Gmo Labeled Food Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: gmo-labeled-food
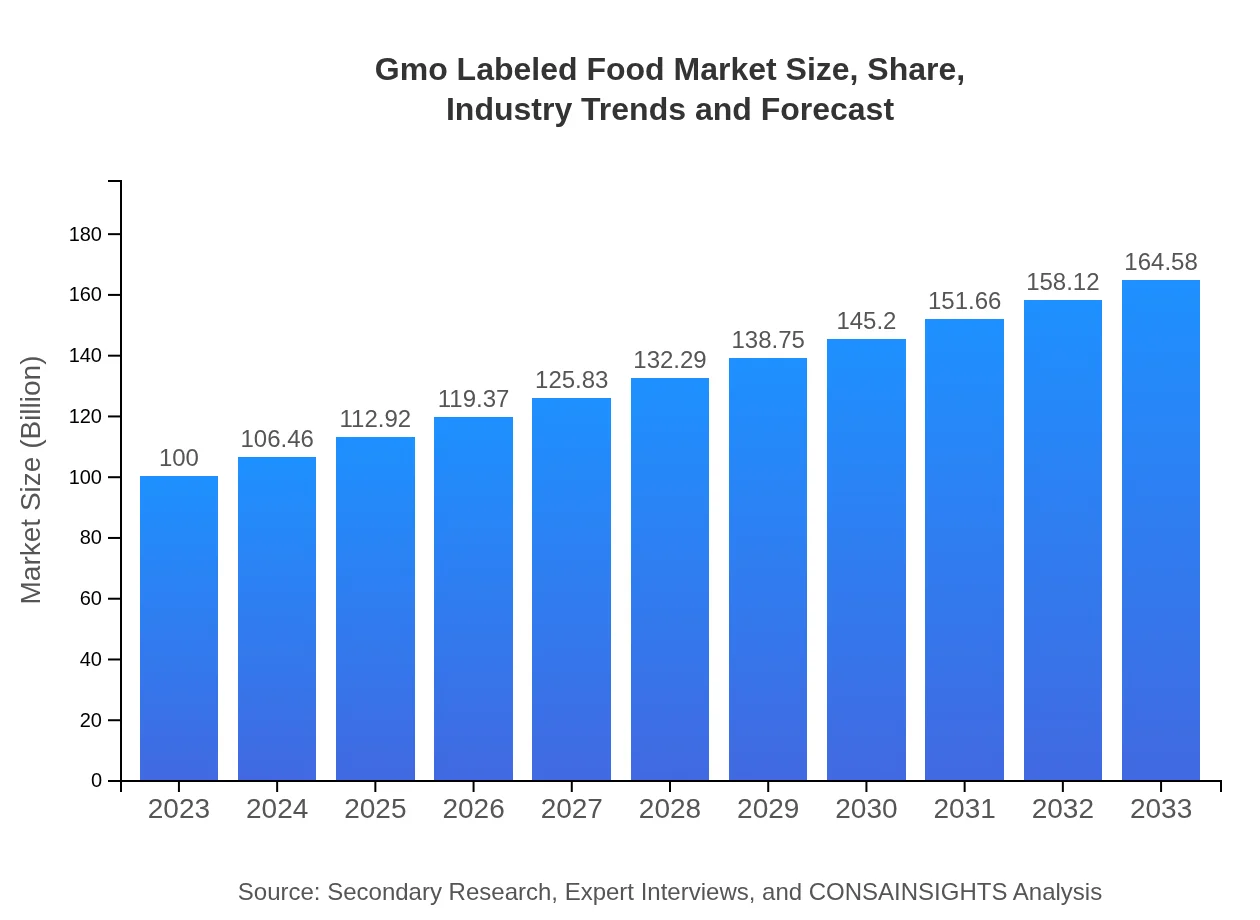
Gmo Labeled Food Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the GMO labeled food market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market trends, size, and segmentation, alongside regional insights and forecasting data.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | Monsanto, Bayer AG, Syngenta AG, DuPont de Nemours, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Gmo Labeled Food Market Overview
Customize Gmo Labeled Food Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Gmo Labeled Food market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Gmo Labeled Food's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Gmo Labeled Food
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Gmo Labeled Food market in 2023?
Gmo Labeled Food Industry Analysis
Gmo Labeled Food Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
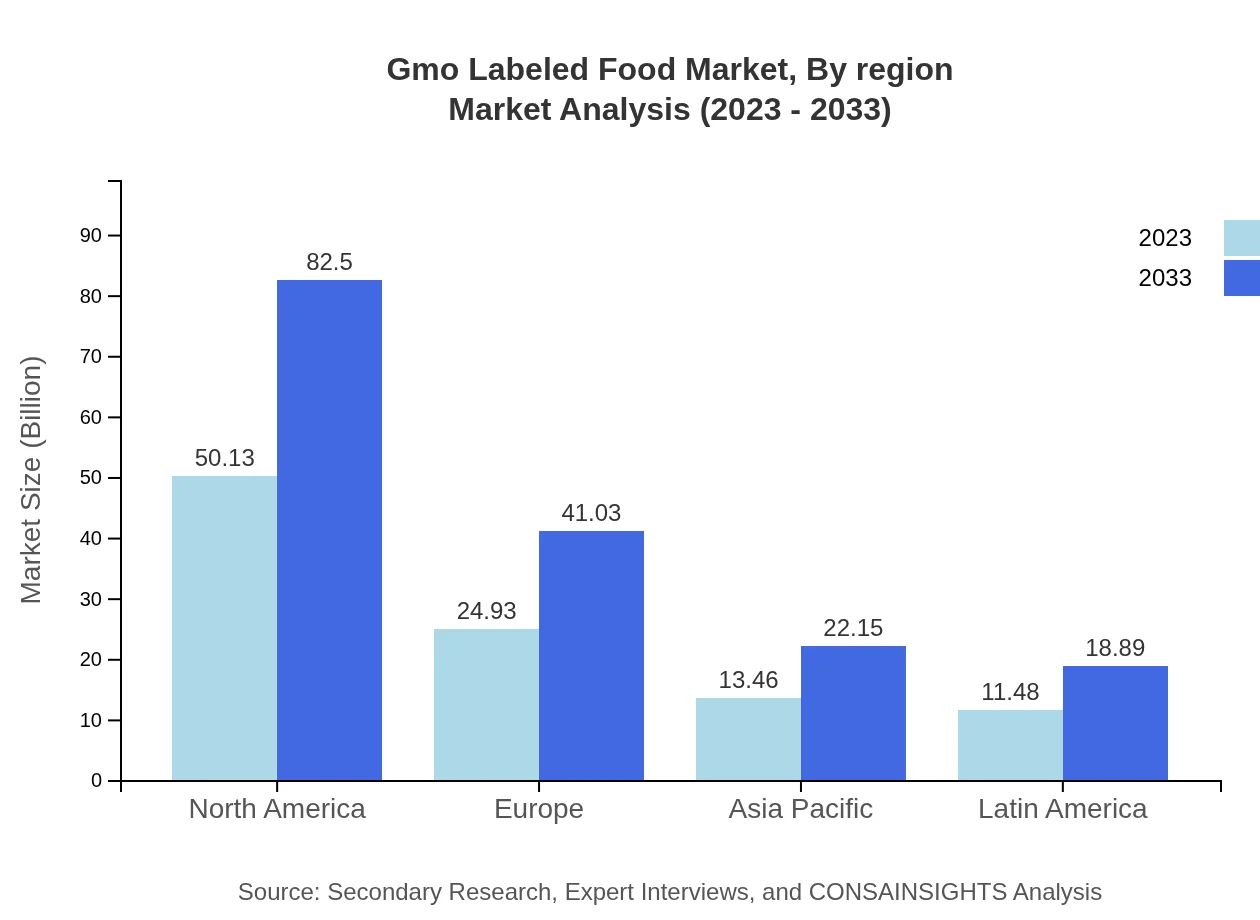
Gmo Labeled Food Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Gmo Labeled Food Market Report:
Europe's GMO labeled food market was valued at $27.92 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $45.95 billion by 2033. European consumers are among the most discerning when it comes to food labeling and integrity. Stringent EU regulations concerning GMO products have created a robust market for labeled food. The growth is fueled by an intensified focus on sustainable farming practices and ethically sourced food.Asia Pacific Gmo Labeled Food Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the GMO labeled food market was valued at $19.30 billion in 2023, with projections to reach $31.76 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, a rising middle class, and increasing health awareness among consumers are key drivers for this market in this region. Additionally, China and India are leading the charge by implementing stricter labeling laws which fuel market growth.North America Gmo Labeled Food Market Report:
North America's GMO labeled food market is anticipated to grow from $35.51 billion in 2023 to $58.44 billion by 2033. The United States remains one of the primary markets for GMO foods, where consumer demand for organic products is propelling companies to label appropriately. Regulatory frameworks supporting transparency further amplify market dynamics. North American firms are leading in innovative labeling solutions to meet evolving consumer expectations.South America Gmo Labeled Food Market Report:
The South American market for GMO labeled food is in its nascent stage, estimated at $5.60 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $9.22 billion by 2033. The increasing impact of agribusiness and eco-friendly consumer movements are critical in shaping this market. The region is witnessing an uptick in organic farming methods that leverage transparency to cater to health-conscious consumers.Middle East & Africa Gmo Labeled Food Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's GMO labeled food market is projected to grow from $11.67 billion in 2023 to $19.21 billion by 2033. Factors driving growth include changing dietary patterns, increasing population, and a growing middle class. Although challenges persist, such as regulatory hurdles and varying consumer acceptance levels, the market shows potential for substantial advancements in the coming years.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
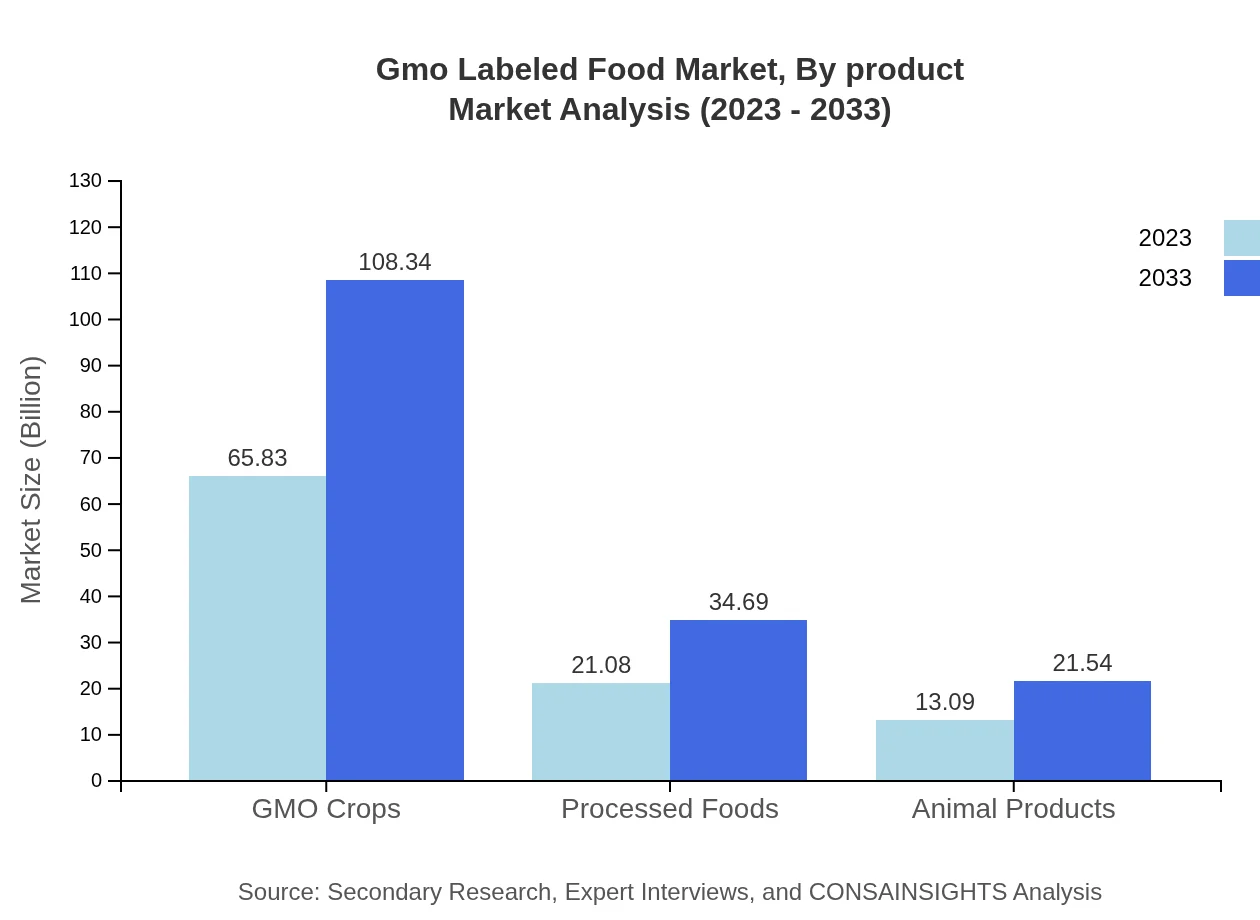
Gmo Labeled Food Market Analysis By Product
In 2023, the segment for GMO crops is projected at $65.83 billion, experiencing a surge towards $108.34 billion by 2033. Processed foods and animal products follow, with projections from $21.08 billion to $34.69 billion, and $13.09 billion to $21.54 billion respectively, showcasing the diverse applications of GMOs in food production.
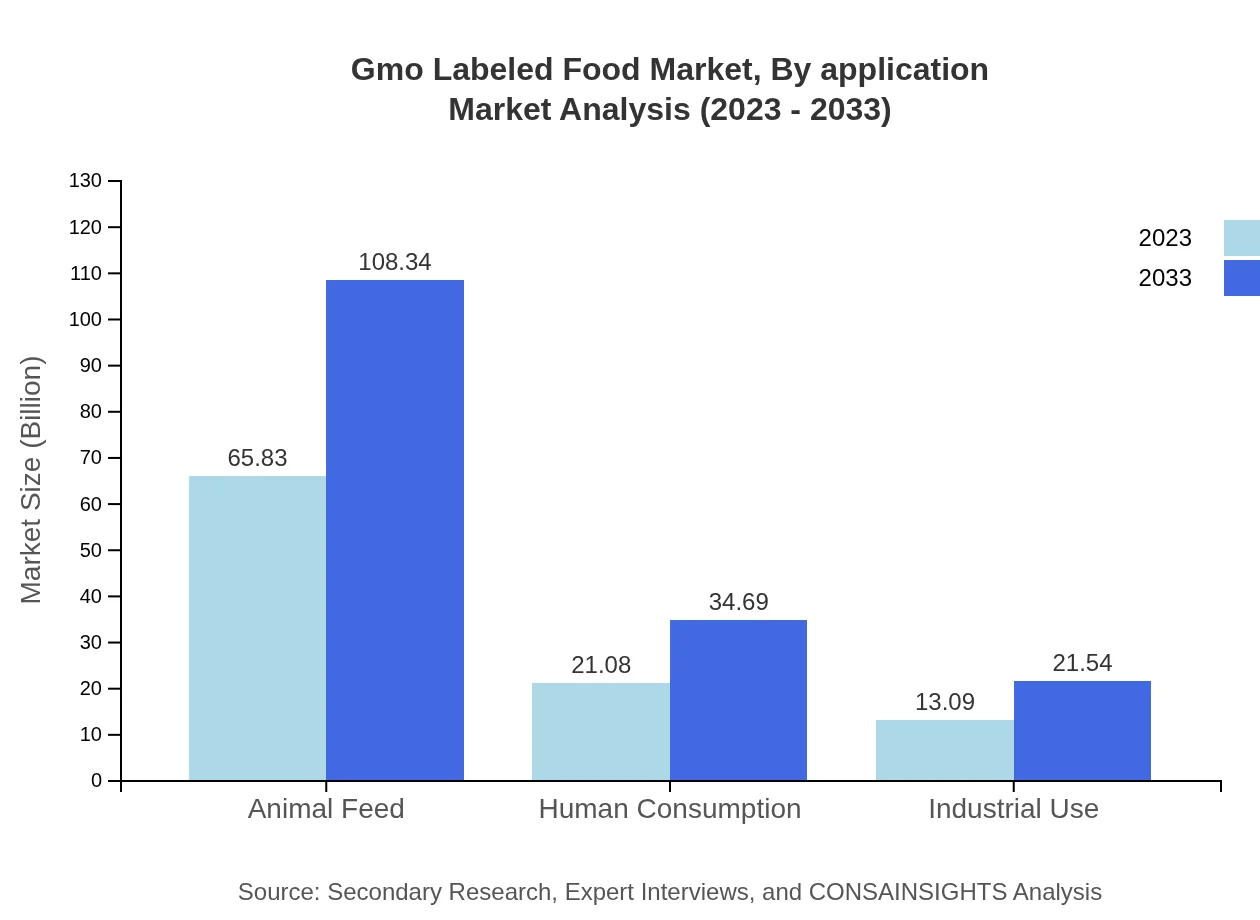
Gmo Labeled Food Market Analysis By Application
The market for GMO labeled foods intended for human consumption stands at $21.08 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $34.69 billion by 2033, highlighting the increasing awareness and health-oriented choices among consumers. The industrial use of GMOs is also rising, with projections from $13.09 billion to $21.54 billion.
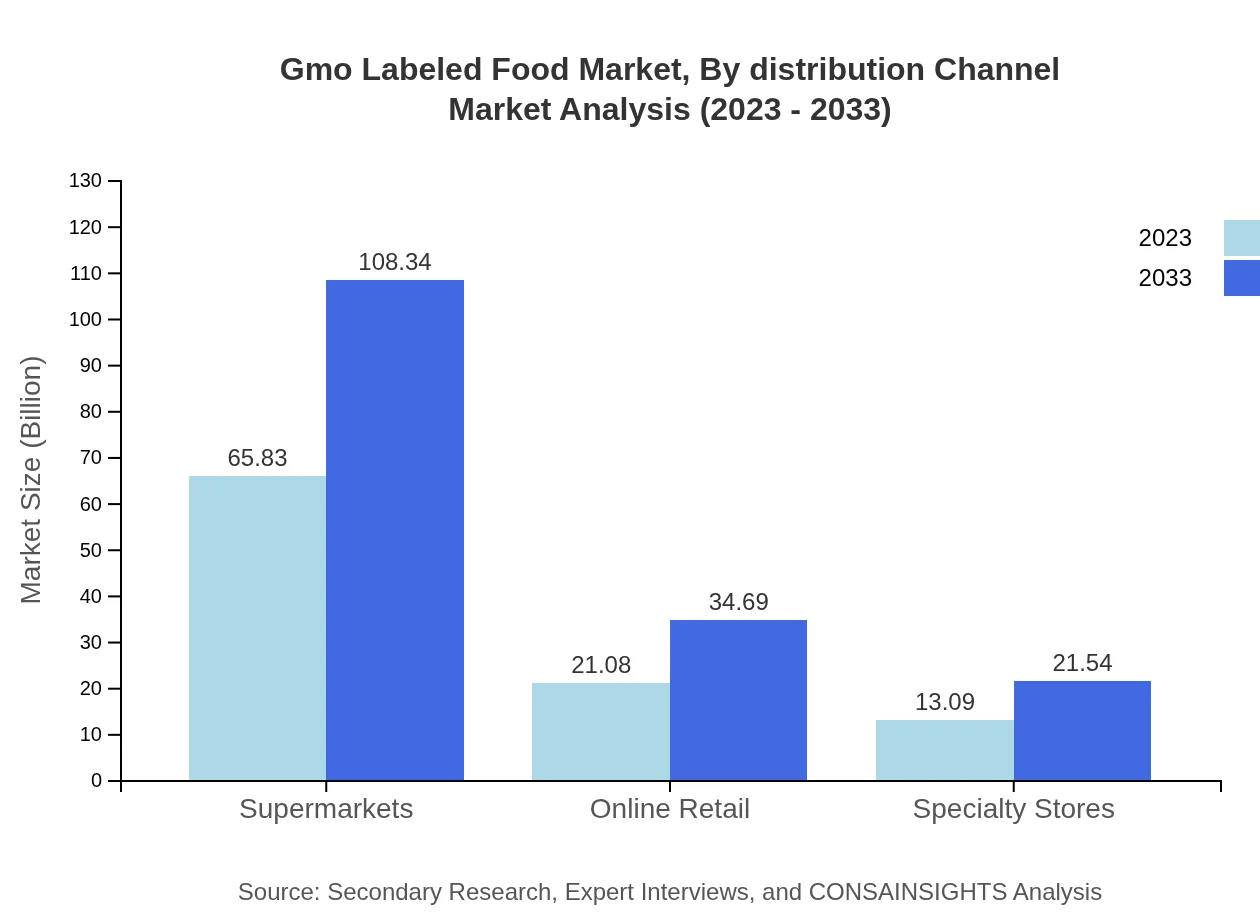
Gmo Labeled Food Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The supermarkets category dominates the distribution channel, with a market size of $65.83 billion in 2023, projected to rise to $108.34 billion by 2033. Online retail also shows promise, expanding from $21.08 billion to $34.69 billion due to increasing digital sales channels.
Gmo Labeled Food Market Analysis By Region
Regional analysis shows North America leading with significant market contributions, followed closely by Europe. The emerging markets in Latin America and Asia Pacific reveal a high potential for growth, particularly as consumer trends shift toward health consciousness and transparency in food labeling.
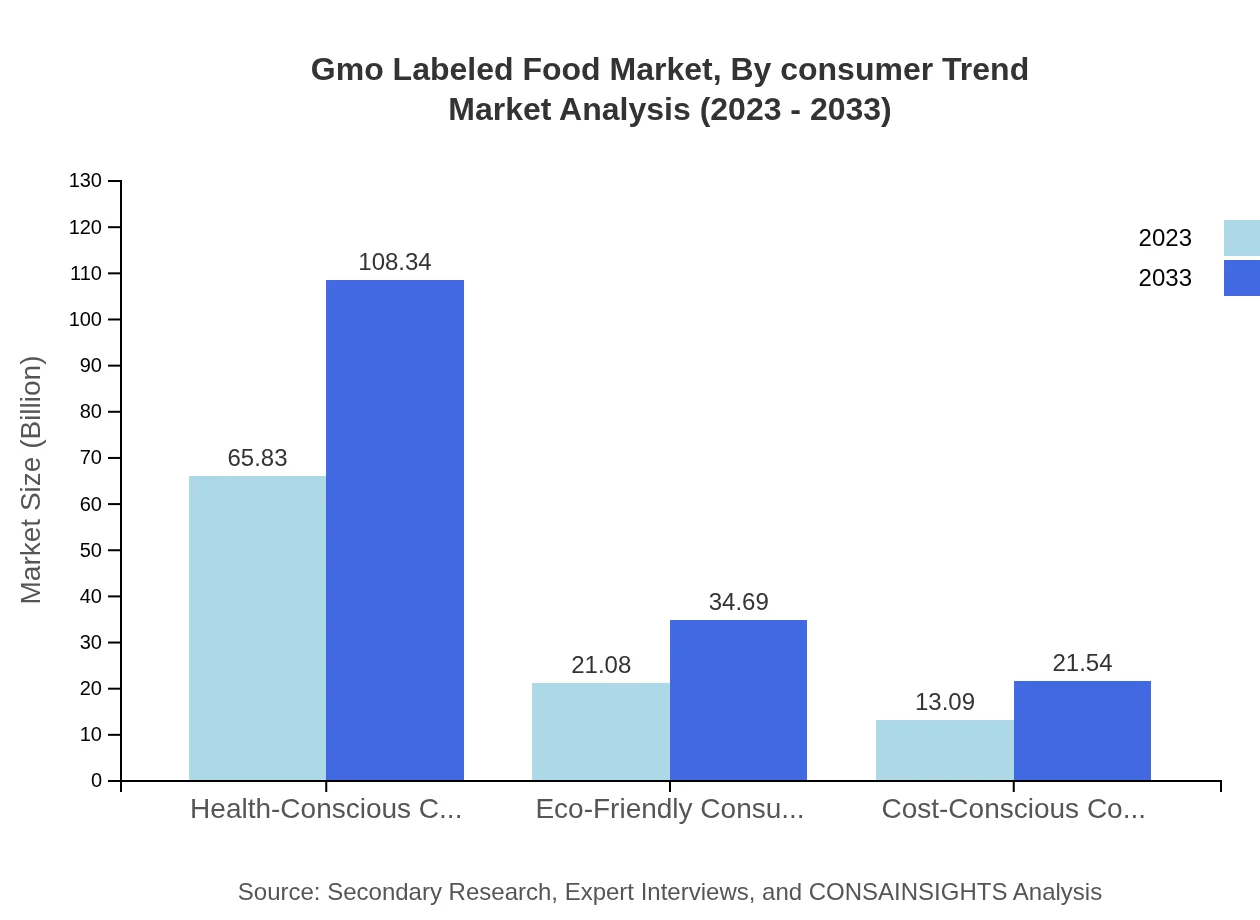
Gmo Labeled Food Market Analysis By Consumer Trend
Health-conscious consumers are forecasted to remain the largest segment, growing from $65.83 billion in 2023 to $108.34 billion by 2033. Eco-friendly consumers and cost-conscious buyers also significantly contribute to market dynamics, indicating varying priorities amongst consumer segments while making purchasing decisions.
Gmo Labeled Food Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Gmo Labeled Food Industry
Monsanto:
Monsanto, a key player in the biotechnology industry, is recognized for its extensive work in GMO seed production, contributing significantly to the advancements in GMO labeled food.Bayer AG:
Bayer AG focuses on agricultural solutions, including developing safe GMO foods, emphasizing innovation and compliance with stringent food safety regulations.Syngenta AG:
Known for its commitment to sustainability, Syngenta AG produces a range of GMO crops that are pivotal in meeting food security challenges globally.DuPont de Nemours, Inc.:
DuPont leads in agricultural biotech advancements, offering GMO crops that enhance product yields and address environmental concerns.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of gmo Labeled Food?
The global GMO-labeled food market is currently valued at approximately $100 million in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% over the next decade, indicating steady growth and consumer interest in labeled genetically modified foods.
What are the key market players or companies in this gmo Labeled Food industry?
Key players in the GMO-labeled food market include major food manufacturers, organic food producers, and agricultural biotech firms. Companies such as Monsanto, DuPont, and local organic brands are instrumental in shaping market dynamics, influencing consumer choices, and distributing GMO-labeled products.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the gmo Labeled Food industry?
Growth in the GMO-labeled food industry is driven by rising consumer demand for transparency and safety in food labeling, increasing health consciousness, and the nutritional advantages perceived by consumers regarding genetically modified crops and their production efficiencies.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the gmo Labeled Food?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the GMO-labeled food market, with its market size expected to increase from $35.51 million in 2023 to an estimated $58.44 million by 2033, reflecting significant consumer engagement and market expansion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the gmo Labeled Food industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the GMO-labeled food industry, allowing clients to gain insights based on unique parameters, target markets, and operational strategies tailored to their business goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this gmo Labeled Food market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive deliverables from the GMO-labeled food market research project, including detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and actionable insights into consumer trends and market segments tailored to their strategic needs.
What are the market trends of gmo Labeled Food?
Current trends in the GMO-labeled food market indicate a growing emphasis on sustainable farming practices, increasing adoption of plant-based diets, and escalating consumer preference for non-GMO options, which collectively influence labeling practices and market strategies.