Gene Delivery Systems Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: gene-delivery-systems
Gene Delivery Systems Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive report analyzes the Gene Delivery Systems market, offering insights on its growth, size, segmentations, technological innovations, and market forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
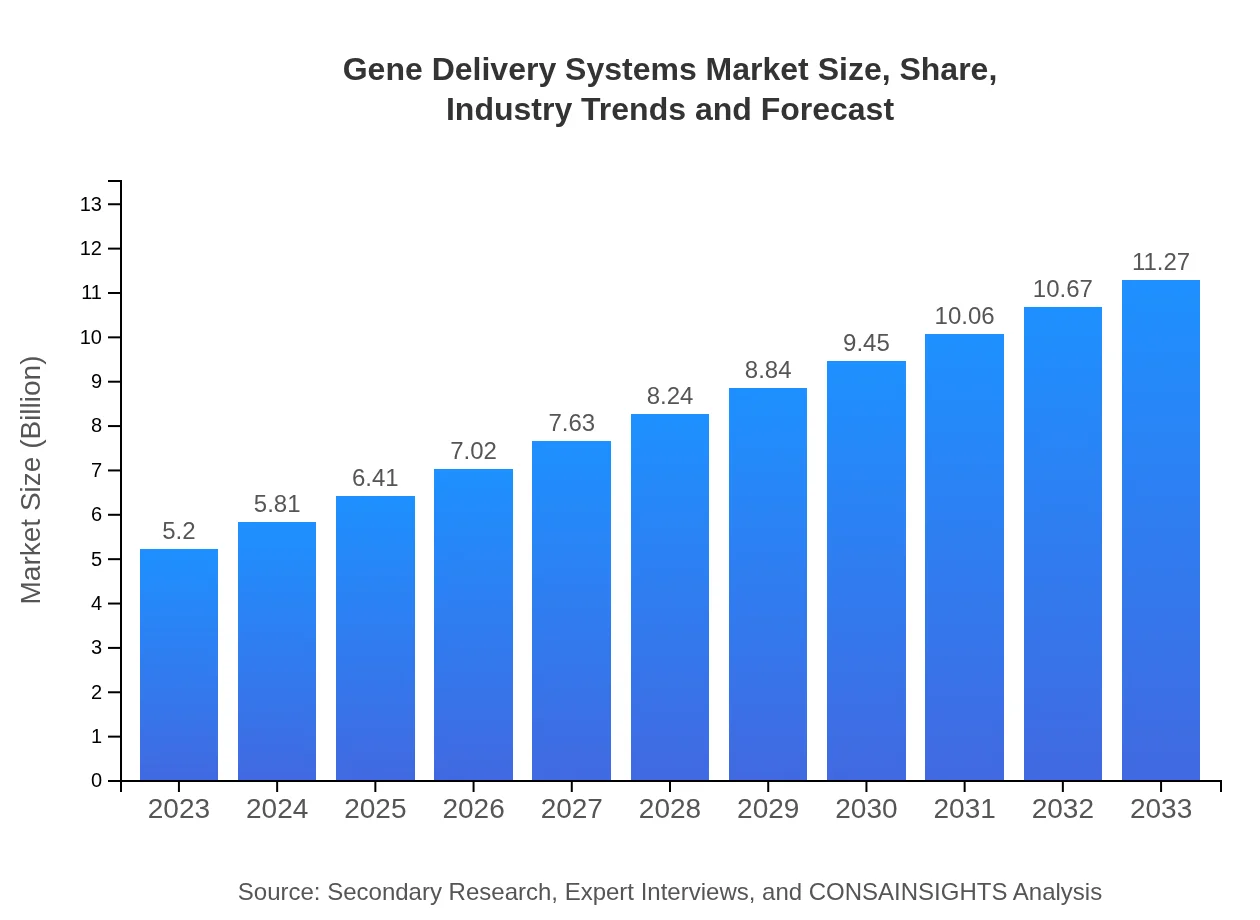
| 2023 Market Size | $5.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $11.27 Billion |
| Top Companies | Spark Therapeutics, Novartis, Gensight Biologics, ADMA Biologics |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Gene Delivery Systems Market Overview
Customize Gene Delivery Systems Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Gene Delivery Systems market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Gene Delivery Systems's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Gene Delivery Systems
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Gene Delivery Systems market in 2023?
Gene Delivery Systems Industry Analysis
Gene Delivery Systems Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Gene Delivery Systems Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Gene Delivery Systems Market Report:
Europe's market is valued at $1.33 billion in 2023, expected to nearly double to $2.88 billion by 2033, driven by increased funding for research and development and a focus on innovative healthcare solutions.Asia Pacific Gene Delivery Systems Market Report:
The Asia Pacific market is valued at $1.11 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $2.42 billion by 2033. Increased investments in healthcare infrastructure and rising incidences of genetic disorders are driving this growth.North America Gene Delivery Systems Market Report:
North America is the largest market at $1.96 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $4.25 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by a strong presence of major pharmaceutical companies and a favorable regulatory environment.South America Gene Delivery Systems Market Report:
With a market size of $0.26 billion in 2023, South America is anticipated to reach $0.56 billion by 2033, influenced by expanding healthcare capabilities and growing awareness of gene therapies.Middle East & Africa Gene Delivery Systems Market Report:
This region holds a market size of $0.54 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $1.16 billion by 2033, as healthcare improvements and adoption of novel therapies grow.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
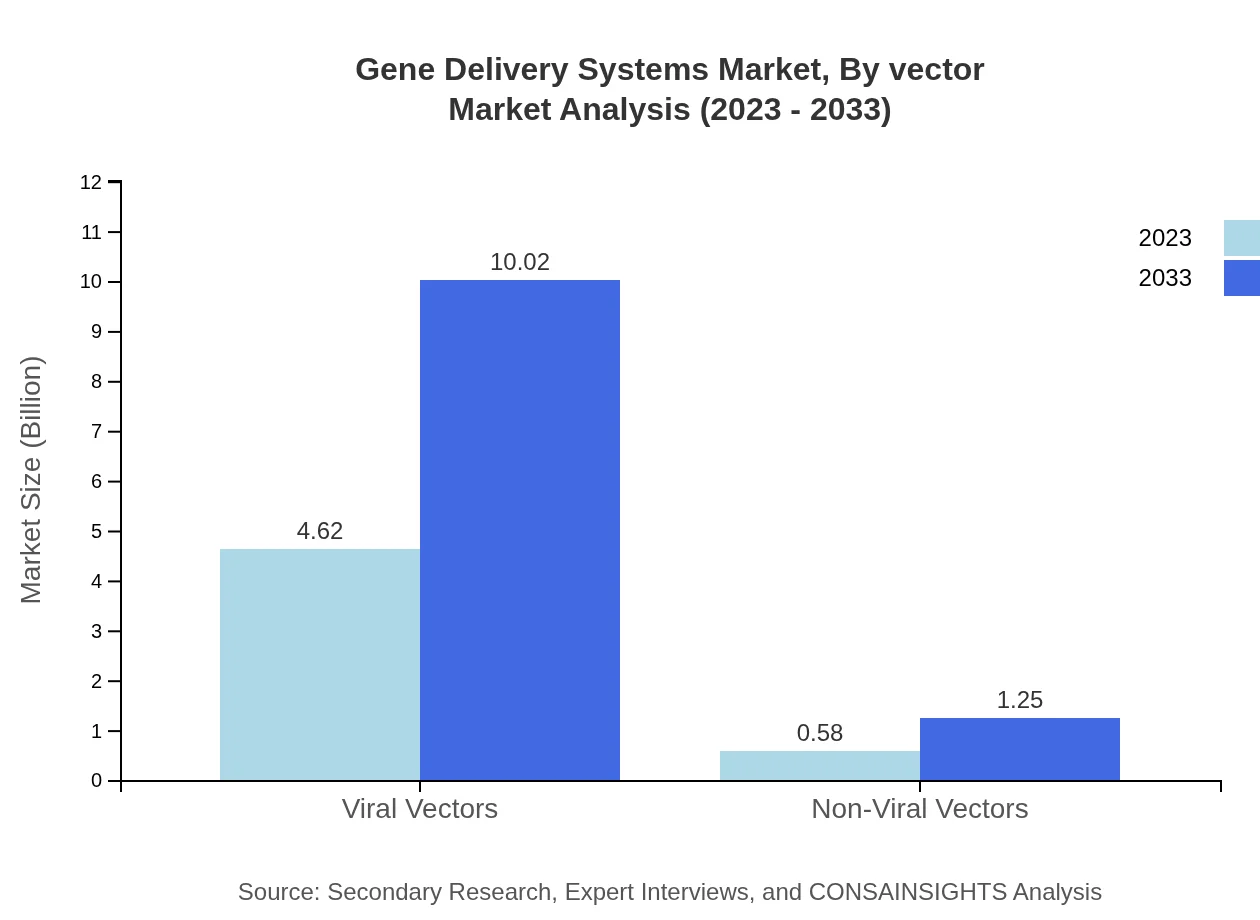
Gene Delivery Systems Market Analysis By Vector
In 2023, the viral vectors segment commands the market with a size of $4.62 billion and is projected to reach $10.02 billion by 2033, holding an 88.92% market share. Non-viral vectors, while smaller at $0.58 billion, are expected to grow to $1.25 billion, reflecting an increasing interest in safer delivery methods.
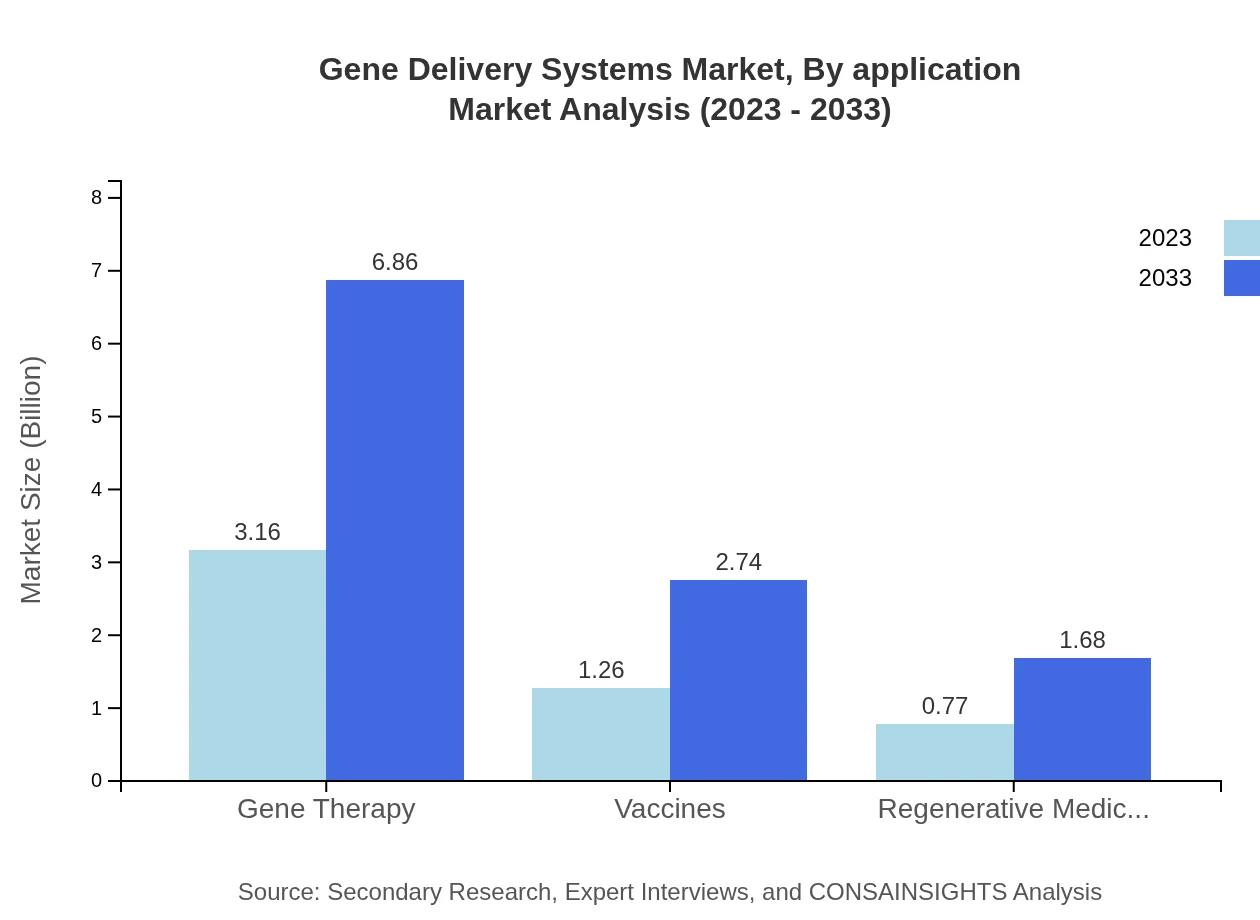
Gene Delivery Systems Market Analysis By Application
The Gene Therapy segment accounts for a significant share, valued at $3.16 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $6.86 billion by 2033. Vaccines and regenerative medicine also show noteworthy growth, supporting the rising trend of precision medicine.
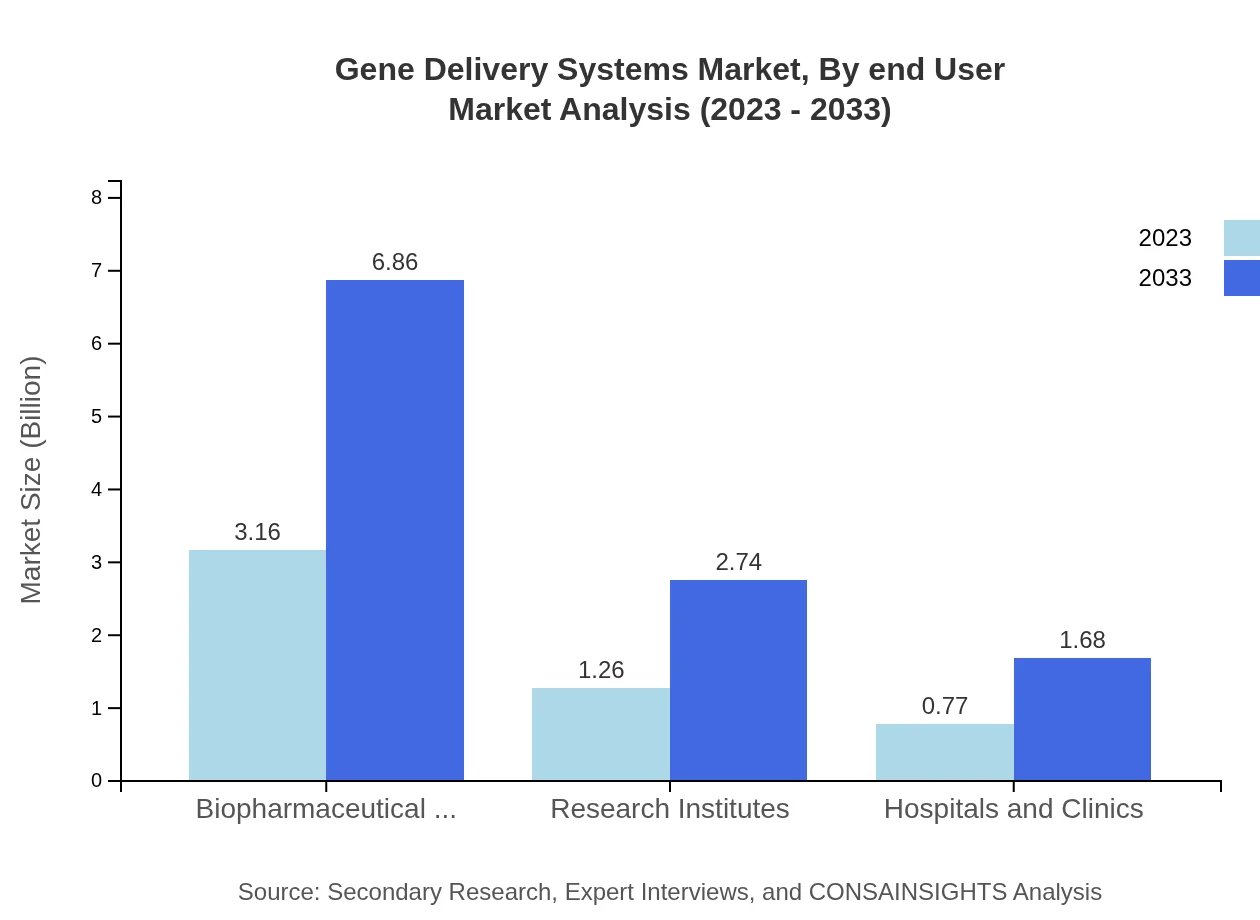
Gene Delivery Systems Market Analysis By End User
Biopharmaceutical companies dominate the market, with $3.16 billion in 2023 expected to grow to $6.86 billion by 2033. Research institutes and hospitals have noteworthy shares as well, reflecting their critical roles in therapeutic development.
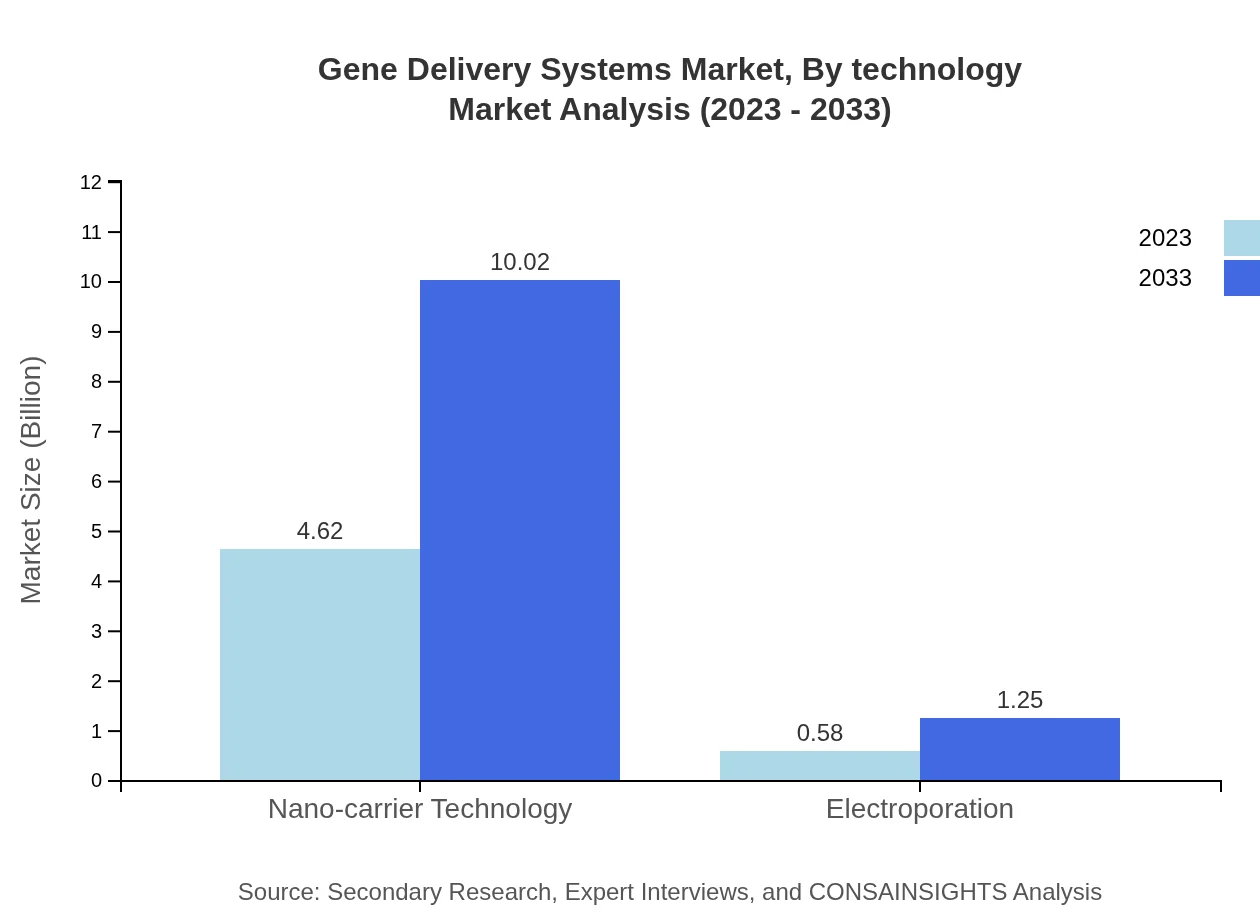
Gene Delivery Systems Market Analysis By Technology
Technologies such as nano-carrier technology hold a significant market presence, valued at $4.62 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $10.02 billion by 2033. Electroporation, while smaller, is also noted for its growing adoption due to its effectiveness in enhancing gene delivery.
Gene Delivery Systems Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in the Gene Delivery Systems Industry
Spark Therapeutics:
A pioneering company specializing in gene therapies to treat debilitating diseases, Spark focuses on innovative delivery methods to enhance patient outcomes.Novartis:
A global healthcare leader, Novartis invests heavily in gene therapies, utilizing advanced delivery systems in their innovative treatments.Gensight Biologics:
Gensight specializes in mitochondrial gene therapies and is recognized for developing novel delivery systems to target complex disorders.ADMA Biologics:
ADMA is a biopharmaceutical company focused on developing and manufacturing specialty plasma-derived immunoglobulin products incorporating advanced gene delivery techniques.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of gene Delivery Systems?
The global gene delivery systems market is projected to reach approximately $5.2 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing demand for advanced therapeutic modalities.
What are the key market players or companies in this gene Delivery Systems industry?
Key players in the gene delivery systems industry include major biopharmaceutical companies and research institutions that drive innovation and development. Their efforts in research and partnerships significantly enhance the market landscape and competitive dynamics.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the gene Delivery Systems industry?
The growth in the gene-delivery-systems industry is driven by advancements in gene therapy research, rising incidences of genetic disorders, and increased funding for related research initiatives. This is further supported by regulatory approvals and market demand for personalized medicine.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the gene Delivery Systems?
The North American region is anticipated to be the fastest-growing in the gene delivery systems market, increasing from $1.96 billion in 2023 to $4.25 billion by 2033. Other regions, like Europe and Asia Pacific, also show significant growth trajectories.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the gene Delivery Systems industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs in the gene delivery systems industry. Clients can access detailed insights based on their requirements, ensuring relevance and precision in the data provided.
What deliverables can I expect from this gene Delivery Systems market research project?
From this market research project, expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analyses, trend reports, competitive landscapes, and forecasts for various segments within the gene delivery systems market.
What are the market trends of gene Delivery Systems?
Current market trends in gene delivery systems include the rising use of viral vectors, significant investments in research for gene therapies, and an emphasis on efficient delivery mechanisms such as nano-carrier technologies, helping to shape future developments.