Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: genetically-modified-food-safety-testing
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing market, detailing market size, trends, segmentation, and regional insights from 2023 to 2033, with a focus on current conditions and future forecasts.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
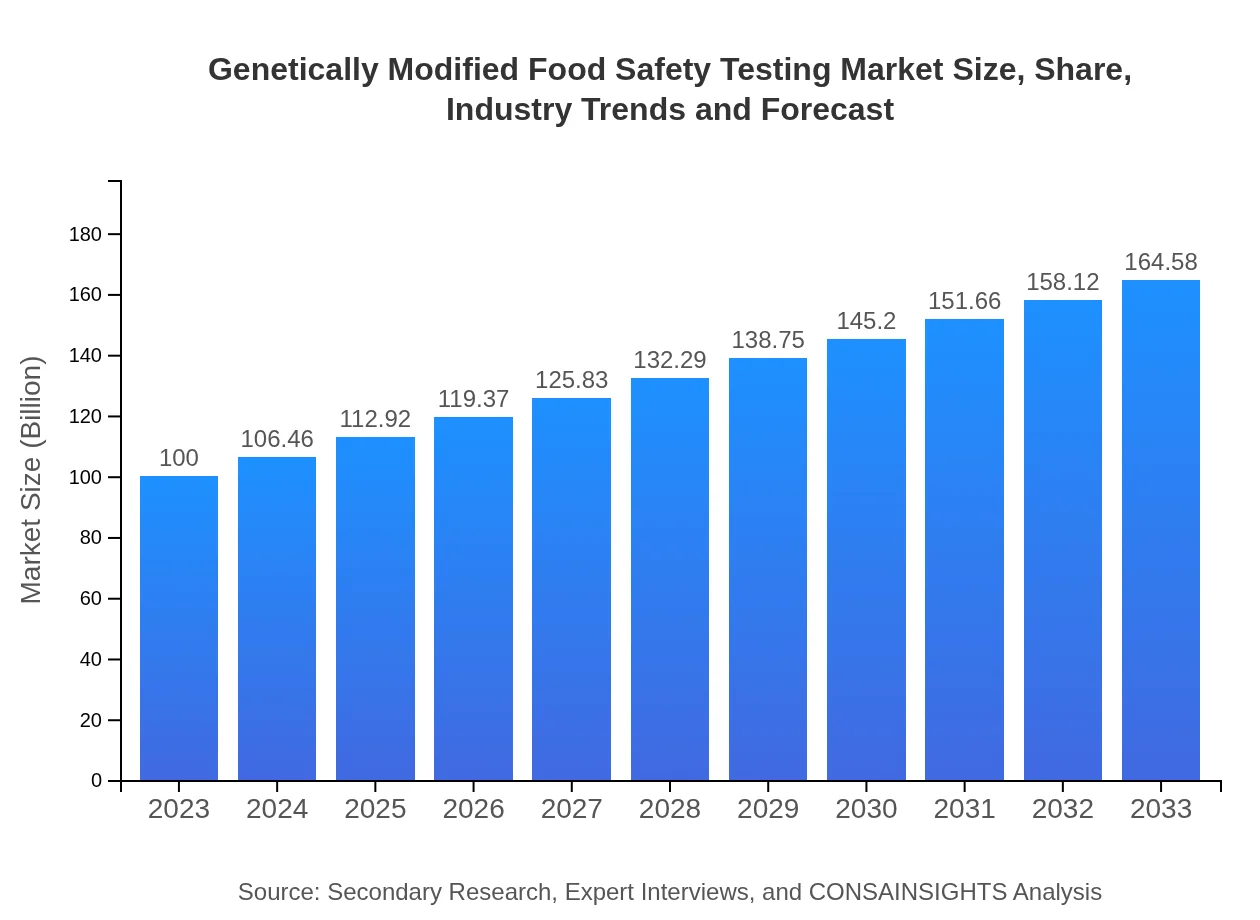
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | SGS S.A., Intertek Group plc, Eurofins Scientific, Eurofins Scientific, TÜV SÜD |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Overview
Customize Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing market in 2023?
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Industry Analysis
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report:
The European market is expected to see growth from $32.36 million in 2023 to $53.26 million by 2033, influenced by stringent EU regulations on GM foods and a high level of consumer awareness regarding food safety concerns. The adoption of advanced testing technologies is also a driving factor in this region.Asia Pacific Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing market is projected to grow from $17.85 million in 2023 to $29.38 million by 2033, fueled by increasing food safety standards and rising GM crop production. Countries like China and India are significant contributors to this growth due to their large agricultural sectors and implementation of stringent regulatory measures.North America Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report:
North America represents the largest market segment, with the size estimated at $36.99 million in 2023 and projected to increase to $60.88 million by 2033. The region benefits from highly developed testing infrastructure, demand for food safety assurances, and robust regulatory frameworks governing GM foods.South America Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report:
The South American market is anticipated to expand from $5.08 million in 2023 to $8.36 million by 2033, driven by the need for enhanced food safety protocols in countries such as Brazil and Argentina, which are major producers of genetically modified crops. Legislative changes and increasing awareness of food safety will further bolster this market.Middle East & Africa Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market for Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing is set to rise from $7.72 million in 2023 to $12.71 million by 2033. Increased agricultural biotechnology adoption and emerging regulatory frameworks focusing on food safety are key contributors to market growth in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
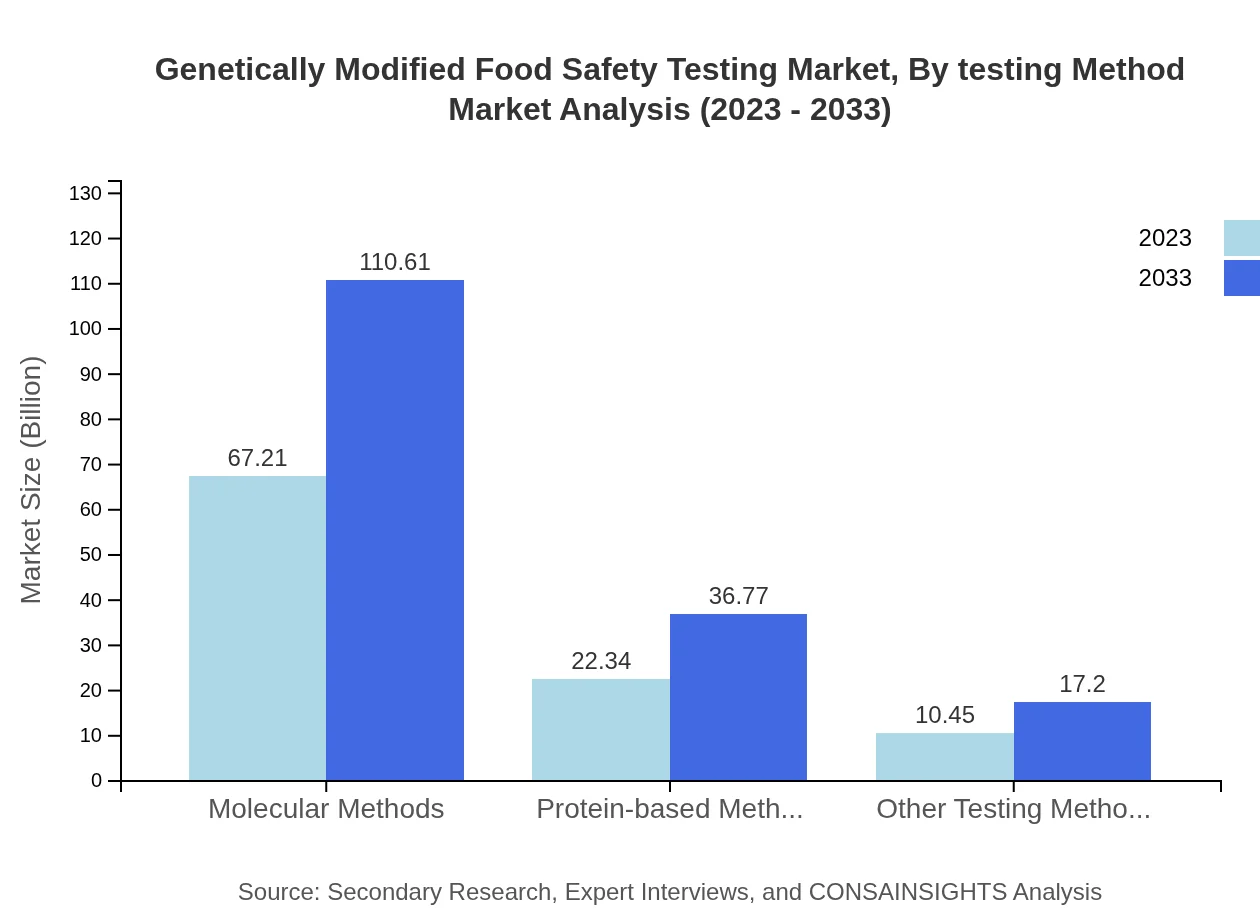
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Analysis By Testing Method
The market segmentation by testing method shows that molecular methods dominate the landscape, with a market size of $67.21 million in 2023, projected to grow to $110.61 million by 2033. Protein-based methods follow, valued at $22.34 million in 2023 and expected to reach $36.77 million by 2033. Other testing methods contribute a smaller share but are crucial for specific applications and niche markets.
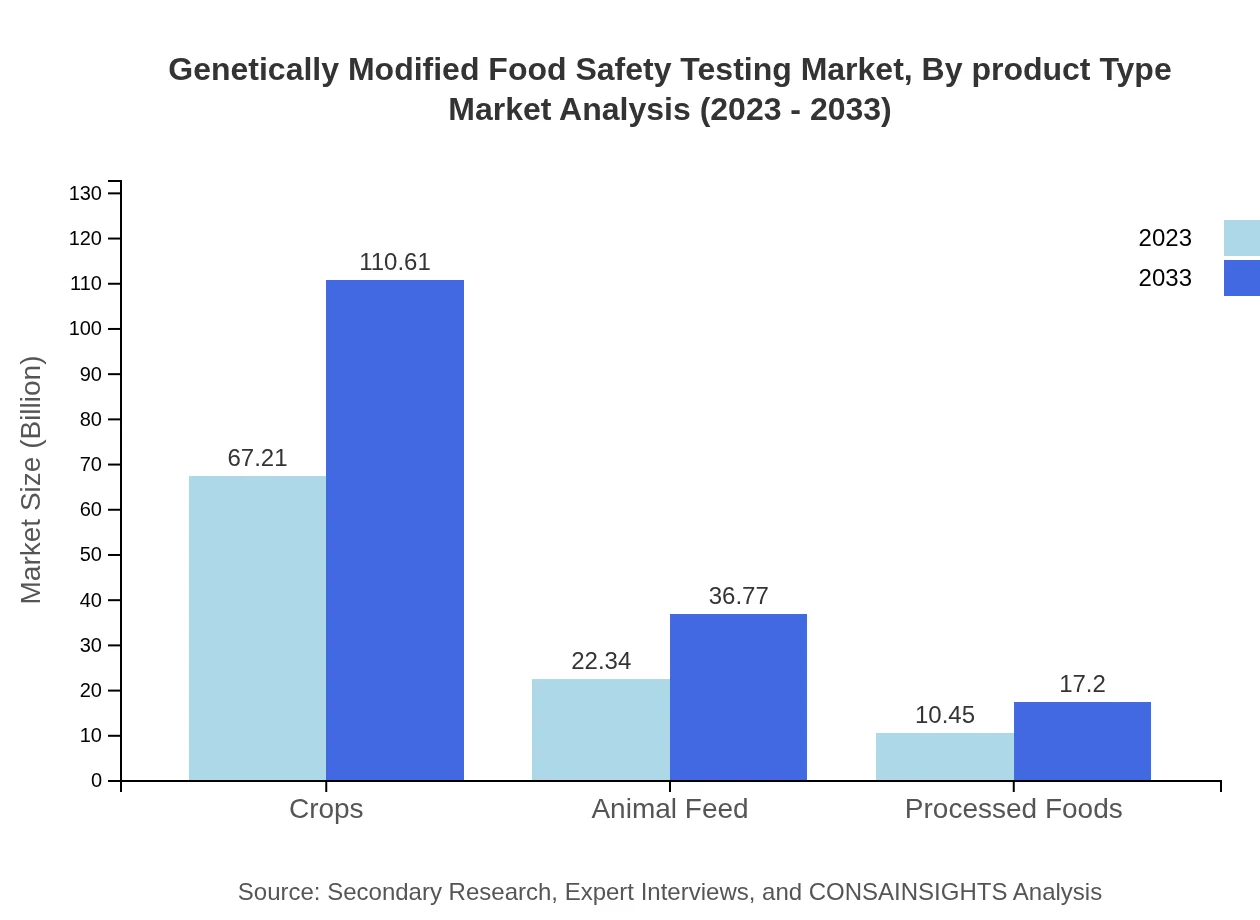
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Analysis By Product Type
In terms of product types, crops represent the largest segment with a market size of $67.21 million in 2023, forecasting growth to $110.61 million in 2033. Animal feed is the second-largest market, valued at $22.34 million in 2023, expected to reach $36.77 million by 2033. Processed foods represent a smaller segment with growth from $10.45 million in 2023 to $17.20 million by 2033, reflecting the evolving landscape of GM food products.
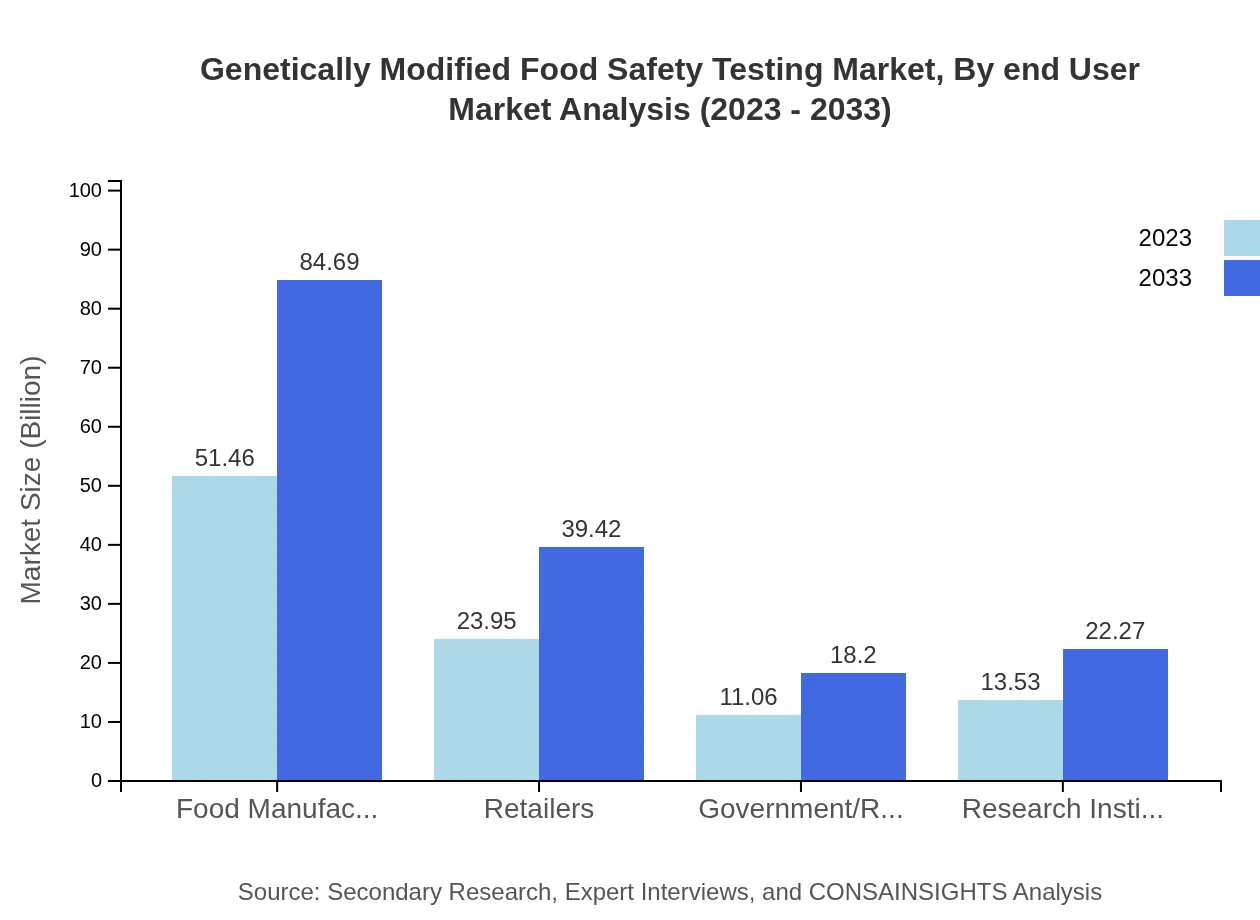
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Analysis By End User
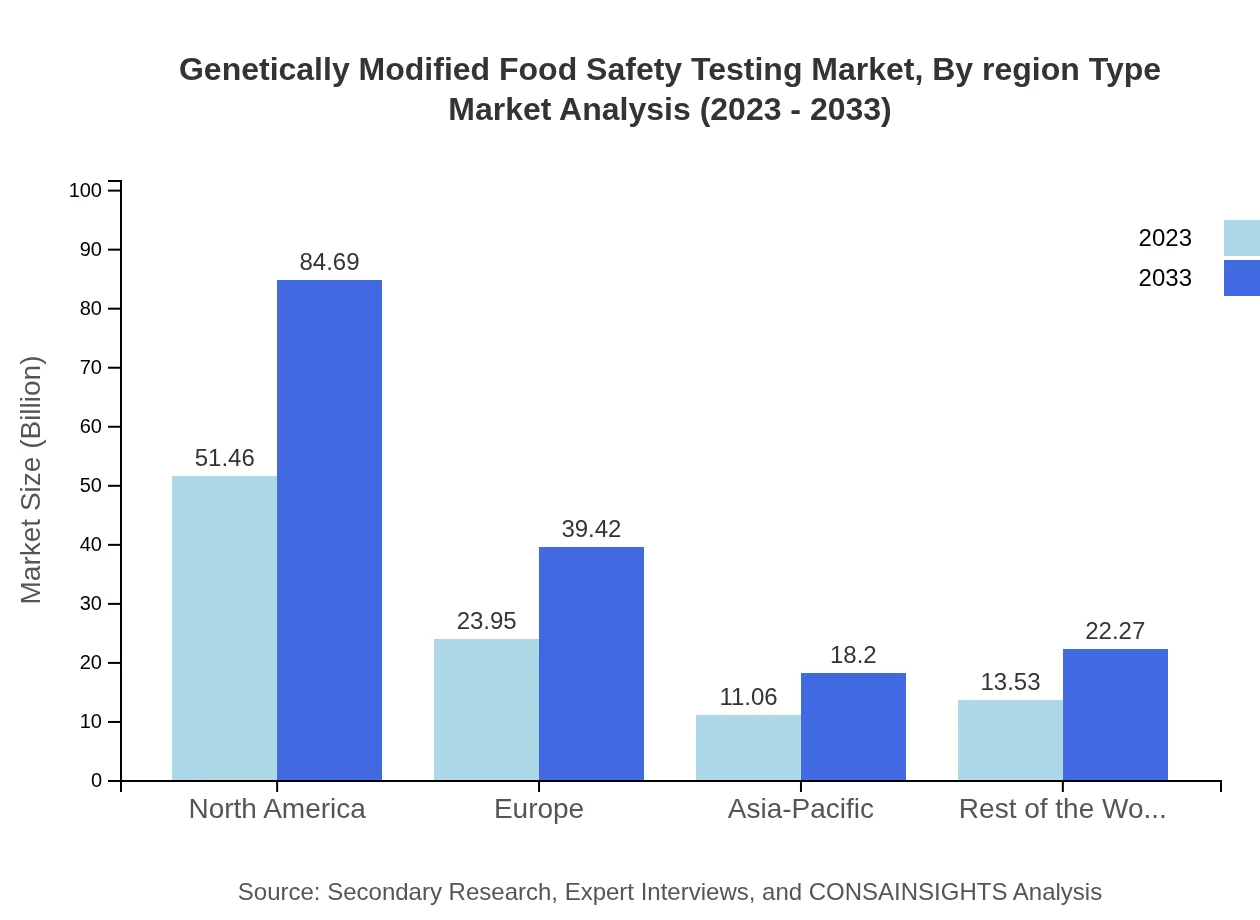
Analyzing the market by end users, food manufacturers are projected to account for a significant share with a market size of $51.46 million in 2023, growing to $84.69 million by 2033. Retailers are also vital players, with market growth from $23.95 million to $39.42 million in the same period. Government and regulatory bodies have a steady share, while research institutes are critical for advancing testing methodologies.
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Analysis By Region Type
The analysis of the market by region highlights North America as the leading market with revenues reflecting the established testing frameworks and regulatory support. Europe follows with stringent regulations shaping the market dynamics. The Asia Pacific region is emerging rapidly due to its agricultural practices and public health efforts, while the Middle East and Africa are expanding as awareness grows and agricultural biotechnology adoption increases.
Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Genetically Modified Food Safety Testing Industry
SGS S.A.:
SGS is a leading inspection, verification, testing, and certification company, providing comprehensive food safety testing services globally, ensuring product compliance and safety standards.Intertek Group plc:
Intertek Group offers a wide array of testing services, including food safety and agricultural testing, ensuring compliance with environmental and health standards in the food industry.Eurofins Scientific:
Eurofins is a global leader in biochemical testing, providing high-quality lab services to ensure the safety and compliance of genetically modified foods across different markets.Eurofins Scientific:
Known for its cutting-edge analytical testing, Eurofins offers services that are critical for assessing GM food safety and regulatory compliance in various markets.TÜV SÜD:
TÜV SÜD provides services ranging from testing and certification to safety assessments for food products, facilitating adherence to regulations surrounding GM foods.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of genetically Modified Food Safety Testing?
The genetically-modified-food-safety-testing market is valued at $100 million in 2023. It is anticipated to grow with a CAGR of 5% over the next decade, reaching significant growth figures as demand for safe food production increases.
What are the key market players or companies in this genetically Modified Food Safety Testing industry?
Key players in the genetically-modified-food-safety-testing industry include leading food safety testing laboratories, biotech firms, and multinational food companies. These entities focus on developing innovative testing methods and enhancing food safety protocols to meet regulatory standards.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the genetically Modified Food Safety Testing industry?
Growth drivers for the genetically-modified-food-safety-testing industry include increasing global population, heightened consumer awareness regarding food safety, and stringent regulations around genetically modified organisms (GMOs) implemented by governments worldwide.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the genetically Modified Food Safety Testing?
The fastest-growing region in the genetically-modified-food-safety-testing market is North America. From 2023 to 2033, the market is projected to increase from $36.99 million to $60.88 million, reflecting a strong demand for rigorous safety testing protocols.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the genetically Modified Food Safety Testing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client specifications in the genetically-modified-food-safety-testing industry. Clients can receive detailed insights and data analytics based on their unique research requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this genetically Modified Food Safety Testing market research project?
From the genetically-modified-food-safety-testing market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market analysis, segmented data, forecasted growth metrics, and insights into regional trends and key market players.
What are the market trends of genetically Modified Food Safety Testing?
Recent trends in the genetically-modified-food-safety-testing market include advancements in molecular testing methods, increased focus on sustainability practices in food production, and growing investments in research and development from food manufacturers.