Frozen Food Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: frozen-food
Frozen Food Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Frozen Food market, focusing on key trends, insights, and projections from 2023 to 2033. It covers market size, segmentation, regional insights, and forecasts to help stakeholders understand the evolving landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
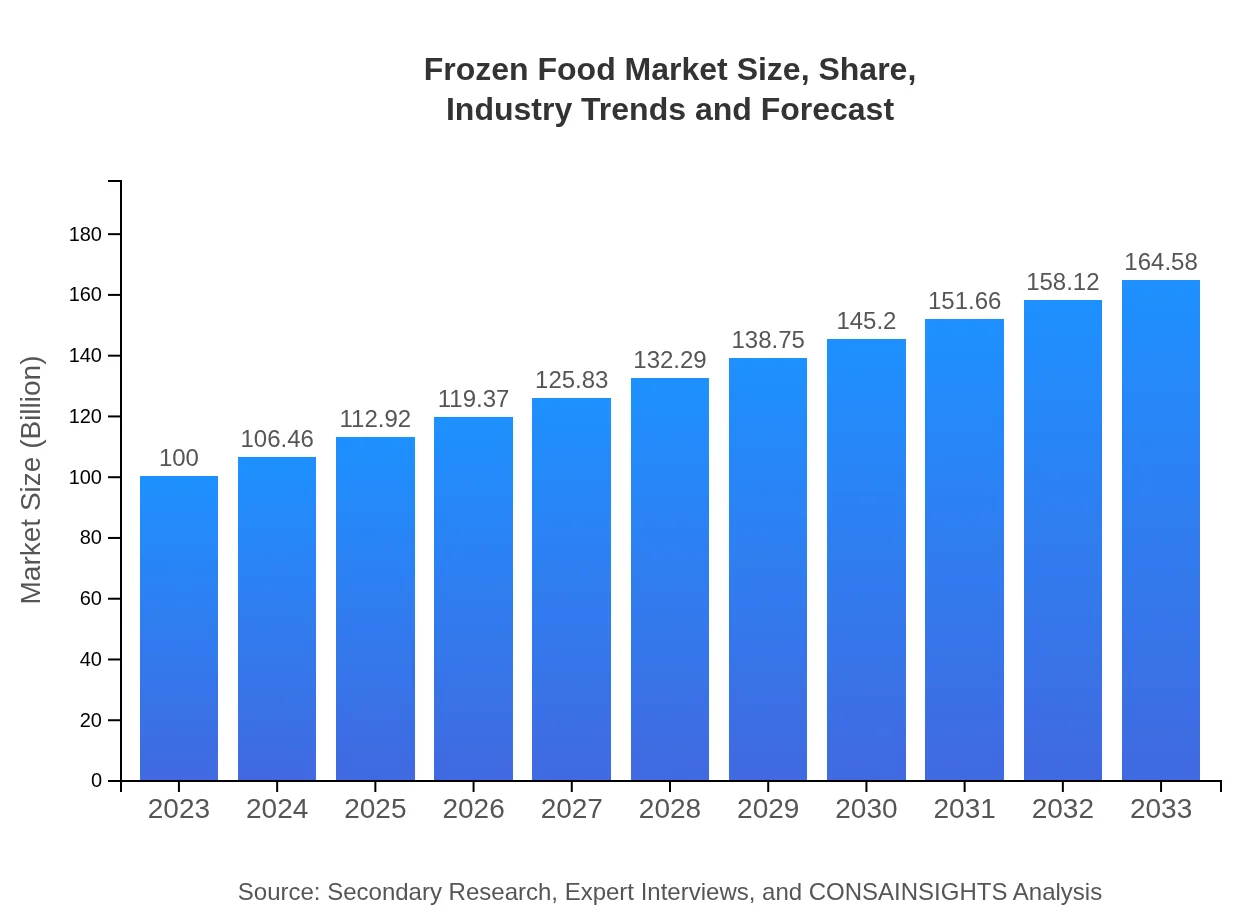
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | Nestlé S.A., Unilever PLC, ConAgra Foods, Inc., McCain Foods Limited, General Mills, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Frozen Food Market Overview
Customize Frozen Food Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Frozen Food market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Frozen Food's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Frozen Food
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Frozen Food market in 2023?
Frozen Food Industry Analysis
Frozen Food Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Frozen Food Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Frozen Food Market Report:
Europe’s frozen food market is valued at $28.25 billion in 2023, expected to reach $46.49 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing strong trends in health and wellness, resulting in increased consumption of frozen vegetables and organic products. The European market is characterized by competitive players innovating to meet the diverse tastes of consumers across various countries.Asia Pacific Frozen Food Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is poised for significant growth, with a market worth $20.45 billion in 2023, projected to reach $33.66 billion by 2033. Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and growing trends in Western-style eating habits are key drivers. Countries like China and India are experiencing robust demand, making them prime markets for frozen food products, particularly in metropolitan areas.North America Frozen Food Market Report:
North America, the largest regional market for frozen food, was valued at $33.51 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $55.15 billion by 2033. Consumer demand for ready-to-eat meals, health-conscious frozen options, and substantial penetration of e-commerce platforms are bolstering market growth. The U.S. remains a leading market, driven by innovations in meal offerings and convenience.South America Frozen Food Market Report:
In South America, the frozen food market is smaller but steadily expanding, with a value of $5.20 billion in 2023 expected to increase to $8.56 billion by 2033. The region’s growth is influenced by an increase in fast-food chains and frozen food offerings in urban grocery stores, coupled with changing dietary preferences and lifestyles.Middle East & Africa Frozen Food Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is valued at $12.59 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow to $20.72 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization and growth in consumer spending are key factors. The region is experiencing an increase in demand for a variety of frozen foods; however, market penetration remains lower relative to developed regions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Frozen Food Market Analysis By Product Type
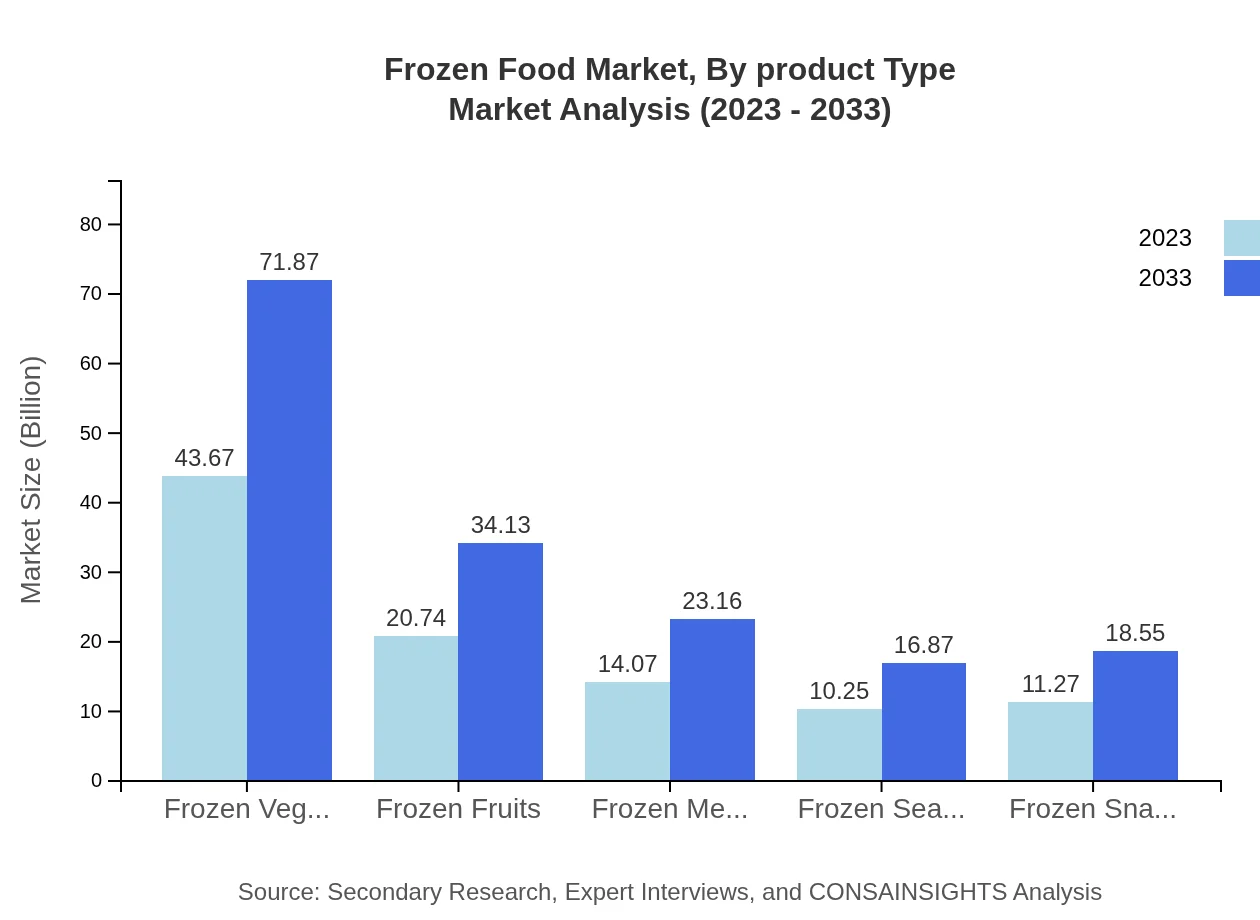
By product type, the Frozen Food market is substantial, with Frozen Vegetables dominating at $43.67 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $71.87 billion by 2033. Following closely are Frozen Fruits at $20.74 billion, projected to grow to $34.13 billion; Frozen Meals at $14.07 billion, with projections of $23.16 billion; Frozen Snacks at $11.27 billion, growing to $18.55 billion; and Frozen Seafood at $10.25 billion, increasing to $16.87 billion.
Frozen Food Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
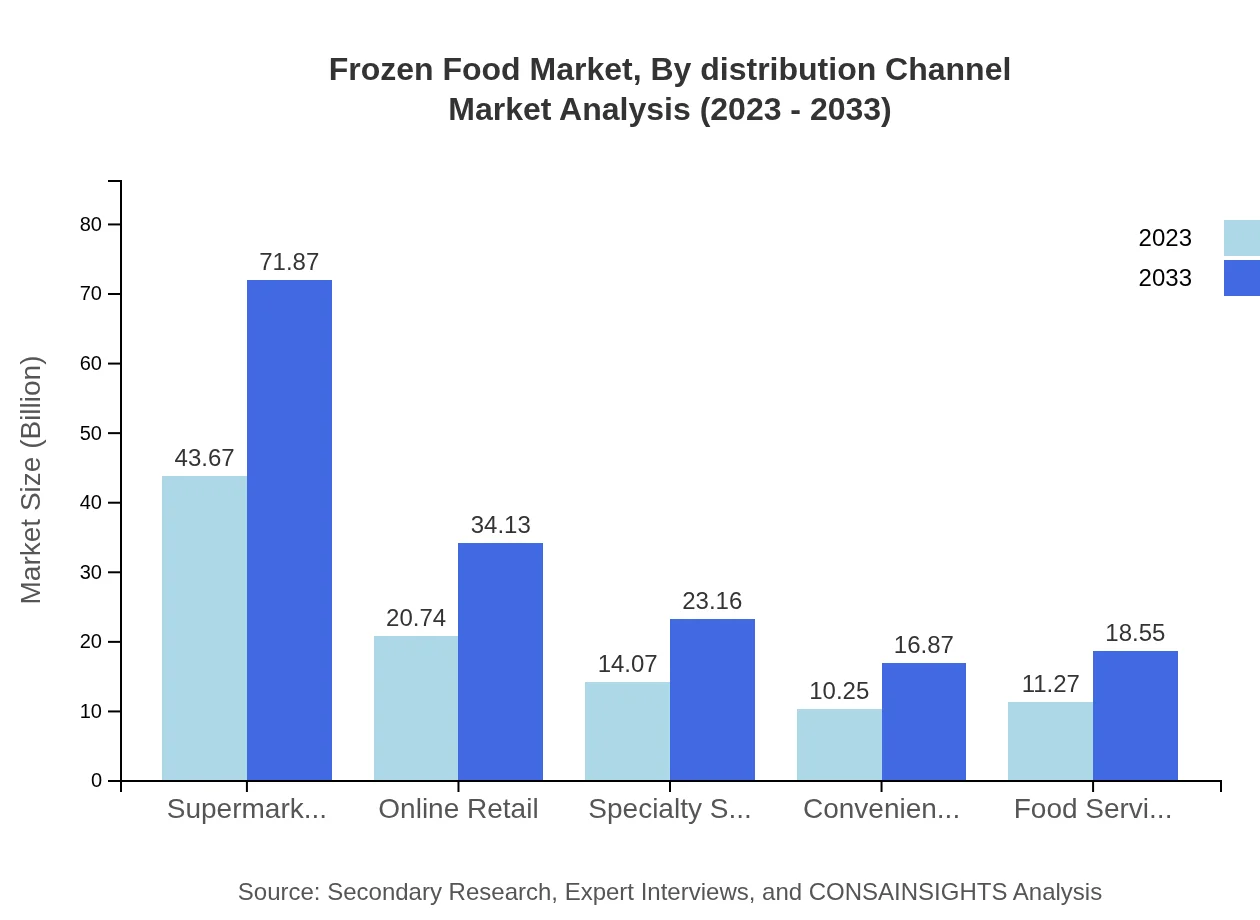
The distribution channel analysis shows Supermarkets/Hypermarkets leading with a market size of $43.67 billion in 2023, growing to $71.87 billion by 2033. Online Retail follows with $20.74 billion expected to reach $34.13 billion. Other channels include Specialty Stores at $14.07 billion growing to $23.16 billion, Convenience Stores at $10.25 billion to $16.87 billion, and Food Service Sector at $11.27 billion expected to grow to $18.55 billion.
Frozen Food Market Analysis By Application
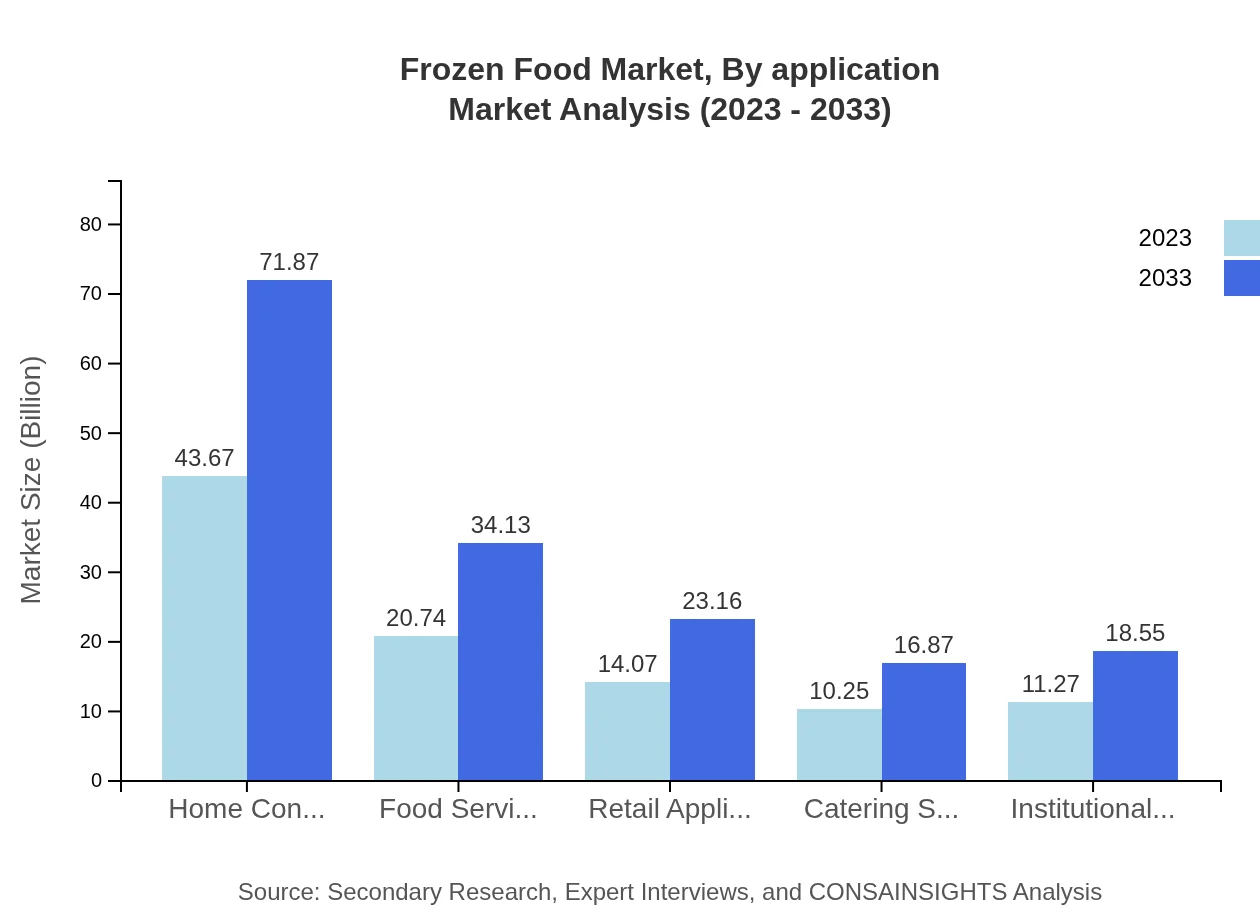
In terms of application, Home Consumption represents a major segment at $43.67 billion in 2023, with expectations of $71.87 billion by 2033. Food Service Applications follow closely, growing from $20.74 billion to $34.13 billion. Institutional Food Services also have a significant role, with projections moving from $11.27 billion to $18.55 billion, showcasing strong demand from catering services and similar establishments.
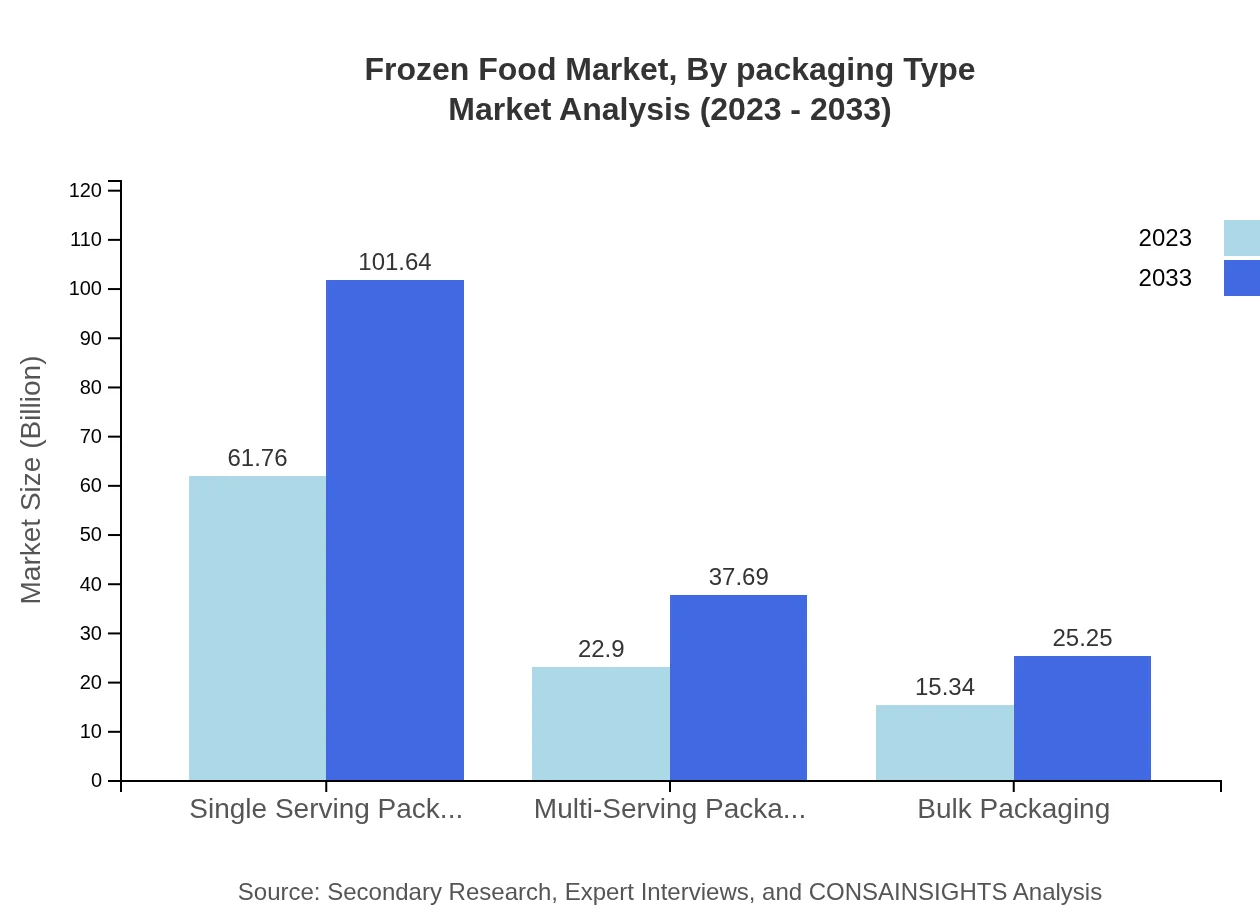
Frozen Food Market Analysis By Packaging Type
The Frozen Food market is largely influenced by packaging types, with Single Serving Packaging leading at $61.76 billion in 2023 and increasing to $101.64 billion by 2033. Multi-Serving Packaging is projected to grow from $22.90 billion to $37.69 billion, while Bulk Packaging will rise from $15.34 billion to $25.25 billion, indicating a preference for convenience in meal portions among consumers.
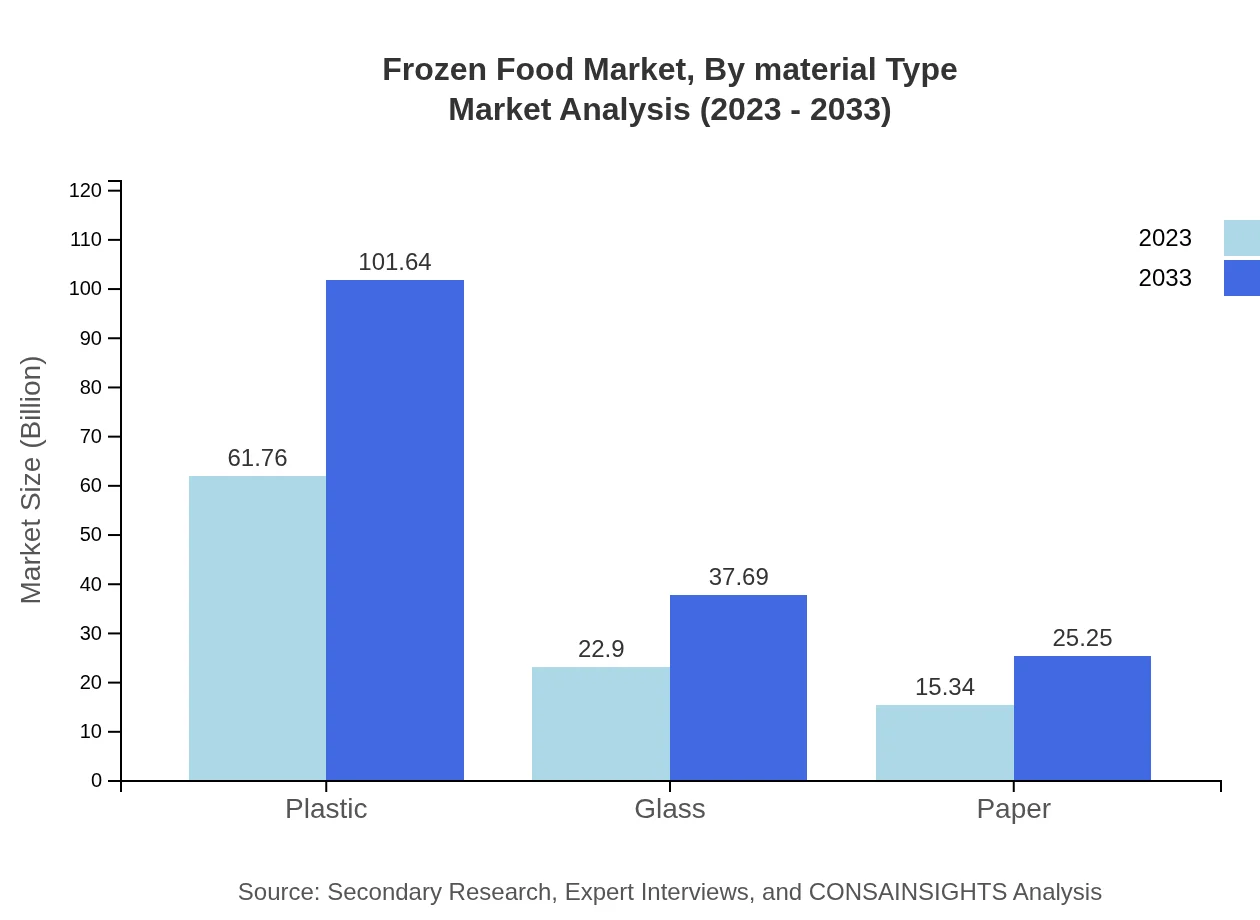
Frozen Food Market Analysis By Material Type
Material types also significantly impact the Frozen Food market. Plastic packaging dominates with a market size of $61.76 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $101.64 billion. Glass packaging is valued at $22.90 billion and is expected to reach $37.69 billion, while paper packaging is forecasted to increase from $15.34 billion to $25.25 billion. These trends reflect the composite demands for both functionality and sustainability in packaging materials.
Frozen Food Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Frozen Food Industry
Nestlé S.A.:
Nestlé is a global leader in frozen food, offering products ranging from frozen meals to vegetables, with a strong emphasis on quality and nutritional value.Unilever PLC:
Unilever is a prominent player in the frozen food space, particularly known for its popular brands that focus on convenience and health.ConAgra Foods, Inc.:
ConAgra offers a variety of frozen food products, emphasizing innovation and consumer trends, catering to both retail and food service sectors.McCain Foods Limited:
A key player in frozen potato products, McCain is renowned for its extensive range of frozen foods focused on quality and sustainability.General Mills, Inc.:
General Mills plays a critical role in the frozen meals segment, providing diverse product options that cater to various consumer preferences and health trends.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of frozen Food?
The frozen food market is currently valued at over $100 million with a projected CAGR of 5%. By 2033, substantial growth is anticipated as consumer preferences shift, increasing accessibility and demand in various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the frozen Food industry?
Key players in the frozen food market include major companies such as Nestle, Conagra Brands, and Kraft Heinz, which drive innovation and maintain significant market shares, influencing trends and growth within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the frozen Food industry?
Growth in the frozen food industry is propelled by changing consumer lifestyles, increasing demand for convenience, better preservation technologies, and a notable shift towards healthier options, reflecting a broader trend toward balanced diets.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the frozen Food market?
North America shows the fastest growth in the frozen food market, increasing from $33.51 billion in 2023 to $55.15 billion by 2033, closely followed by Europe and Asia Pacific, reflecting evolving consumer behaviors.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the frozen Food industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data, tailoring insights specific to client needs in the frozen food industry, allowing businesses to leverage detailed analytics for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this frozen Food market research project?
From the frozen food market research project, clients can expect comprehensive market analysis reports, detailed segmentation data, regional insights, and projections, highlighting evolving trends for informed business strategies.
What are the market trends of frozen Food?
Current trends in the frozen food market include a rise in plant-based options, sustainable packaging innovations, and increasing online retail activities, reflecting changing consumer preferences towards health and convenience.