Frozen Bread Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: frozen-bread
Frozen Bread Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Frozen Bread market, including insights on market size, trends, segmentation, regional analysis, and forecast for the period 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
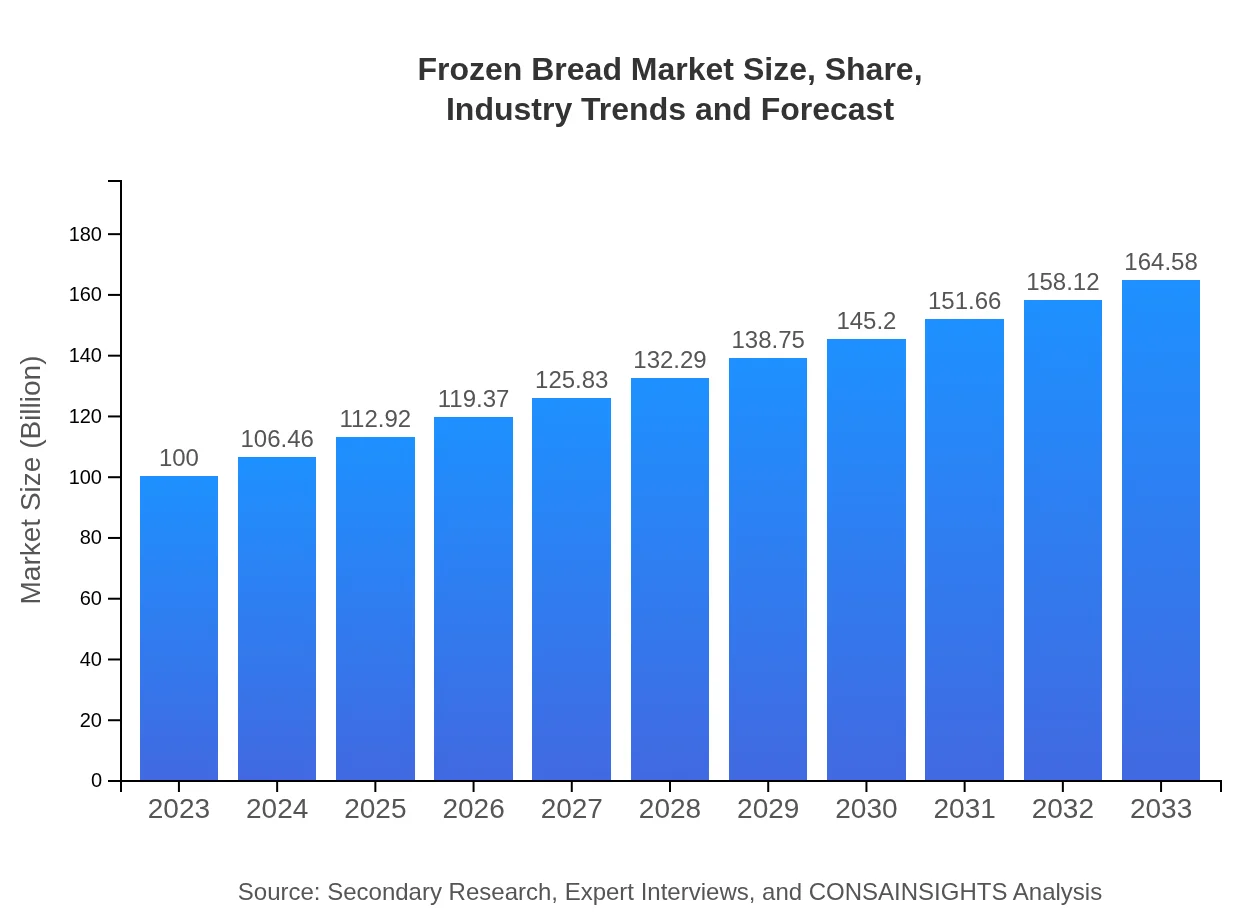
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | Bimbo Bakeries USA, Flowers Foods, Group Bimbo, Kraft Foods, Pinnacle Foods |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Frozen Bread Market Overview
Customize Frozen Bread Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Frozen Bread market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Frozen Bread's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Frozen Bread
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Frozen Bread market in 2023?
Frozen Bread Industry Analysis
Frozen Bread Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Frozen Bread Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Frozen Bread Market Report:
The European Frozen Bread market is anticipated to grow from $26.12 billion in 2023 to $42.99 billion by 2033. This region showcases heightened demand for organic and health-oriented frozen bread products, driving numerous product launches by established brands.Asia Pacific Frozen Bread Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Frozen Bread market is expected to grow from $21.92 billion in 2023 to $36.08 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization, changing lifestyles, and a rising preference for convenience foods among the busy population.North America Frozen Bread Market Report:
North America holds a substantial share in the Frozen Bread market, with estimates of $35.02 billion in 2023, growing to $57.63 billion by 2033. The region's growth is supported by high consumption rates, innovation in product offerings, and a stable supply chain for frozen food products.South America Frozen Bread Market Report:
The South American Frozen Bread market is projected to grow from $4.18 billion in 2023 to $6.88 billion by 2033, fueled by the changing eating habits and increased accessibility of frozen foods in urban areas.Middle East & Africa Frozen Bread Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is expected to rise from $12.76 billion in 2023 to $21.00 billion by 2033. The growth can be attributed to the increased adoption of western eating habits coupled with rising disposable incomes among consumers.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Frozen Bread Market Analysis By Type
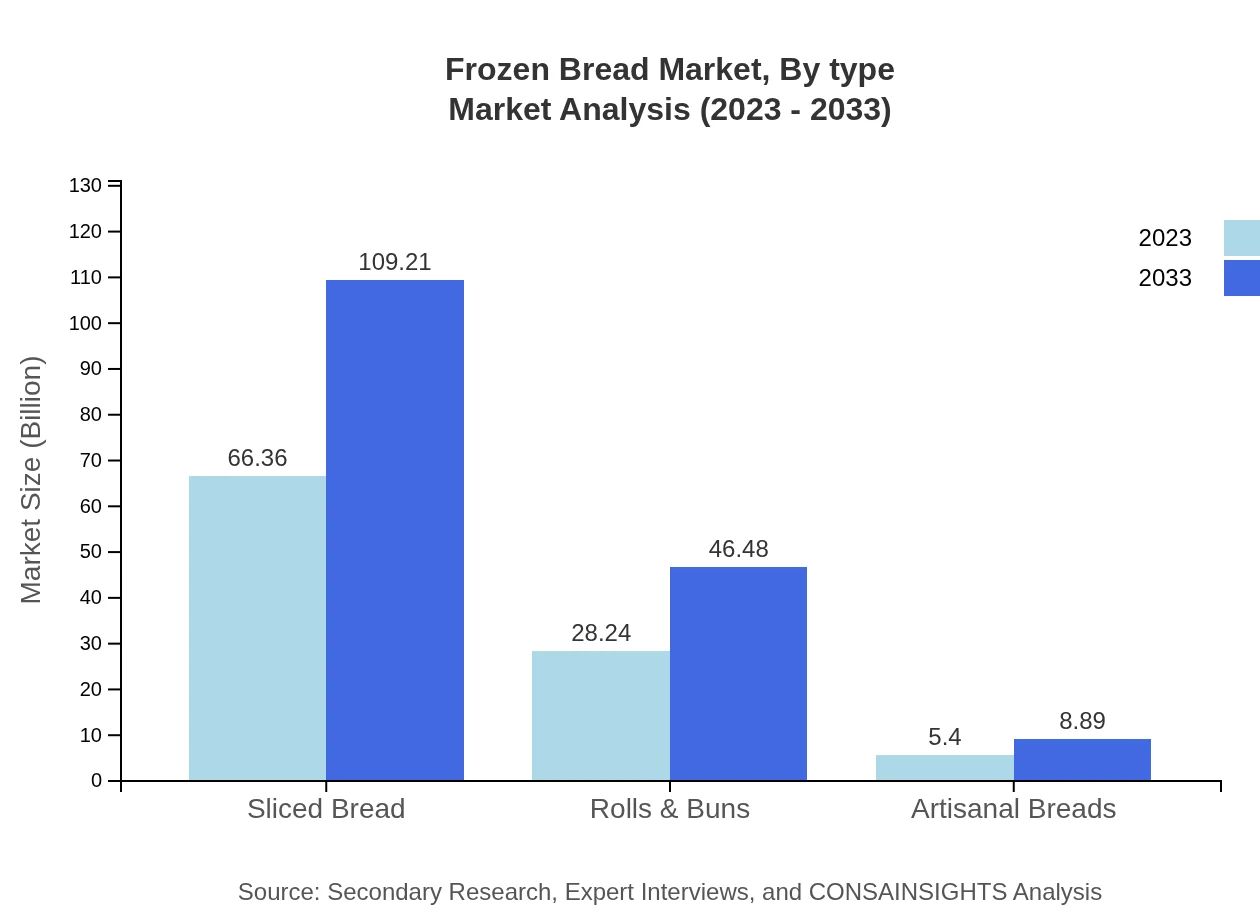
The market is largely segmented into Sliced Bread, Rolls & Buns, and Artisanal Breads. Sliced Bread is projected to grow from $66.36 billion in 2023 to $109.21 billion by 2033, dominating the market share. Rolls & Buns are also expected to see substantial growth, from $28.24 billion to $46.48 billion. Artisanal Breads, while smaller, are gaining traction among health-conscious consumers, projected to increase from $5.40 billion to $8.89 billion.
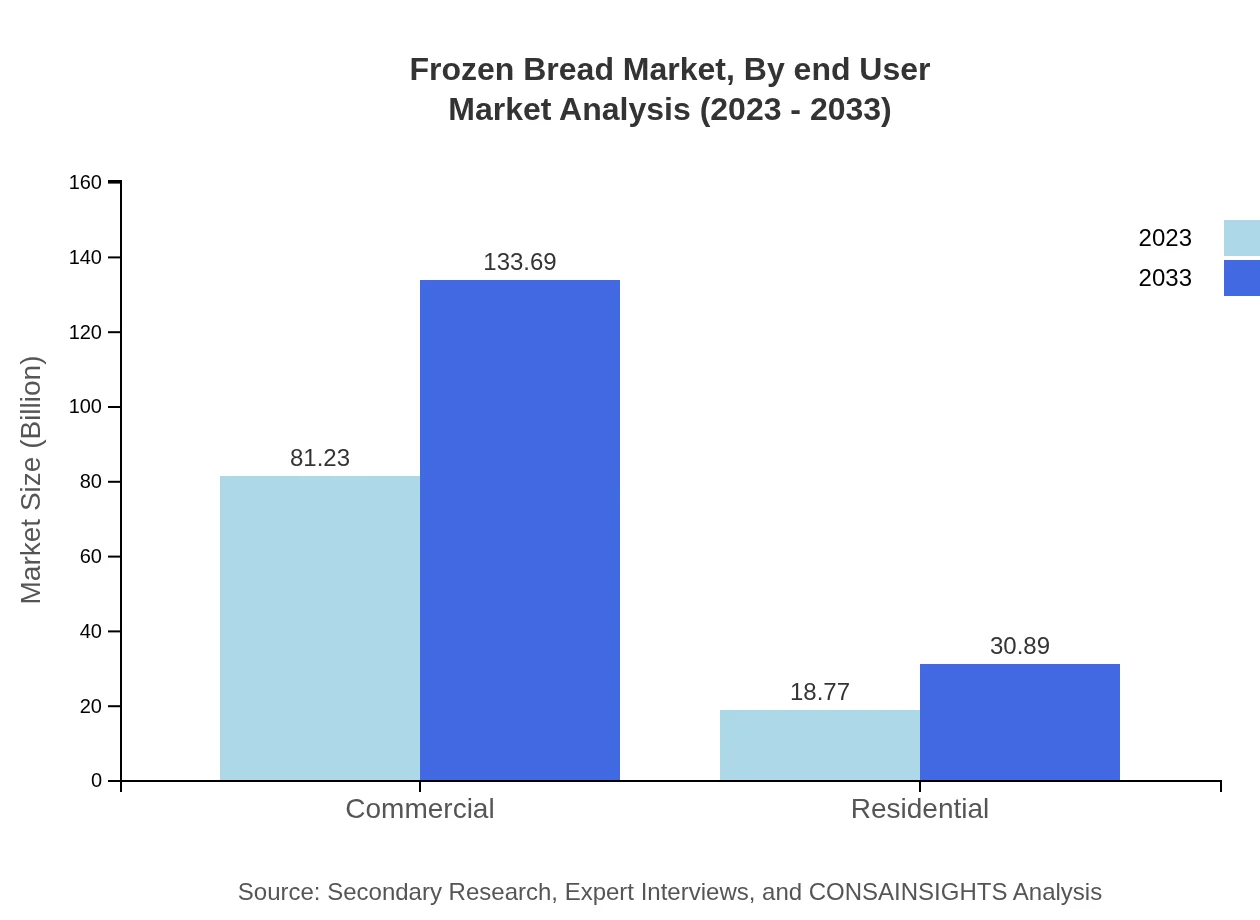
Frozen Bread Market Analysis By Application
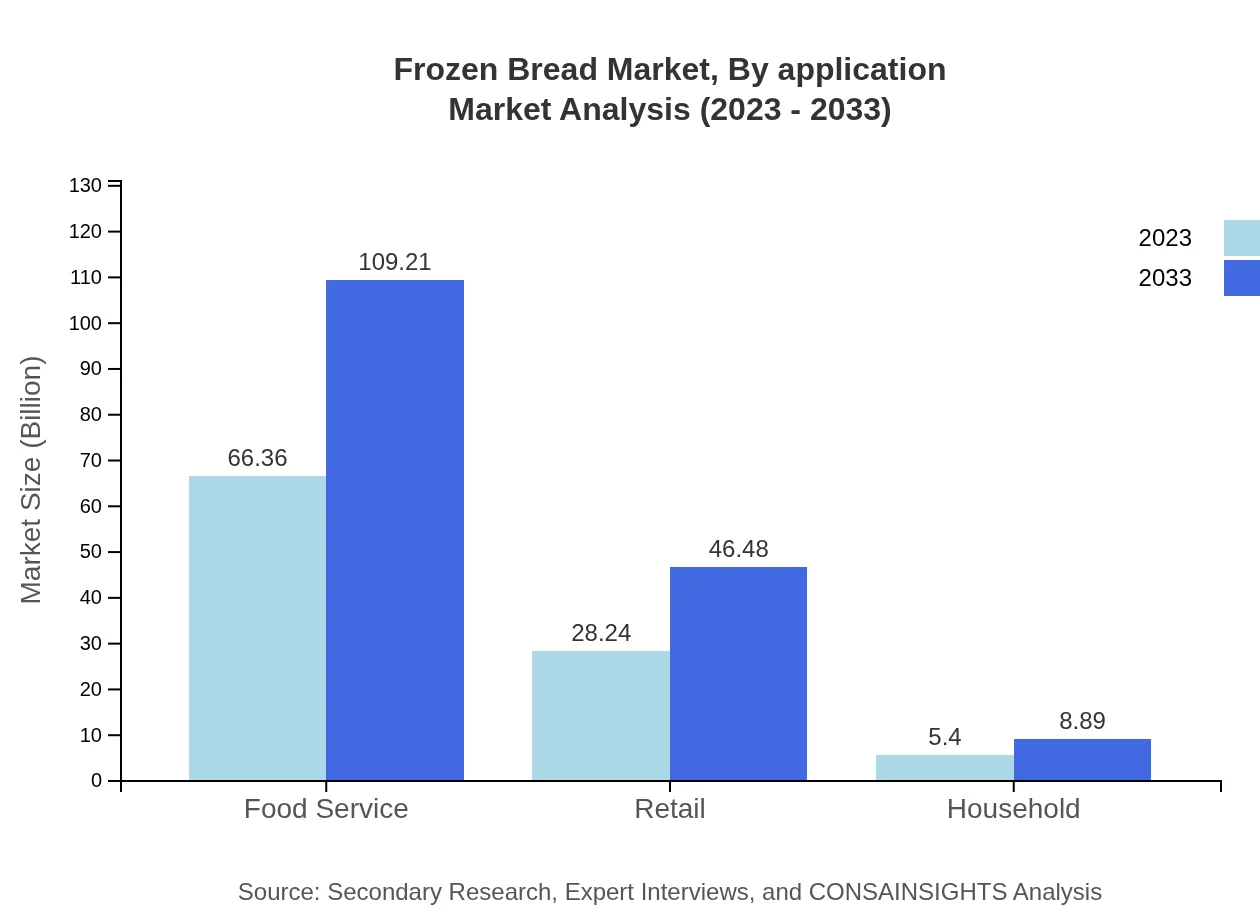
Applications are segmented into Commercial and Residential. The Commercial segment, including food service and retail applications, holds a leading market share and is set to grow from $81.23 billion in 2023 to $133.69 billion by 2033. The Residential segment is also expected to expand, growing from $18.77 billion to $30.89 billion, reflecting an upsurge in home-cooked meals.
Frozen Bread Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
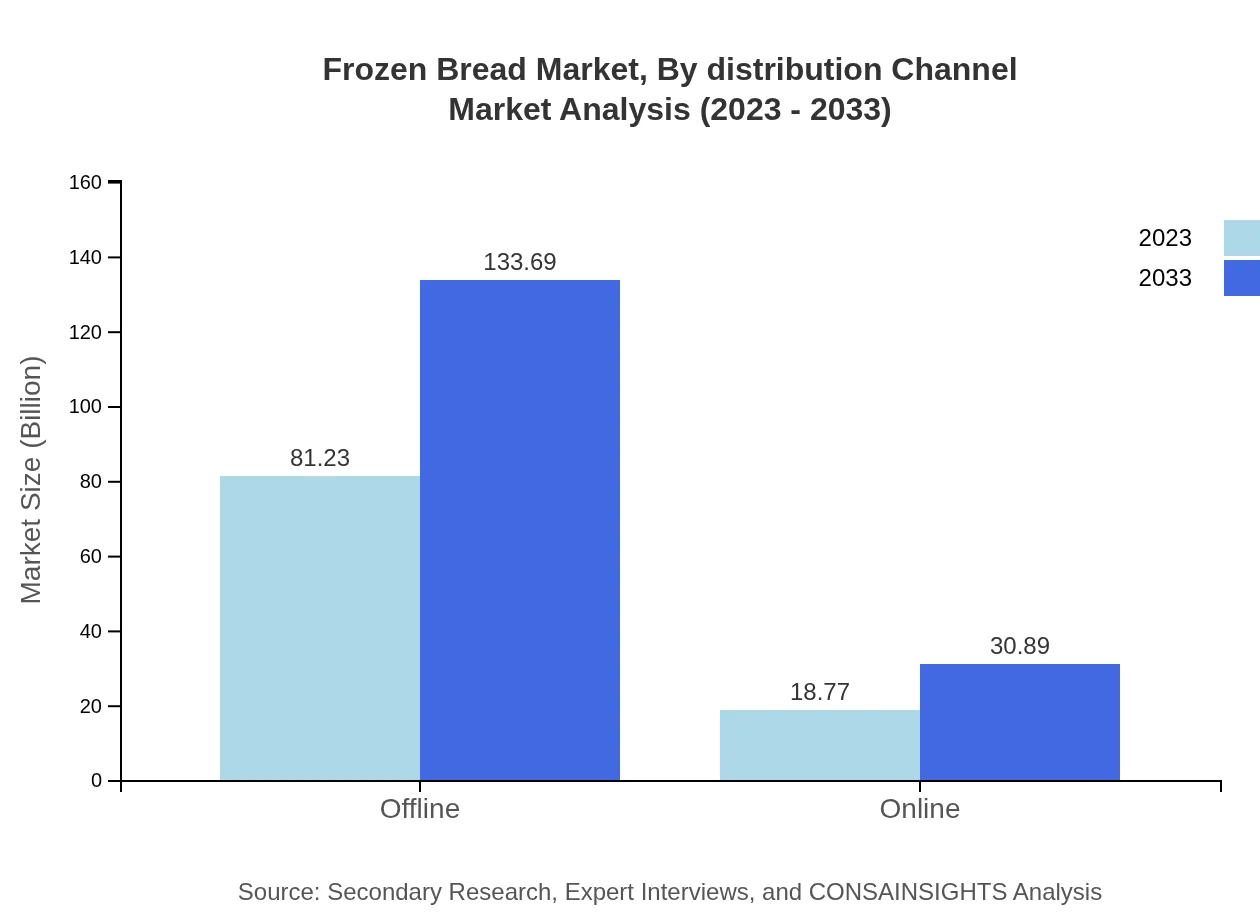
Distribution channels include Offline and Online segments. The Offline segment, which accounts for $81.23 billion in 2023, will rise significantly to $133.69 billion by 2033. Conversely, the Online segment, driven by digital transformation and increased online purchases, is expected to grow from $18.77 billion to $30.89 billion.
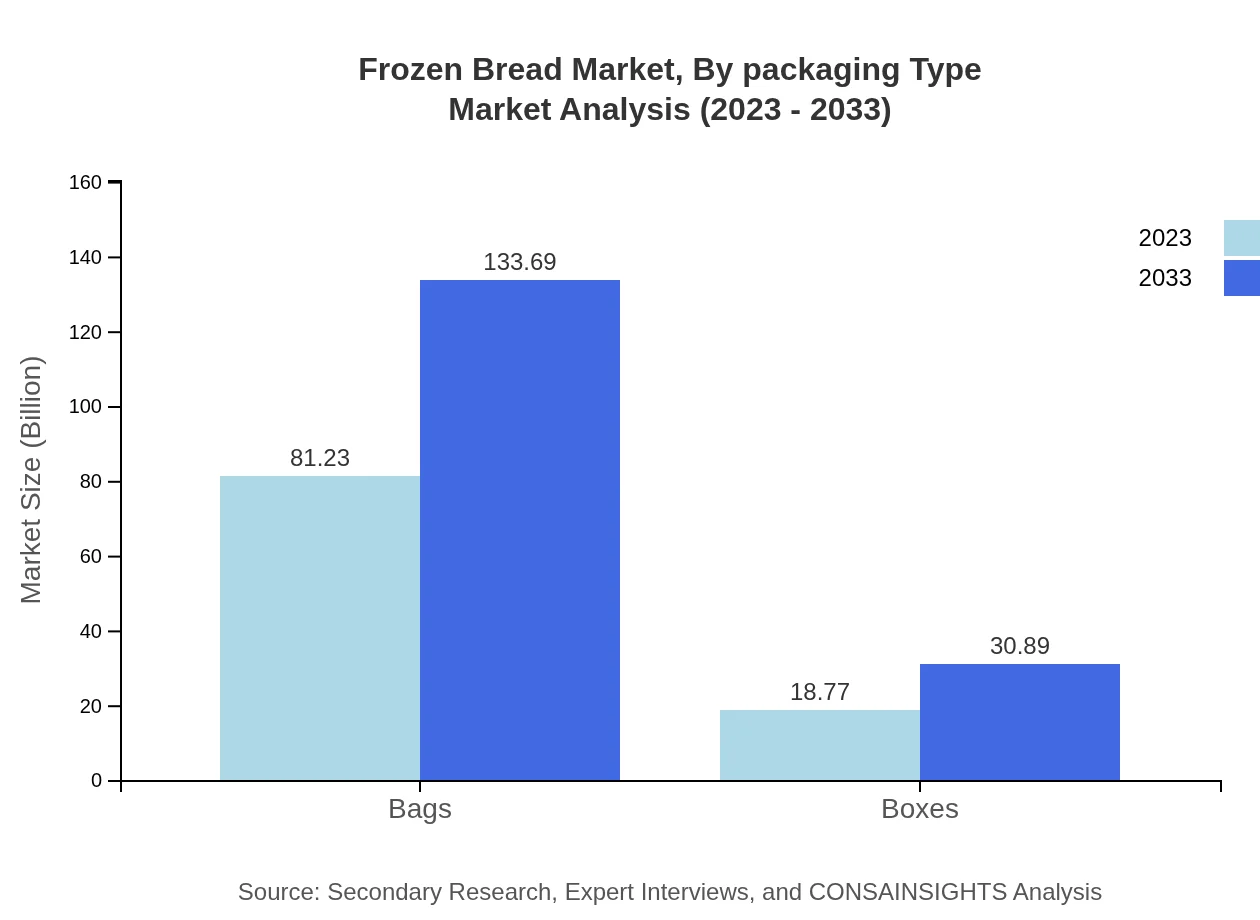
Frozen Bread Market Analysis By Packaging Type
Packaging types are segmented into Bags and Boxes. Bags dominate the market, with sizes from $81.23 billion rising to $133.69 billion by 2033. Boxes are also expected to expand, growing from $18.77 billion to $30.89 billion, as consumers seek convenience in packaging.
Frozen Bread Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment comprises Food Service and Retail. The Food Service segment is significant, projected to maintain its share as demand grows for prepared and easy-to-serve products in restaurants and cafes, expected to grow from $66.36 billion to $109.21 billion. Retail ensures the availability of frozen bread to consumers, growing from $28.24 billion to $46.48 billion.
Frozen Bread Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Frozen Bread Industry
Bimbo Bakeries USA:
Bimbo Bakeries is a leading supplier of fresh and frozen bread products known for their innovative marketing and product development in the frozen bread category.Flowers Foods:
Flowers Foods is a prominent player in the bakery industry, providing a variety of frozen bread products that appeal to diverse consumer preferences.Group Bimbo:
Group Bimbo is a global leader in the manufacturing of bakery products, including frozen bread, focusing on sustainability and health-conscious options.Kraft Foods:
Kraft Foods produces a range of frozen meals, including innovative frozen bread solutions aimed at capturing market share within the fast-moving consumer goods sector.Pinnacle Foods:
Pinnacle Foods offers a variety of frozen bread products, emphasizing quality and freshness to meet the needs of modern consumers.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of frozen Bread?
As of 2023, the market size of the frozen bread industry is approximately $100 million, with a projected CAGR of 5% from 2023 to 2033, indicating steady growth in consumer demand and market expansion.
What are the key market players or companies in this frozen Bread industry?
Key players in the frozen bread market include major food manufacturers and international brands focused on innovation, product quality, and sustainability, driving competitiveness in the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the frozen Bread industry?
Growth in the frozen bread industry is primarily driven by rising consumer convenience, increasing demand for ready-to-eat products, and innovative offerings tailored to diverse dietary needs and preferences.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the frozen Bread?
The fastest-growing region in the frozen bread market is Europe, expected to grow from $26.12 million in 2023 to $42.99 million by 2033, indicating substantial regional demand and expansion opportunities.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the frozen Bread industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the frozen bread industry, helping clients make informed decisions based on detailed insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this frozen Bread market research project?
Deliverables from the frozen bread market research project include comprehensive reports, market size analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape reviews, and actionable insights tailored to business needs.
What are the market trends of frozen bread?
Key market trends in frozen bread include a shift towards premium and artisanal options, an increase in health-conscious choices, and the growing popularity of online retail as a distribution channel.