Frozen Processed Food Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: frozen-processed-food
Frozen Processed Food Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report comprehensively analyzes the Frozen Processed Food market from 2023 to 2033, covering key insights on market size, growth forecasts, regional analysis, industry trends, and major players. It aims to provide stakeholders with detailed data-driven insights to guide strategic decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
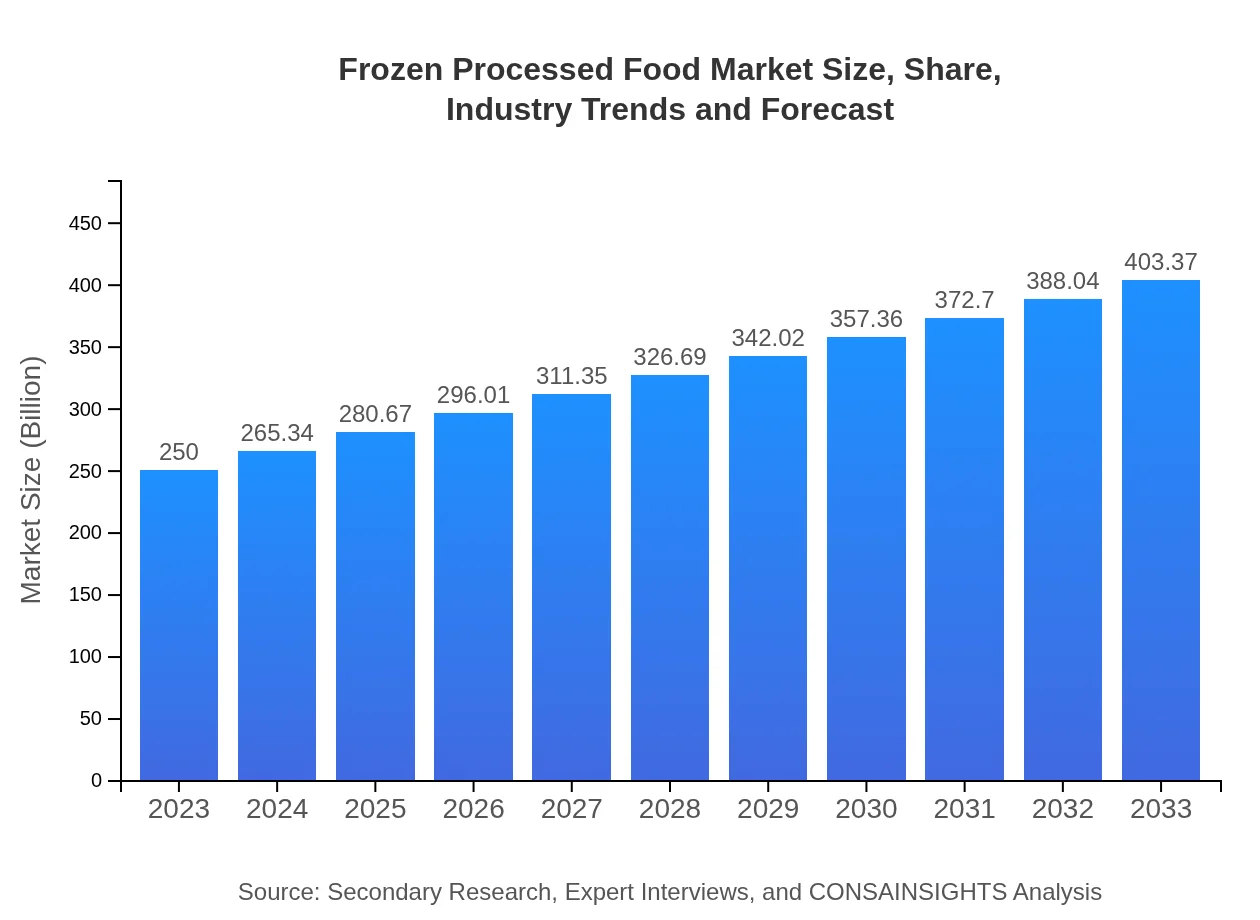
| 2023 Market Size | $250.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $403.37 Billion |
| Top Companies | Nestlé S.A., Unilever, Tyson Foods, Inc., Conagra Brands, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Frozen Processed Food Market Overview
Customize Frozen Processed Food Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Frozen Processed Food market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Frozen Processed Food's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Frozen Processed Food
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Frozen Processed Food market in 2023?
Frozen Processed Food Industry Analysis
Frozen Processed Food Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Frozen Processed Food Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Frozen Processed Food Market Report:
In Europe, the Frozen Processed Food market size is forecasted to grow from 85.17 billion USD in 2023 to 137.43 billion USD by 2033. European consumers increasingly favor frozen products, especially organic and ethical brands.Asia Pacific Frozen Processed Food Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Frozen Processed Food market is projected to expand from a valuation of 46.82 billion USD in 2023 to approximately 75.55 billion USD by 2033, driven by rising incomes, urbanization, and evolving food preferences.North America Frozen Processed Food Market Report:
North America leads in Frozen Processed Food consumption, valued at 87.88 billion USD in 2023, anticipated to reach 141.79 billion USD by 2033. The consumer trend towards convenience foods significantly drives this growth.South America Frozen Processed Food Market Report:
The South American market, albeit smaller at 4.45 billion USD in 2023, is expected to grow to 7.18 billion USD by 2033. The growth is fueled by increasing demand for frozen ready-to-eat options.Middle East & Africa Frozen Processed Food Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to increase from 25.68 billion USD in 2023 to 41.43 billion USD by 2033, supported by improvements in infrastructure and logistics facilitating better distribution.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
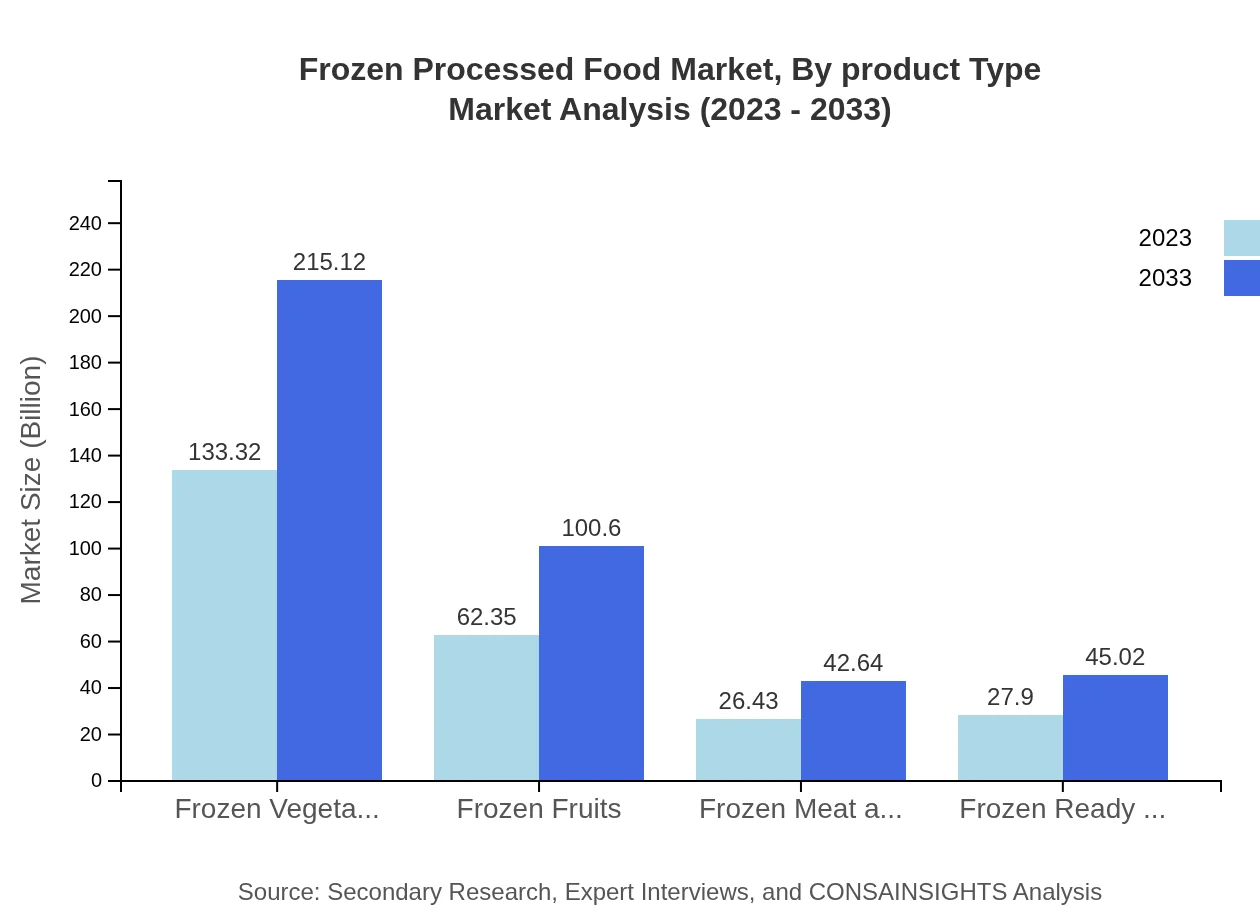
Frozen Processed Food Market Analysis By Product Type
The product types in the Frozen Processed Food market include frozen vegetables, fruits, meats, seafood, and ready meals. Frozen vegetables dominate the market, valued at 133.32 billion USD in 2023, and projected to reach 215.12 billion USD by 2033. Frozen fruits and ready meals also show promise, with projected increases from 62.35 billion USD to 100.60 billion USD and from 27.90 billion USD to 45.02 billion USD respectively.
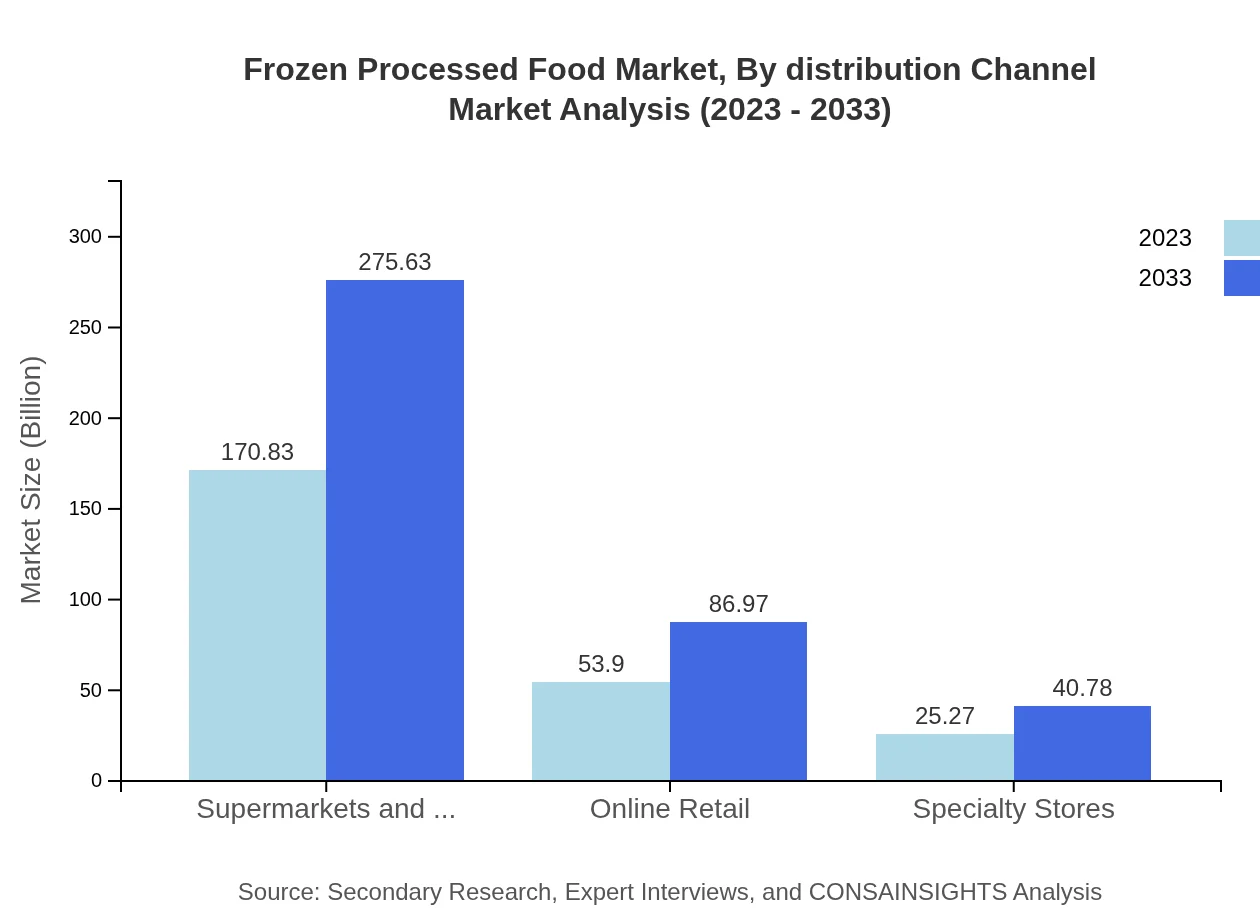
Frozen Processed Food Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The market is primarily served through supermarkets and hypermarkets, commanding a market size of 170.83 billion USD in 2023, expected to grow to 275.63 billion USD by 2033. Online retail is also gaining traction, slated to grow from 53.90 billion USD to 86.97 billion USD over the forecast period.
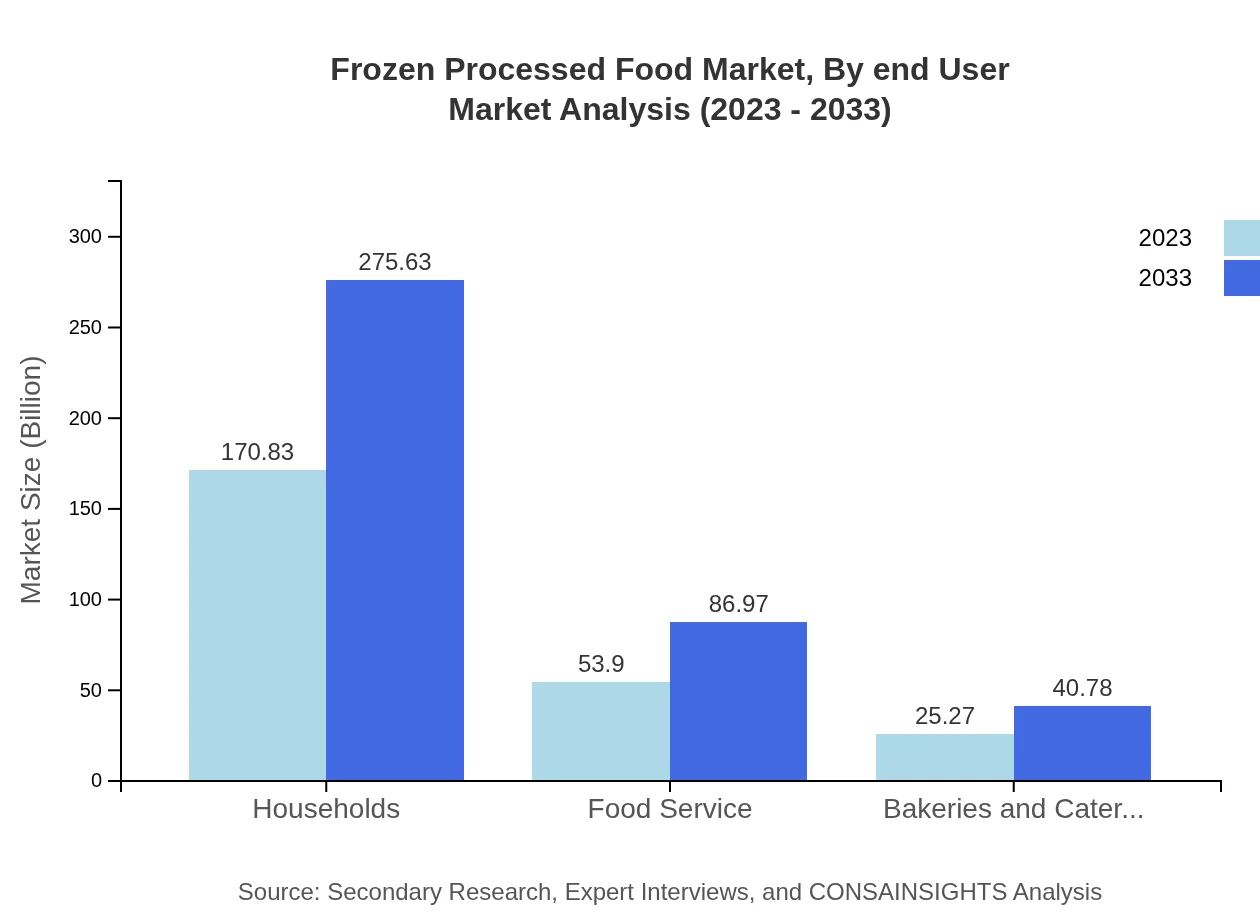
Frozen Processed Food Market Analysis By End User
Households are the dominant end-user segment, showcasing significant growth from 170.83 billion USD in 2023 to 275.63 billion USD by 2033. The food service sector, including restaurants, is also growing, from 53.90 billion USD to 86.97 billion USD during the same period.
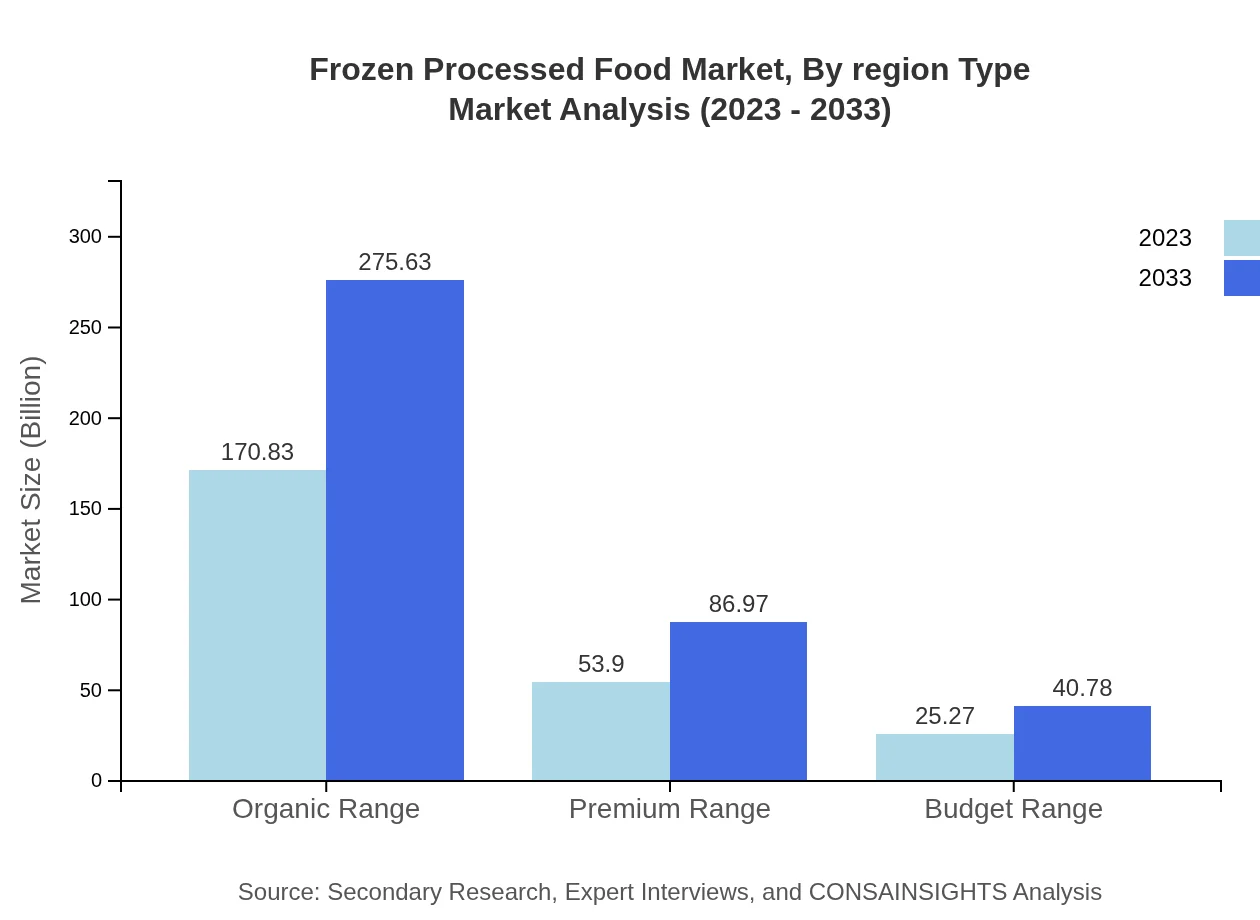
Frozen Processed Food Market Analysis By Region Type
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe are the largest markets for Frozen Processed Food, with significant growth rates expected in the Asia Pacific region. Each region is adapting to changing consumer preferences, with a noticeable shift towards organic and premium frozen products.
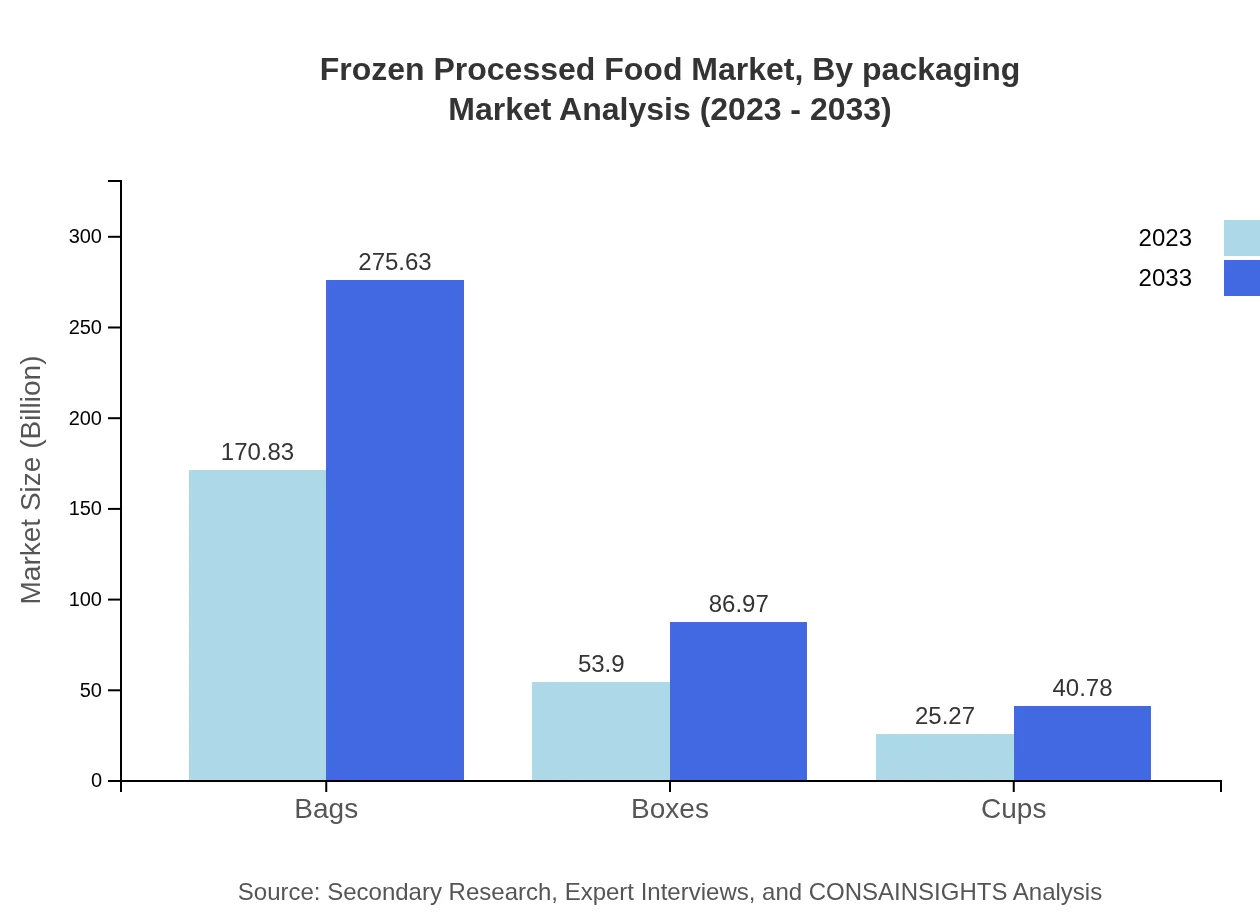
Frozen Processed Food Market Analysis By Packaging
Packaging plays a crucial role in product appeal and preservation. Flexible and sustainable packaging solutions are gaining popularity. The market for bags is projected to grow from 170.83 billion USD in 2023 to 275.63 billion USD by 2033, with boxes and cups also showing significant growth.
Frozen Processed Food Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Frozen Processed Food Industry
Nestlé S.A.:
Nestlé is a leading company in the frozen processed food sector, offering a wide range of products including frozen meals, desserts, and snacks. Its commitment to quality and innovation has placed it at the forefront of the market.Unilever:
With a diverse portfolio of frozen foods, Unilever is well-known for its brands that focus on convenience and health. It has made significant investments in sustainable sourcing and product development.Tyson Foods, Inc.:
Tyson Foods is a major player in frozen meat and poultry products. The company emphasizes quality control and supply chain efficiency, ensuring fresh frozen options for consumers.Conagra Brands, Inc.:
Conagra specializes in frozen meal solutions and snacks. The brand is recognized for its innovations geared towards health, convenience, and variety to meet changing consumer preferences.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of frozen Processed Food?
The global frozen processed food market was valued at approximately $250 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% over the next decade. This growth points to an expanding consumer demand for frozen convenience foods.
What are the key market players or companies in the frozen Processed Food industry?
Key players in the frozen processed food market include Nestlé, Conagra Brands, General Mills, and Unilever. These companies dominate through diversified product lines, strong distribution networks, and continuous innovation in frozen food offerings to meet evolving consumer preferences.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the frozen processed food industry?
Factors driving growth in the frozen processed food industry include rising demand for convenience foods, increasing urbanization, growing health consciousness, and technological advancements in freezing methods that preserve food quality and taste, making them more appealing to consumers.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the frozen processed food market?
The Asia-Pacific region is currently the fastest-growing market for frozen processed foods, projected to grow from $46.82 billion in 2023 to $75.55 billion by 2033. Factors include rising disposable incomes and a shift towards modern retail formats.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the frozen Processed Food industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored specifically for the frozen processed food industry. This includes insights into various segments, regional analysis, and competitive landscape assessments to meet specific client needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this frozen Processed Food market research project?
Deliverables from this market research project include comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, consumer insights, and detailed breakdowns by region and segment, providing actionable strategies for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of frozen Processed Food?
Current trends in the frozen processed food market include a growing emphasis on organic offerings, increased demand for ready-to-eat meals, technological innovations in packaging, and a shift towards environmentally friendly practices in production and distribution.