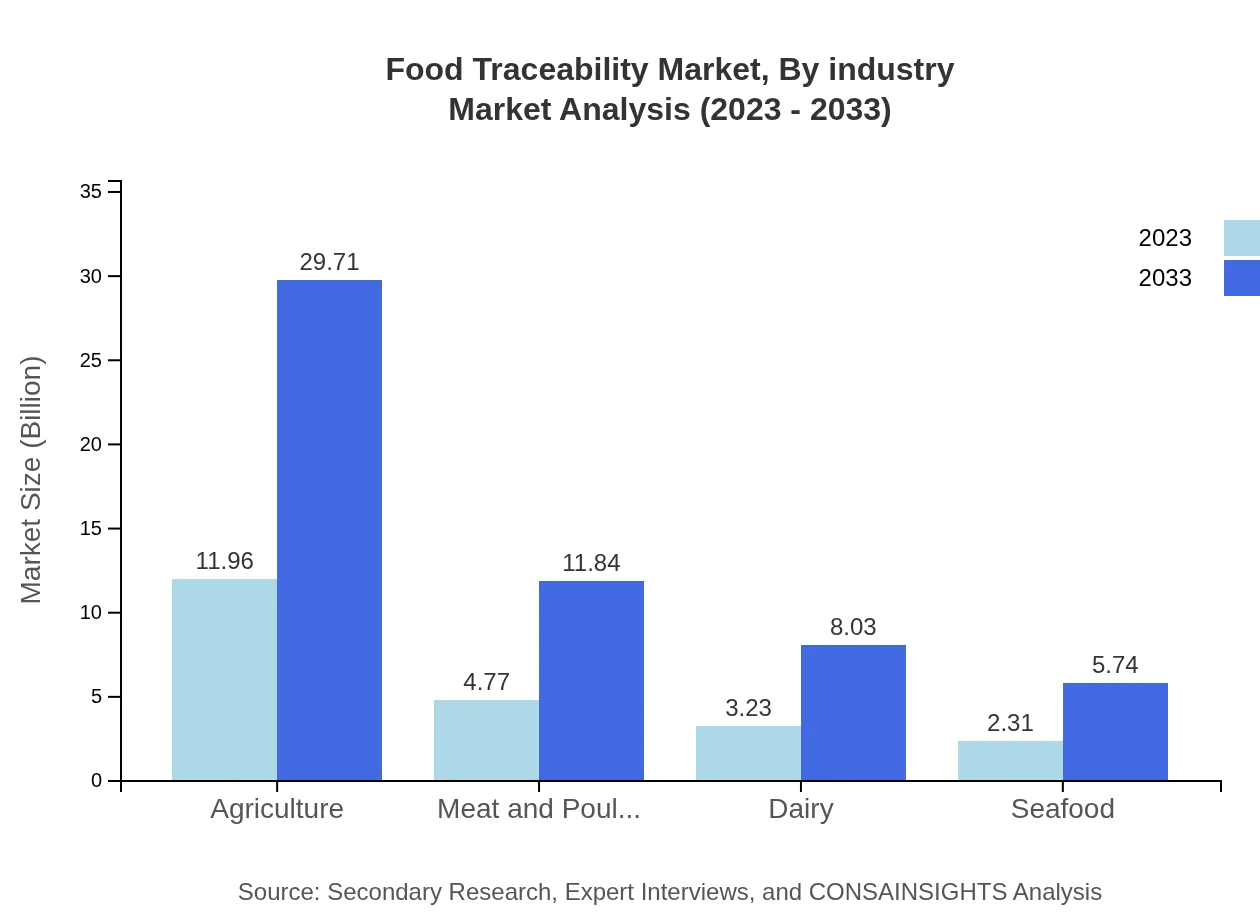
The industry segment is dominated by the agriculture sector, projected to grow from $11.96 billion in 2023 to $29.71 billion by 2033, highlighting the importance of traceability in sustainable agricultural practices. The meat and poultry sector follows closely, with a market increase from $4.77 billion to $11.84 billion, reflecting concerns regarding food safety and hygiene management.
Food Traceability Market Analysis By Region
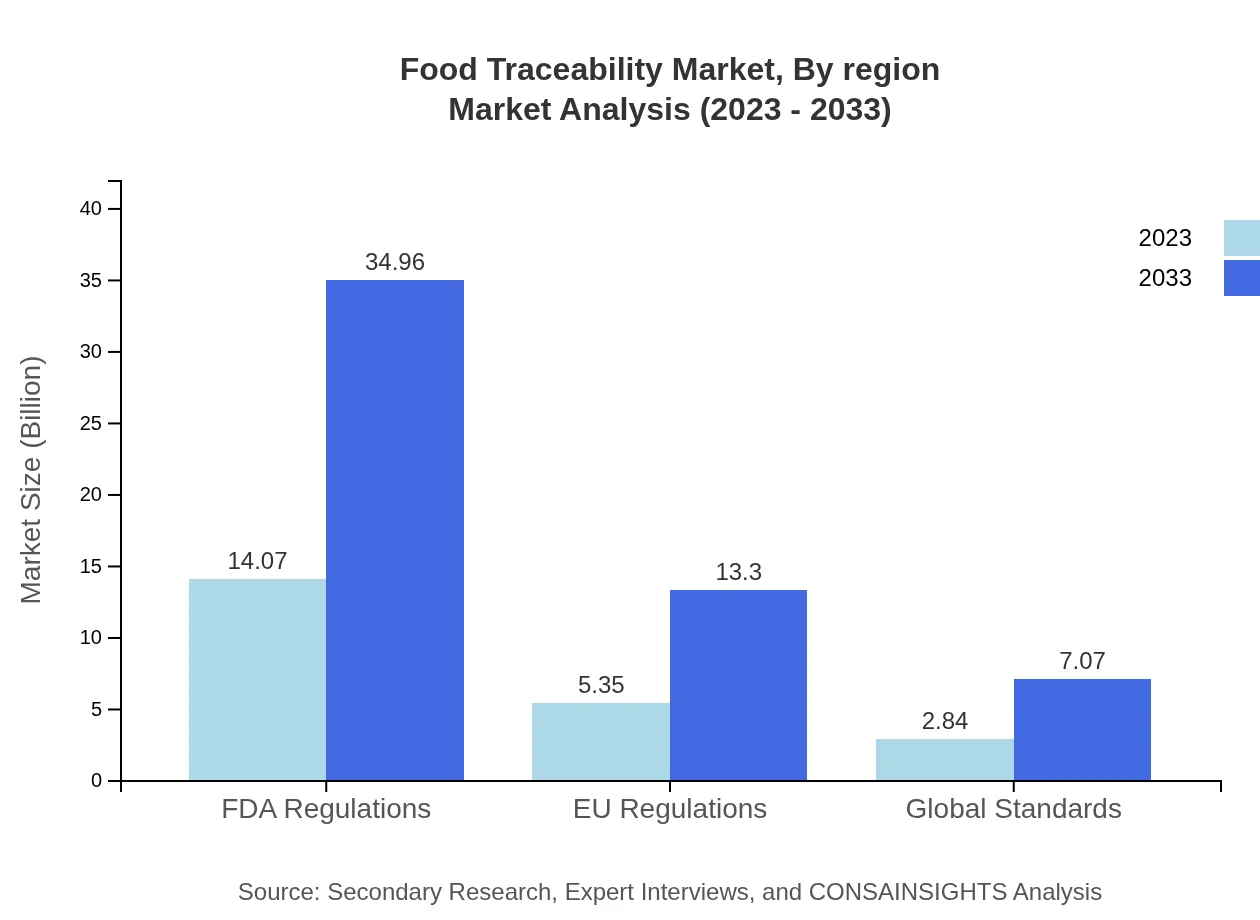
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in shaping the Food Traceability market. FDA Regulations account for a significant market share, with a size of $14.07 billion (2023) expected to rise to $34.96 billion by 2033. Similarly, EU regulations are critical, starting at $5.35 billion and reaching $13.30 billion in 2033. These regulations enhance consumer trust and set benchmarks for industry practices globally.
Food Traceability Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Food Traceability Industry
IBM:
IBM offers advanced blockchain solutions that facilitate secure and transparent food supply chain tracking, promoting food safety and authenticity.Zebra Technologies:
Zebra Technologies provides RFID and barcode technologies that enhance product tracking and monitoring capabilities throughout the food supply chain.SAP SE:
SAP SE develops comprehensive supply chain management solutions that integrate traceability features to ensure compliance and product safety.Pfizer :
Pfizer leads the market with extensive compliance and regulatory management software that bolsters food safety initiatives across various sectors.Sysco Corporation:
Sysco is a leading foodservice distributor that implements traceability solutions to enhance food safety and quality assurance for its products.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of food Traceability?
The food traceability market is expected to reach approximately $22.27 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.2% from its current valuation. This growth is driven by increasing demand for transparency in food supply chains.
What are the key market players or companies in the food Traceability industry?
Key players in the food traceability industry include major companies such as IBM, SAP, and Oracle, which offer advanced technology solutions for traceability. Other notable players include food safety experts and blockchain technology providers.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the food traceability industry?
The growth in the food traceability industry is primarily driven by rising food safety regulations, increasing consumer awareness about food origins, and technological advancements. Companies are adopting traceability solutions to manage risks and comply with regulatory mandates.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the food traceability market?
In the food traceability market, Europe is the fastest-growing region, projected to increase from $7.58 billion in 2023 to $18.84 billion by 2033, showing significant growth opportunities due to stringent regulations and a focus on food safety.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the food traceability industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights provides customized market report data for the food traceability industry. Our tailored reports can address specific client needs, focusing on segments, regions, and emerging trends to help businesses make informed decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this food traceability market research project?
From our food traceability market research project, you can expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, key player insights, segment data, and regional forecasts, along with actionable recommendations for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of food traceability?
Current trends in the food traceability market include the integration of blockchain technology, increased use of RFID systems, and enhanced supply chain management solutions. Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and quality control measures.