General Crop Farming Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: general-crop-farming
General Crop Farming Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides comprehensive insights into the General Crop Farming market from 2023 to 2033, including market size, growth trends, segmentation, and regional analysis, highlighting key factors driving the industry and future forecasts.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
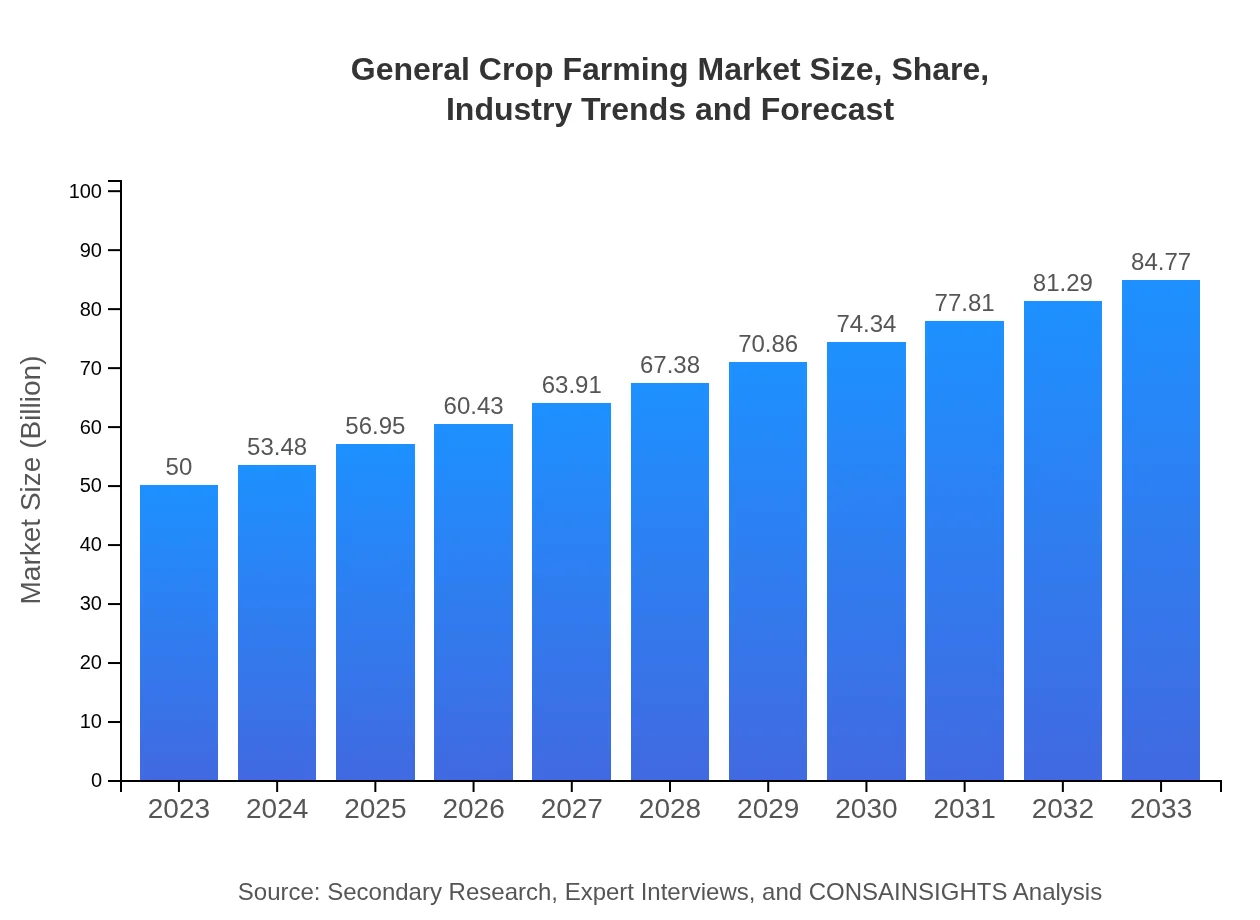
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $84.77 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill, Inc., Bayer AG, Syngenta AG, Deere & Company, ADM (Archer Daniels Midland Company) |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
General Crop Farming Market Overview
Customize General Crop Farming Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of General Crop Farming market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand General Crop Farming's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in General Crop Farming
What is the Market Size & CAGR of General Crop Farming market in 2023?
General Crop Farming Industry Analysis
General Crop Farming Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
General Crop Farming Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe General Crop Farming Market Report:
Europe's market is estimated to be $14.38 billion in 2023, potentially reaching $24.38 billion by 2033. The region prioritizes organic farming, sustainability, and adheres to strict regulatory standards that promote environmentally friendly farming techniques.Asia Pacific General Crop Farming Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region shows significant potential in the General Crop Farming market, with a market size of approximately $8.95 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $15.17 billion by 2033. The region is home to some of the largest agricultural producers, and growing populations coupled with urbanization are increasing food demand, driving investments in agricultural technology.North America General Crop Farming Market Report:
North America leads the market with a size of $19.46 billion in 2023, forecasted to escalate to $32.99 billion by 2033. The U.S. is a key player in the global agricultural market, leveraging technology and innovation to optimize production and meet the growing demand for diverse crops.South America General Crop Farming Market Report:
In South America, the General Crop Farming market is valued at around $3.38 billion in 2023, with expectations to reach $5.73 billion by 2033. The region benefits from favorable climate conditions for diverse crop production, particularly soybeans and cereals, and is increasingly focusing on sustainable agricultural practices.Middle East & Africa General Crop Farming Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is valued at $3.83 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $6.49 billion by 2033. Despite facing challenges like water scarcity, the region is adopting innovative farming techniques to enhance crop yields and promote food security.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
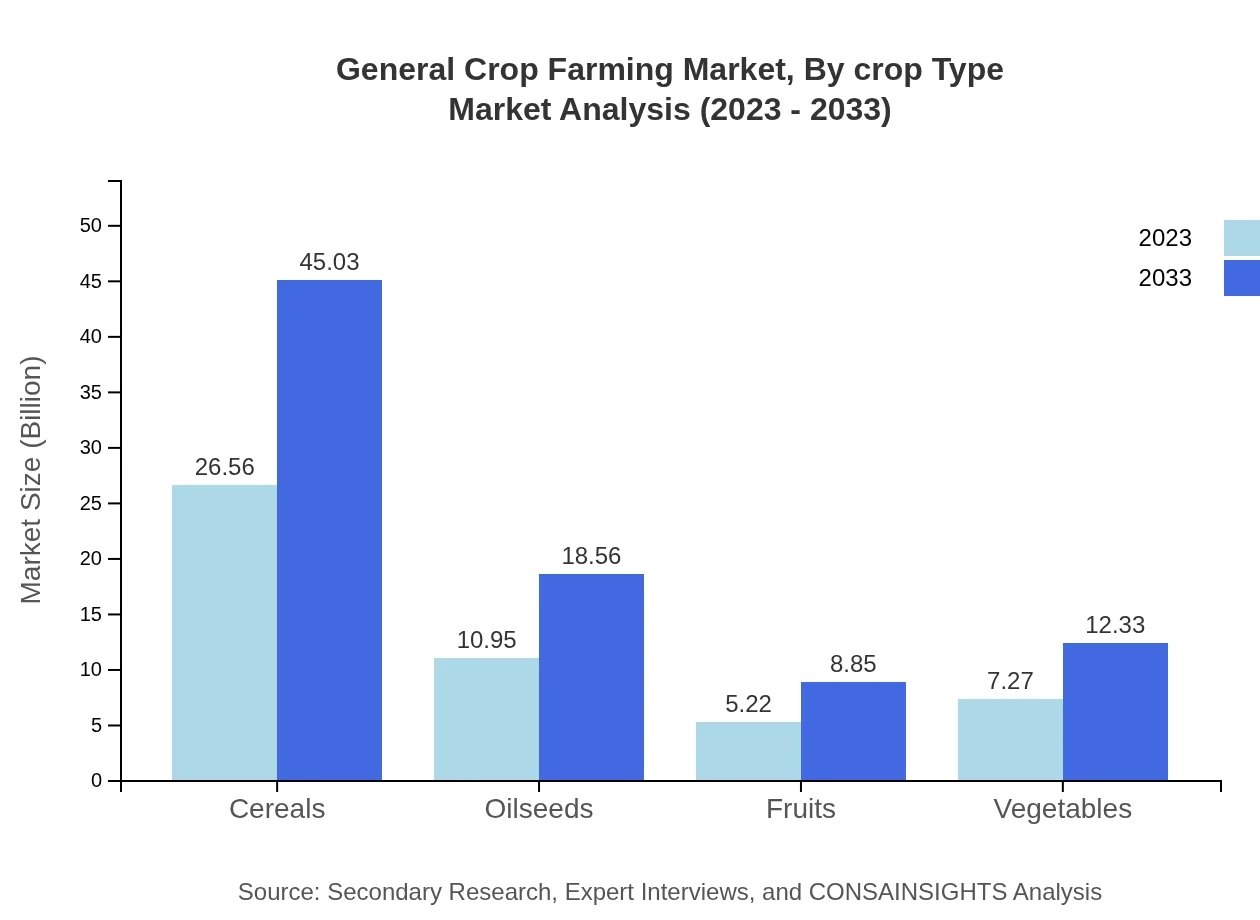
General Crop Farming Market Analysis By Crop Type
The crop type segment represents diverse agricultural products, notably cereals, which held a market size of $26.56 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $45.03 billion by 2033. Fruits follow with significant growth potential, expanding from $5.22 billion to $8.85 billion, while vegetables and oilseeds also play essential roles in this segment, contributing to the overall market performance.
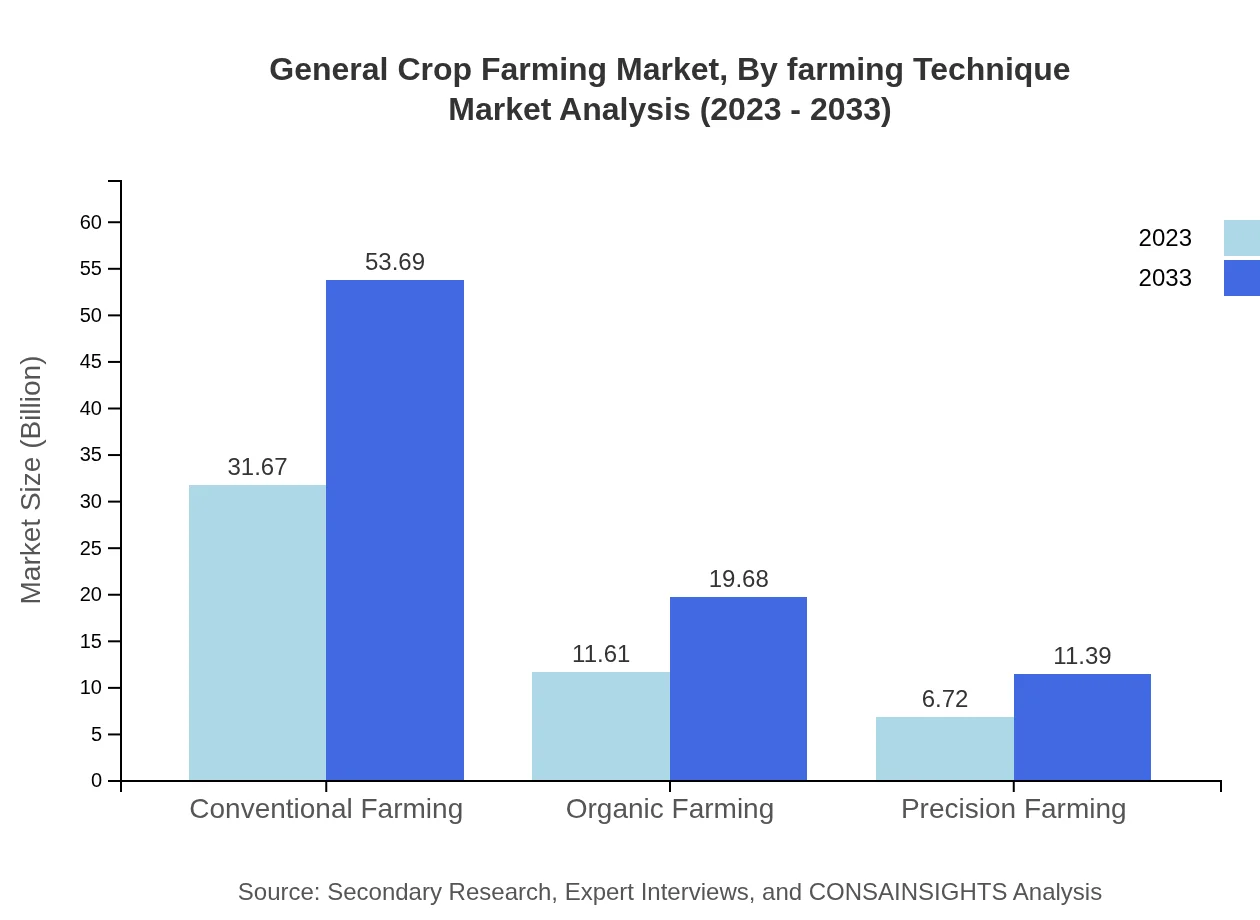
General Crop Farming Market Analysis By Farming Technique
Farming techniques are categorized into conventional, organic, and precision farming. As of 2023, conventional farming holds the largest market share at 63.34%, valued at $31.67 billion, whereas organic farming is continuously gaining traction, expected to grow from $11.61 billion to $19.68 billion by 2033. Precision farming is emerging with increased adoption of technology, forecasting growth from $6.72 billion to $11.39 billion within the same period.
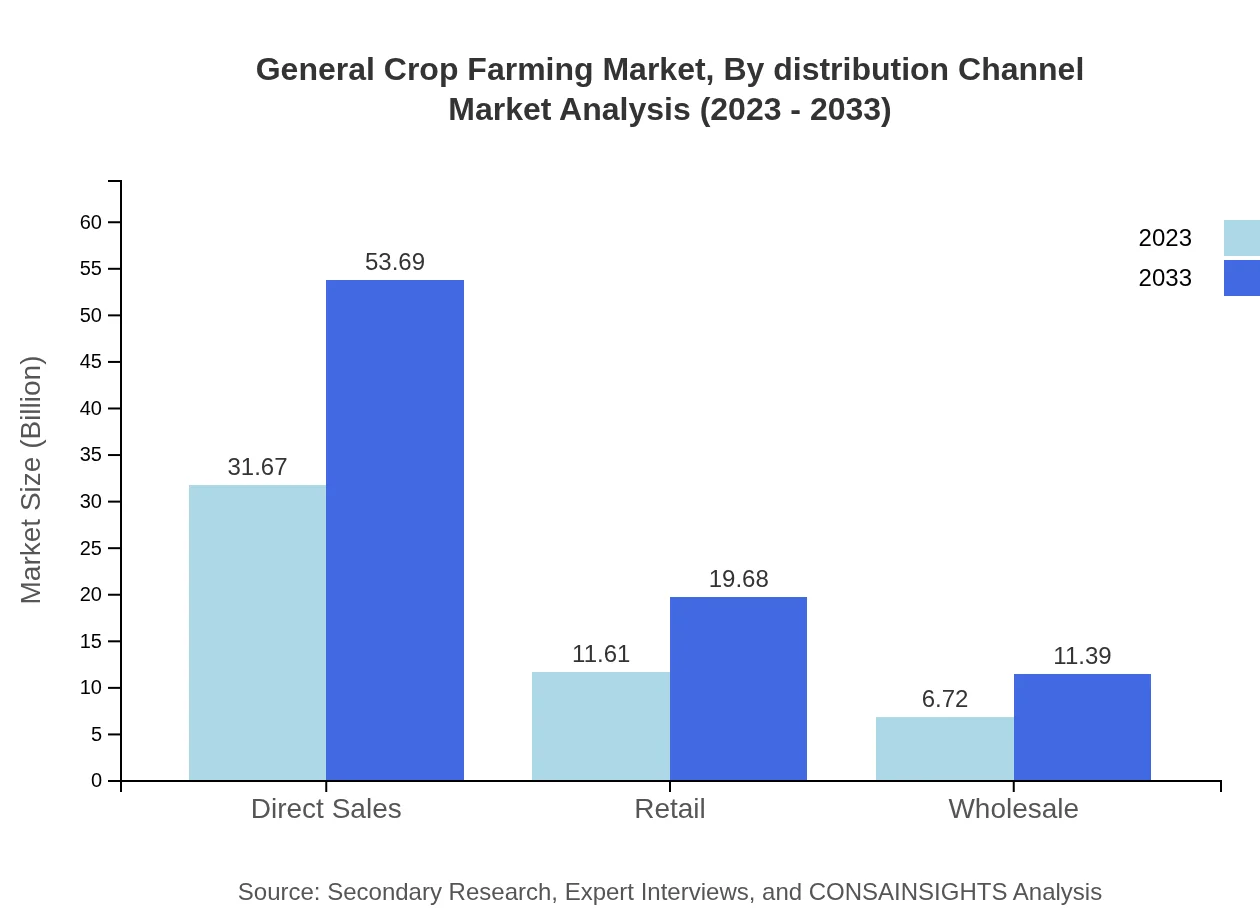
General Crop Farming Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels for agricultural products include direct sales, retail, and wholesale. Direct sales command a significant portion of the market, valued at $31.67 billion in 2023, while retail channels, valued at $11.61 billion, are also crucial, particularly among consumers favoring direct purchase from producers. Wholesale avenues are projected to expand as supply chains become more integrated.
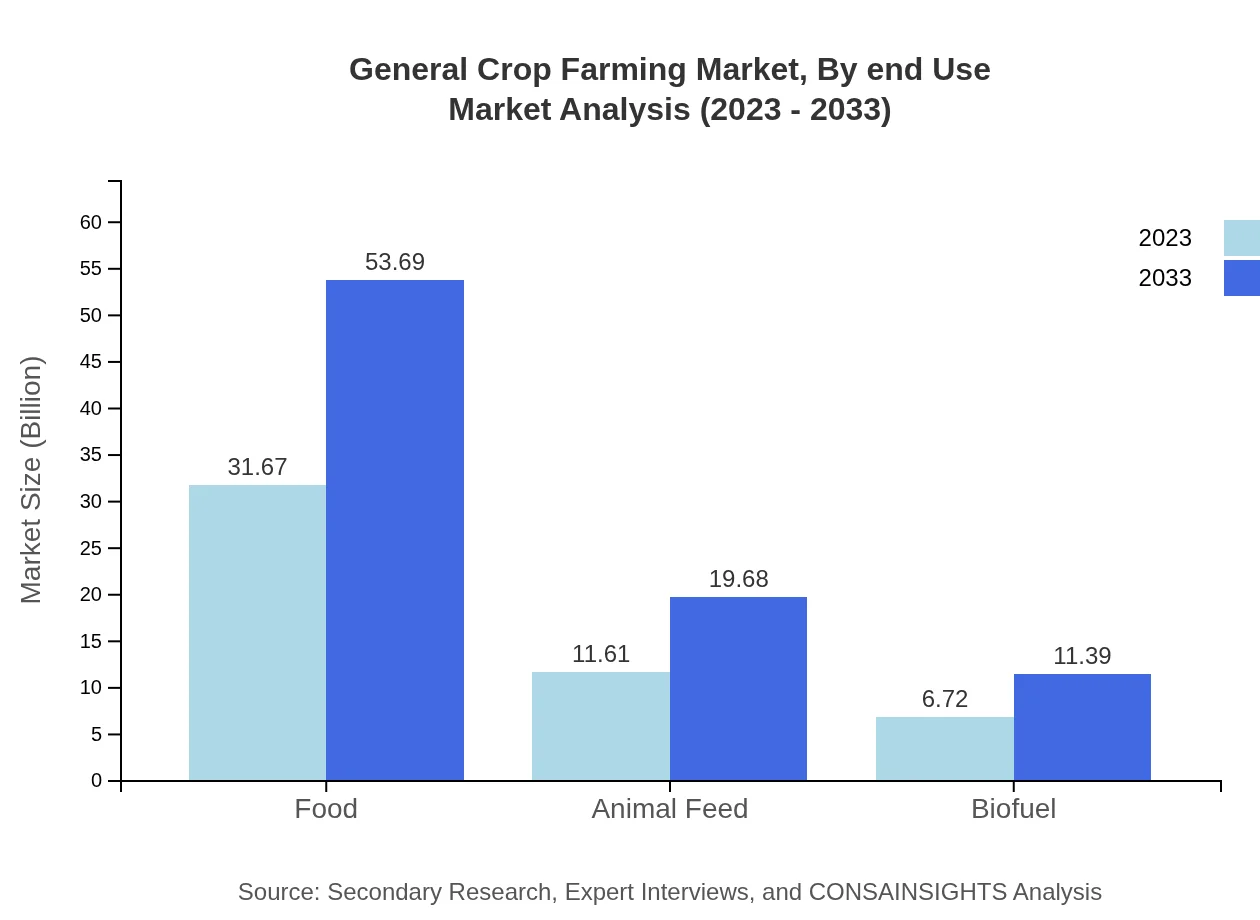
General Crop Farming Market Analysis By End Use
Crops are primarily used for food production, animal feed, and biofuel. The segment for food production is dominant, indicating robustness in consumer food consumption patterns. Animal feed represents a growing sector, with its size expected to reach $19.68 billion by 2033 from $11.61 billion, crucial in supporting livestock industries. Biofuel production is also emerging, emphasizing the versatility of crop usage.
General Crop Farming Market Analysis By Region
Global General Crop Farming Market, By Region Market Analysis (2023 - 2033)
Regional analysis reveals distinct characteristics, with North America leading due to technological advancements, while Asia Pacific demonstrates impressive growth potential due to increased population and food demand. Europe focuses on sustainability, affecting market development, while South America capitalizes on its climatic advantages for agricultural productivity. The Middle East and Africa face challenges but are innovating to improve food security.
General Crop Farming Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in General Crop Farming Industry
Cargill, Inc.:
Cargill is a leading global provider of food, agriculture, financial, and industrial products and services. It is heavily involved in crop production and agricultural technology, driving innovations that enhance yield and quality.Bayer AG:
Bayer is a significant player in the global crop science industry, providing innovative seeds and crop protection solutions to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability.Syngenta AG:
Syngenta is a top agricultural company that focuses on seeds and crop protection. It plays a crucial role in advancing agricultural practices and producing high-yield crop varieties.Deere & Company:
Deere & Company specializes in agricultural machinery and technology, offering advanced tools and solutions that enhance farming efficiency and output.ADM (Archer Daniels Midland Company):
ADM is a global leader in food processing and agricultural services, significantly impacting crop farming by facilitating the supply chain and crop marketing.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of general crop farming?
The general crop farming market is estimated to reach a size of $50 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2023 onwards. This growth reflects increasing demands for food production and sustainable practices in farming.
What are the key market players or companies in this general crop farming industry?
The general crop farming industry comprises major players such as Cargill, Archer Daniels Midland Company, Bunge Limited, and Syngenta, which dominate the market. Their continuous innovations and strategic partnerships contribute to the industry’s overall growth and competitive landscape.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the general crop farming industry?
Key drivers of growth in the general crop farming industry include rising population, increasing food demand, technological advancements in farming practices, and a shift towards sustainable and organic farming methods. These factors collectively bolster market expansion over the forecast period.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the general crop farming?
The North America region is the fastest-growing market for general crop farming, projected to reach $32.99 billion by 2033, up from $19.46 billion in 2023. Strong agricultural practices and technological adaptation fuel this rapid growth.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the general crop farming industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific client needs in the general crop farming industry. These reports provide in-depth analysis, helping businesses to make informed decisions based on market trends and forecasts.
What deliverables can I expect from this general crop farming market research project?
From the general crop farming market research project, you can expect detailed reports that include market size, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, driver and trend identification, and actionable insights to support strategic planning and investment decisions.
What are the market trends of general crop farming?
Current trends in the general crop farming market include the rise in organic farming, adoption of precision farming techniques, and increasing investments in agri-tech. These trends highlight a significant shift towards sustainable practices and efficiency in crop production.