Fresh Food Packaging Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: fresh-food-packaging
Fresh Food Packaging Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the Fresh Food Packaging market, covering its size, growth forecasts, and various influencing factors from 2023 to 2033. It highlights key market trends, segmentation, and regional analyses to offer a clear picture of future market dynamics.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
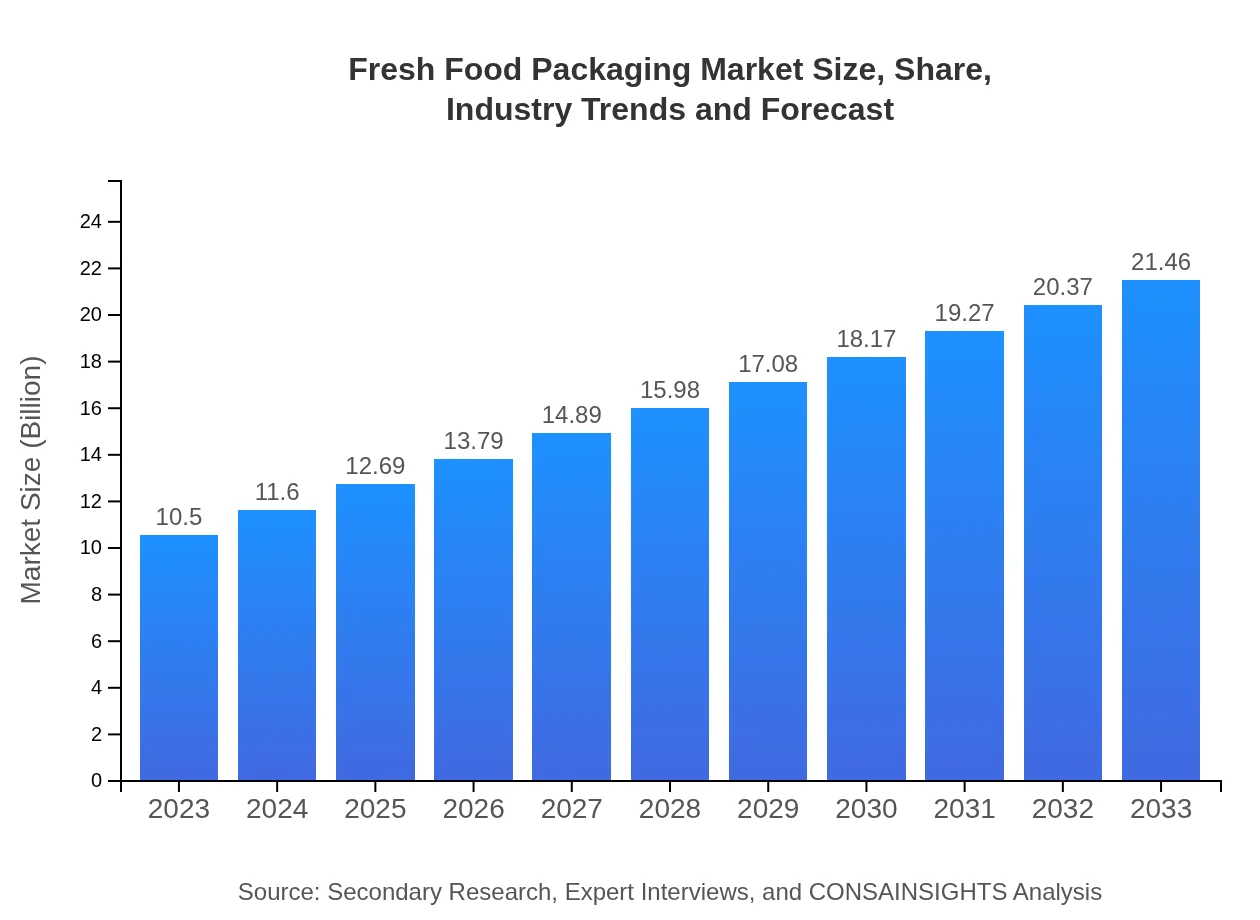
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $21.46 Billion |
| Top Companies | Amcor plc, Sealed Air Corporation, Tetra Pak, Berry Global Inc., Mondi Group |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Fresh Food Packaging Market Overview
Customize Fresh Food Packaging Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Fresh Food Packaging market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Fresh Food Packaging's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Fresh Food Packaging
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Fresh Food Packaging market in 2023 and 2033?
Fresh Food Packaging Industry Analysis
Fresh Food Packaging Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Fresh Food Packaging Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market Report:
Europe's Fresh Food Packaging market is anticipated to grow from $2.75 billion in 2023 to $5.62 billion by 2033. The region is characterized by high standards for food safety and quality, along with stringent regulations promoting sustainable practices in packaging.Asia Pacific Fresh Food Packaging Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Fresh Food Packaging market is expected to grow from $2.10 billion in 2023 to $4.29 billion by 2033, indicating robust growth driven by urbanization and rising disposable incomes. Countries like China and India are significant contributors, with increasing investments in food security and supply chain efficiency.North America Fresh Food Packaging Market Report:
North America represents a significant portion of the Fresh Food Packaging market, with an expected increase from $3.61 billion in 2023 to $7.37 billion by 2033. The U.S. and Canada are leading markets due to their strong regulatory frameworks and consumer preference for premium and organic food products.South America Fresh Food Packaging Market Report:
The South American market for Fresh Food Packaging is projected to rise from $0.85 billion in 2023 to $1.73 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by the expanding food and beverage industry, along with greater environmental awareness among consumers, leading to a demand for sustainable packaging solutions.Middle East & Africa Fresh Food Packaging Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Fresh Food Packaging market is expected to transition from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $2.45 billion by 2033. The growth here is propelled by increasing investment in food infrastructure and greater attention to food safety, driven by a rising population and urbanization.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
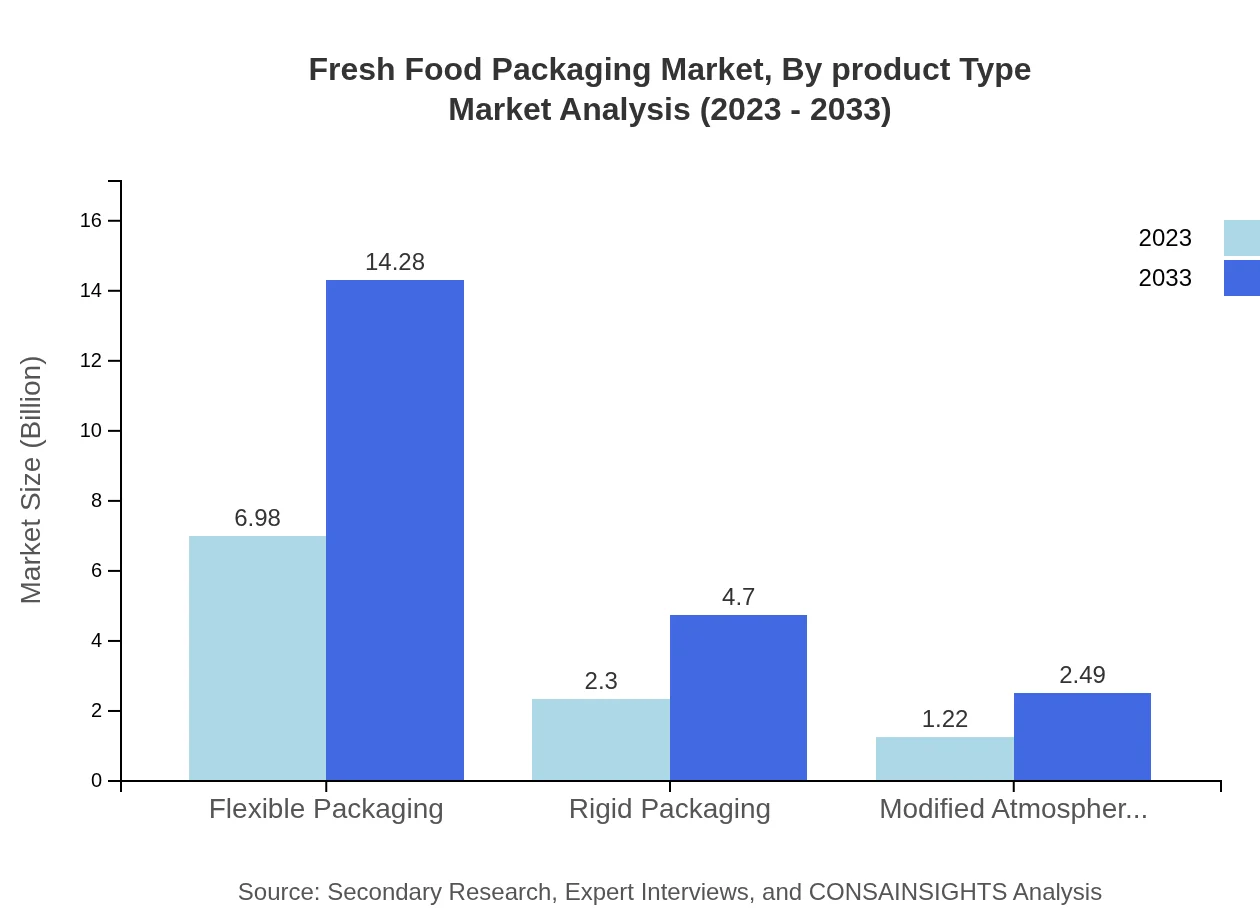
Fresh Food Packaging Market Analysis By Product Type
The Fresh Food Packaging market by product type includes segments such as Flexible Packaging and Rigid Packaging. Flexible Packaging alone is projected to grow from $6.98 billion in 2023 to $14.28 billion by 2033, highlighting its dominance and versatility in the sector. Rigid Packaging is also expected to see growth from $2.30 billion to $4.70 billion during the same period, reflecting steady demand.
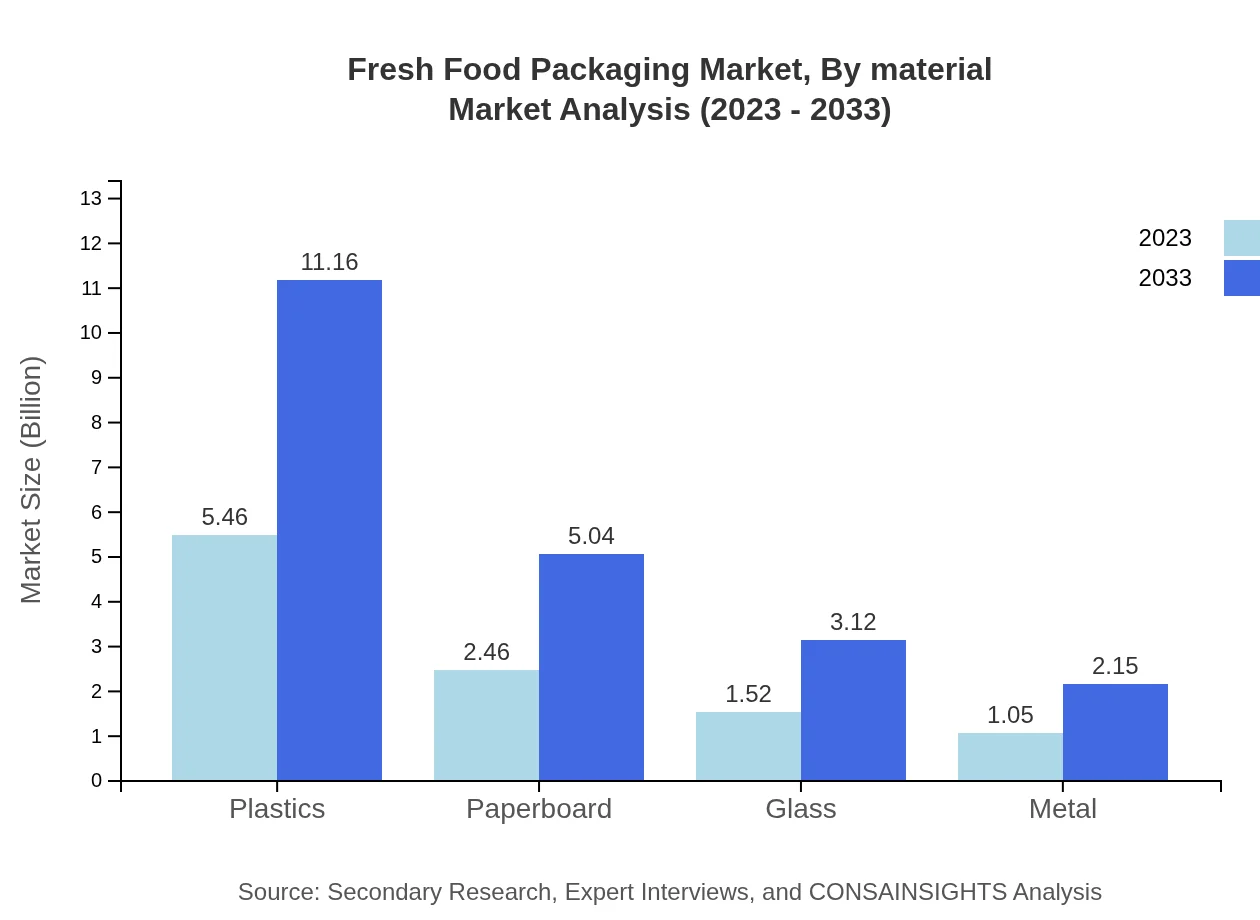
Fresh Food Packaging Market Analysis By Material
The market can also be analyzed by material type, with key segments including Plastics, Paperboard, Glass, and Metal. Plastics represent the largest share with a market size projected to grow from $5.46 billion in 2023 to $11.16 billion by 2033. Paperboard and Glass also play essential roles, with respective sizes growing from $2.46 billion to $5.04 billion and $1.52 billion to $3.12 billion.
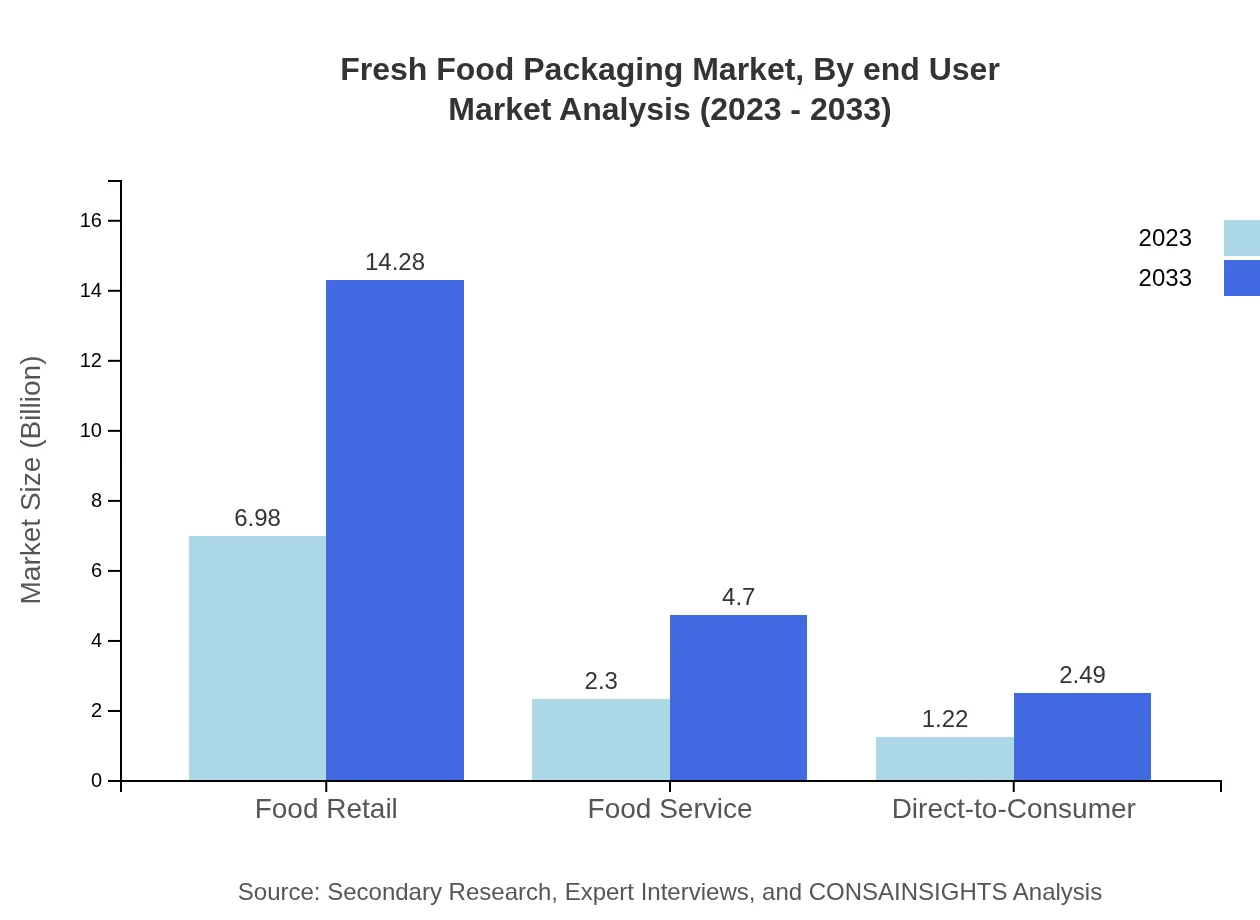
Fresh Food Packaging Market Analysis By End User
The Fresh Food Packaging market is segmented by end-user, notably including Food Retail, Food Service, and Direct-to-Consumer. Food Retail continues to dominate, with market sizes expected to climb from $6.98 billion in 2023 to $14.28 billion by 2033, capturing a significant share of the market due to consumer preference for supermarket and grocery store shopping.
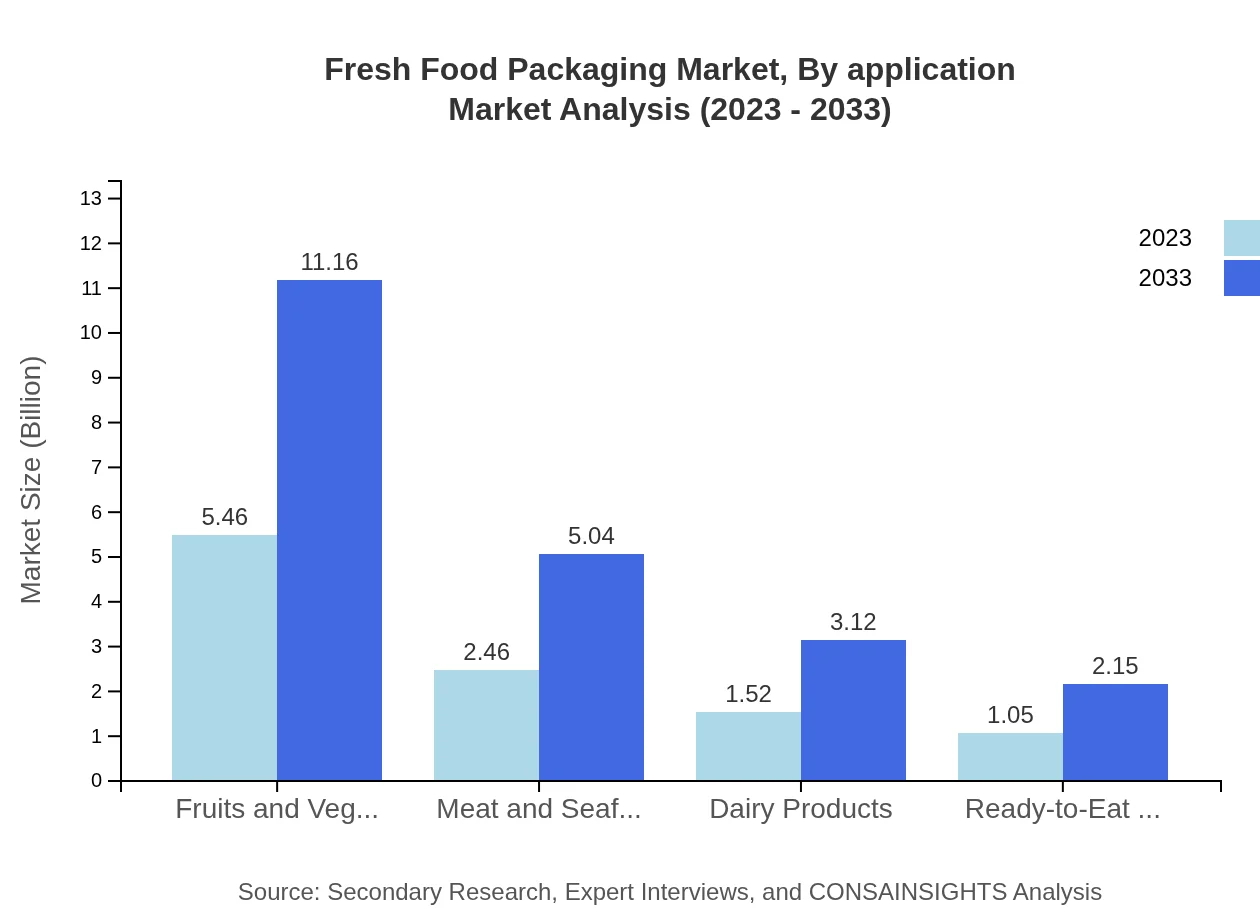
Fresh Food Packaging Market Analysis By Application
The application segments include Fruits and Vegetables, Meat and Seafood, Dairy Products, and Ready-to-Eat Meals. The Fruits and Vegetables segment is expected to exhibit robust growth, with market potential rising from $5.46 billion to $11.16 billion over the forecast period.
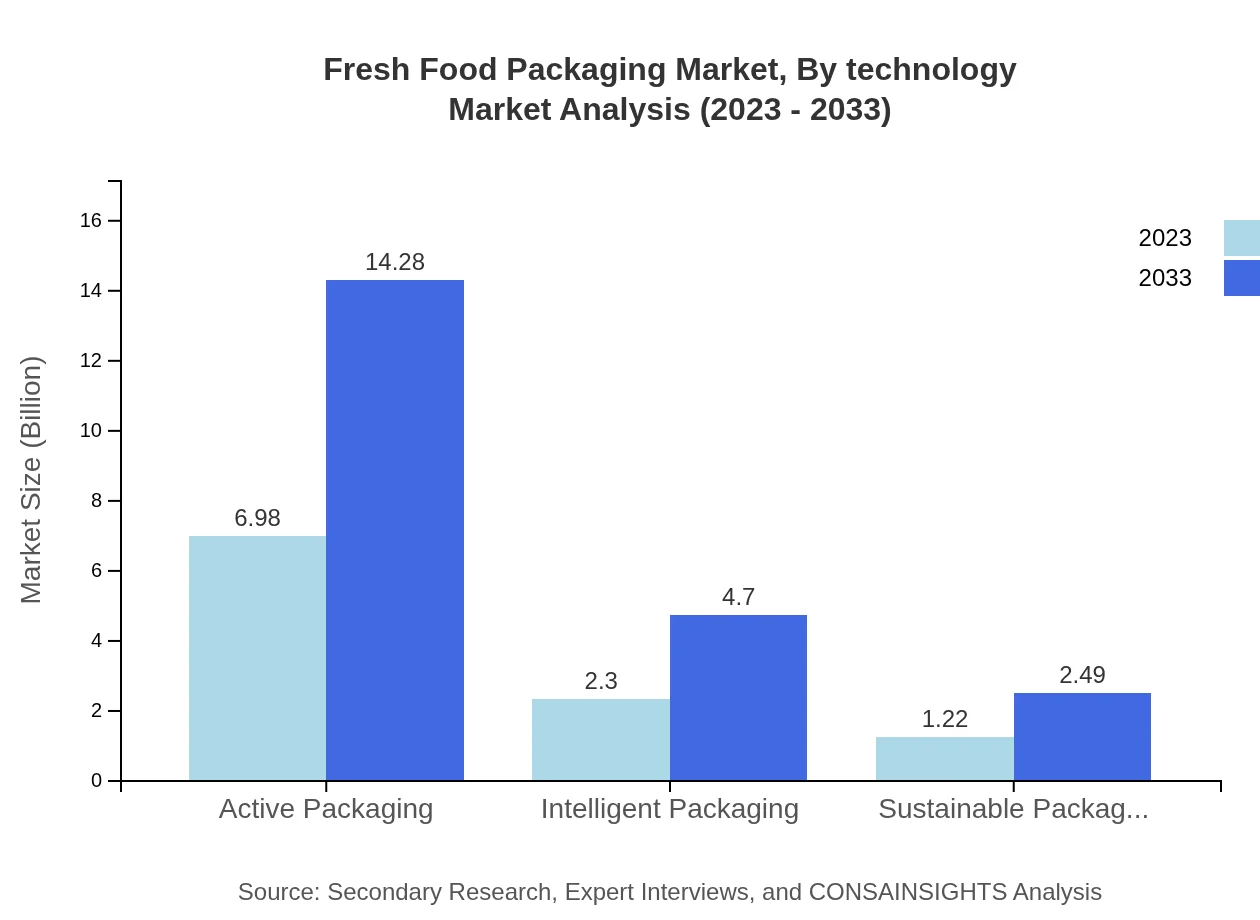
Fresh Food Packaging Market Analysis By Technology
Advancements in technology, such as Active Packaging and Intelligent Packaging, are revolutionizing the Fresh Food Packaging industry. Active Packaging is projected to lead the market with significant growth from $6.98 billion to $14.28 billion, underlining the trend towards smart solutions that enhance product freshness.
Fresh Food Packaging Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Fresh Food Packaging Industry
Amcor plc:
Amcor is a global leader in responsible packaging solutions, offering a wide range of sustainable packaging options across various sectors including food, beverage, and pharmaceuticals.Sealed Air Corporation:
Sealed Air specializes in innovative packaging solutions to protect goods during transportation. Their focus on reducing food waste through freshness and safety is pivotal to their operations.Tetra Pak:
Tetra Pak is known for its food processing and packaging solutions, particularly in liquid food packaging, emphasizing sustainability and innovation.Berry Global Inc.:
Berry Global offers diverse packaging solutions chemical and consumer markets, focusing on environmentally-friendly materials and product development.Mondi Group:
Mondi provides packaging and paper solutions, committed to sustainability and innovation, catering primarily to the food sector.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of fresh Food Packaging?
The fresh food packaging market is valued at $10.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2%, reaching an estimated size of $19.25 billion by 2033. This robust growth highlights the increasing demand for efficient food packaging solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in this fresh Food Packaging industry?
Key players in the fresh food packaging industry include industry giants like Amcor Limited, Sealed Air Corporation, Berry Global, Inc., and Smurfit Kappa Group. These companies are known for their innovative packaging technologies and sustainable solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the fresh food packaging industry?
Growth in the fresh food packaging industry is primarily driven by rising consumer demand for convenience, an increase in online grocery shopping, and a growing focus on sustainability. These factors encourage manufacturers to innovate and adopt eco-friendly packaging.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the fresh food packaging?
The fastest-growing region in the fresh food packaging market is North America, projected to increase from $3.61 billion in 2023 to $7.37 billion by 2033. The region's growth is driven by advancements in packaging technology and consumer trends favoring fresh produce.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the fresh food packaging industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the fresh food packaging industry. Clients can access detailed analyses, regional insights, and segmented data to make informed decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this fresh food packaging market research project?
Deliverables from the fresh food packaging market research project include comprehensive market reports, trend analysis, regional data breakdowns, competitive landscape assessments, and forecasts of market growth across various segments.
What are the market trends of fresh food packaging?
Current trends in fresh food packaging include a shift towards sustainable materials, increased use of active and intelligent packaging, and innovations in flexible packaging solutions. These trends reflect consumer preferences for eco-friendly and functional packaging options.