Fungal Protein Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: fungal-protein
Fungal Protein Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the fungal protein market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market size, growth rate, segmentation, regional trends, technological advancements, product performance, key players, and future forecasts.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
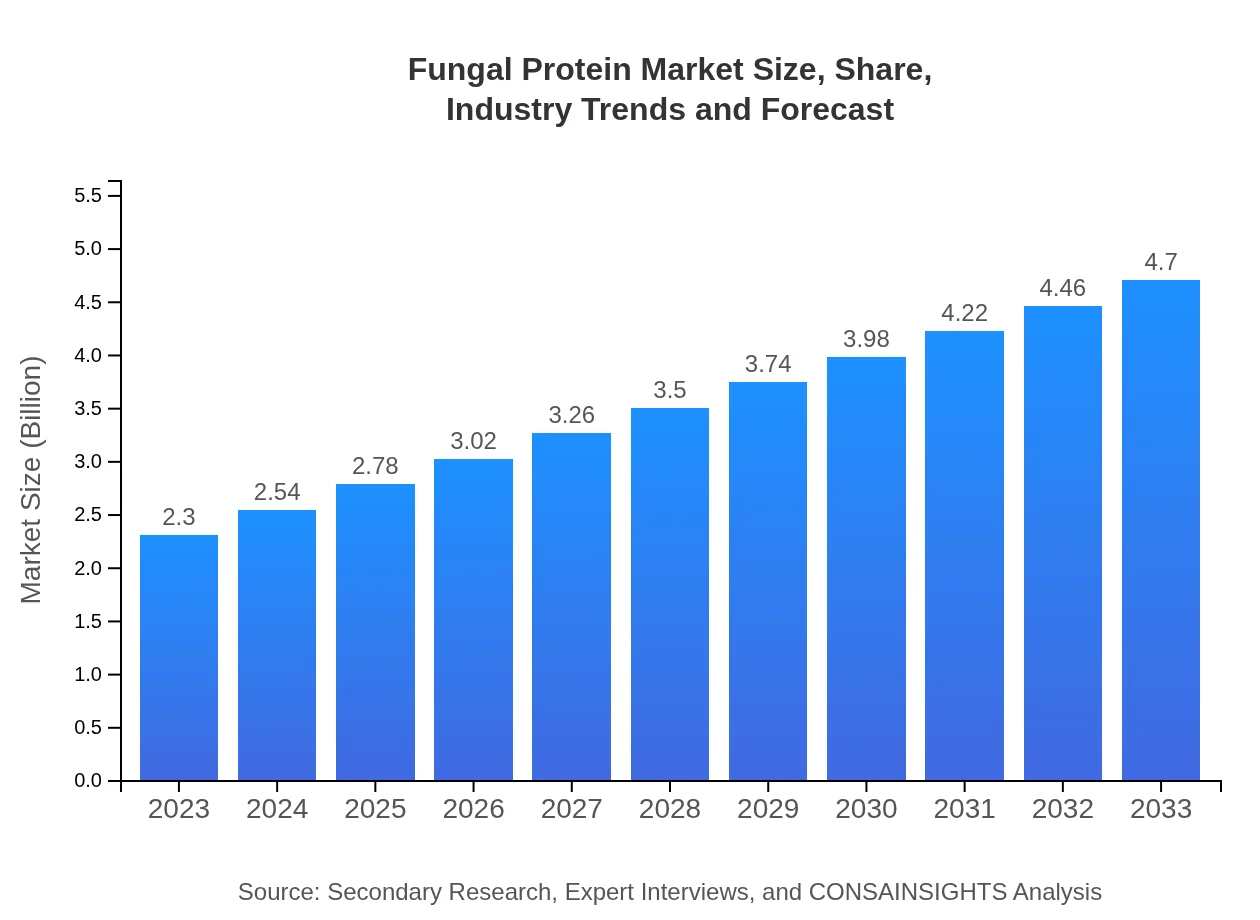
| 2023 Market Size | $2.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $4.70 Billion |
| Top Companies | Fungi Perfecti, MycoTechnology, Ecovative Design |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Fungal Protein Market Overview
Customize Fungal Protein Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Fungal Protein market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Fungal Protein's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Fungal Protein
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Fungal Protein market in 2023?
Fungal Protein Industry Analysis
Fungal Protein Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Fungal Protein Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Fungal Protein Market Report:
In Europe, the fungal protein market is worth $0.57 billion as of 2023, expected to double to $1.16 billion by 2033. Factors include stringent regulations supporting sustainable practices and an increasing vegan population.Asia Pacific Fungal Protein Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific fungal protein market is valued at $0.49 billion, projected to grow to $1.00 billion by 2033. Growing populations and a shift towards protein-rich diets, especially in countries like China and India, are spurring market growth.North America Fungal Protein Market Report:
North America is a mature market for fungal proteins, with 2023 valuations estimated at $0.75 billion. By 2033, it is forecasted to reach $1.53 billion. The strong demand for plant-based proteins and innovations in food technology bolsters this region.South America Fungal Protein Market Report:
The South American fungal protein market stands at $0.22 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $0.45 billion by 2033. Increased adoption of functional foods and dietary supplements contributes to this growth in Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Fungal Protein Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market for fungal proteins is valued at $0.28 billion in 2023, with a projection of $0.56 billion by 2033. The region's growing health-conscious consumer base drives demand for alternative protein sources.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
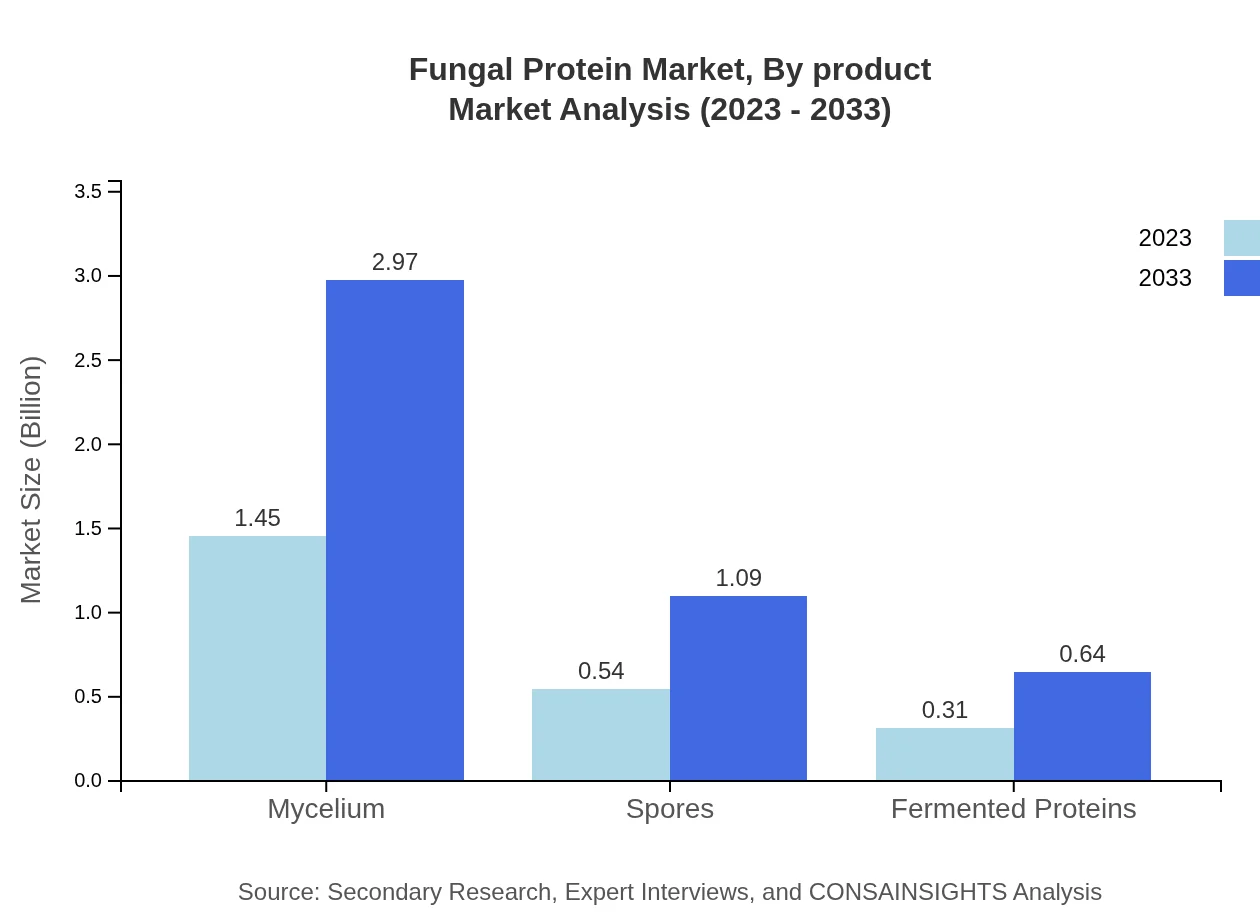
Fungal Protein Market Analysis By Product
Mycelium, currently valued at $1.45 billion in 2023, will become a $2.97 billion segment by 2033. Spores and fermented proteins contribute significantly as well, with spores projected to grow from $0.54 billion to $1.09 billion in the same timeframe.
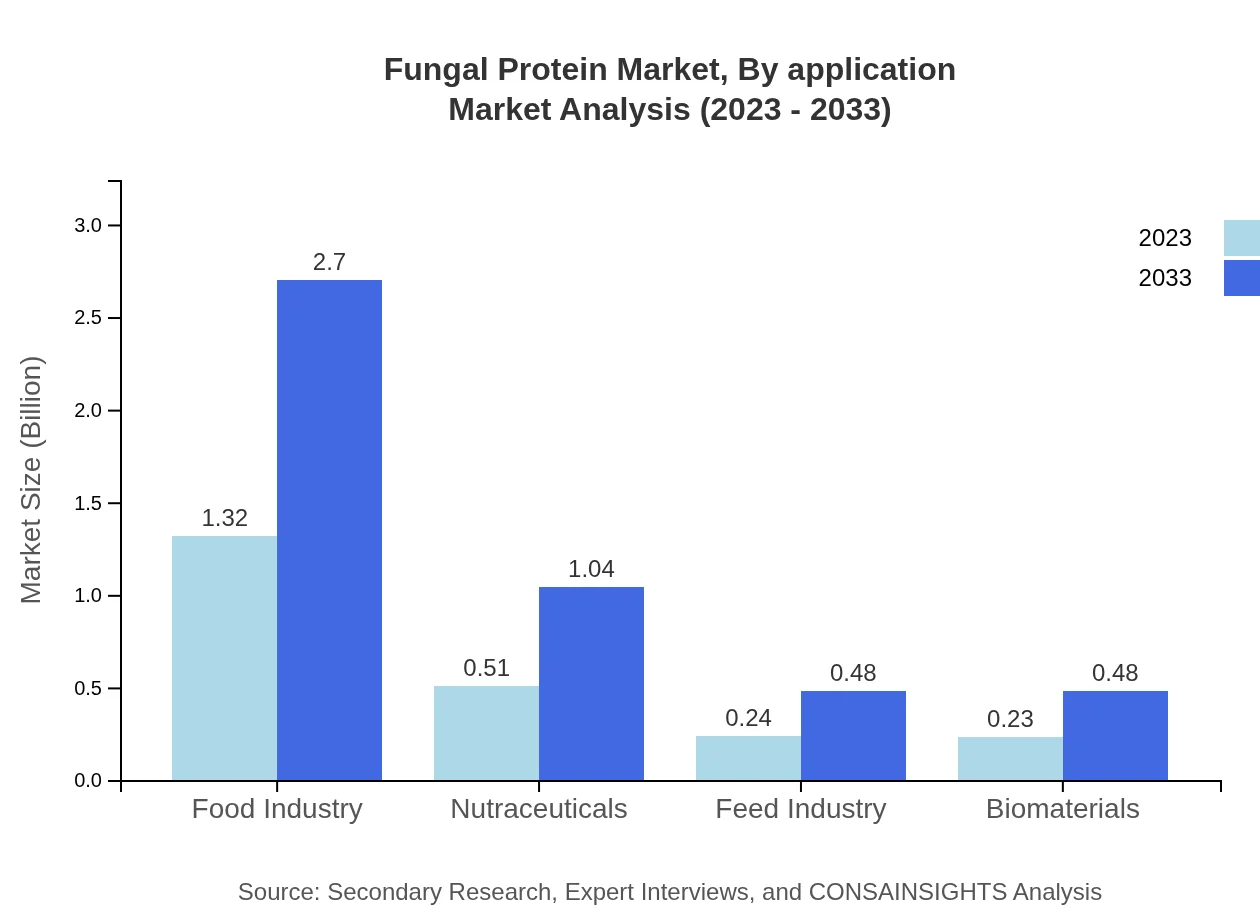
Fungal Protein Market Analysis By Application
In food services, the market value will increase from $1.45 billion in 2023 to $2.97 billion by 2033. Nutraceutical applications are significant too, expanding from $0.51 billion to $1.04 billion.
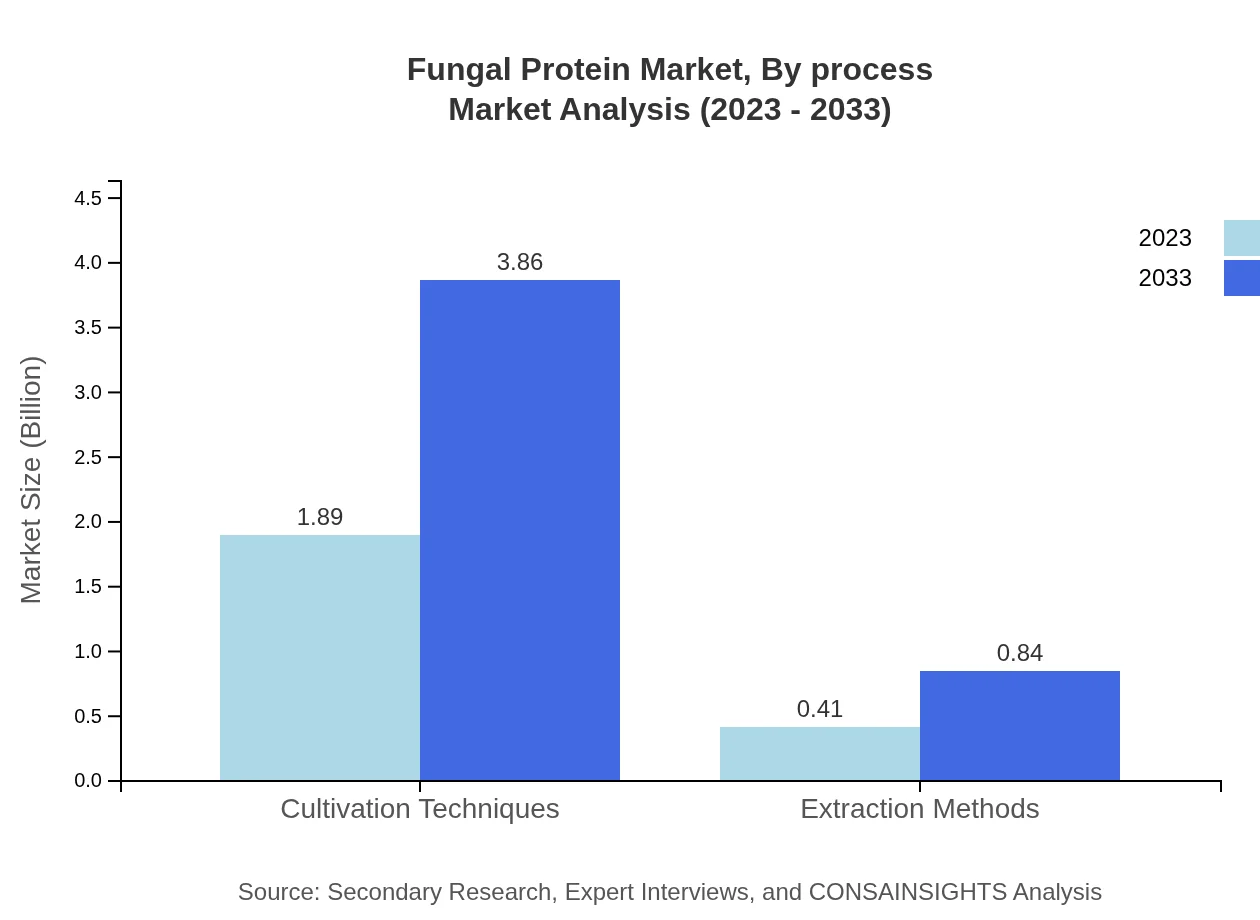
Fungal Protein Market Analysis By Process
Cultivation techniques dominate the market, valued at $1.89 billion in 2023 and expected to rise to $3.86 billion by 2033, representing an essential factor in production scalability.
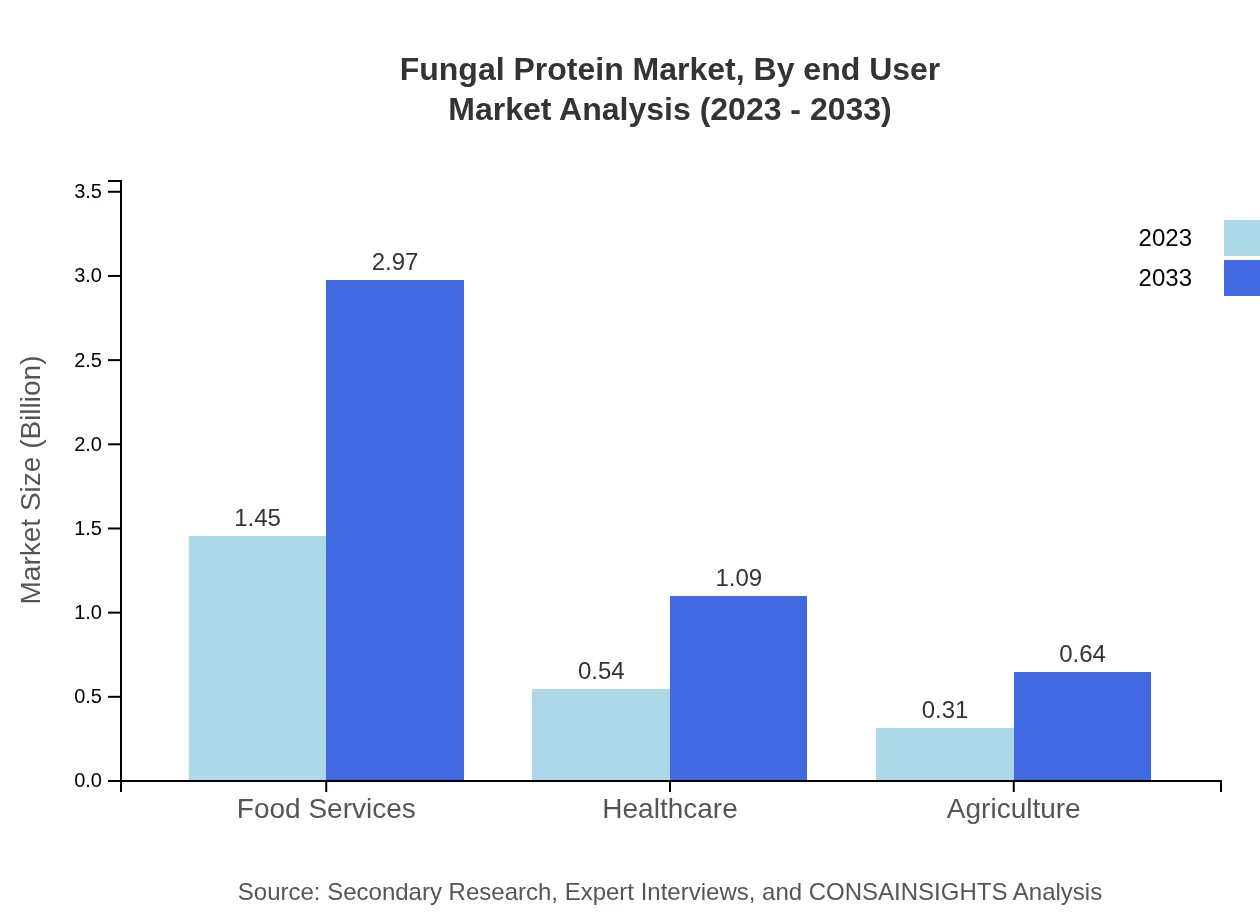
Fungal Protein Market Analysis By End User
Food industry applications account for the largest portion, growing from $1.32 billion in 2023 to $2.70 billion by 2033, catering to the increasing demand for alternative sources of protein.
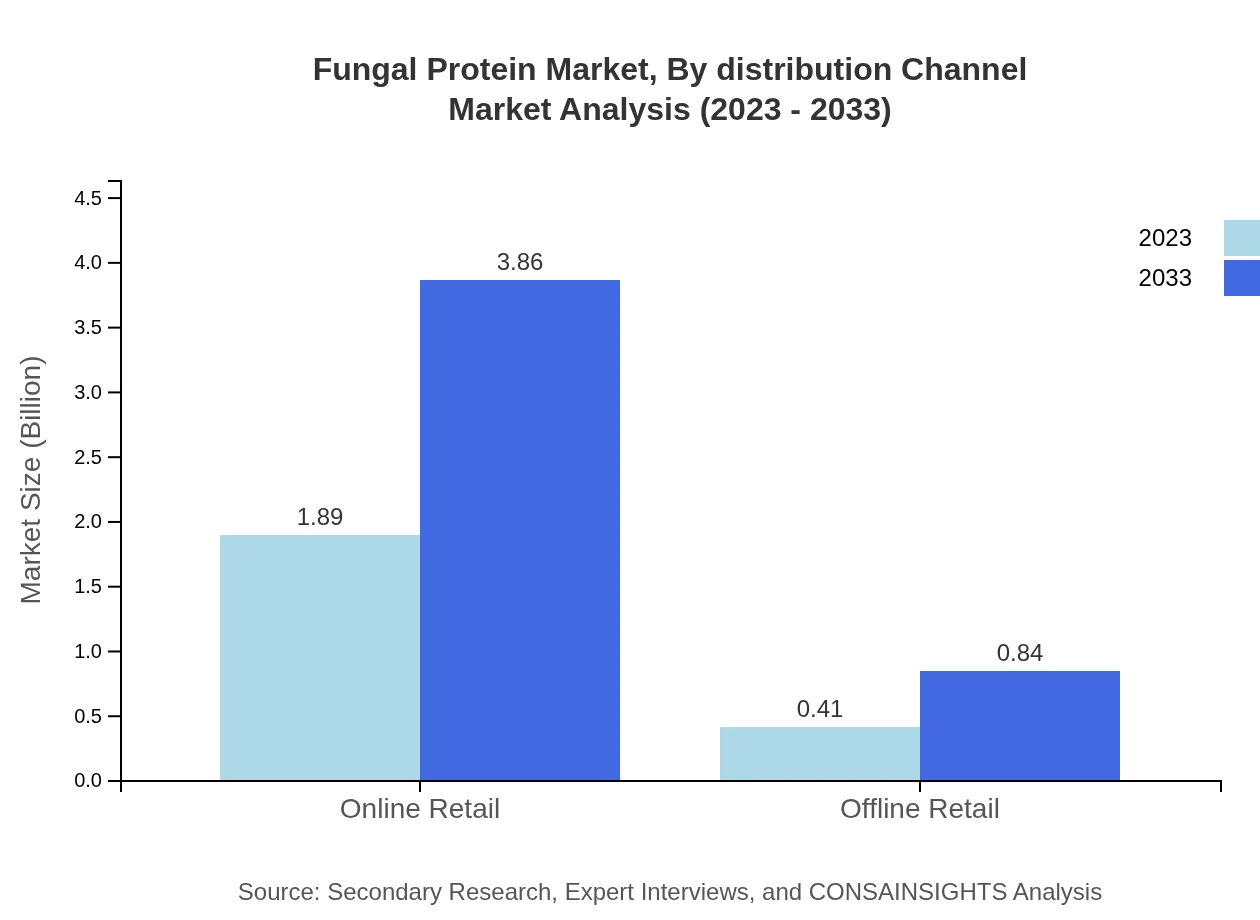
Fungal Protein Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Online retail saves the largest share, expected to grow from $1.89 billion to $3.86 billion. This growth is driven by changing consumer purchasing behaviors towards e-commerce.
Fungal Protein Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Fungal Protein Industry
Fungi Perfecti:
Known for pioneering mycelium-based products, Fungi Perfecti leads with innovation in the health food sector.MycoTechnology:
A leader in developing mushroom-based protein powders, promoting sustainable sourcing of production practices.Ecovative Design:
Specializes in mycelium materials and sustainable packaging solutions, contributing to the food and biomaterials industries.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of fungal Protein?
The fungal protein market is projected to reach approximately $2.3 billion by 2033, reflecting a steady CAGR of 7.2% from 2023. This growth indicates a robust demand for sustainable protein sources as consumers seek alternatives to traditional meat.
What are the key market players or companies in the fungal Protein industry?
Key players in the fungal protein industry include major companies known for innovative protein solutions. They are deeply involved in research and development, ensuring sustainable production processes and a wide array of fungal protein-based products catering to diverse consumer needs.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the fungal Protein industry?
The growth of the fungal protein industry is driven by rising consumer demand for sustainable food sources, increased health awareness, and the versatility of fungal proteins in various applications from food to nutraceuticals. Innovations in cultivation and extraction methods further enhance market growth.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the fungal Protein market?
The Asia Pacific region is projected to experience the fastest growth in the fungal protein market, increasing from $0.49 billion in 2023 to an estimated $1.00 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by rising populations and shifting dietary preferences towards protein alternatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the fungal Protein industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the fungal protein industry. Clients can obtain targeted insights that reflect their unique business requirements, including market trends, competitive analysis, and regional specifics.
What deliverables can I expect from this fungal Protein market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis reports, growth forecasts, market segmentation data, and competitive landscape assessments. Additionally, visual data representations such as charts and graphs will enhance understanding of key insights.
What are the market trends of fungal Protein?
Current market trends in fungal protein show a significant increase in online retail presence, with this segment projected to grow from $1.89 billion in 2023 to $3.86 billion by 2033. Consumers are increasingly opting for eco-friendly, nutritious protein sources, influencing market dynamics.