Fresh Apple Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: fresh-apple
Fresh Apple Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the Fresh Apple market, covering market trends, regional analysis, competitive landscape, and future forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
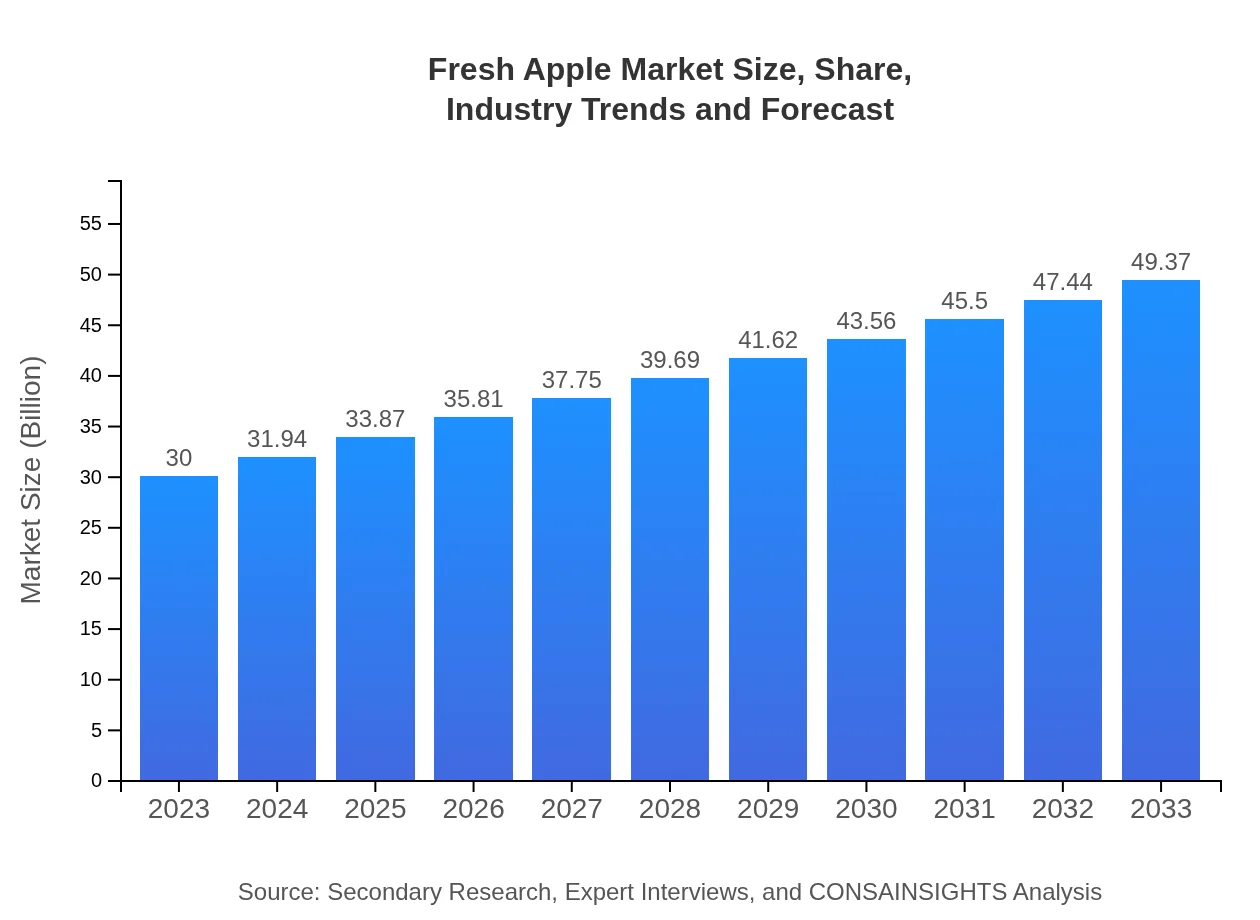
| 2023 Market Size | $30.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $49.37 Billion |
| Top Companies | Washington Apple Commission, Stemilt Growers, Grimmway Farms, Lyman Orchards |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Fresh Apple Market Overview
Customize Fresh Apple Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Fresh Apple market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Fresh Apple's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Fresh Apple
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Fresh Apple market in 2023?
Fresh Apple Industry Analysis
Fresh Apple Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Fresh Apple Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Fresh Apple Market Report:
The European Fresh Apple market, valued at $7.60 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $12.51 billion by 2033, fueled by growing consumer preference for organic products and sustainable farming practices.Asia Pacific Fresh Apple Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Fresh Apple market was valued at $6.22 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $10.23 billion by 2033, driven by population growth, rising urbanization, and increasing health consciousness.North America Fresh Apple Market Report:
North America represents a significant market, with values expected to rise from $10.02 billion in 2023 to $16.49 billion in 2033. This increase is bolstered by innovative marketing strategies and expanding product lines tailored to consumers.South America Fresh Apple Market Report:
The South American market for Fresh Apples is anticipated to grow from $2.94 billion in 2023 to $4.83 billion in 2033. This growth is attributed to increasing export activities and a favorable climate for apple cultivation.Middle East & Africa Fresh Apple Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to grow from $3.23 billion in 2023 to $5.31 billion by 2033, driven by increasing health awareness and the region's critical investment in agricultural technology.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Fresh Apple Market Analysis By Variety
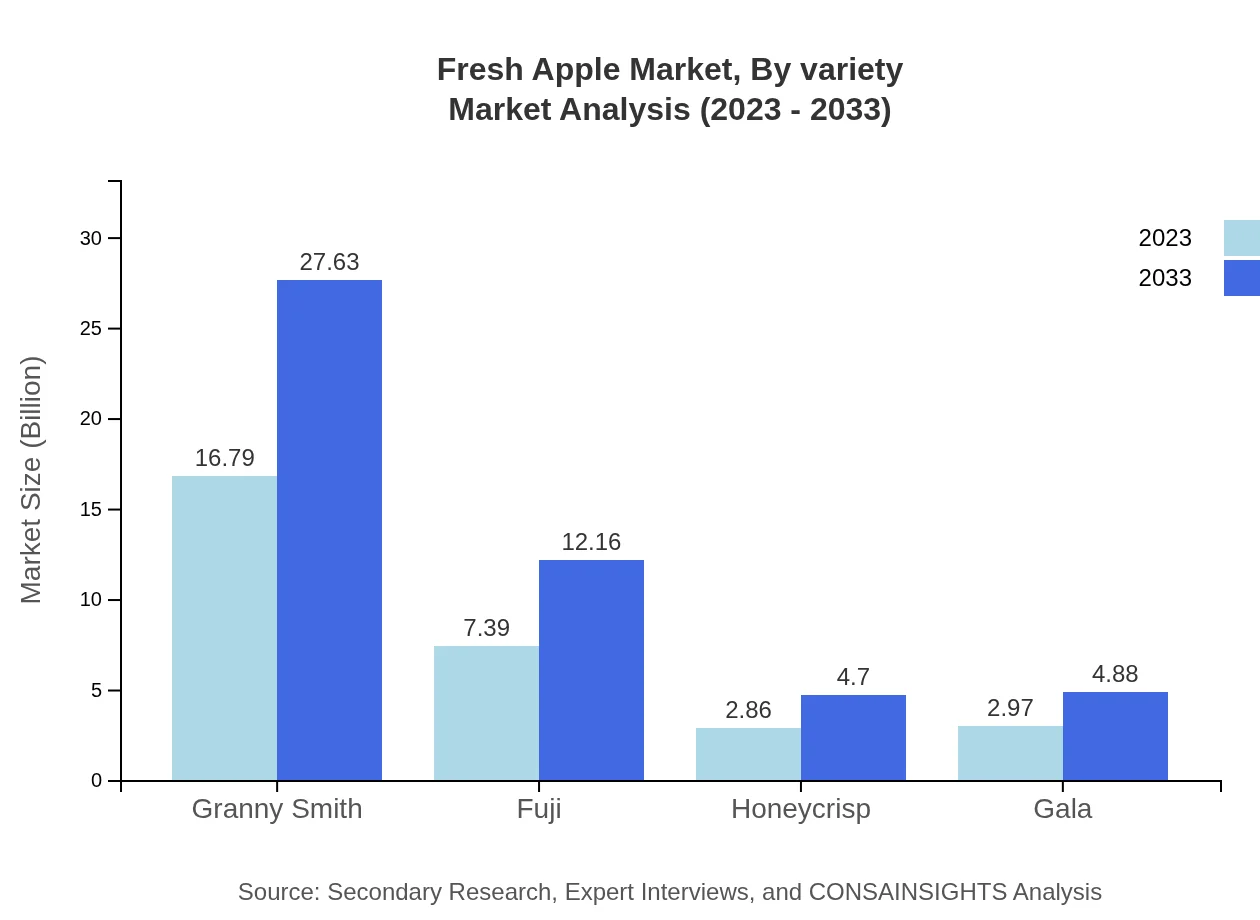
The Fresh Apple market, segmented by variety, shows that Granny Smith leads with an impressive growth from $16.79 billion in 2023 to $27.63 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of 55.97%. Fuji also holds significant importance, growing from $7.39 billion to $12.16 billion, with a stable share of 24.62%. Honeycrisp and Gala, while smaller, are growing rapidly, indicating a diversification of consumer preferences.
Fresh Apple Market Analysis By Packaging
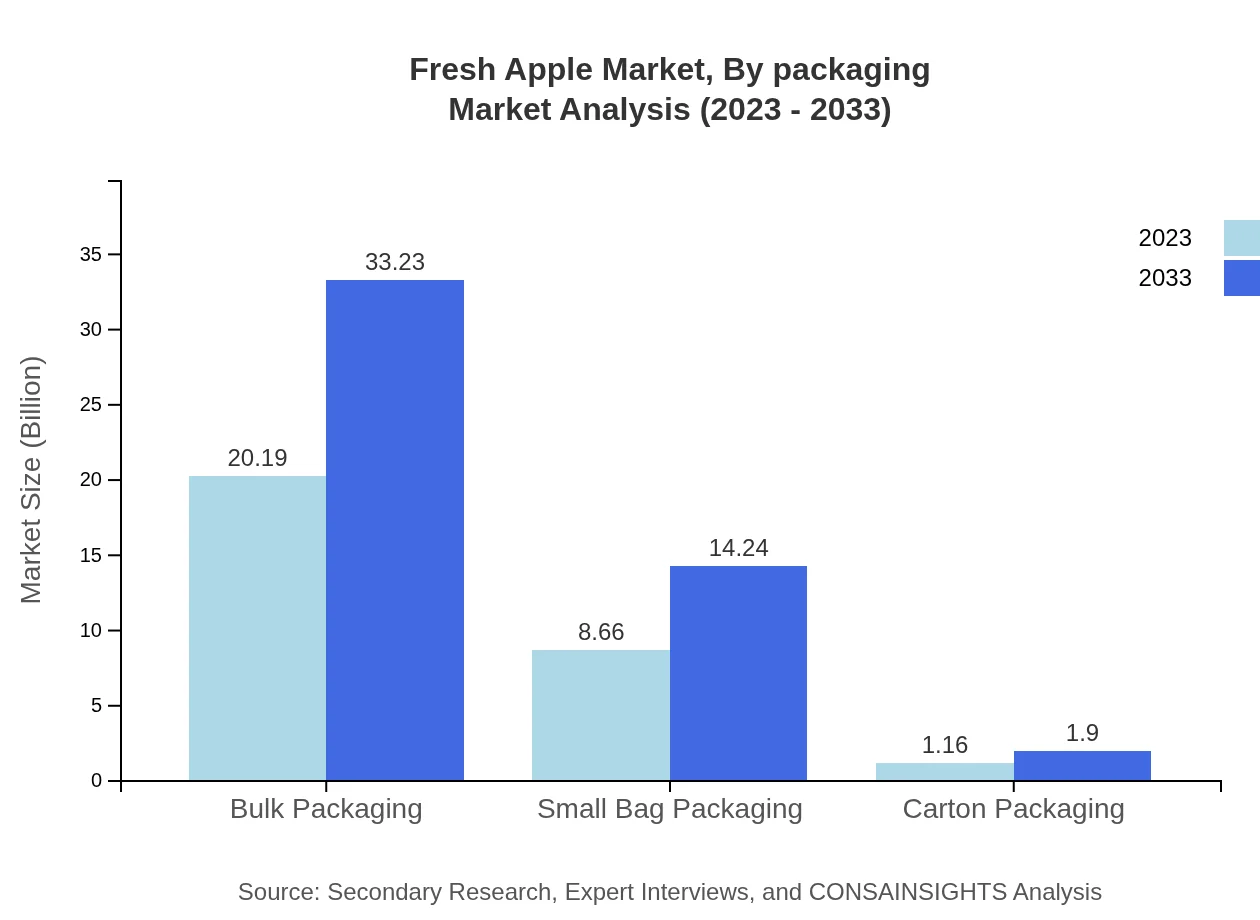
The packaging segment shows a strong performance, with bulk packaging leading at $20.19 billion in 2023, expected to reach $33.23 billion by 2033, capturing a market share of 67.3%. In contrast, small bag packaging and carton packaging, while smaller segments, exhibit promising growth rates, highlighting the demand for convenience among consumers.
Fresh Apple Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
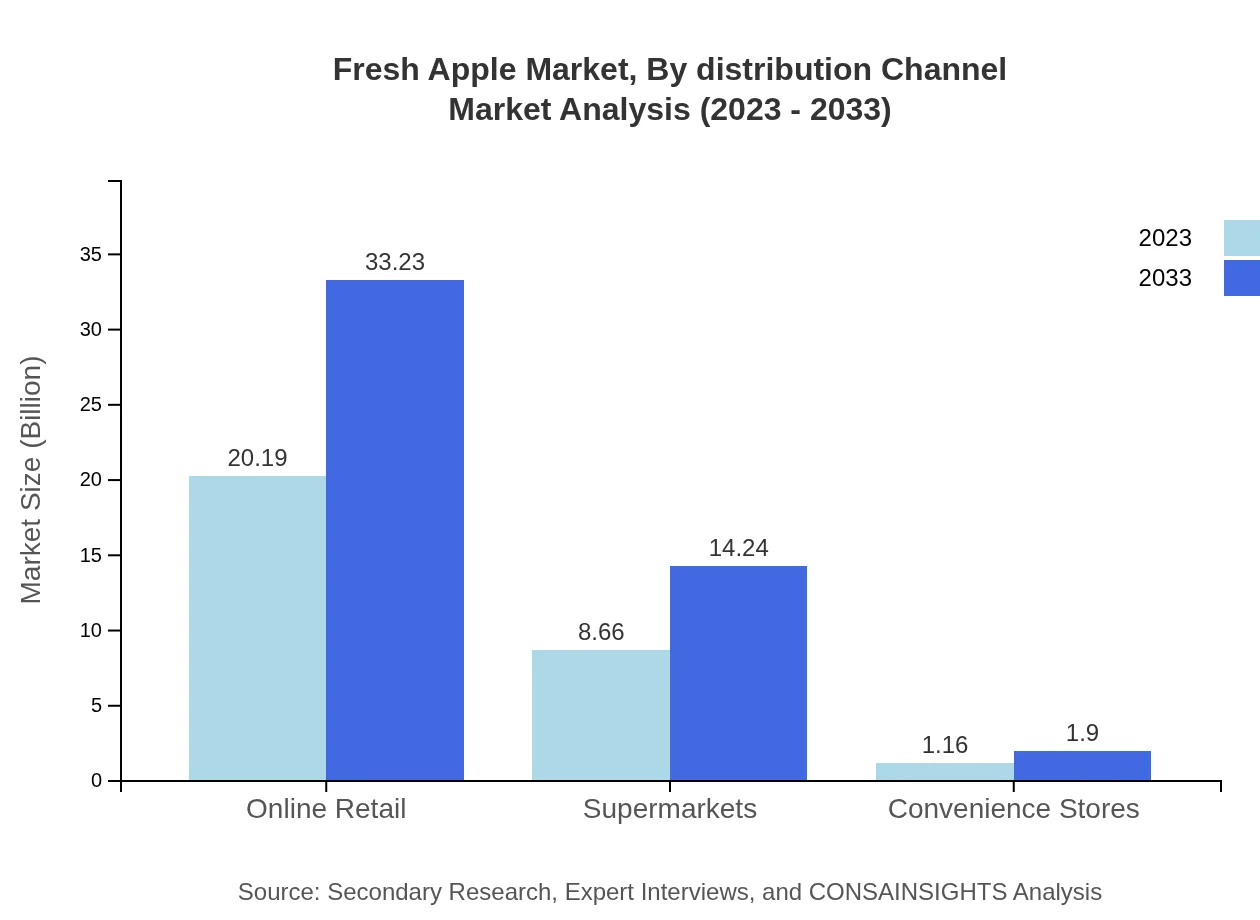
Distribution channels are evolving, with online retail leading the way, projected to grow from $20.19 billion in 2023 to $33.23 billion by 2033, maintaining dominance with a share of 67.3%. Supermarkets are also significant, while convenience stores are the smallest channel but cater to impulse purchases, indicating a diverse distribution approach.
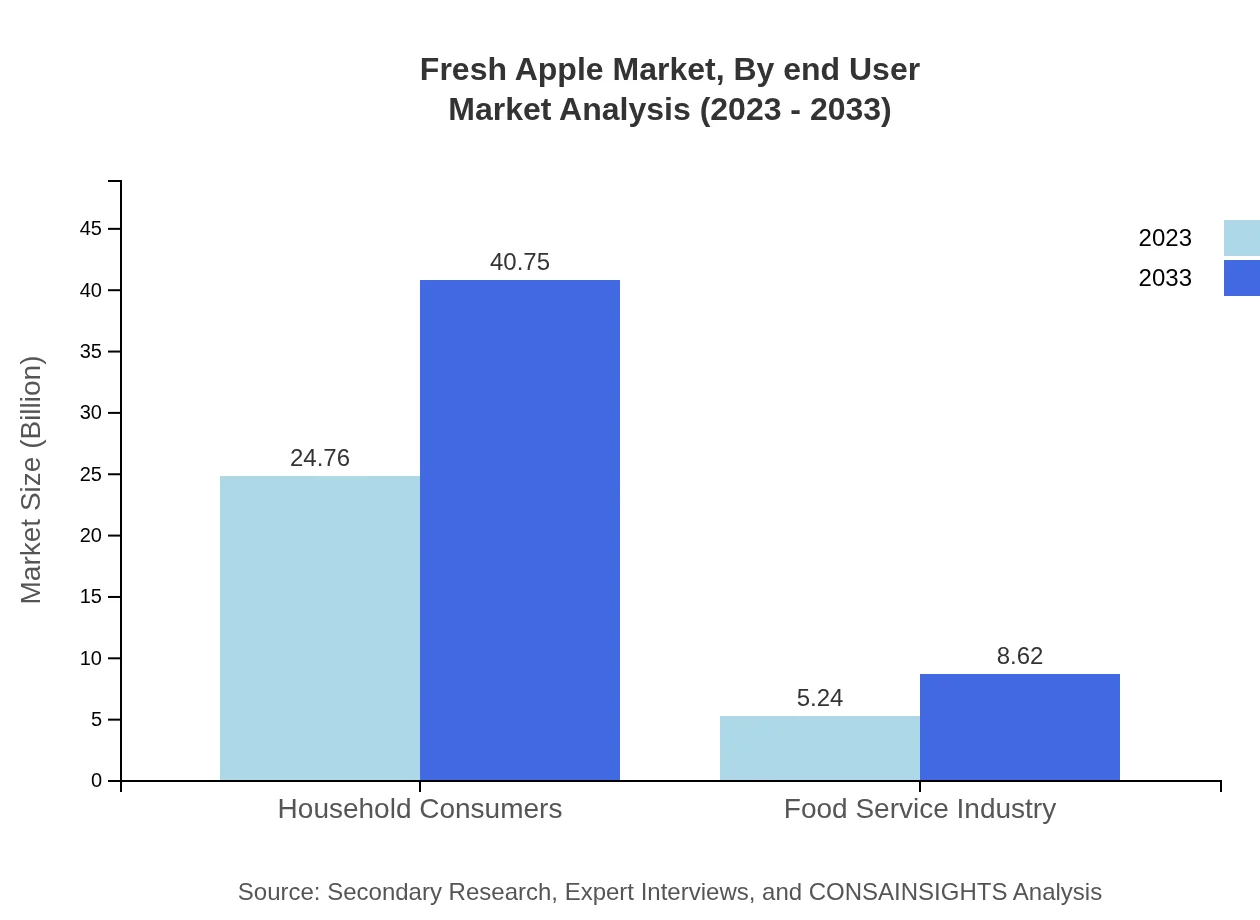
Fresh Apple Market Analysis By End User
Household consumers represent the largest end-user segment, with a market size of $24.76 billion in 2023, growing to $40.75 billion by 2033, covering an 82.54% market share. The food service industry shows healthy growth potential, underlining the need for fresh apples in restaurants and cafes.
Fresh Apple Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Fresh Apple Industry
Washington Apple Commission:
A leading organization promoting Washington state-grown apples, known for their superior taste and quality, and driving export initiatives.Stemilt Growers:
A prominent grower and shipper of fresh apples in the United States, recognized for its innovative farming practices and commitment to sustainable agriculture.Grimmway Farms:
One of the largest organic producers of apples in the country, focusing on healthy food production and sustainable farming techniques.Lyman Orchards:
An established grower with a reputation for high-quality apple production, specializing in diverse apple varieties to meet market demands.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of fresh Apple?
The global fresh apple market is valued at approximately $30 billion with a projected CAGR of 5%. This growth indicates strong consumer demand and favorable market conditions for the fresh apple industry over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the fresh Apple industry?
Key players in the fresh apple market include major producers and distributors such as Washington Apple Commission, Stemilt Growers, and Honeybear Brands. These companies engage in innovative agricultural practices, distribution networks, and marketing strategies to strengthen their market positions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the fresh apple industry?
Essential factors driving the growth of the fresh apple industry include increasing health consciousness among consumers, rising demand for organic produce, and innovative packaging solutions. These elements create opportunities for market expansion while catering to diverse consumer preferences.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the fresh apple market?
The fastest-growing region for the fresh apple market is projected to be North America, with market size increasing from $10.02 billion in 2023 to $16.49 billion by 2033, showcasing a robust demand for apples.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the fresh apple industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs within the fresh apple industry. This includes in-depth analysis and data that align with the unique requirements of businesses and stakeholders.
What deliverables can I expect from this fresh apple market research project?
Deliverables from the fresh apple market research project include comprehensive market size insights, growth projections, competitive analysis, segmented market data, and trend identification to aid strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of fresh apples?
Key trends in the fresh apple market include a growing preference for organic apples, increased use of e-commerce for sales, and innovations in packaging. These trends reflect changing consumer behaviors and technological advancements in the industry.