Geographic Information System Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: geographic-information-system
Geographic Information System Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report presents an in-depth analysis of the Geographic Information System (GIS) market from 2023 to 2033. It covers market size, growth rate forecasts, regional insights, industry developments, and key players driving this sector.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
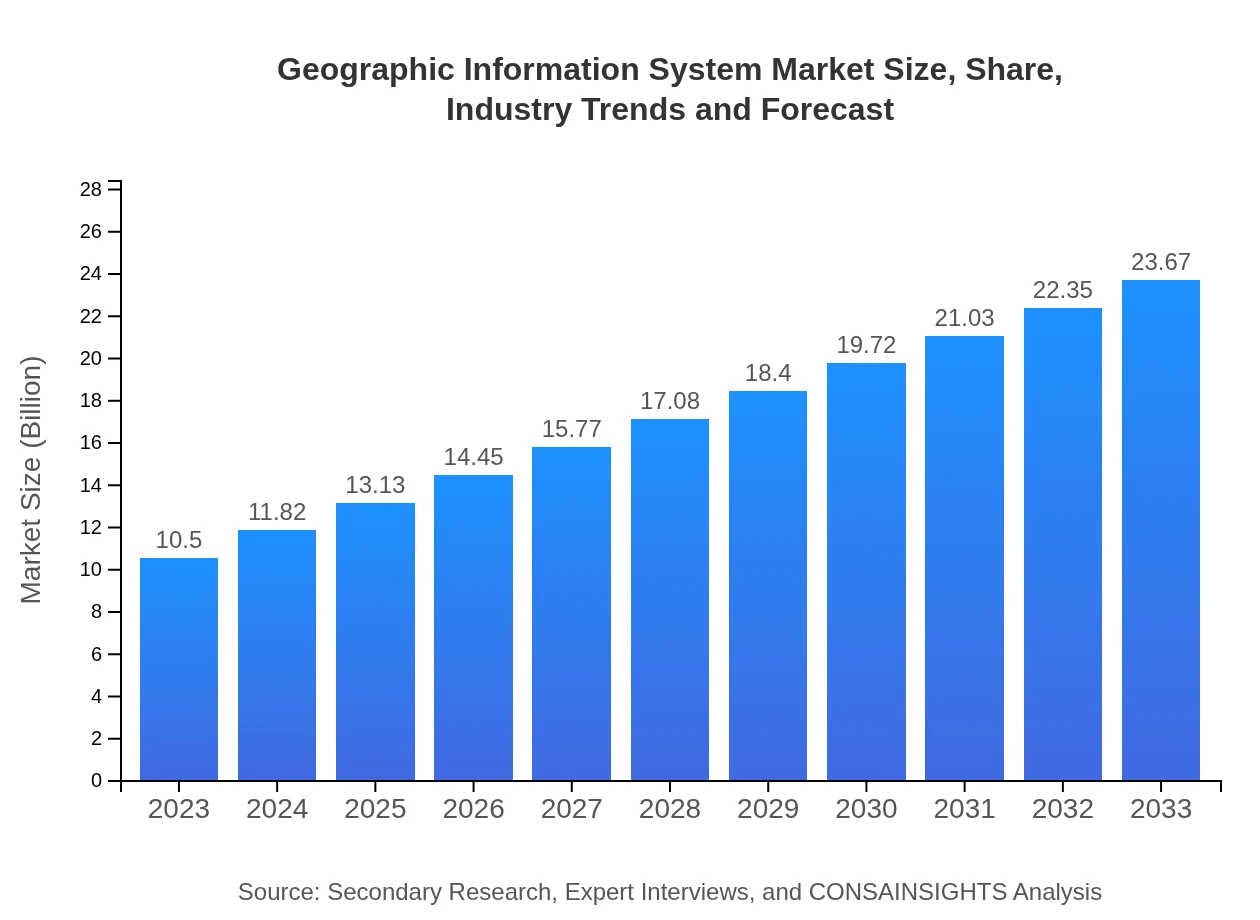
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $23.67 Billion |
| Top Companies | Esri, Hexagon AB, Autodesk, Inc., Trimble Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Geographic Information System Market Overview
Customize Geographic Information System Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Geographic Information System market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Geographic Information System's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Geographic Information System
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Geographic Information System market in 2023?
Geographic Information System Industry Analysis
Geographic Information System Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Geographic Information System Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Geographic Information System Market Report:
The European GIS market is projected to rise from $2.92 billion in 2023 to $6.58 billion in 2033. Factors fueling this growth include a strong emphasis on environmental sustainability, government regulations promoting the use of GIS in urban planning, and advancements in related technologies like spatial big data analytics.Asia Pacific Geographic Information System Market Report:
The Asia Pacific GIS market is projected to grow from $2.02 billion in 2023 to $4.55 billion in 2033. Growth drivers include rapid urbanization and government initiatives focusing on developing smart cities. Additionally, investments in transportation infrastructure and the rising adoption of cloud-based solutions are set to enhance market development in this region.North America Geographic Information System Market Report:
North America is anticipated to experience significant growth from $3.80 billion in 2023 to $8.58 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by high adoption rates of GIS technology in government bodies, environmental monitoring agencies, and commercial enterprises. The United States leads in technological advancements within GIS applications.South America Geographic Information System Market Report:
The South American GIS market is expected to expand from $0.87 billion in 2023 to $1.96 billion in 2033. Factors contributing to growth include increased investment in infrastructure projects and heightened demand for geographic data analytics in agriculture and natural resource management.Middle East & Africa Geographic Information System Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa GIS market is expected to grow from $0.89 billion in 2023 to $2.00 billion in 2033. Increasing investments in public infrastructure and urbanization, particularly in Gulf Cooperation Council countries, are propelling demand for GIS applications across various sectors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
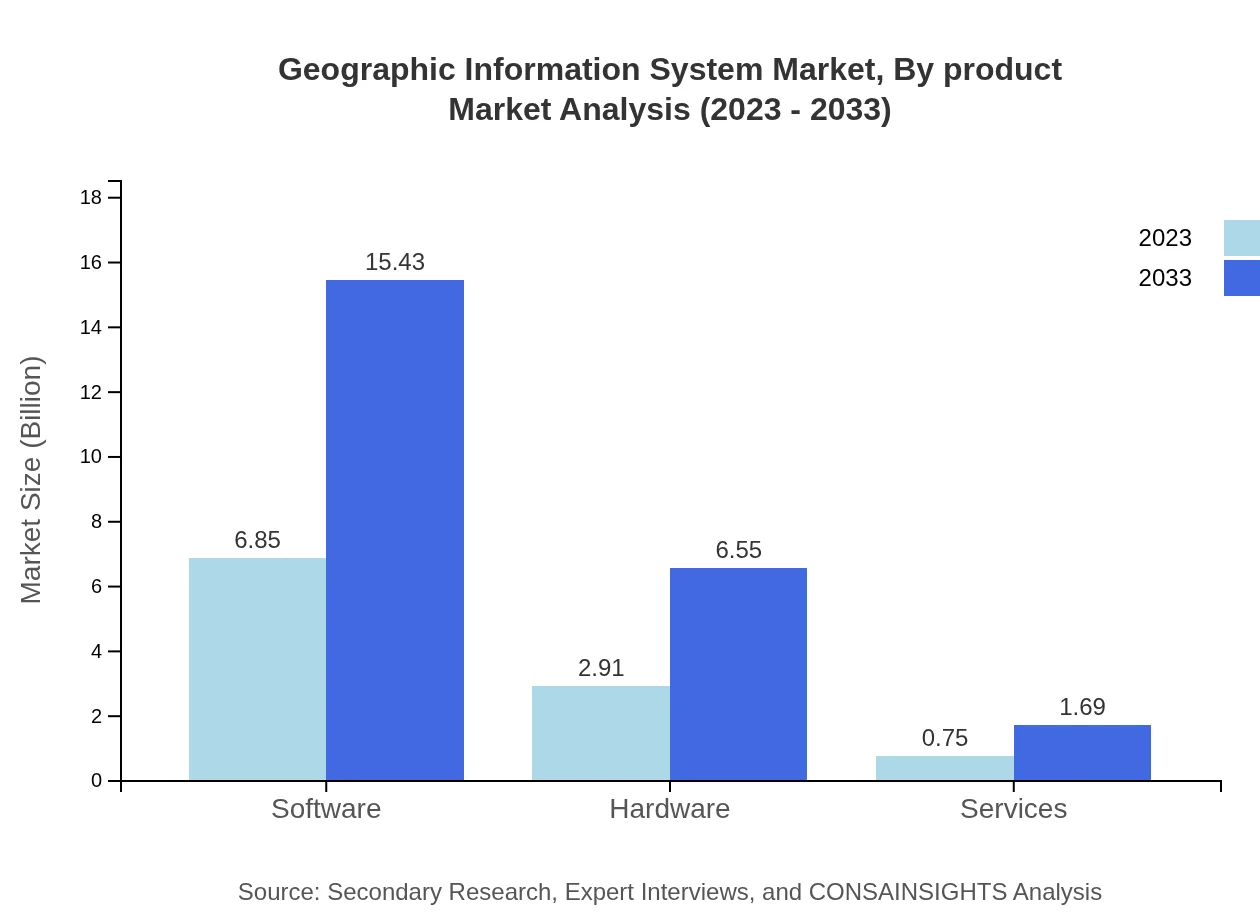
Geographic Information System Market Analysis By Product
The GIS market can be divided into several product types, predominantly software, hardware, and services. Software holds the largest market share at $6.85 billion in 2023, growing to $15.43 billion by 2033, owing to increasing software integration with analytics and machine learning. Hardware is projected to grow from $2.91 billion to $6.55 billion, driven by increased demand for advanced technologies. Services also represent a growing segment, from $0.75 billion to $1.69 billion, reflecting the importance of implementation and support.
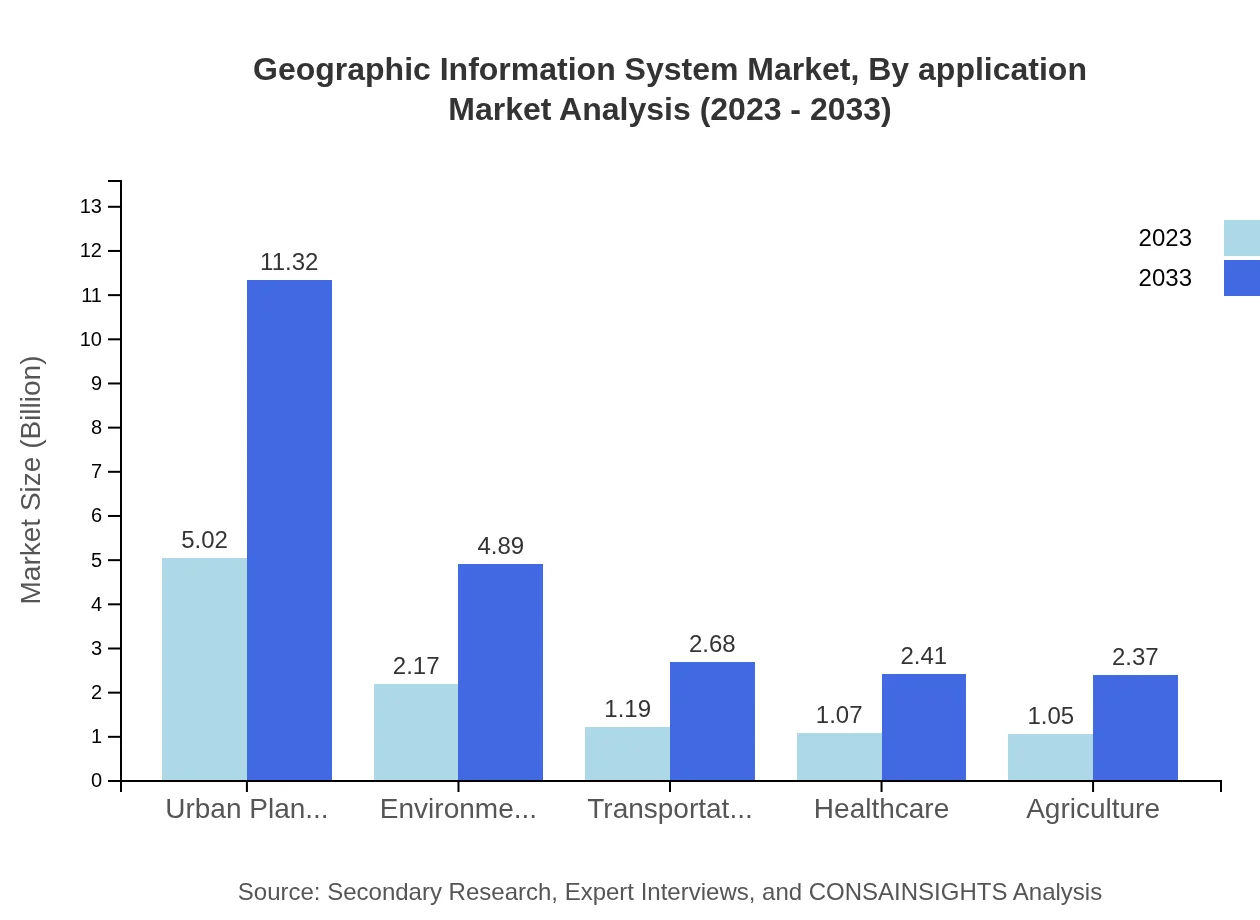
Geographic Information System Market Analysis By Application
GIS applications are vital across various sectors. In 2023, Remote Sensing dominates with a market size of $8.79 billion, expected to reach $19.82 billion by 2033. Urban Planning and Environmental Management are also significant, valued at $5.02 billion and $2.17 billion respectively in 2023. Transportation and Healthcare are steadily growing niches, highlighting GIS's pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiencies in myriad applications.
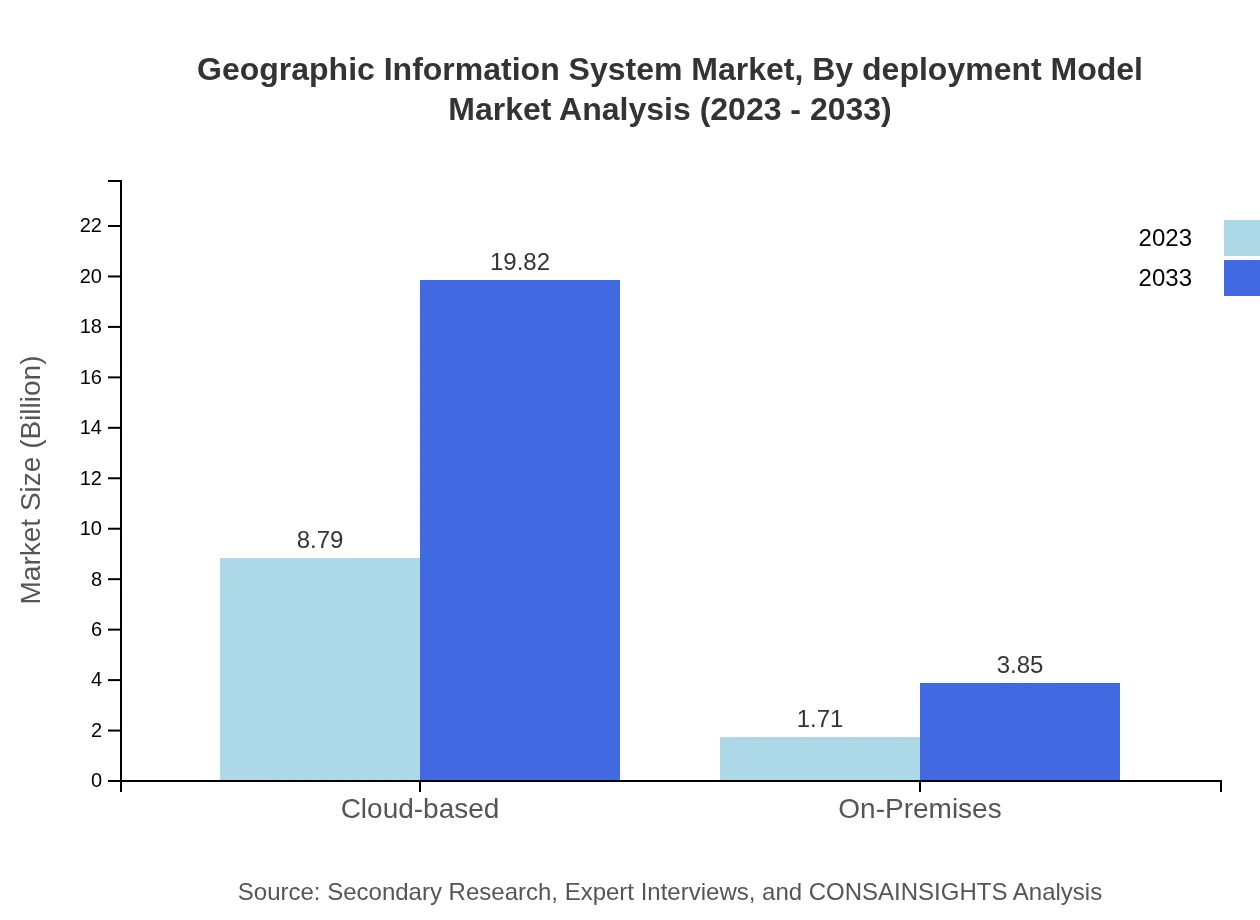
Geographic Information System Market Analysis By Deployment Model
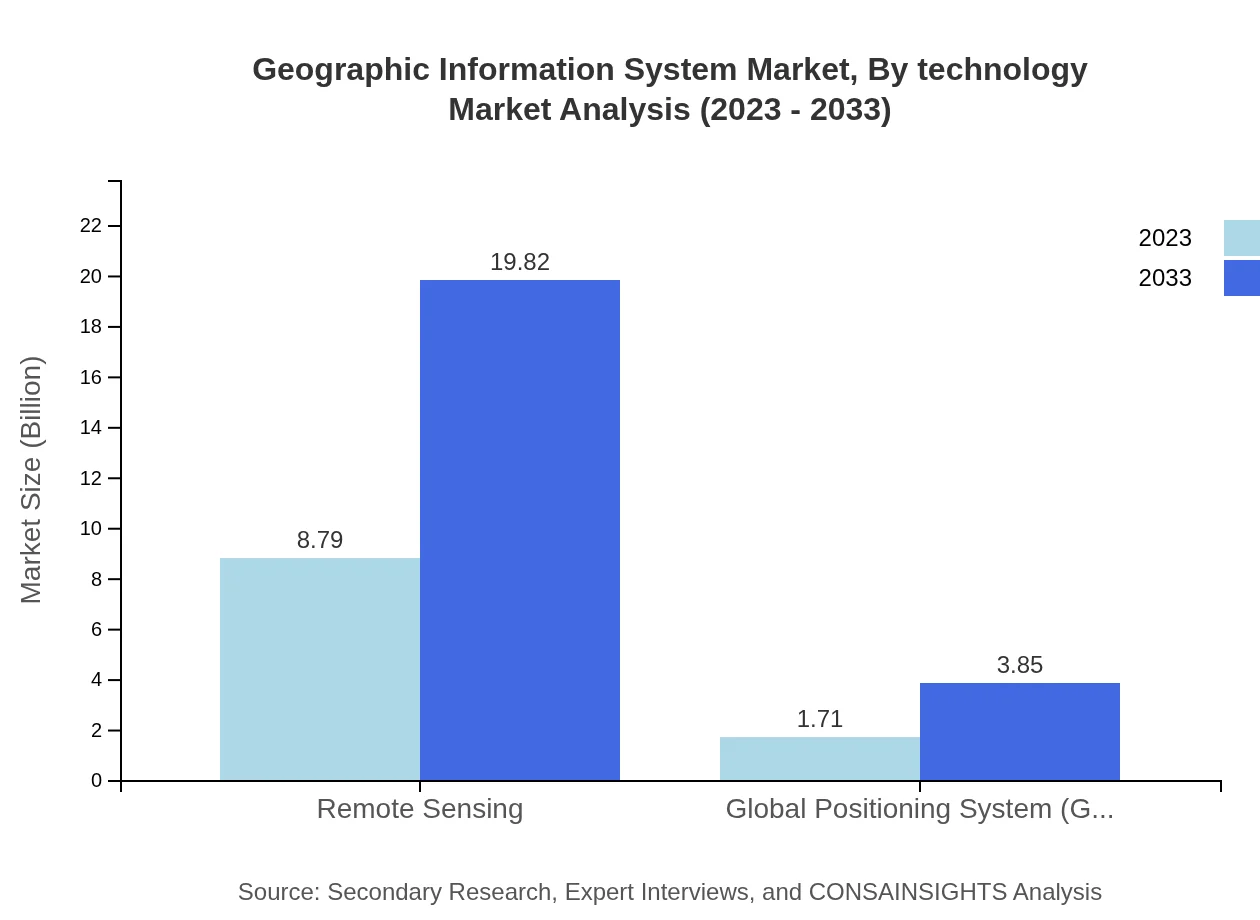
Deployment models in the GIS market include Cloud-based and On-Premises solutions. Cloud-based models dominate with a size of $8.79 billion in 2023, forecasted to grow to $19.82 billion. The flexibility and cost-effectiveness of cloud solutions drive this growth, while On-Premises solutions show a steady rise from $1.71 billion to $3.85 billion, appealing to organizations with stringent data control needs.
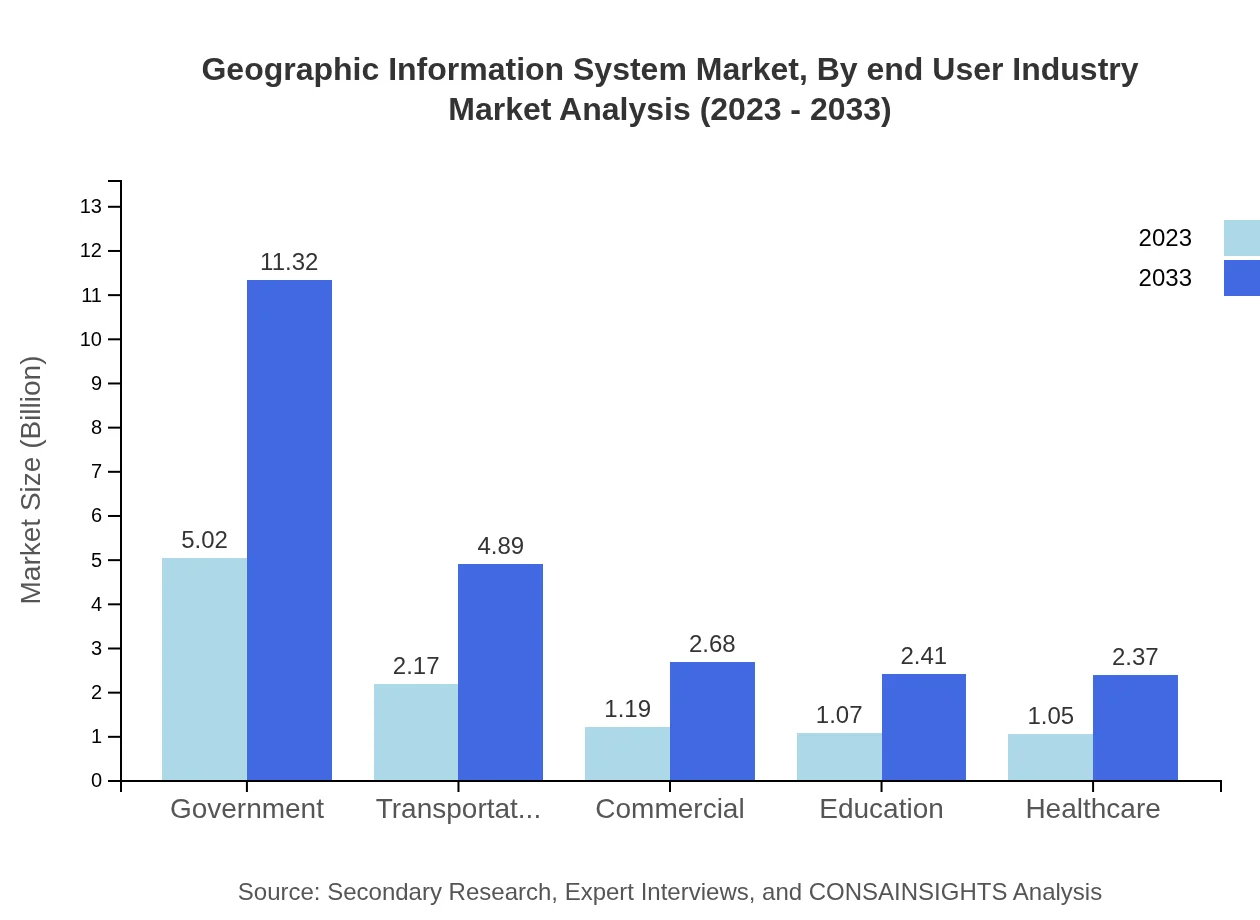
Geographic Information System Market Analysis By End User Industry
Various industries contribute to the GIS market, including Government, Commercial, and Transportation sectors. Government usage leads with a market of $5.02 billion in 2023, projected to grow significantly due to increased investments in public services. The Transportation industry, combined with Utilities, holds a market of $2.17 billion, indicating rising adoption of GIS solutions for infrastructure development.
Geographic Information System Market Analysis By Technology
Innovations in technology are enhancing the GIS market, particularly through the integration of AI, big data, and machine learning. These technologies facilitate advanced data interpretations and spatial analyses, boosting market efficiency. Remote sensing technology, which is hugely popular for mapping and surveying applications, holds a significant share of the market that is expected to grow in the forthcoming years.
Geographic Information System Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Geographic Information System Industry
Esri:
A pioneer in GIS technology, Esri provides a comprehensive suite of software focused on mapping and spatial analysis, enabling organizations to visualize and analyze data.Hexagon AB:
Hexagon AB specializes in digital solutions, particularly in the areas of sensor through to software, including powerful GIS platforms that drive accuracy in mapping applications.Autodesk, Inc.:
Autodesk offers advanced solutions for the architecture, engineering, and construction industries, incorporating GIS tools that streamline project workflows.Trimble Inc.:
Trimble provides advanced location-based solutions that integrate GIS technologies with global positioning systems to facilitate precision in mapping and surveying.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Geographic Information System?
The Geographic Information System market is projected to reach approximately $10.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% from a base value of $10.5 billion in 2023. This growth indicates a strong demand for geospatial technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in this Geographic Information System industry?
Key players in the Geographic Information System market include Esri, Hexagon AB, Autodesk, and Trimble Inc., among others. These companies dominate through innovation, extensive product portfolios, and strategic partnerships, ensuring a competitive edge in the market.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Geographic Information System industry?
The growth of the Geographic Information System industry is driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for geospatial data in various sectors, smart city initiatives, and the need for effective environmental management. These elements push the industry's expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Geographic Information System?
The fastest-growing region in the Geographic Information System market is expected to be North America, which is projected to grow from $3.80 billion in 2023 to $8.58 billion by 2033. This growth reflects significant investments in geospatial technologies by various industries.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Geographic Information System industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs in the Geographic Information System industry. This ensures that businesses receive relevant insights that align with their strategic goals and market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this Geographic Information System market research project?
Deliverables from the Geographic Information System market research project include comprehensive market analysis, segmentation reports, competitive landscape overview, regional growth insights, and future forecasts, allowing clients to make informed decisions.
What are the market trends of Geographic Information System?
Current trends in the Geographic Information System industry include an increased adoption of cloud-based solutions, integration of AI and machine learning for enhanced data analysis, and a focus on sustainability in urban planning and environmental management.