Genotyping Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: genotyping
Genotyping Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Genotyping market from 2023 to 2033, covering market size, trends, segment performances, and regional insights to equip stakeholders with critical data for decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
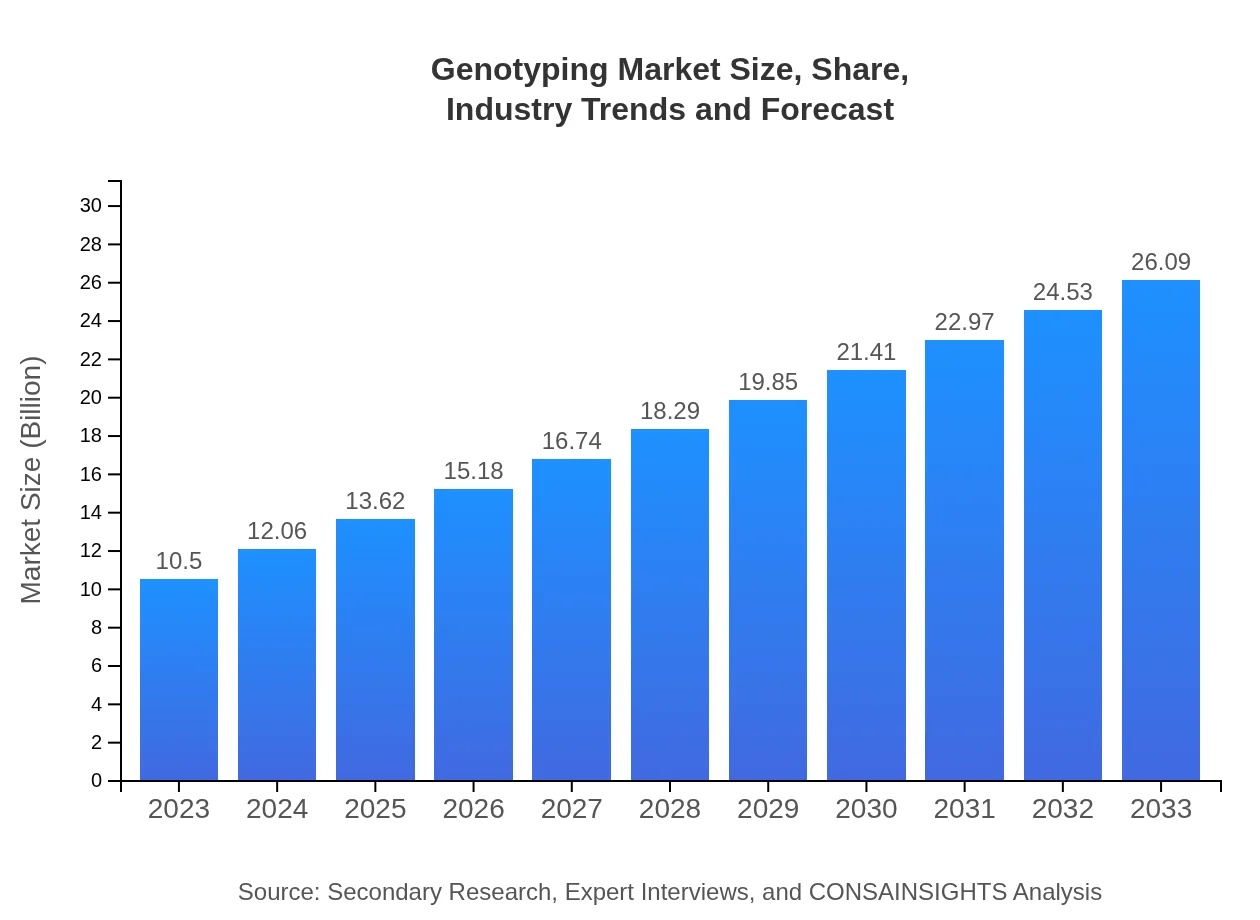
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $26.09 Billion |
| Top Companies | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illumina, Inc., Roche Holding AG, Agilent Technologies, Qiagen N.V. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Genotyping Market Overview
Customize Genotyping Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Genotyping market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Genotyping's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Genotyping
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Genotyping market in 2023?
Genotyping Industry Analysis
Genotyping Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
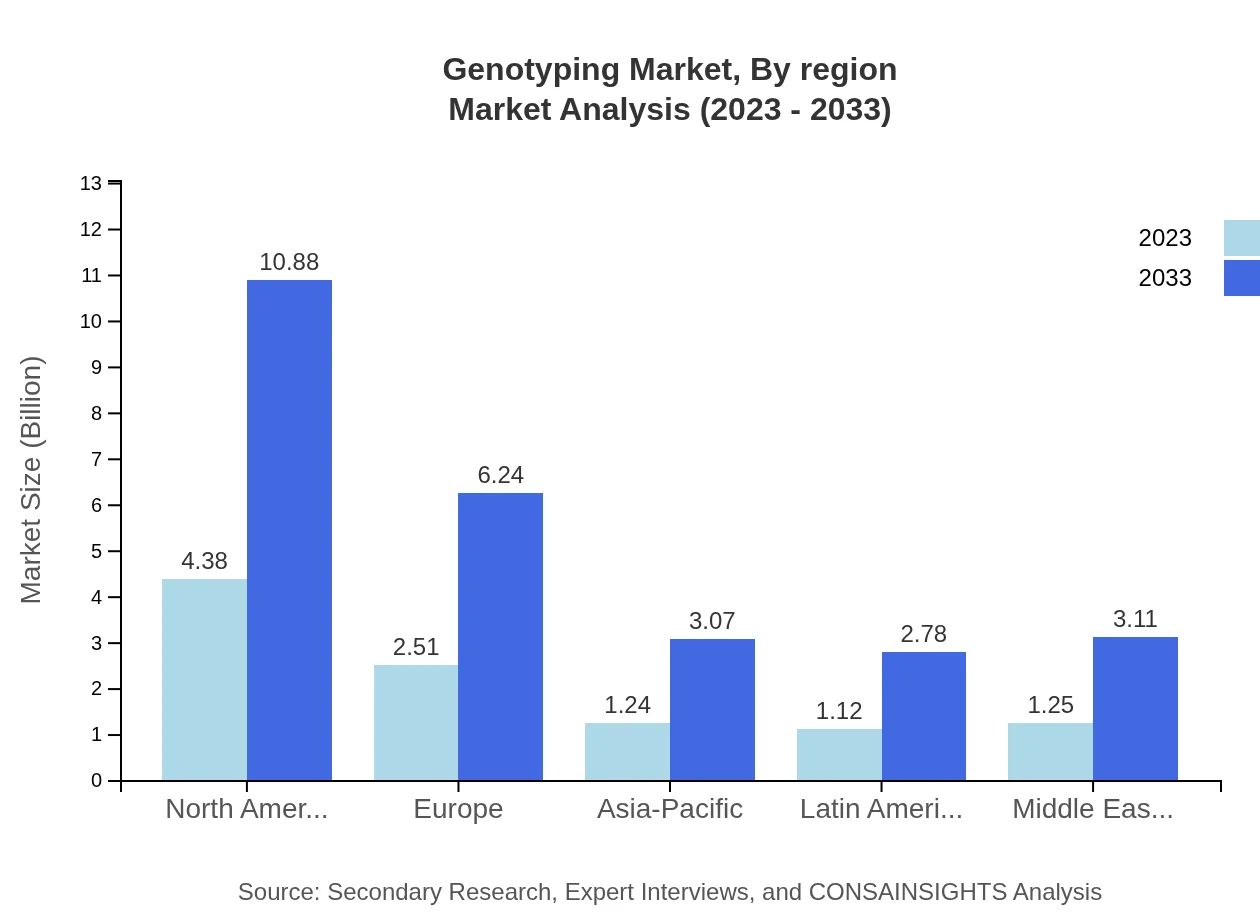
Genotyping Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Genotyping Market Report:
The Genotyping market in Europe is projected to expand from $2.83 billion in 2023 to $7.03 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a robust regulatory framework and a proactive approach to personalized medicine, with countries such as Germany and the UK taking the lead in adopting advanced genotyping technologies.Asia Pacific Genotyping Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Genotyping market is expected to grow from $2.00 billion in 2023 to $4.97 billion by 2033, reflecting a significant rise in genetic testing awareness and healthcare infrastructure improvements. Countries like China and India are major contributors, driven by increased genomic research funding and growth in the biotechnology sector.North America Genotyping Market Report:
North America remains the largest market, expected to grow from $4.01 billion in 2023 to $9.96 billion by 2033. The presence of leading biotech and pharmaceutical companies, along with high healthcare spending on genetic testing, are major drivers. Innovative technologies and strong support from research institutions further bolster the market.South America Genotyping Market Report:
The South American market for Genotyping is projected to increase from $0.43 billion in 2023 to $1.06 billion by 2033. Contributing factors include advancements in agricultural applications of genotyping, growing research initiatives, and supportive government policies aimed at enhancing healthcare systems.Middle East & Africa Genotyping Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Genotyping market is anticipated to climb from $1.24 billion in 2023 to $3.08 billion by 2033. Key growth drivers include the rising prevalence of genetic disorders, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the implementation of programs to enhance genetic research capabilities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
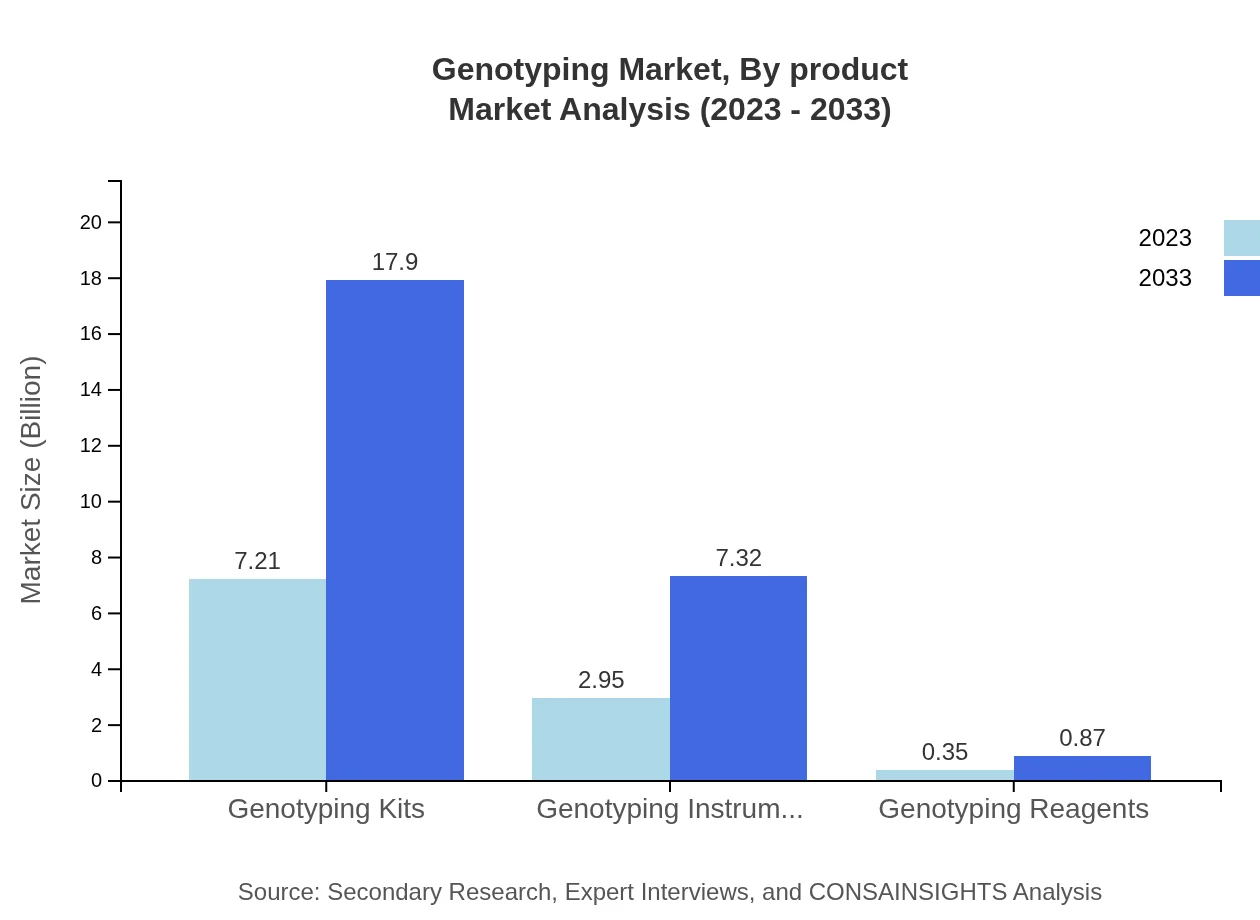
Genotyping Market Analysis By Product
The Genotyping Market is primarily driven by the sale of Genotyping Kits, which represent a market size of $7.21 billion in 2023, growing to $17.90 billion by 2033, thus capturing 68.62% market share. Genotyping Instruments and Reagents are also important segments, with their respective sizes at $2.95 billion and $0.35 billion in 2023. Instruments are expected to grow to $7.32 billion while reagents move to $0.87 billion by 2033.
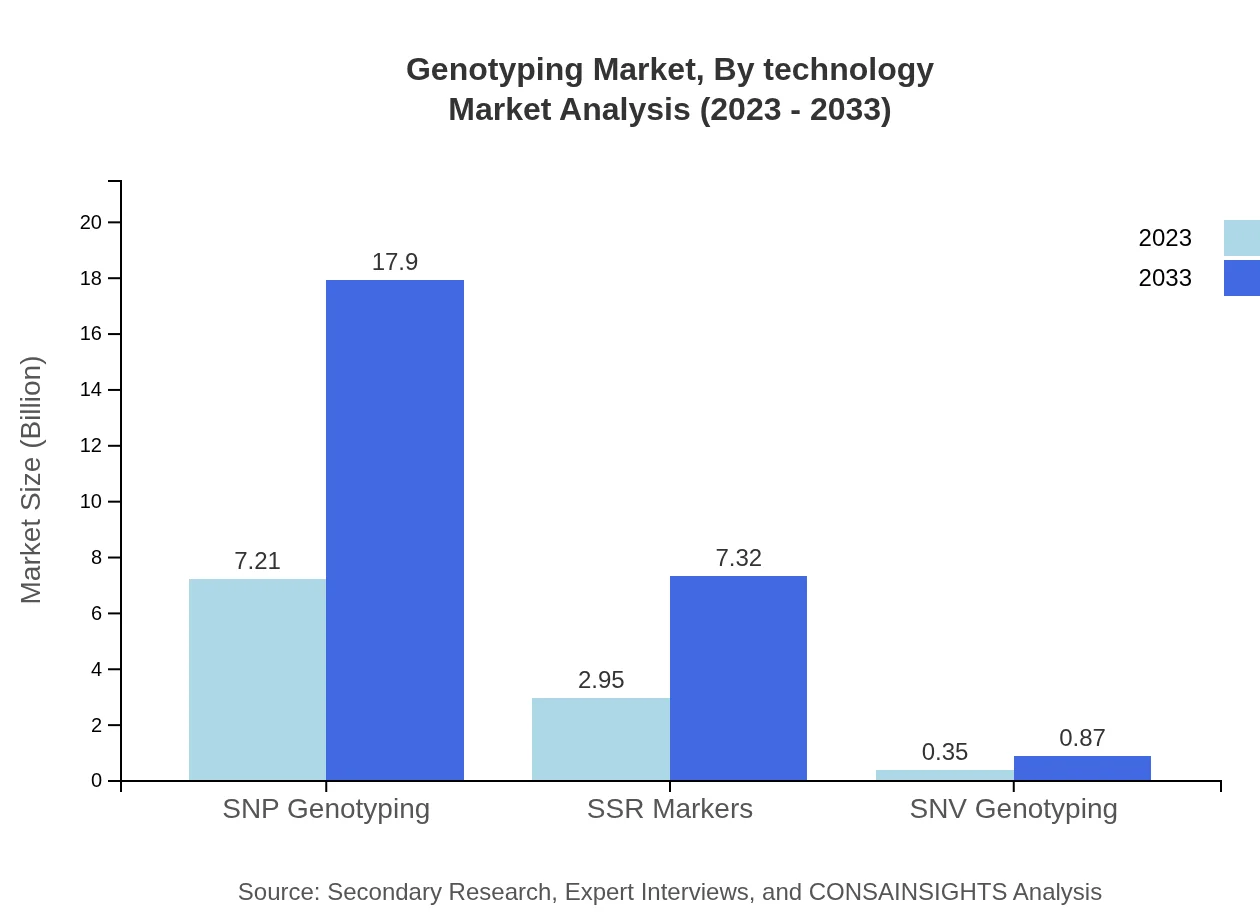
Genotyping Market Analysis By Technology
The major technologies leading the Genotyping market include SNP Genotyping and SSR Markers. SNP Genotyping dominates with an anticipated market increase from $7.21 billion in 2023 to $17.90 billion by 2033, holding a substantial market share of 68.62%. Innovations in sequencing technologies continue to enhance the capabilities and applications of these methods.
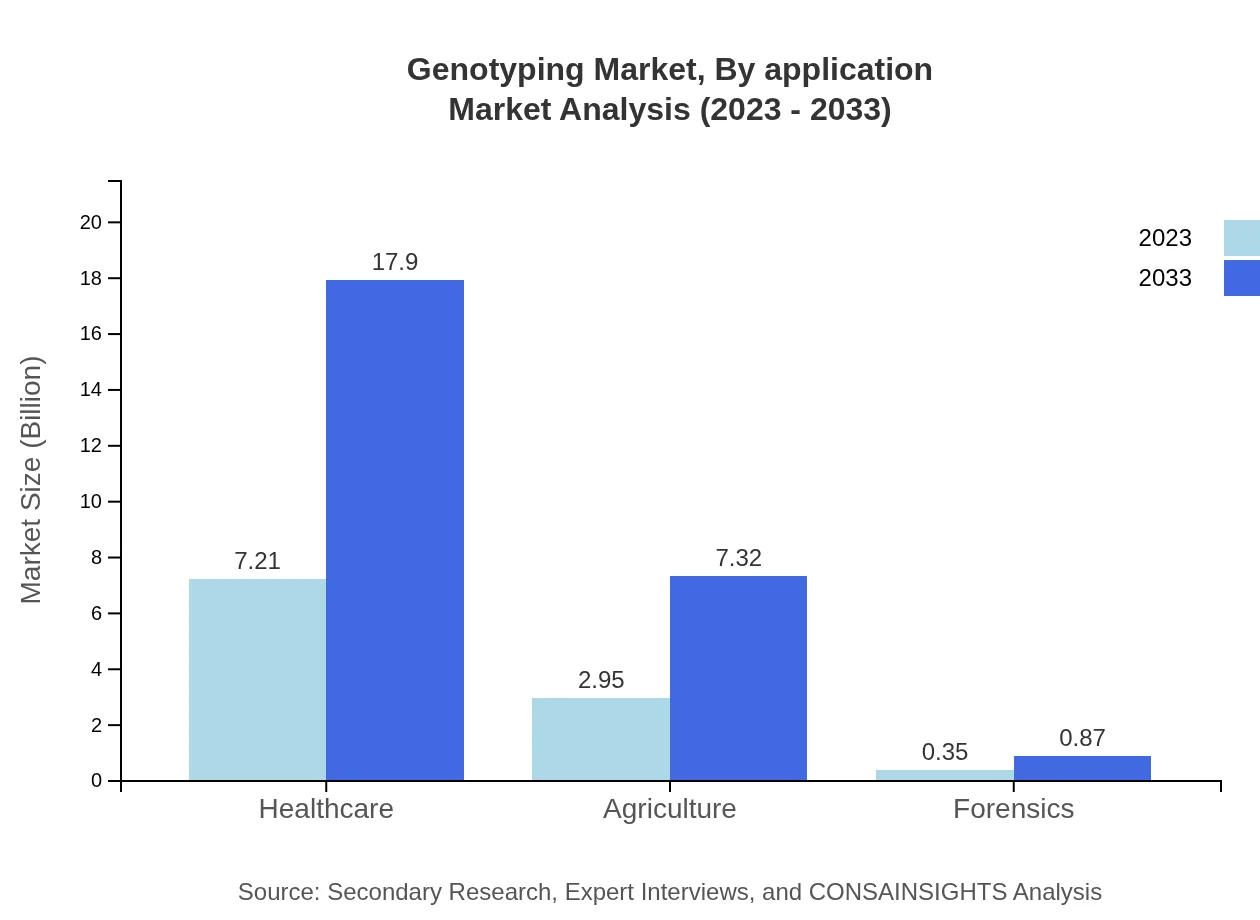
Genotyping Market Analysis By Application
Applications of Genotyping span healthcare, agriculture, forensics, and more. The healthcare segment, accounting for $7.21 billion in 2023 and forecasted to reach $17.90 billion by 2033, holds a significant market share. This is followed by agriculture, which is expected to see growth from $2.95 billion to $7.32 billion, due to the rising demand for genetically modified crops.
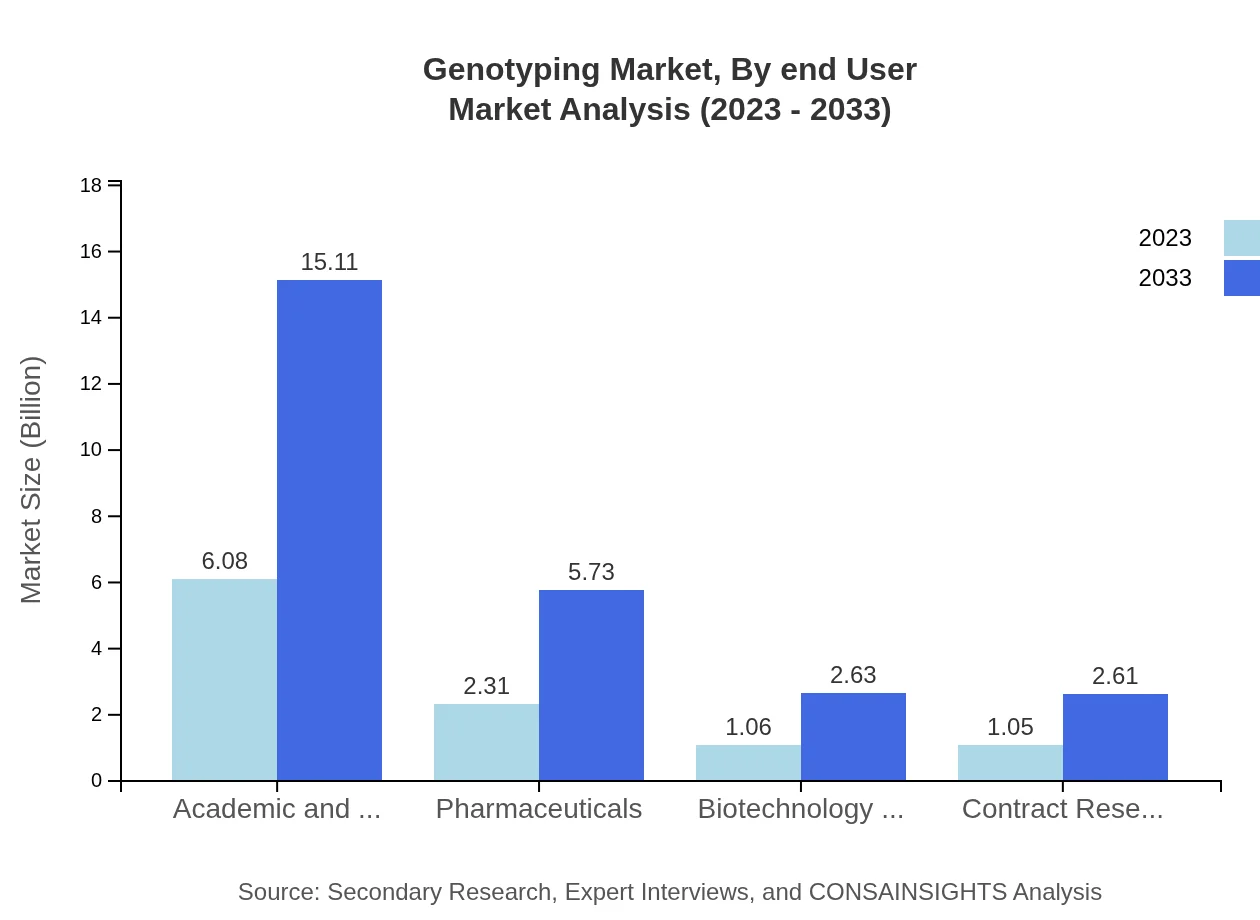
Genotyping Market Analysis By End User
The primary end-users of Genotyping services include academic and research institutions, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology companies, and contract research organizations. Academic institutions, with a market size of $6.08 billion in 2023, are predicted to increase to $15.11 billion by 2033, alongside pharmaceuticals that are forecasted to rise from $2.31 billion to $5.73 billion in the same period.
Genotyping Market Analysis By Region
Regional segmentation reveals that North America leads in both market size and growth potential, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific. Each region is shaping its strategies based on specific healthcare demands and technological advancements, with distinct opportunities for growth in emerging markets.
Genotyping Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Genotyping Industry
Thermo Fisher Scientific:
A leading provider of laboratory equipment, reagents, and diagnostics, Thermo Fisher Scientific is at the forefront of Genotyping technology innovations.Illumina, Inc.:
Illumina is renowned for its role in genetic sequencing technologies and solutions, significantly contributing to the expansion of the Genotyping market.Roche Holding AG:
Roche is a key player in the healthcare space, focusing on diagnostic technologies and personalized medicine options, influencing Genotyping advancements.Agilent Technologies:
Agilent provides comprehensive solutions for Genotyping, including instruments and software for researchers and clinical laboratories.Qiagen N.V.:
Qiagen specializes in sample and assay technologies, offering products crucial for Genotyping applications across various research fields.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of genotyping?
The global genotyping market is projected to reach approximately $10.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.2% from 2023. This significant growth reflects the increasing demand for genetic testing and personalized medicine.
What are the key market players or companies in the genotyping industry?
Key players in the genotyping market include Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illumina, Roche, Qiagen, and Agilent Technologies. These companies are major contributors to advancements in genotyping technologies and hold significant market shares.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the genotyping industry?
Key drivers of growth in the genotyping industry include rising demand for personalized medicine, increased prevalence of genetic disorders, and advancements in genomics technologies that enhance diagnostic accuracy and research capabilities.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the genotyping market?
The fastest-growing region in the genotyping market is projected to be Europe, expanding from $2.83 billion in 2023 to $7.03 billion by 2033. Asia-Pacific and North America also show strong growth potential in this sector.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the genotyping industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the genotyping industry, ensuring insights that match individual business requirements and strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this genotyping market research project?
From the genotyping market research project, you can expect detailed reports including market size, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, segmentation breakdowns, and regional insights to help inform strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of genotyping?
Market trends in genotyping include a shift towards SNP genotyping techniques, a rise in investments in personalized medicine, and increasing use of genotyping in agricultural applications, addressing diverse consumer needs and clinical outcomes.