Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: gallium-arsenide-gaas-wafer
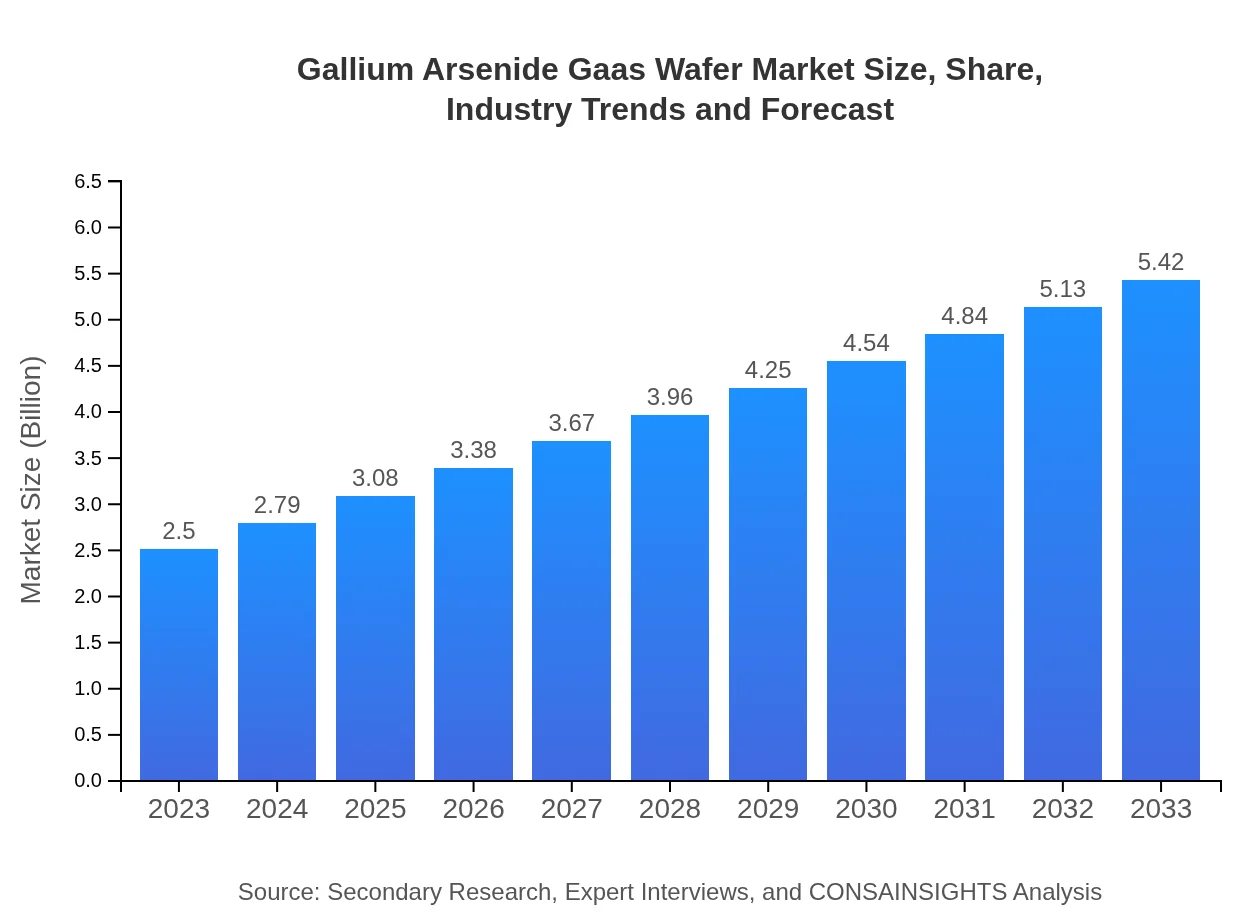
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the Gallium Arsenide GaAs Wafer market, compiling significant insights, trends, and forecast data for the years 2023 to 2033, focusing on market dynamics, segmentation, technological advancements, and key players shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $2.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $5.42 Billion |
| Top Companies | Freiberger Compound Materials GmbH, Aixtron SE, Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd., Skyworks Solutions, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Overview
Customize Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer market in 2023?
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Industry Analysis
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report:
The European market for Gallium Arsenide wafers is forecasted to grow from $0.74 billion in 2023 to $1.62 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by substantial investments in research and development and the increasing use of GaAs in various high-tech applications.Asia Pacific Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to experience significant market growth, with the market expected to rise from $0.49 billion in 2023 to $1.07 billion by 2033. Key drivers include the rapid expansion of consumer electronics and telecommunications sectors, coupled with increased production capabilities in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.North America Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report:
North America is expected to witness robust market expansion, growing from $0.85 billion in 2023 to $1.85 billion by 2033. The growth will be fueled by advancements in telecommunications infrastructure, particularly with 5G rollout, and the concentration of leading technology firms in the region.South America Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report:
In South America, the Gallium Arsenide wafer market is anticipated to grow from $0.13 billion in 2023 to $0.27 billion by 2033. This growth will be bolstered by rising investments in the telecommunications sector and an increasing demand for consumer electronics as emerging markets develop.Middle East & Africa Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to increase from $0.28 billion in 2023 to $0.61 billion by 2033, supported by growing telecommunications networks and an emerging focus on renewable energy applications utilizing GaAs technology.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
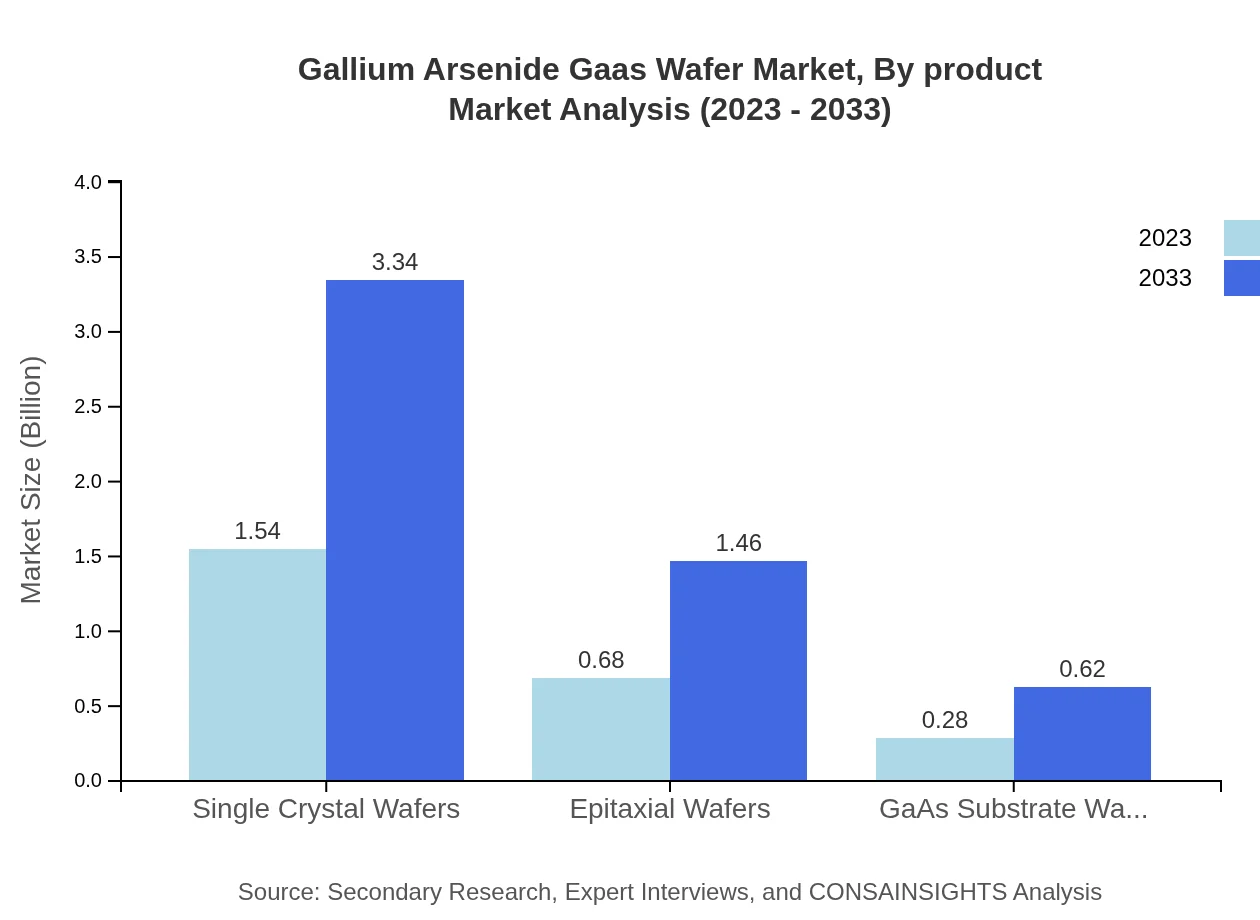
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Analysis By Product
The Gallium Arsenide wafer market showcases a clear distinction between high purity GaAs wafers and low purity variants. High purity GaAs wafers dominate the market due to their extensive use in telecommunications and semiconductor applications, contributing significantly to the overall market revenue.
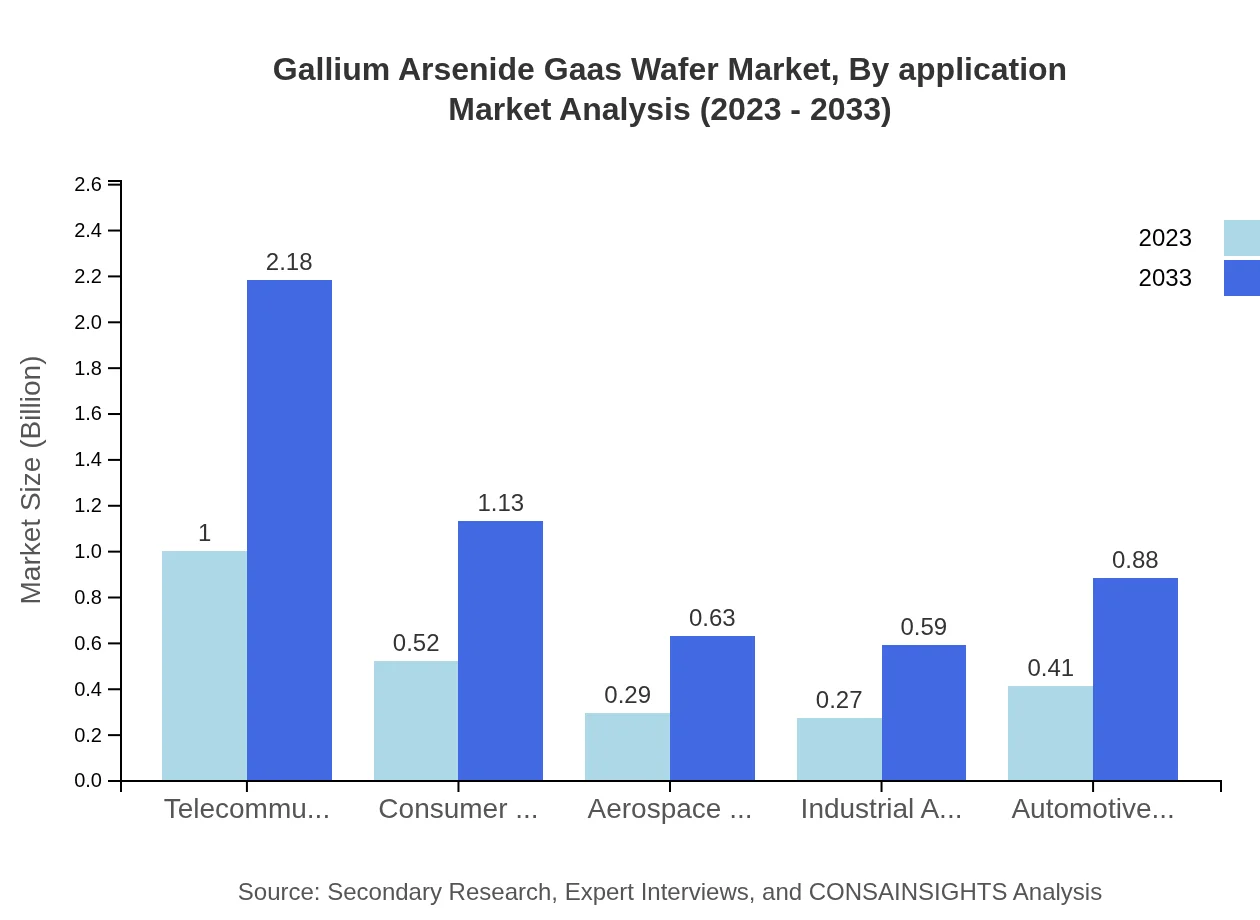
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the telecommunications segment holds the largest market share given the increasing demand for high-frequency devices. Other notable applications include electronics, aerospace, and defense, which significantly leverage GaAs wafers for their efficiency and performance.
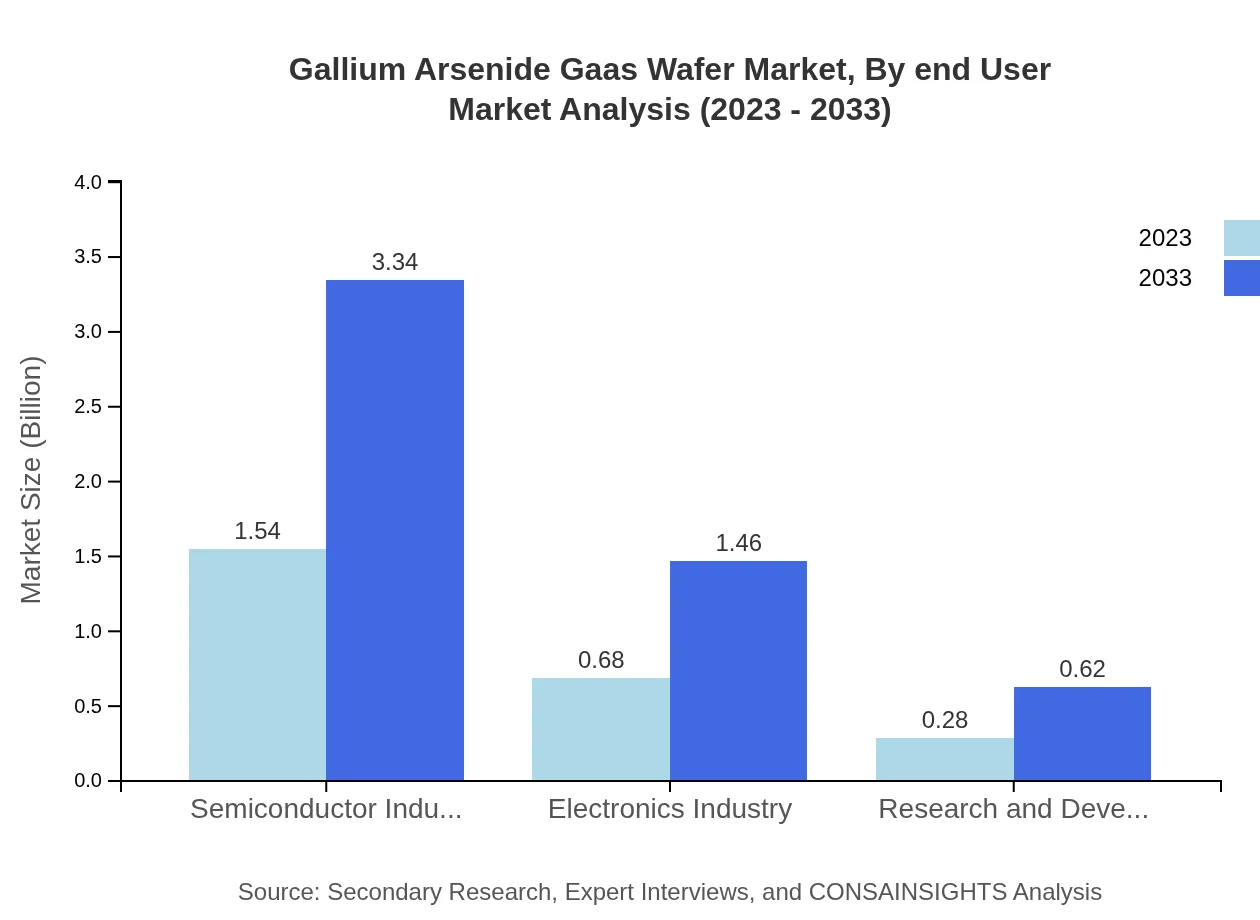
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries play a crucial role in determining the direction of the Gallium Arsenide wafer market. Telecommunications, consumer electronics, and aerospace sectors are key contributors, showcasing a growing reliance on advanced semiconductor materials for better efficiency and performance.
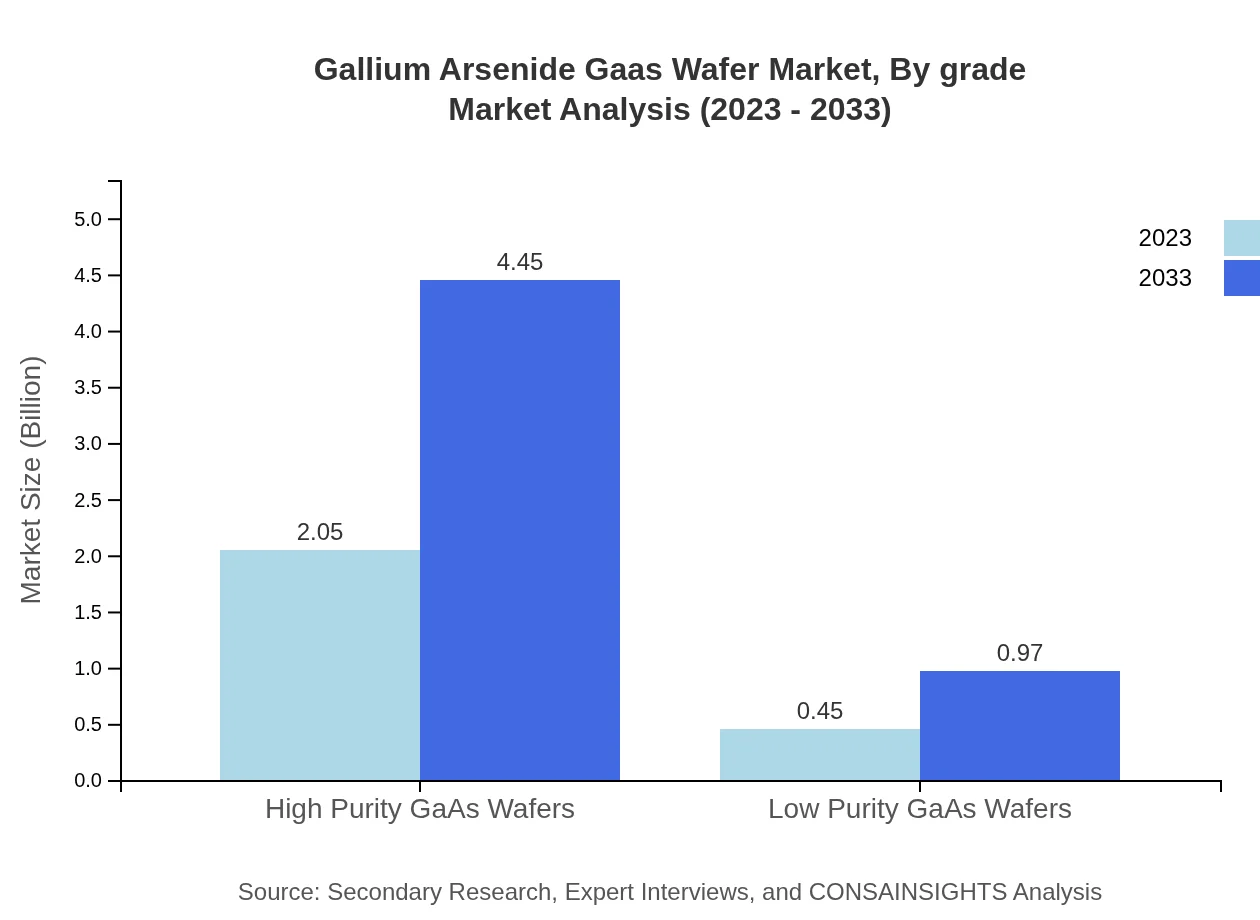
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Analysis By Grade
The market is segmented into high purity and low purity GaAs grades; high purity wafers are prevalent in most high-end applications due to their superior electrical characteristics, while low purity wafers cater to niche markets with cost-sensitive applications.
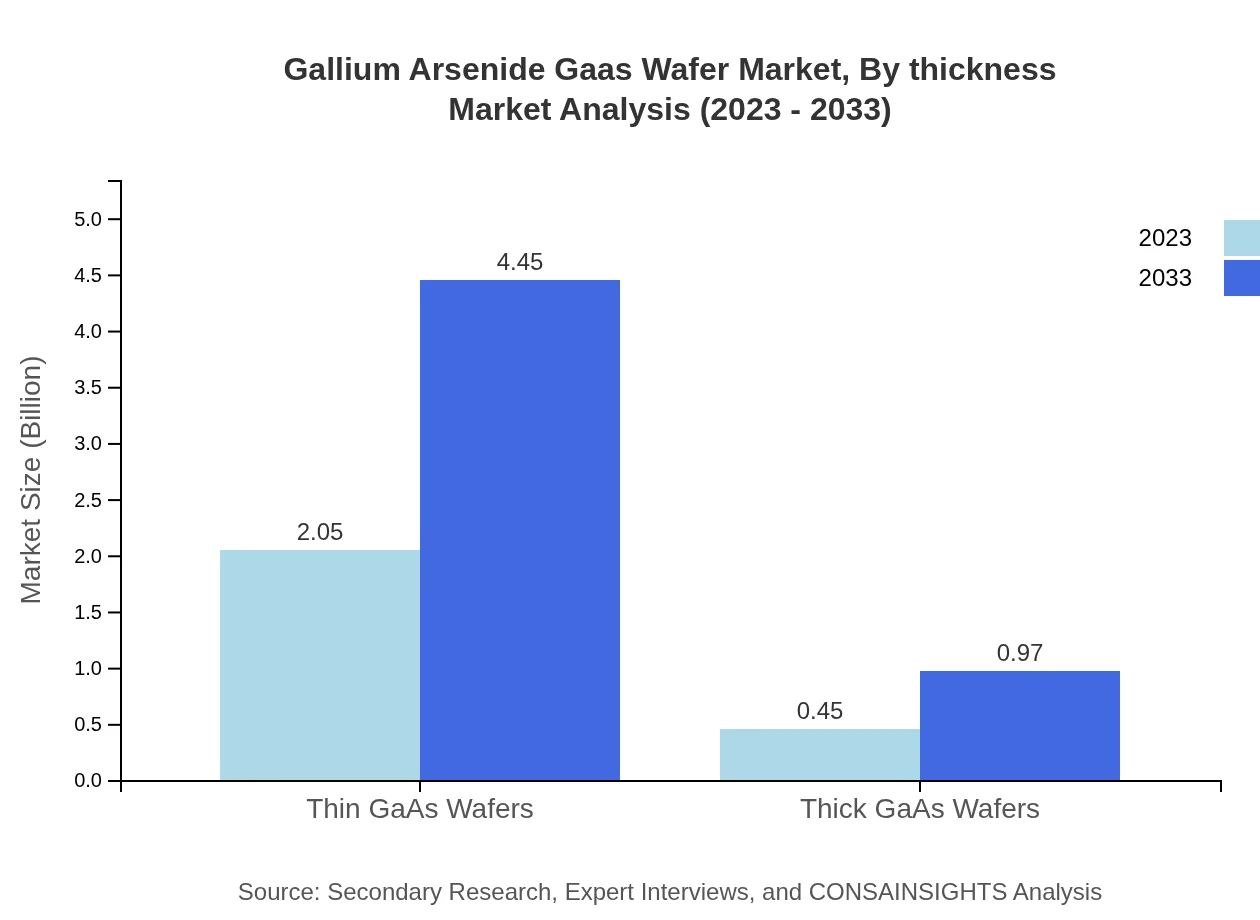
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Analysis By Thickness
Thin and thick GaAs wafers serve different applications, with thin wafers leading the market due to their suitability for high-frequency devices and compact electronic components. The demand for thick wafers is also growing with applications in more robust electronic components.
Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Gallium Arsenide Gaas Wafer Industry
Freiberger Compound Materials GmbH:
Freiberger is a leading manufacturer of GaAs wafers, known for their high-quality substrates used in optoelectronics and telecommunications sectors.Aixtron SE:
Aixtron provides advanced equipment for GaAs wafer manufacturing, enhancing production efficiency and enabling the development of next-generation semiconductor applications.Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.:
Sumitomo is a major player in the GaAs market, offering a wide range of products while being involved in significant R&D efforts pushing GaAs applications forward.Skyworks Solutions, Inc.:
Skyworks specializes in analog semiconductors and is recognized for their innovative contributions to wireless communications through GaAs technology.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) Wafer?
The Gallium Arsenide Wafer market is valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 7.8% over the next decade, highlighting its growth potential driven by advancements in semiconductor technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in the Gallium Arsenide Wafer industry?
Key players in the Gallium Arsenide Wafer market include prominent semiconductor manufacturers and suppliers such as IQE, Freiberger Compound Materials, and AXT, providing various types of GaAs materials for different applications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Gallium Arsenide Wafer industry?
Growth in the Gallium Arsenide Wafer market is driven by increasing demand in telecommunications and aerospace sectors, advancements in consumer electronics, and the need for high-efficiency semiconductor materials in various applications.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Gallium Arsenide Wafer market?
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing significant growth in the Gallium Arsenide Wafer market, with expected market size increasing from $0.49 billion in 2023 to $1.07 billion by 2033, reflecting a booming semiconductor industry.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Gallium Arsenide Wafer industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data for the Gallium Arsenide Wafer industry, allowing clients to receive specific insights aligning with their unique business needs and market scenarios.
What deliverables can I expect from this Gallium Arsenide Wafer market research project?
Deliverables from the Gallium Arsenide Wafer market research project include comprehensive market analysis, trend reports, competitive landscape insights, and customized data tailored to strategic planning and decision-making.
What are the market trends of Gallium Arsenide Wafer?
Current market trends indicate a shift towards high-purity GaAs wafers for advanced applications, increased investment in semiconductor technology, and a focus on innovative solutions to meet growing consumer electronics demand.