Genetic Testing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: genetic-testing
Genetic Testing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Genetic Testing market, including detailed insights on market size, growth trends, segmentation, technological advancements, and regional developments from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
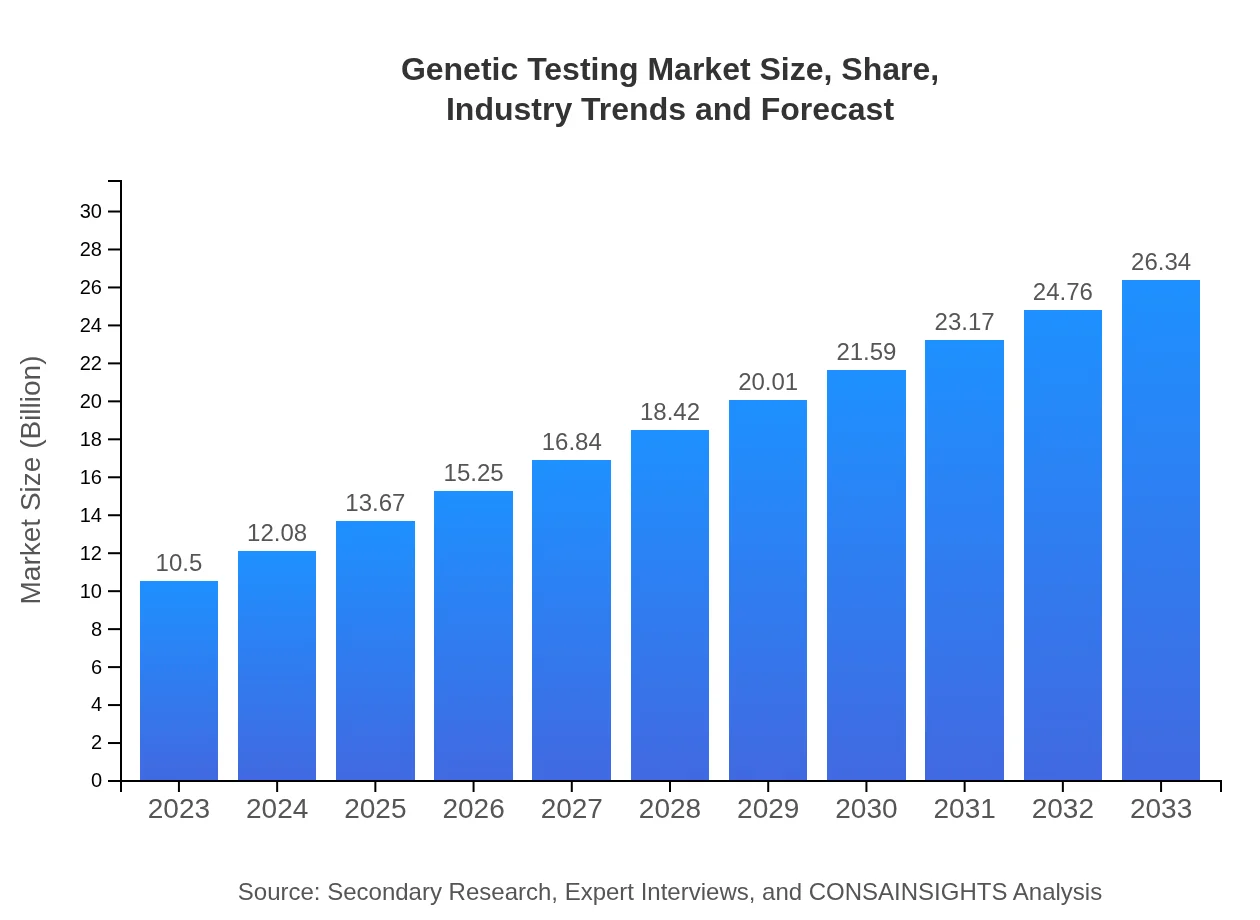
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $26.34 Billion |
| Top Companies | Illumina, Inc., Abbott Laboratories, Myriad Genetics, Roche Diagnostics, Thermo Fisher Scientific |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Genetic Testing Market Overview
Customize Genetic Testing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Genetic Testing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Genetic Testing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Genetic Testing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Genetic Testing market in 2023?
Genetic Testing Industry Analysis
Genetic Testing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Genetic Testing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Genetic Testing Market Report:
Europe's market size stood at $2.59 billion in 2023, with forecasts indicating growth to $6.51 billion by 2033. Increasing focus on precision medicine and advancements in technological capabilities are primary growth drivers in this region.Asia Pacific Genetic Testing Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the genetic testing market was valued at $2.01 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $5.04 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and rising awareness about genetic disorders and preventive healthcare.North America Genetic Testing Market Report:
North America dominated the genetic testing market with a value of $4.00 billion in 2023, projected to surge to $10.04 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a well-established healthcare framework, high rates of adoption of advanced technologies, and significant investments in genetic research.South America Genetic Testing Market Report:
South America had a market size of approximately $0.91 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $2.28 billion by 2033. The increasing prevalence of genetic diseases and improving healthcare infrastructure are significant contributors to this growth.Middle East & Africa Genetic Testing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region was valued at $0.98 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $2.47 billion by 2033. Emerging economies are beginning to invest in genetic testing solutions, which will catalyze market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
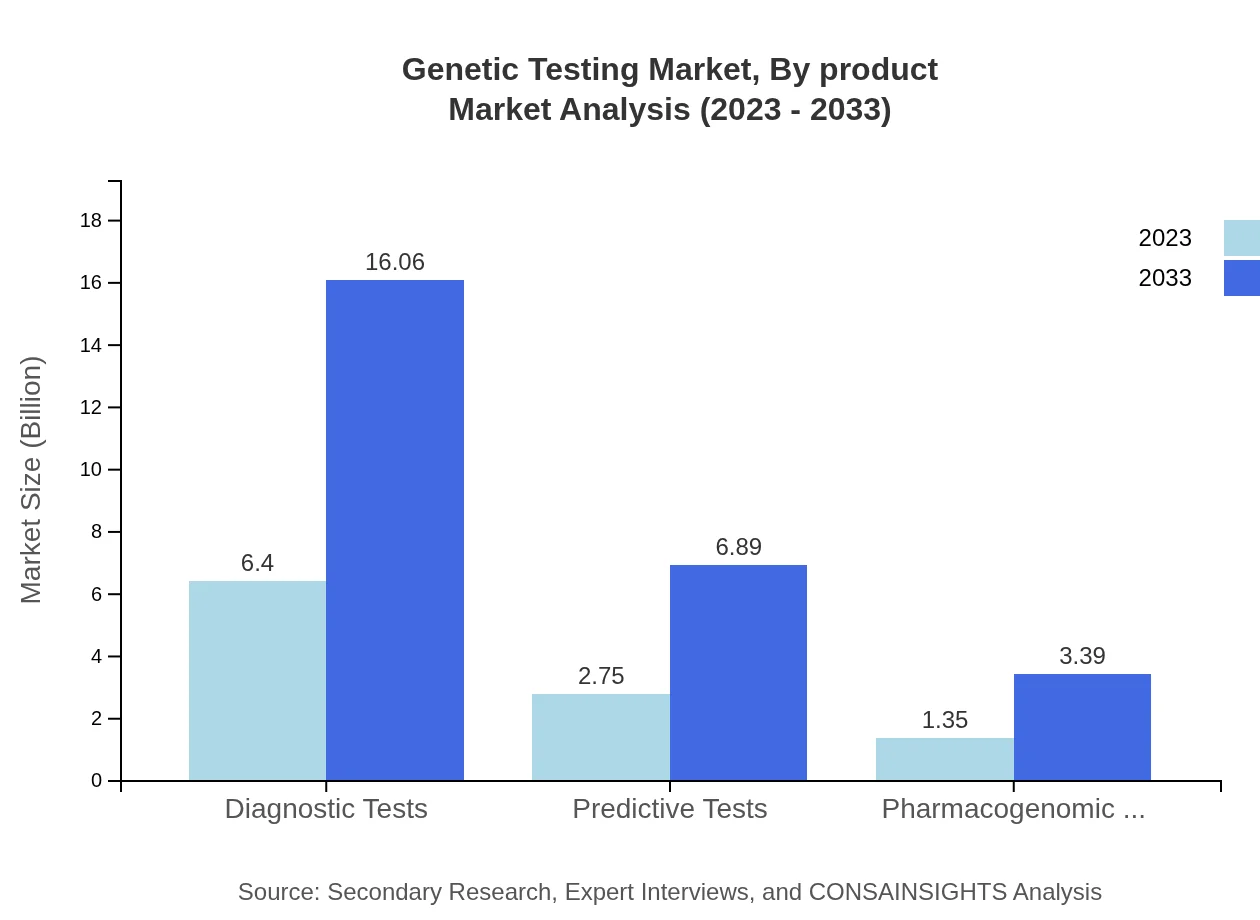
Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Product
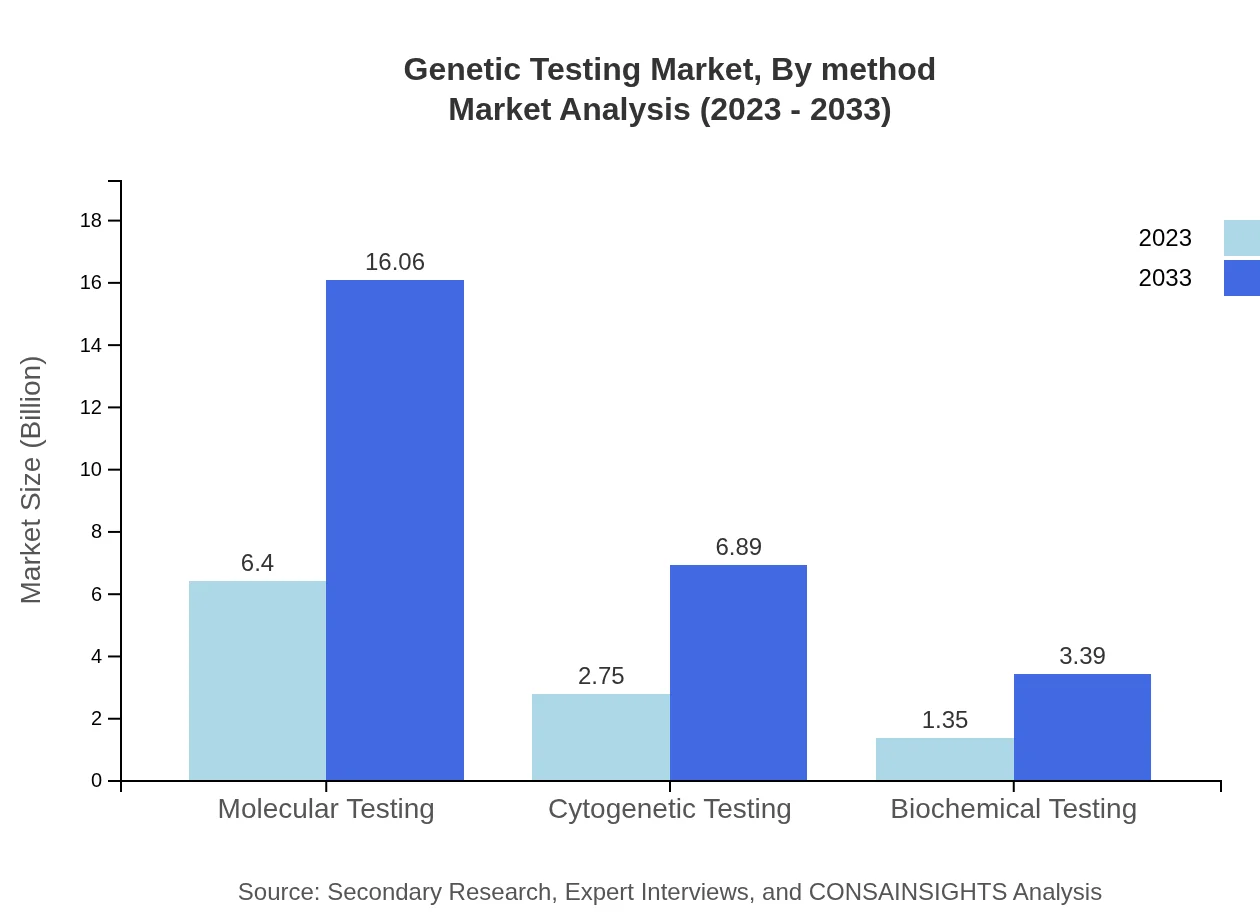
The Molecular Testing segment is the largest, valued at $6.40 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $16.06 billion by 2033, accounting for 60.98% of the market. Cytogenetic Testing holds a market share of 26.16%, with an expected growth from $2.75 billion in 2023 to $6.89 billion by 2033. Biochemical Testing is expected to grow from $1.35 billion to $3.39 billion, maintaining a 12.86% market share.
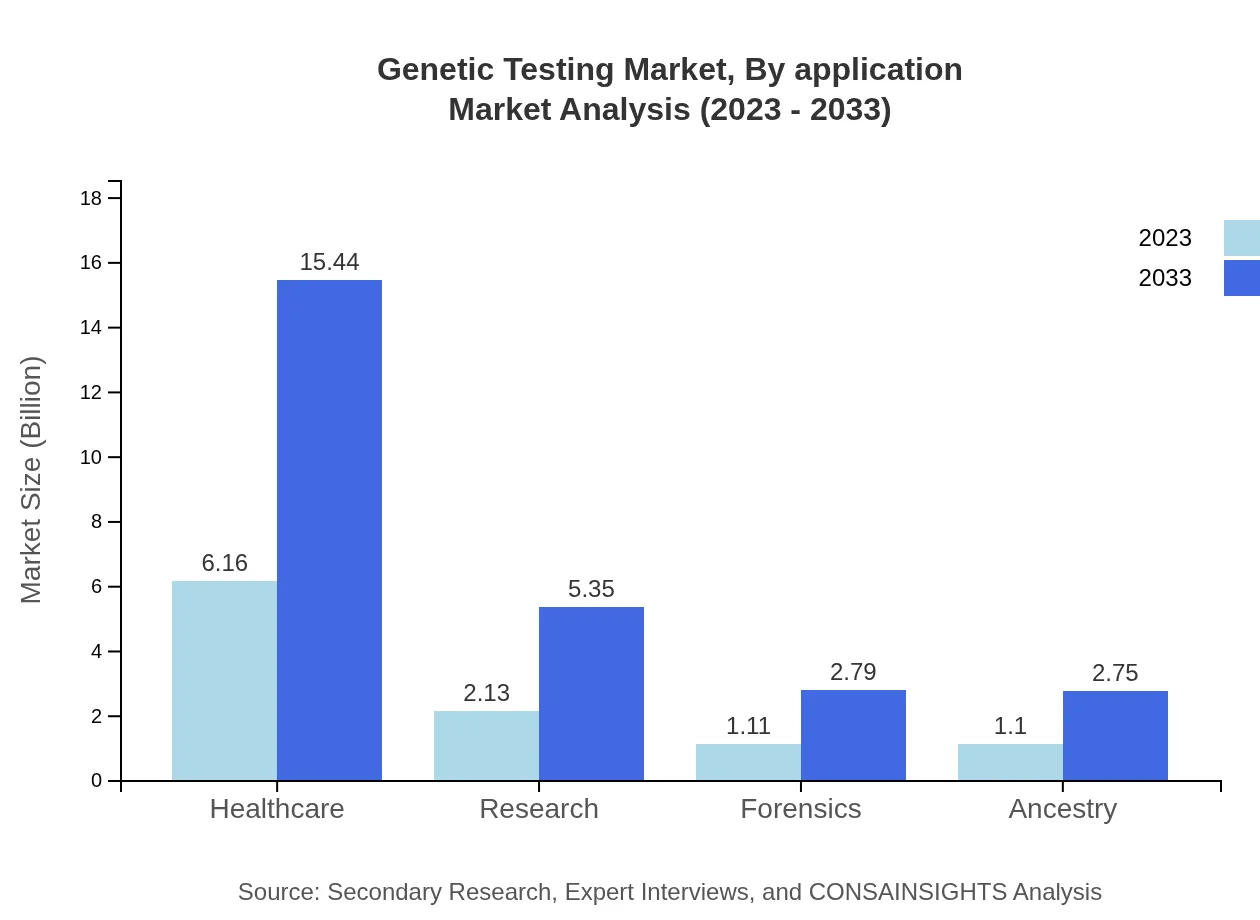
Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Application
The market segments by application include Diagnostics, Predictive Tests, and Pharmacogenomic Tests. Diagnostic tests dominate the market with 60.98% share, projected to grow from $6.40 billion to $16.06 billion. Predictive and Pharmacogenomic tests have shares of 26.16% and 12.86%, expected to grow significantly by 2033.
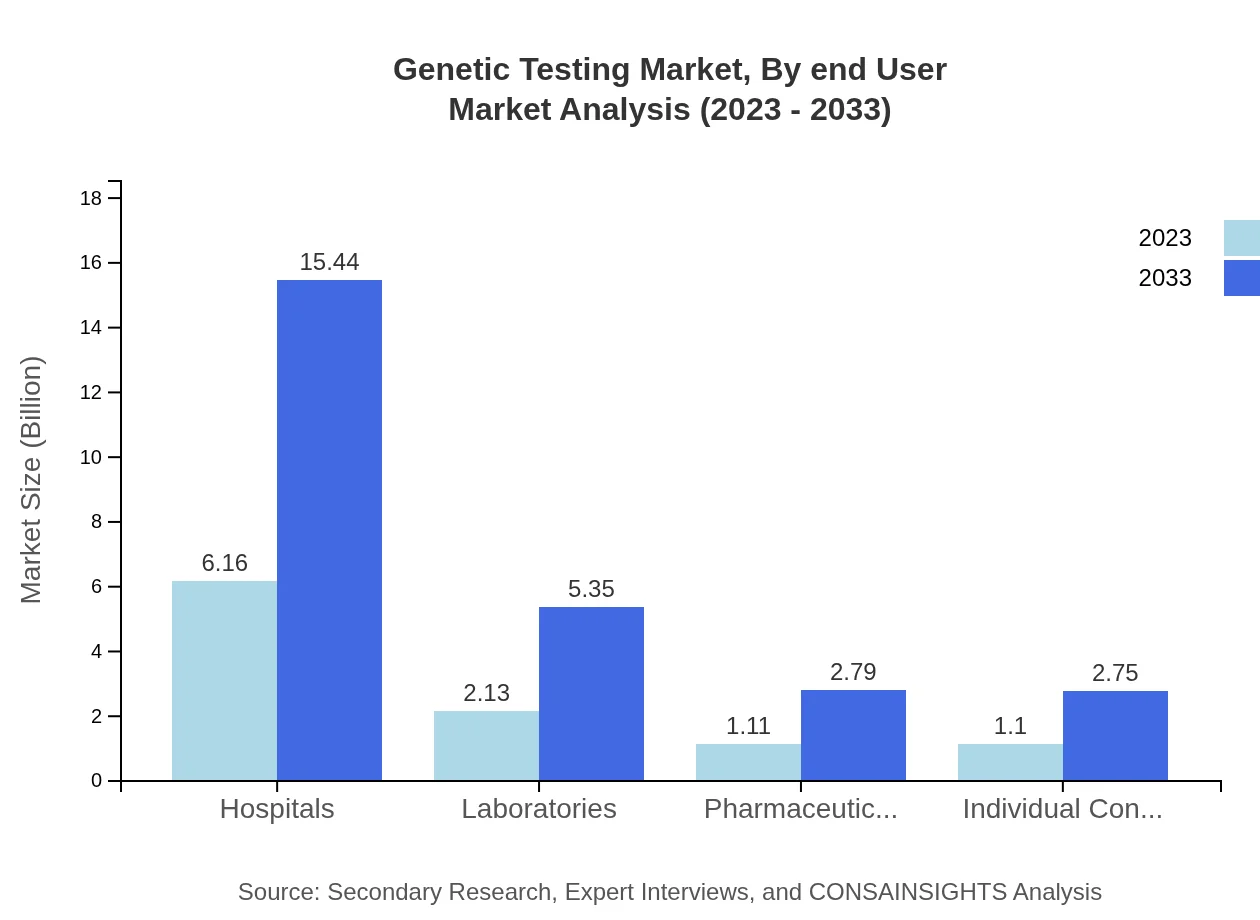
Genetic Testing Market Analysis By End User
Hospitals are the leading end-user segment, projected to expand from $6.16 billion in 2023 to $15.44 billion by 2033, with a market share of 58.63%. Laboratories and pharmaceutical companies will also see growth, with laboratory testing set to grow from $2.13 billion to $5.35 billion.
Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Method
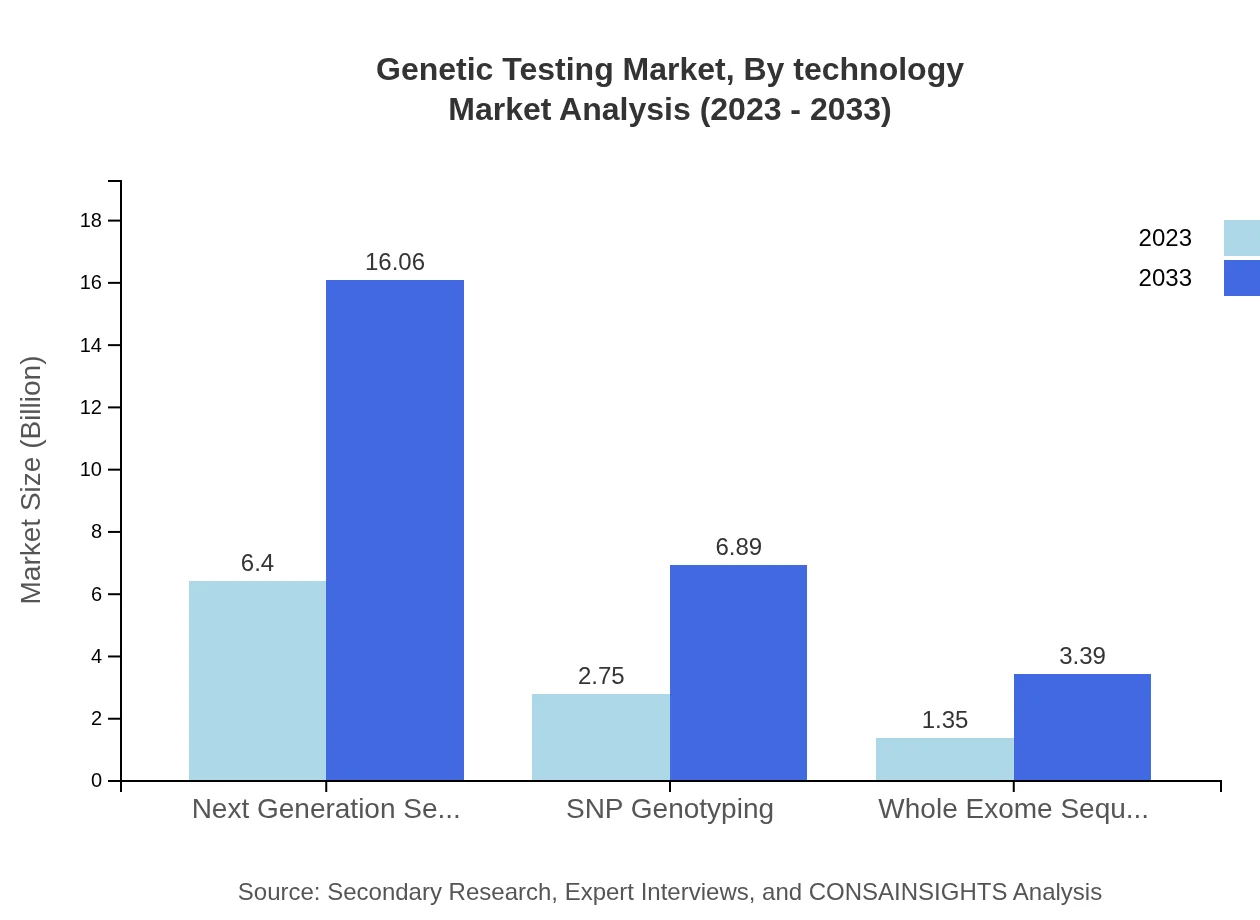
Key methods include Next Generation Sequencing, SNP Genotyping, and Whole Exome Sequencing. NGS leads with $6.40 billion in 2023, expected to reach $16.06 billion by 2033. SNP Genotyping and Whole Exome Sequencing exhibit significant growth rates as well, enhancing the overall testing capabilities.
Genetic Testing Market Analysis By Technology
The market utilizes various technologies, with advancements paving the way for more efficient testing methods. Innovations in digital tools and bioinformatics are revolutionizing genetic testing, enhancing accuracy, and reducing costs, leading to wider adoption.
Genetic Testing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Genetic Testing Industry
Illumina, Inc.:
Illumina leads the market with its advanced sequencing technology and has a significant presence in clinical diagnostics and personalized medicine.Abbott Laboratories:
A global leader in diagnostics, Abbott offers a wide range of genetic testing solutions, focusing on improving patient outcomes.Myriad Genetics:
Specializing in hereditary cancer testing, Myriad has pioneered genetic testing services that help patients make informed healthcare decisions.Roche Diagnostics:
With a strong portfolio in molecular diagnostics, Roche is committed to developing innovative genetic testing solutions for various applications.Thermo Fisher Scientific:
Known for its comprehensive range of genetic testing technologies, Thermo Fisher enables advancements in genomic research and clinical applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of genetic testing?
The genetic testing market is projected to reach approximately $10.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% from a current value in 2023. This growth reflects increasing consumer demand for personalized medicine and advanced diagnostic tools.
What are the key market players or companies in the genetic testing industry?
Key players in the genetic testing market include Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Roche, and QIAGEN. These companies lead innovation in molecular testing and genetic diagnostics, significantly influencing market trends and technological advancements.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the genetic testing industry?
Growth in the genetic testing industry is driven by rising incidences of genetic disorders, increasing awareness of personalized medicine, technological advancements in genetic testing methods, and the growing emphasis on preventive healthcare practices among consumers.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the genetic testing market?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the genetic testing market, projected to grow from $4.00 billion in 2023 to $10.04 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by strong healthcare infrastructure and high demand for innovative genetic testing solutions.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the genetic testing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the genetic testing industry. This service includes in-depth analysis and insights based on specific client needs, ensuring relevant and actionable data.
What deliverables can I expect from this genetic testing market research project?
Deliverables from the genetic testing market research project include comprehensive market analysis reports, segmentation insights, competitive landscape details, forecasts, and actionable recommendations based on the current and projected market trends.
What are the market trends of genetic testing?
Market trends in genetic testing include increased adoption of next-generation sequencing, growing demand for direct-to-consumer genetic tests, and enhanced focus on precision medicine, pushing healthcare forward with innovations in diagnostics and treatment.