Generic Drugs Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: generic-drugs
Generic Drugs Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Generic Drugs market, covering market size, growth trends, segmentation, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It highlights insights across various regions and product types while identifying key industry players and emerging trends.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
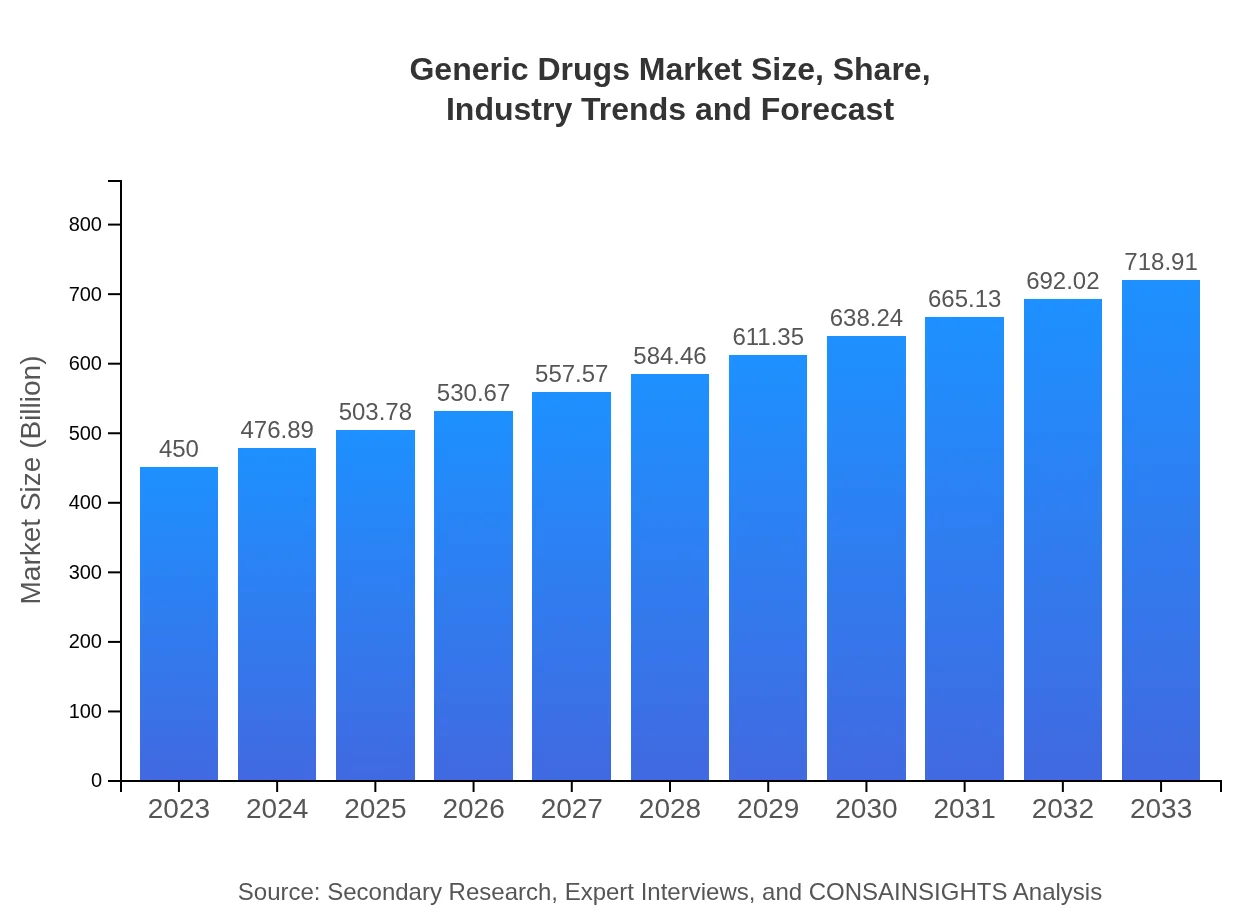
| 2023 Market Size | $450.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $718.91 Billion |
| Top Companies | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Sandoz (Novartis), Mylan N.V., Amgen Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Generic Drugs Market Overview
Customize Generic Drugs Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Generic Drugs market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Generic Drugs's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Generic Drugs
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Generic Drugs market in 2023 and 2033?
Generic Drugs Industry Analysis
Generic Drugs Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Generic Drugs Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Generic Drugs Market Report:
Europe is also poised for robust growth, with the market expected to rise from $124.02 billion in 2023 to $198.13 billion by 2033. Market dynamics are influenced by rigorous regulatory oversight, patent expirations of major drugs, and an aging population. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France show substantial investments in generic drug production, enhancing their position in the global market.Asia Pacific Generic Drugs Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the generic drugs market is projected to grow from $87.98 billion in 2023 to $140.55 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, increased government initiatives aimed at promoting healthcare accessibility, and a growing emphasis on affordable alternative medications propels this growth. Countries like India and China are at the forefront, demonstrating significant advancements in generic drug production and export.North America Generic Drugs Market Report:
North America holds a significant share of the global generic drugs market, reaching $154.13 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $246.23 billion by 2033. The strong presence of established generic drug manufacturers, coupled with mounting pressure to control healthcare costs, drives the growth in this region. The United States remains a key market, supporting a consumer-driven shift towards generics amidst high healthcare costs.South America Generic Drugs Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to increase from $23.45 billion in 2023 to $37.46 billion by 2033. Factors like rising healthcare expenditures, evolving regulatory frameworks, and dynamic demographic changes contribute to the expansion of the generic drugs market. Brazil and Argentina lead the region in terms of market size and growth potential, driven by increasing healthcare reforms to make treatments more affordable.Middle East & Africa Generic Drugs Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is forecasted to grow from $60.44 billion in 2023 to $96.55 billion by 2033. Increased healthcare infrastructure development and rising public spending on health are pivotal factors driving this region's growth. Opportunities exist particularly in countries like South Africa and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, where government initiatives promote generic drug use.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
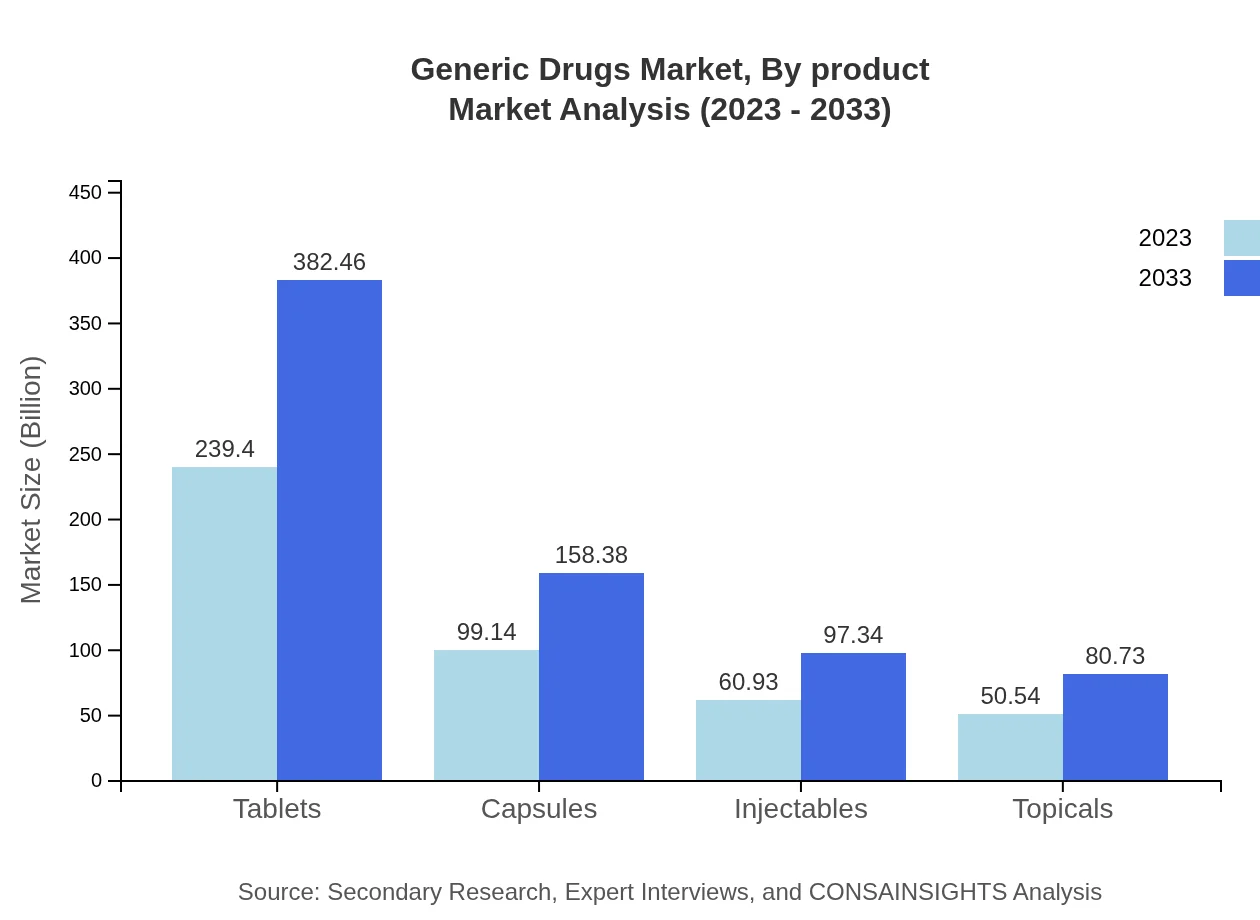
Generic Drugs Market Analysis By Product
The product segmentation of generic drugs includes various forms like tablets, capsules, injectables, and topicals. Tablets and capsules dominate the market, comprising significant shares of the overall market size. In 2023, tablets alone account for $239.40 billion, projected to reach $382.46 billion by 2033. Capsules are closely following with a market size of $99.14 billion in 2023, growing to $158.38 billion by 2033.
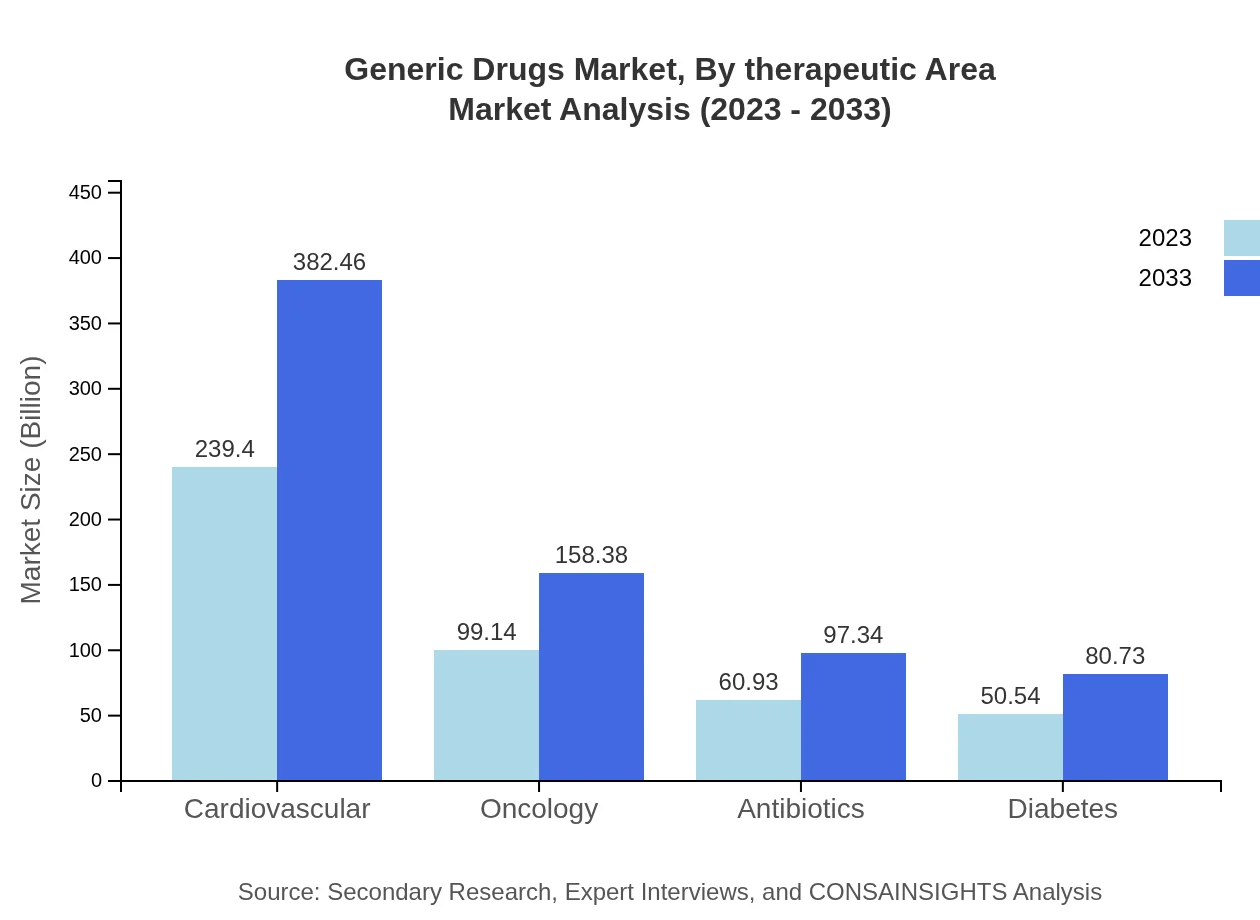
Generic Drugs Market Analysis By Therapeutic Area
Therapeutic area segmentation reveals that cardiovascular drugs represent the largest share in the generic sector, valued at $239.40 billion in 2023 and anticipated to grow to $382.46 billion by 2033. Oncology and antibiotics also represent significant segments with a market size of $99.14 billion and $60.93 billion in 2023, respectively. Each therapeutic category's growth is supported by rising disease prevalence and the push for affordable treatment options.
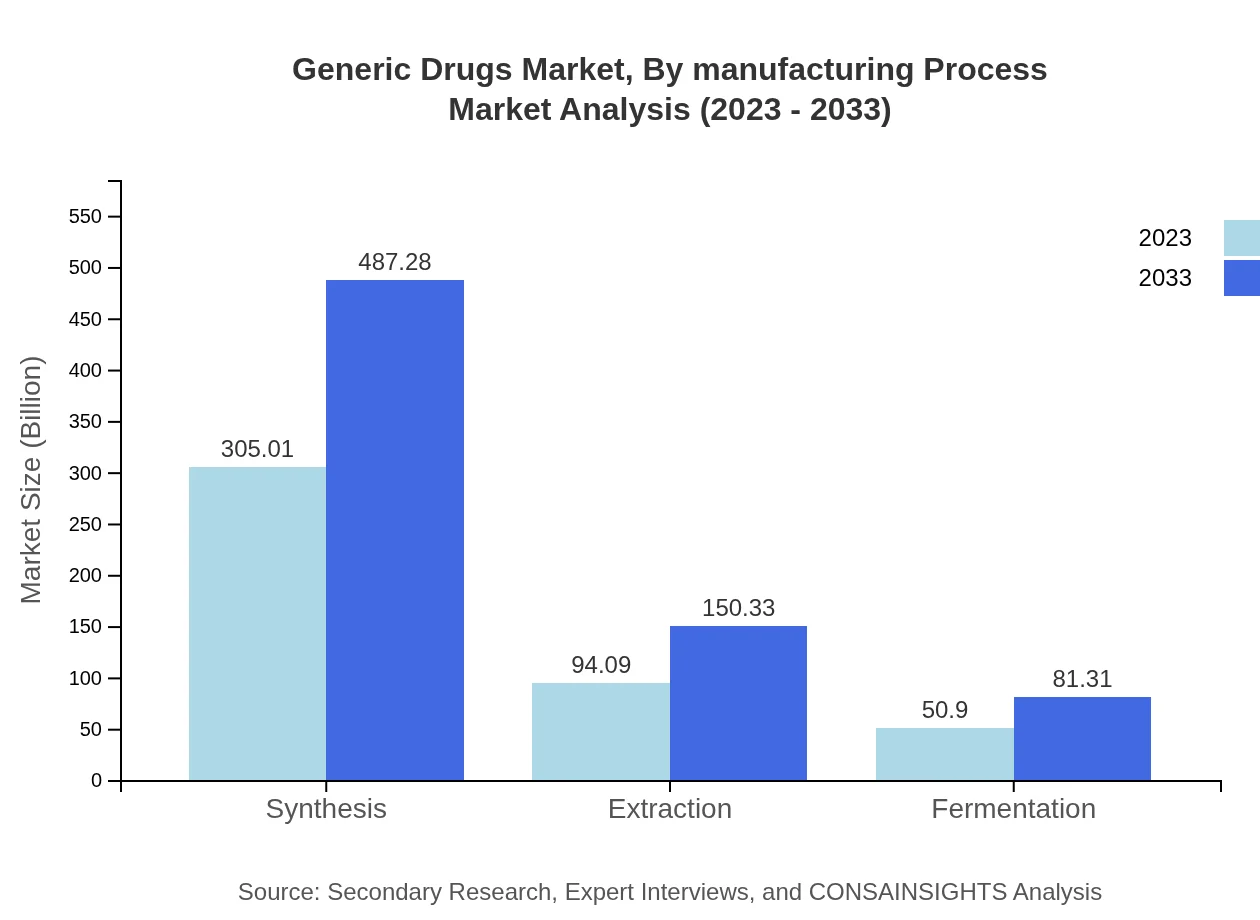
Generic Drugs Market Analysis By Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing processes for generic drugs encompass synthesis, extraction, and fermentation. Synthesis leads the sector, with a market size of $305.01 billion in 2023, reflecting its widespread application in producing diverse medications. Additionally, extraction and fermentation processes are gaining traction, providing alternatives and specialty generic compounds.
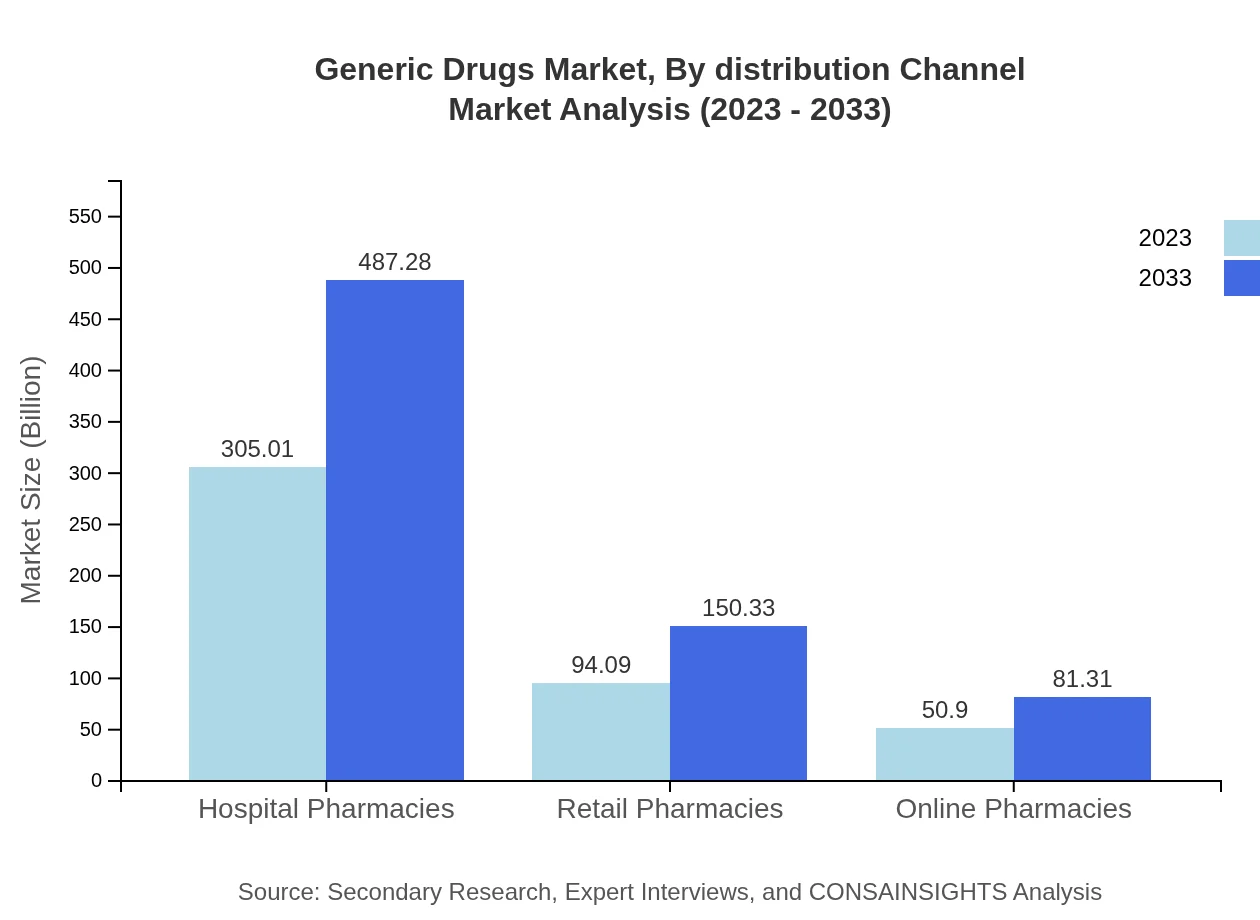
Generic Drugs Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels for generic drugs include hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online pharmacies. Hospital pharmacies account for the largest share, valued at $305.01 billion in 2023, emphasizing their crucial role in delivering medications during patient care. Retail pharmacies represent a significant avenue for consumer access with $94.09 billion in 2023, while online pharmacies are expanding rapidly, reaching $50.90 billion in the same year.
Generic Drugs Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Generic Drugs Industry
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.:
As one of the largest generic drug manufacturers globally, Teva offers a wide range of generic pharmaceuticals across various therapeutic classes, emphasizing affordable access to medications.Sandoz (Novartis):
Sandoz is a global leader in generic pharmaceuticals, recognized for its commitment to quality and innovation in developing generic versions of branded medicines, enhancing patient access across the globe.Mylan N.V.:
Mylan is a prominent player in the generic market, focusing on expanding its portfolio through strategic acquisitions and a robust pipeline of generic products that serve numerous therapeutic areas.Amgen Inc.:
Although primarily a biotechnology company, Amgen is increasing its footprint in the generic drugs sector through partnerships and collaboration in drug development.Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.:
Sun Pharma focuses on comprehensive generics and specialty pharmaceuticals, enhancing its presence in both emerging and developed markets while ensuring affordability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of generic Drugs?
The global market size for generic drugs is projected to reach approximately $450 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.7% from 2023. This growth is driven by increased healthcare access and competition in drug pricing.
What are the key market players or companies in the generic Drugs industry?
Key players in the generic drugs industry include large pharmaceutical companies like Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Sandoz (Novartis), Mylan, and Amgen, among others. These companies focus on producing a range of generic medications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the generic Drugs industry?
The growth of the generic drugs market is driven by factors such as the rising demand for affordable medications, patent expirations of branded drugs, increasing government initiatives for generic production, and advancements in pharmaceutical technology.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the generic Drugs market?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing in the generic drugs market, with a projected growth from $87.98 billion in 2023 to $140.55 billion by 2033. This is due to increasing healthcare investments and growing populations.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the generic Drugs industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the generic drugs industry. Clients can request detailed insights based on particular market segments or regions for better strategic planning.
What deliverables can I expect from this generic Drugs market research project?
From the research project, you can expect comprehensive market analysis, segmented data reports, competitive landscape insights, and trend identification, along with actionable recommendations for strategic decision-making in the generic drugs sector.
What are the market trends of generic Drugs?
Current trends in the generic drugs market include increased adoption of biosimilars, advancements in drug formulation technologies, a shift towards online pharmacies, and the growth of hospital pharmacy segments, indicating a dynamic and evolving landscape.