Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: genetically-modified-seeds
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the Genetically Modified Seeds market, covering key insights, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It includes detailed sections on market size, segmentation, regional analysis, and leading players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
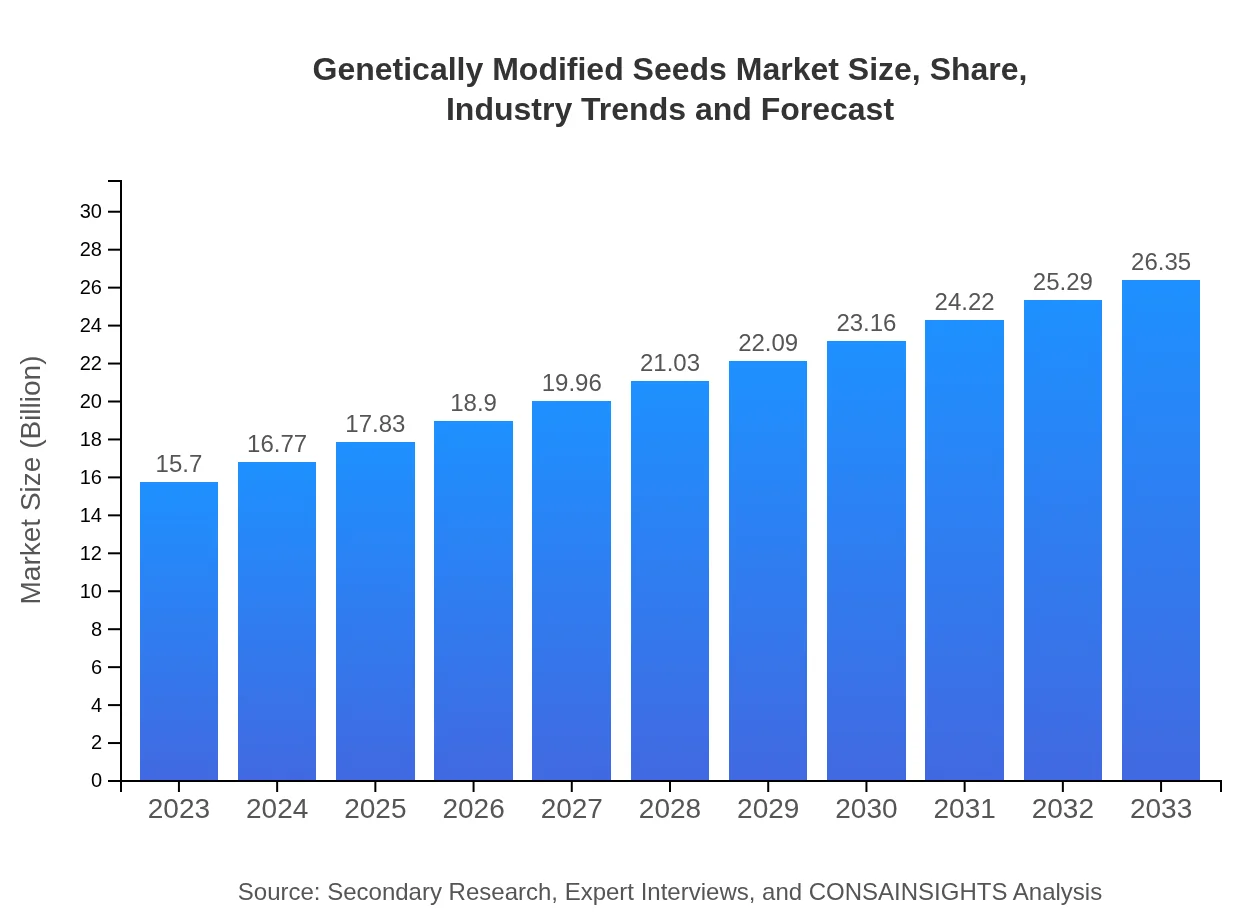
| 2023 Market Size | $15.70 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $26.35 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto (Bayer), DuPont Pioneer, Syngenta, BASF, Corteva Agriscience |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Overview
Customize Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Genetically Modified Seeds market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Genetically Modified Seeds's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Genetically Modified Seeds
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Genetically Modified Seeds market in 2023?
Genetically Modified Seeds Industry Analysis
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report:
Europe is witnessing a gradual increase, with market figures expected to rise from $5.62 billion in 2023 to $9.43 billion by 2033. However, stringent regulations on GMOs and public skepticism pose challenges. Yet, ongoing research and policy adaptations promise a cautious but steady growth.Asia Pacific Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report:
In Asia Pacific, the market is projected to expand from $2.90 billion in 2023 to $4.87 billion by 2033. Government initiatives to promote agricultural productivity and rising population pressures fuel this growth. Countries like India and China are leading adopters, with significant investments in biotech research.North America Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report:
North America dominates the market, with expectations of growth from $5.18 billion in 2023 to $8.70 billion in 2033. The U.S. leads in GM seed adoption, fueled by technological advancements and farmer familiarity with biotech solutions, ensuring a stable growth framework.South America Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report:
The market in South America indicates a downturn, projected to decrease from $-0.09 billion in 2023 to $-0.15 billion by 2033, primarily due to regulatory constraints against GM crop cultivation in certain countries, alongside fluctuating agricultural policies.Middle East & Africa Genetically Modified Seeds Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is anticipated to grow from $2.09 billion in 2023 to $3.51 billion in 2033. Increasing food security efforts and adoption of modern agricultural practices in regions like South Africa are key growth drivers.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
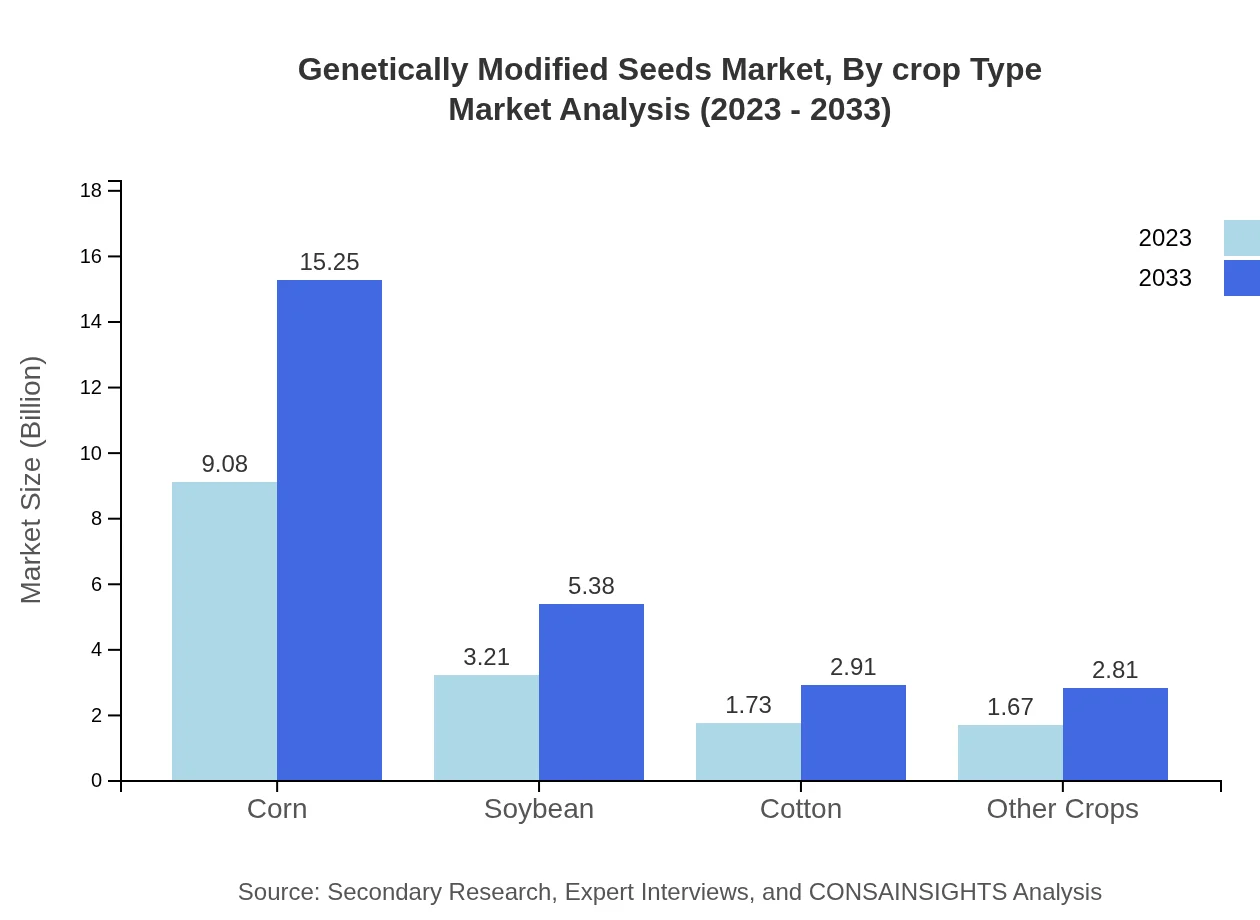
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Analysis By Crop Type
In terms of crop type, corn leads the segment with a market size expected to increase from $9.08 billion in 2023 to $15.25 billion by 2033, capturing approximately 57.86% of the market share. Soybeans follow closely, projected to grow from $3.21 billion to $5.38 billion. Cotton witnesses a moderate growth rate from $1.73 billion to $2.91 billion, and other crops collectively showcasing a growing segment with rising innovations.
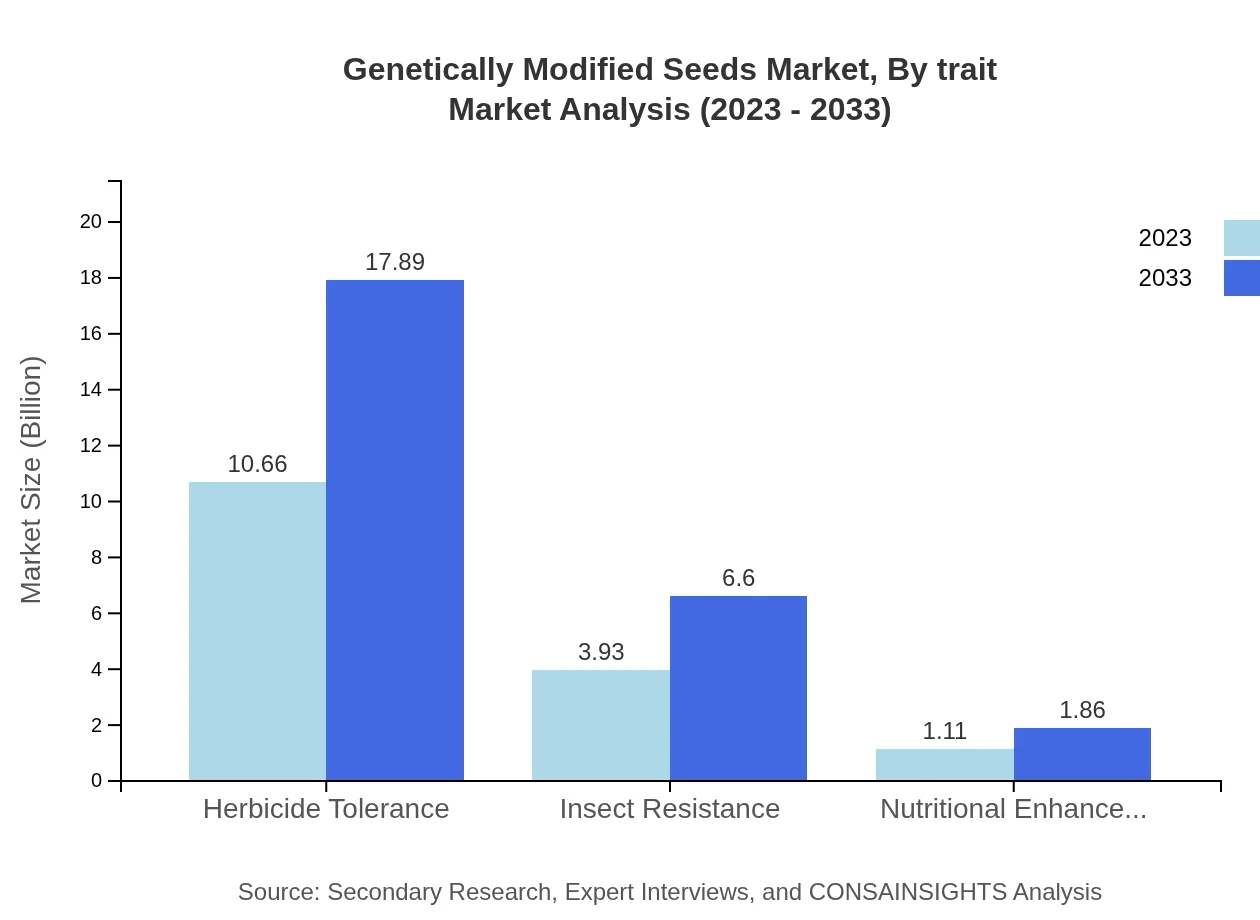
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Analysis By Trait
The market by trait is dominated by herbicide tolerance, harnessing a size of $10.66 billion in 2023, expected to reach $17.89 billion by 2033 with a steady share of 67.88%. Insect-resistant seeds account for 25.05% of the market, growing from $3.93 billion to $6.60 billion. Nutritional enhancement contributes smaller but significant functionality, projected to grow from $1.11 billion to $1.86 billion.
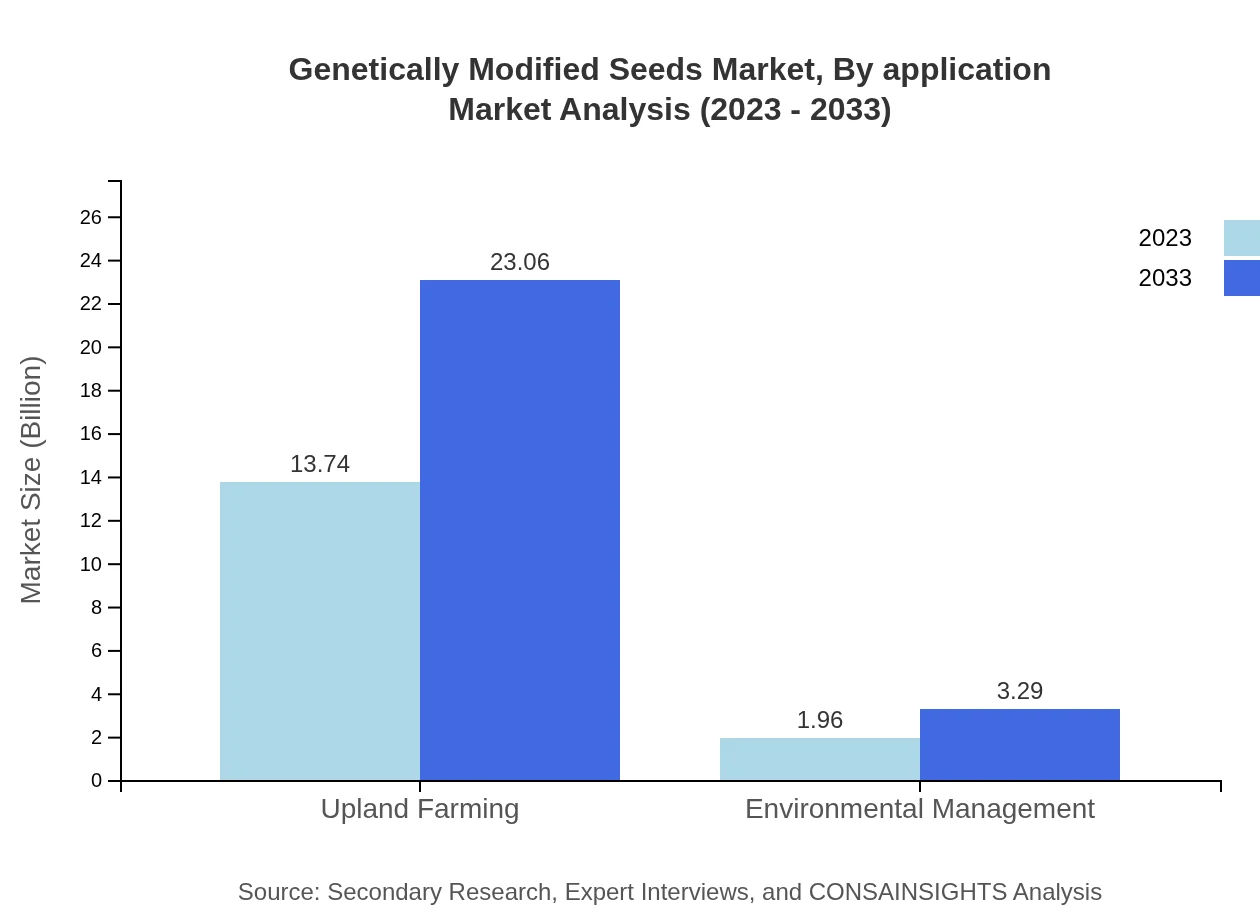
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Analysis By Application
The application market predominantly includes direct sales witnessing robust growth from $13.74 billion in 2023 to $23.06 billion by 2033, holding a dominant share of 87.5%. Retail channels are anticipated to growth from $1.96 billion to $3.29 billion, reflecting changing purchasing patterns and increased access to agricultural products.
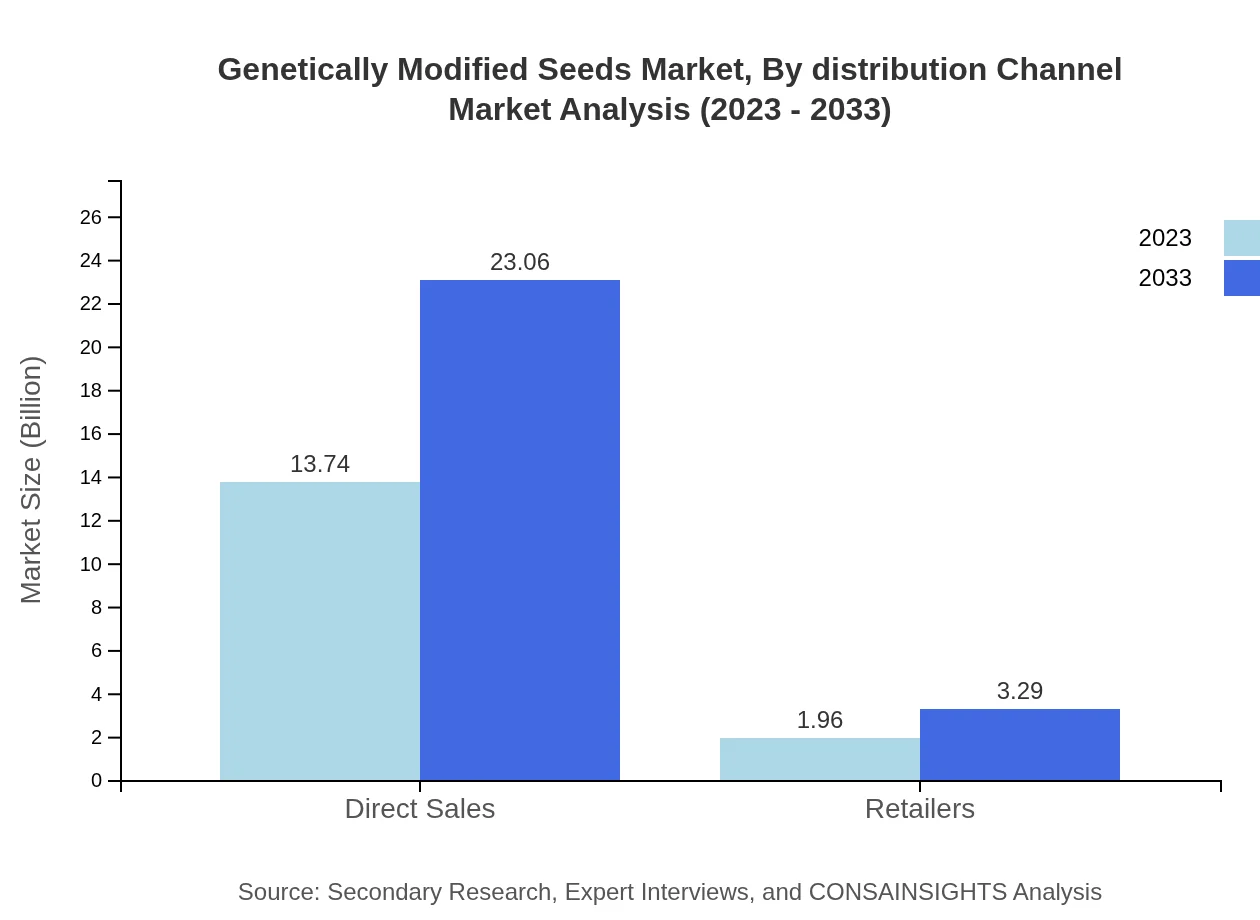
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels encompass a variety of segments with direct sales leading the market expected to increase from $13.74 billion to $23.06 billion, holding a consistent share of 87.5%. Retailers will also see an uptick from $1.96 billion to $3.29 billion, emphasizing growing accessibility and acceptance of GM products.
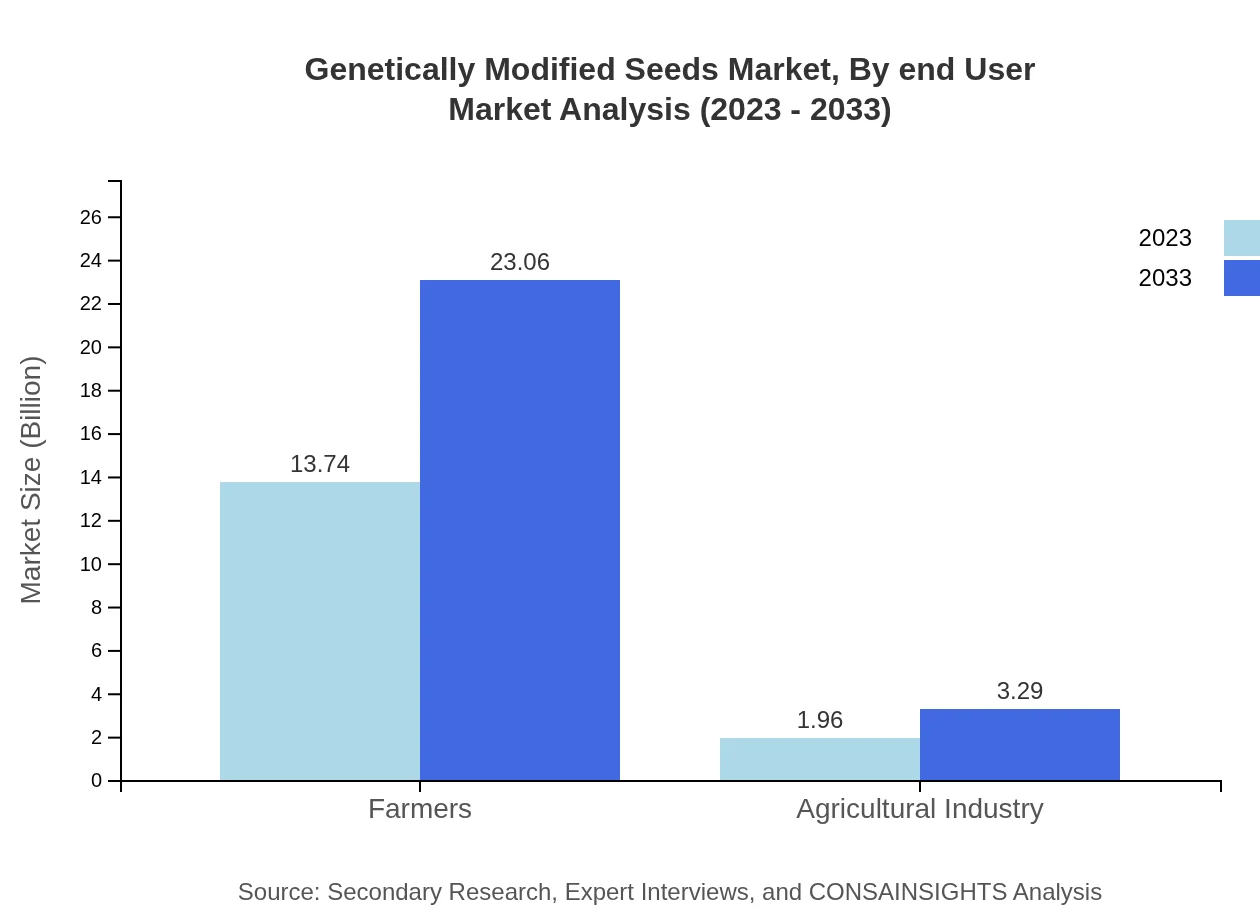
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Analysis By End User
The end-user market primarily includes farmers and the agricultural industry. Farmers dominate with a size increasing from $13.74 billion to $23.06 billion, retaining a share of 87.5%. The agricultural sector's contribution is noted with growth from $1.96 billion to $3.29 billion, reflecting essential dependencies on enhanced crop technologies.
Genetically Modified Seeds Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Genetically Modified Seeds Industry
Monsanto (Bayer):
Monsanto, a subsidiary of Bayer, is a prominent player in the biotechnology industry, focusing on developing genetically modified seeds that are optimized for agricultural efficiency and sustainability.DuPont Pioneer:
DuPont Pioneer is a leading agricultural biotech firm, known for its advanced seed technologies and various GM products that support global food security and sustainable farming practices.Syngenta:
Syngenta is a key figure in agricultural innovation, offering a wide range of genetically modified seeds designed for superior yield and disease resistance to enhance crop productivity.BASF:
BASF is involved in genetic crop improvement initiatives with a focus on developing innovative seed traits that offer agricultural solutions to meet food demands sustainably.Corteva Agriscience:
Corteva Agriscience, a new leader formed from DowDuPont, focuses on producing genetically modified seeds that meet emerging agricultural challenges while promoting sustainable practices.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of genetically Modified Seeds?
The global genetically-modified seeds market is valued at approximately $15.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2%, reaching significant expansion by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this genetically Modified Seeds industry?
Key players in the genetically-modified seeds industry include major agribusiness firms such as Monsanto, DuPont, Syngenta, Bayer, and BASF, which lead through innovation and product offerings across various crop segments.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the genetically Modified Seeds industry?
Key growth drivers include rising global food demand, advancements in biotechnology, increased resistance to pests and diseases, improved yield efficiency, and a growing focus on sustainable agricultural practices.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the genetically Modified Seeds?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for genetically-modified seeds, projected to grow from $2.90 billion in 2023 to $4.87 billion by 2033, driven by population growth and agricultural modernization.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the genetically Modified Seeds industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data for the genetically-modified seeds industry to suit specific client needs, ensuring relevant insights for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this genetically Modified Seeds market research project?
Deliverables include a comprehensive market analysis report, segmented insights, current trends, regional assessments, competitive landscape analysis, and projections to inform investment decisions.
What are the market trends of genetically Modified Seeds?
Current market trends include an increase in demand for herbicide-tolerant seeds, advancements in nutritional enhancement technology, and the growing adoption of genetically-modified technologies in emerging markets.