Gmo Seed Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: gmo-seed
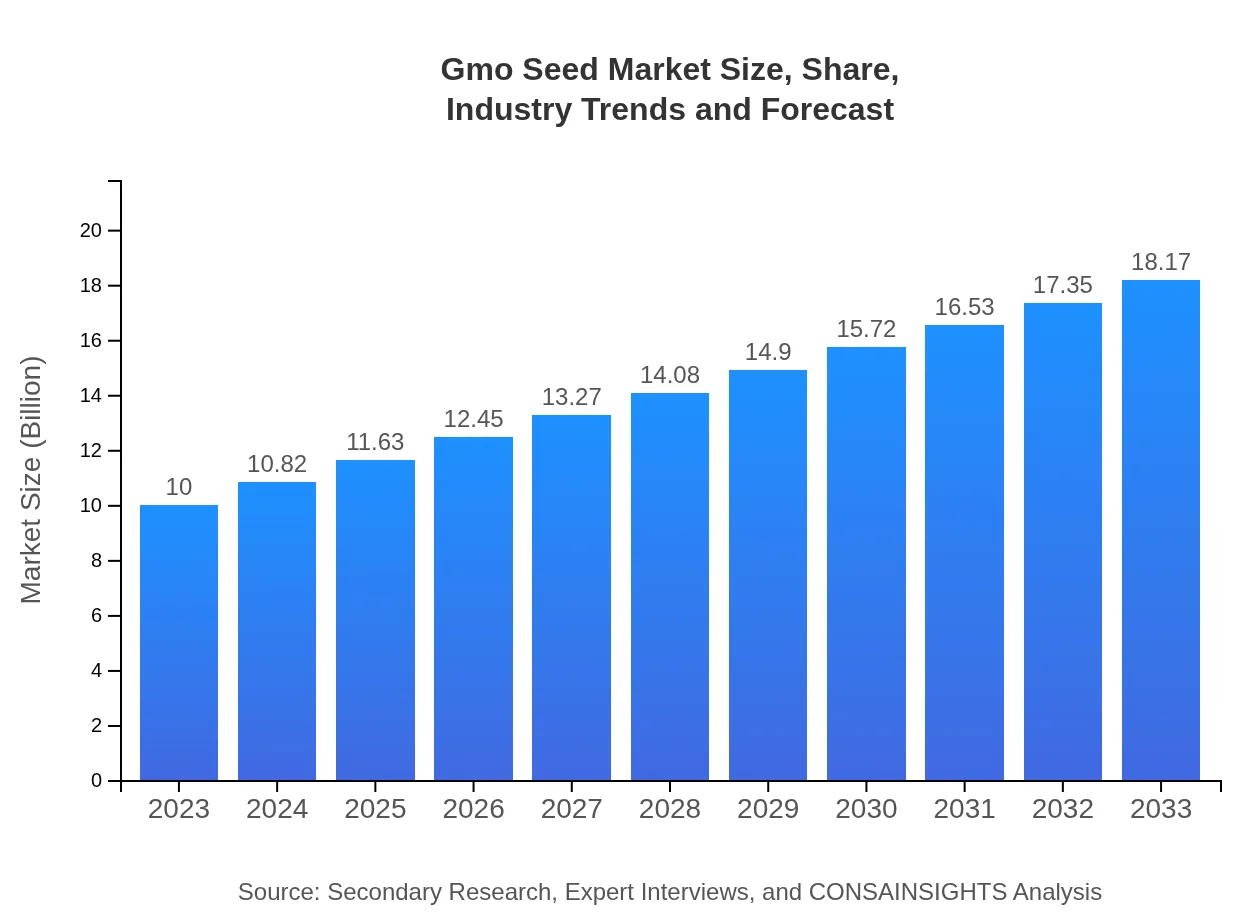
Gmo Seed Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Gmo Seed market, highlighting key insights, market dynamics, and trends from 2023 to 2033. It also offers forecasts and regional analyses, aiming to equip stakeholders with valuable data for informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.17 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto, DuPont Pioneer, Syngenta |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Gmo Seed Market Overview
Customize Gmo Seed Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Gmo Seed market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Gmo Seed's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Gmo Seed
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Gmo Seed market in 2023?
Gmo Seed Industry Analysis
Gmo Seed Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Gmo Seed Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Gmo Seed Market Report:
Europe's Gmo Seed market is anticipated to grow from $2.73 billion in 2023 to $4.95 billion by 2033. However, consumer resistance and stringent regulations are notable barriers. Despite this, there is a growing trend towards accepting genetically modified ingredients in sustainable agricultural practices.Asia Pacific Gmo Seed Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Gmo Seed market is projected to grow from $1.93 billion in 2023 to $3.50 billion in 2033. Factors such as rapid population growth and increasing demand for food security drive market expansion. Countries such as India and China are leading in the adoption of GMO crops, with supportive governmental policies promoting agricultural biotechnology.North America Gmo Seed Market Report:
North America remains the largest Gmo Seed market, with valuations rising from $3.72 billion in 2023 to an estimated $6.76 billion by 2033, driven by advanced agricultural practices and substantial adoption of GMO corn and soybeans. The sophisticated infrastructure and high investment in biotech R&D further solidify its dominance.South America Gmo Seed Market Report:
The South American Gmo Seed market is expected to increase from $0.52 billion in 2023 to $0.94 billion in 2033. Brazil and Argentina are key players in this region, using genetically modified seeds to increase efficiency in soy and corn production. However, regulatory challenges and public sentiment surrounding GMOs will play a significant role in determining market growth.Middle East & Africa Gmo Seed Market Report:
The Gmo Seed market in the Middle East and Africa is set to grow from $1.11 billion in 2023 to $2.01 billion in 2033. Increasing agricultural development initiatives and the need for food security in drought-prone areas will enhance the adoption of GMO technology.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
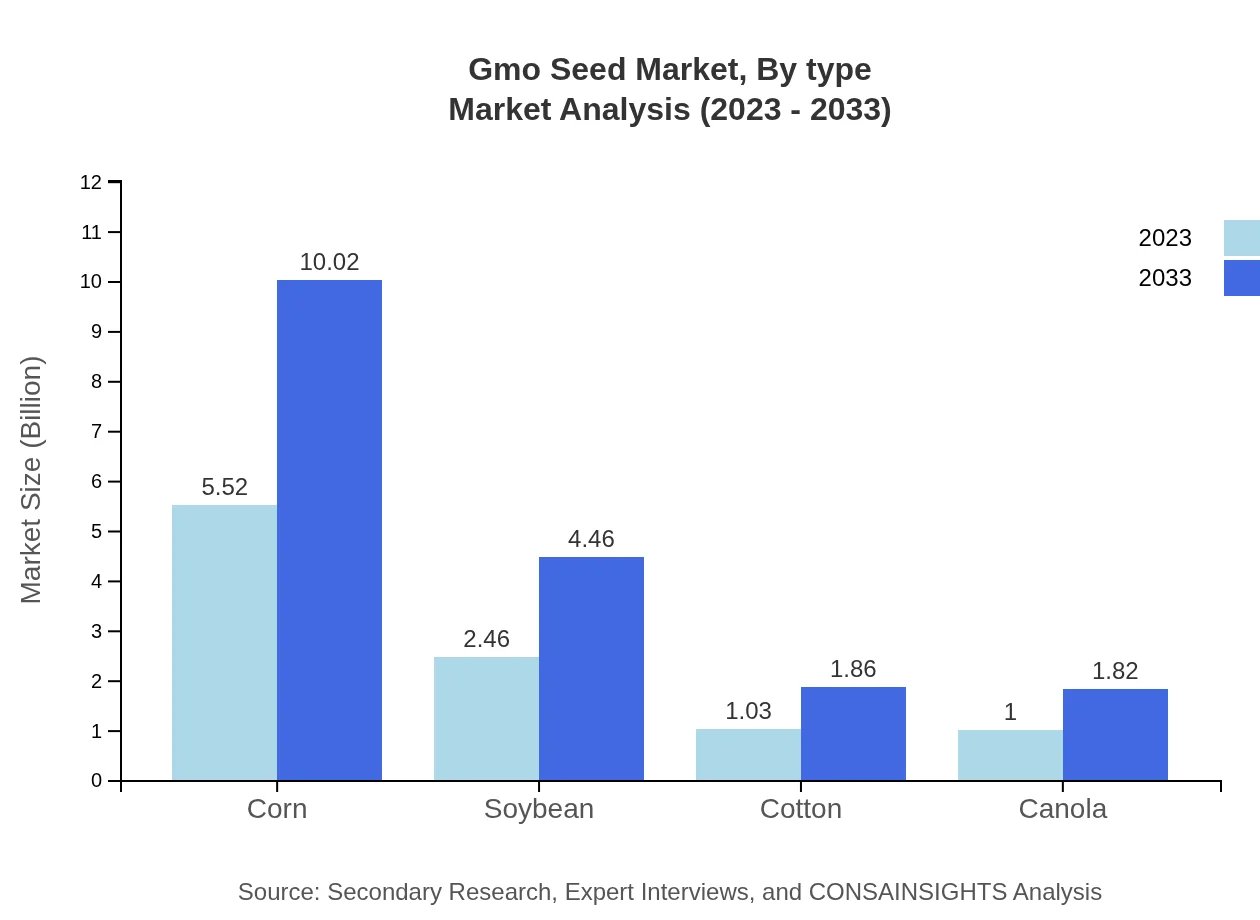
Gmo Seed Market Analysis By Type
The Gmo Seed market, segmented by type, focuses on corn, soybean, cotton, and canola. In 2023, corn holds the largest market size at $5.52 billion and retains a share of 55.17%, projected to grow to $10.02 billion by 2033. Soybeans and cotton also represent significant shares, with soybeans valued at $2.46 billion in 2023, enhancing agricultural sustainability.
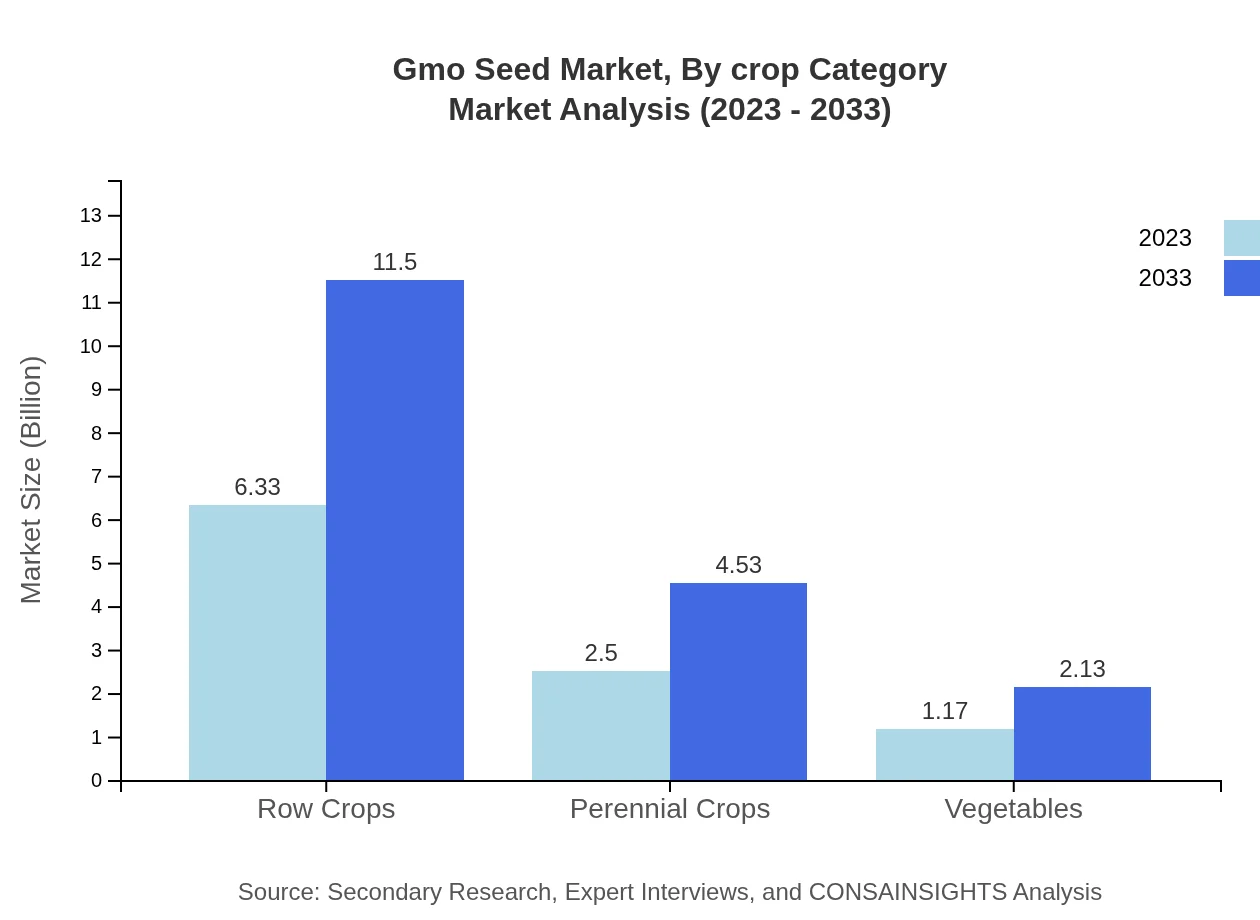
Gmo Seed Market Analysis By Crop Category
Key crop categories including animal feed, human consumption, and biofuels will witness notable growth. The market for animal feed is projected to escalate from $6.33 billion in 2023 to $11.50 billion in 2033, reflecting the increasing use of GMO corn and soybean in livestock production and the biofuel sector.
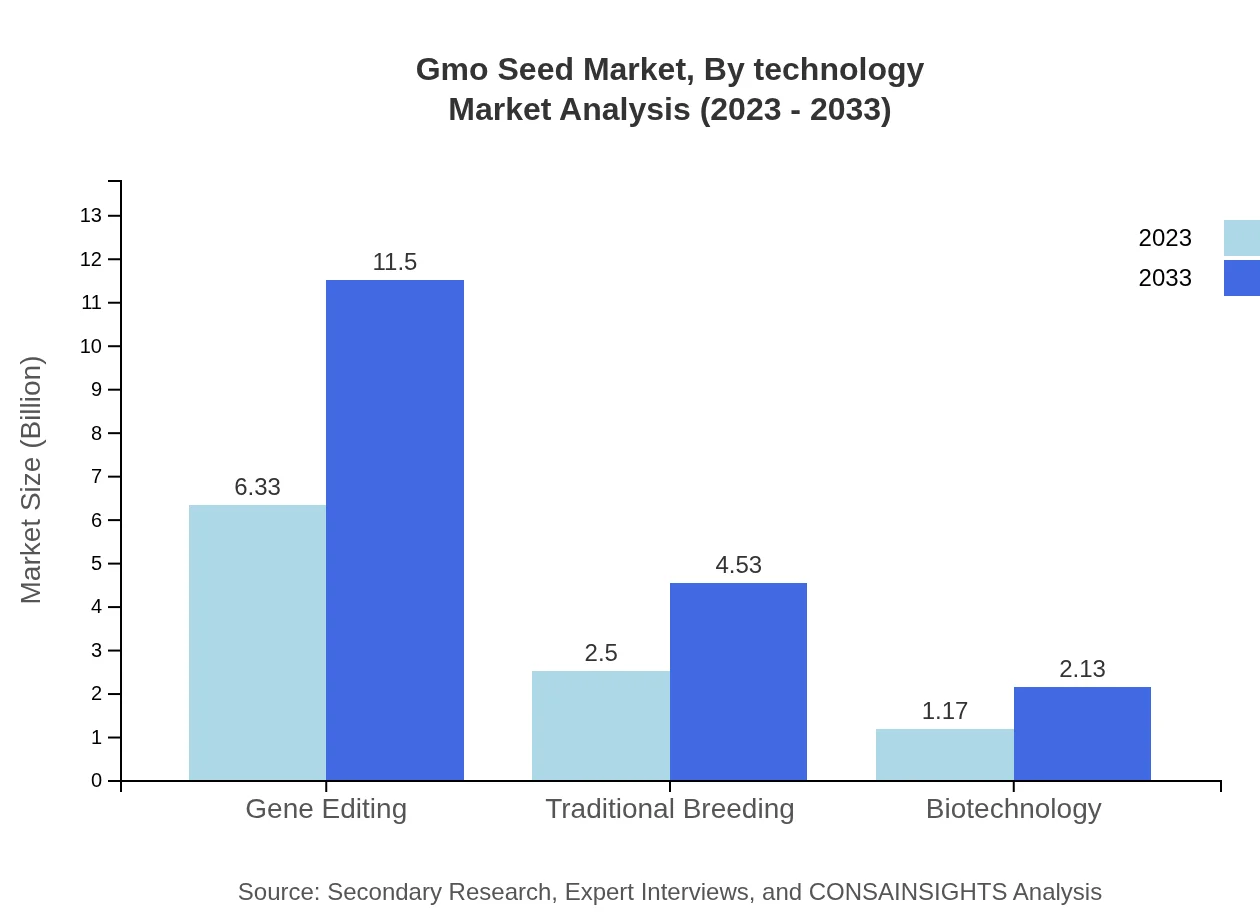
Gmo Seed Market Analysis By Technology
Technological categories like gene editing and traditional breeding are vital for Gmo Seed development. Gene editing will maintain a significant market share at 63.33%, projected to enhance crop resilience and yield. Traditional breeding methods remain relevant, forecasted at $2.50 billion in 2023, reinforcing conventional agricultural practices.
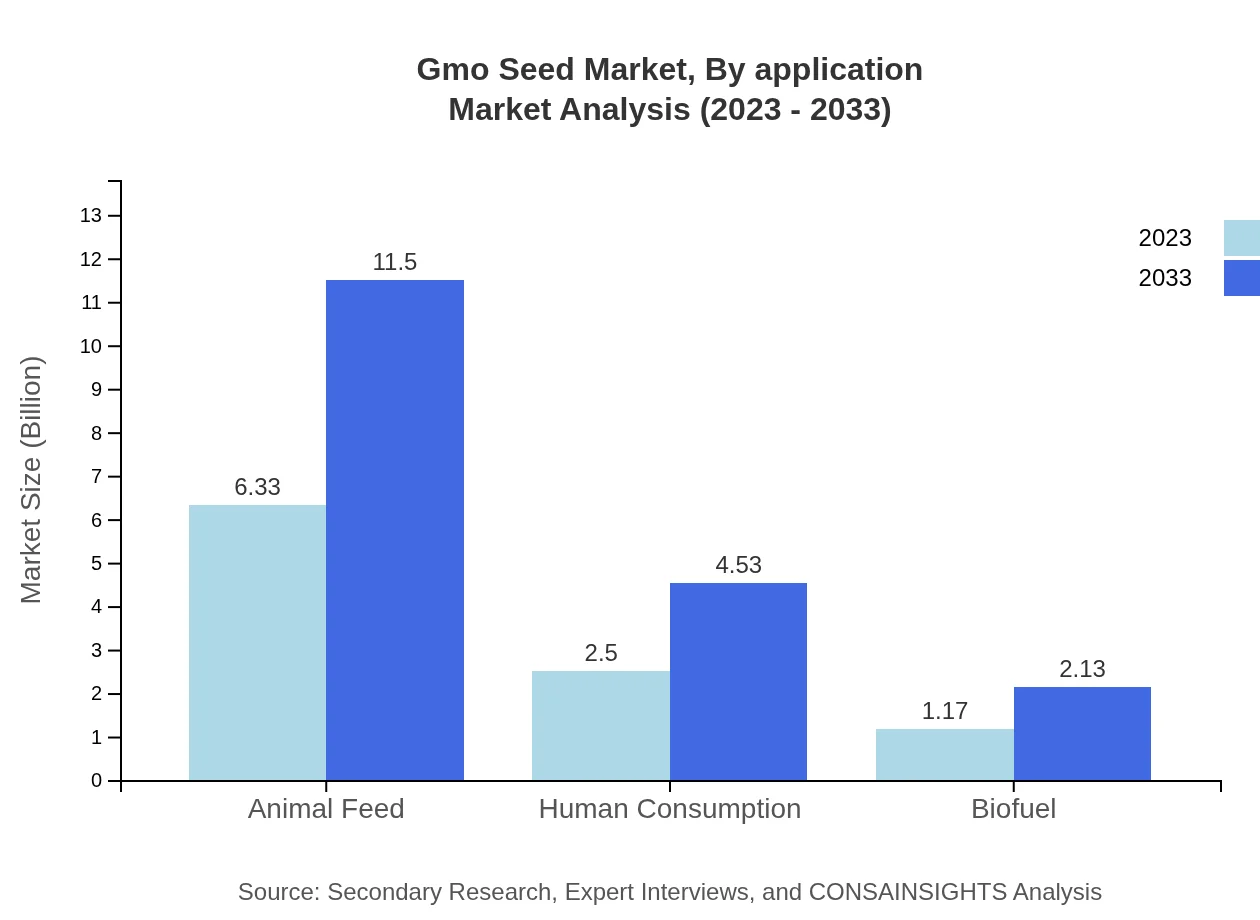
Gmo Seed Market Analysis By Application
Applications are abundant in sectors such as animal feed, human consumption, and biofuels. The application segment for animal feed remains dominant, constituting around 63.33% of market share in 2023, backed by rising livestock production to meet global meat demand.
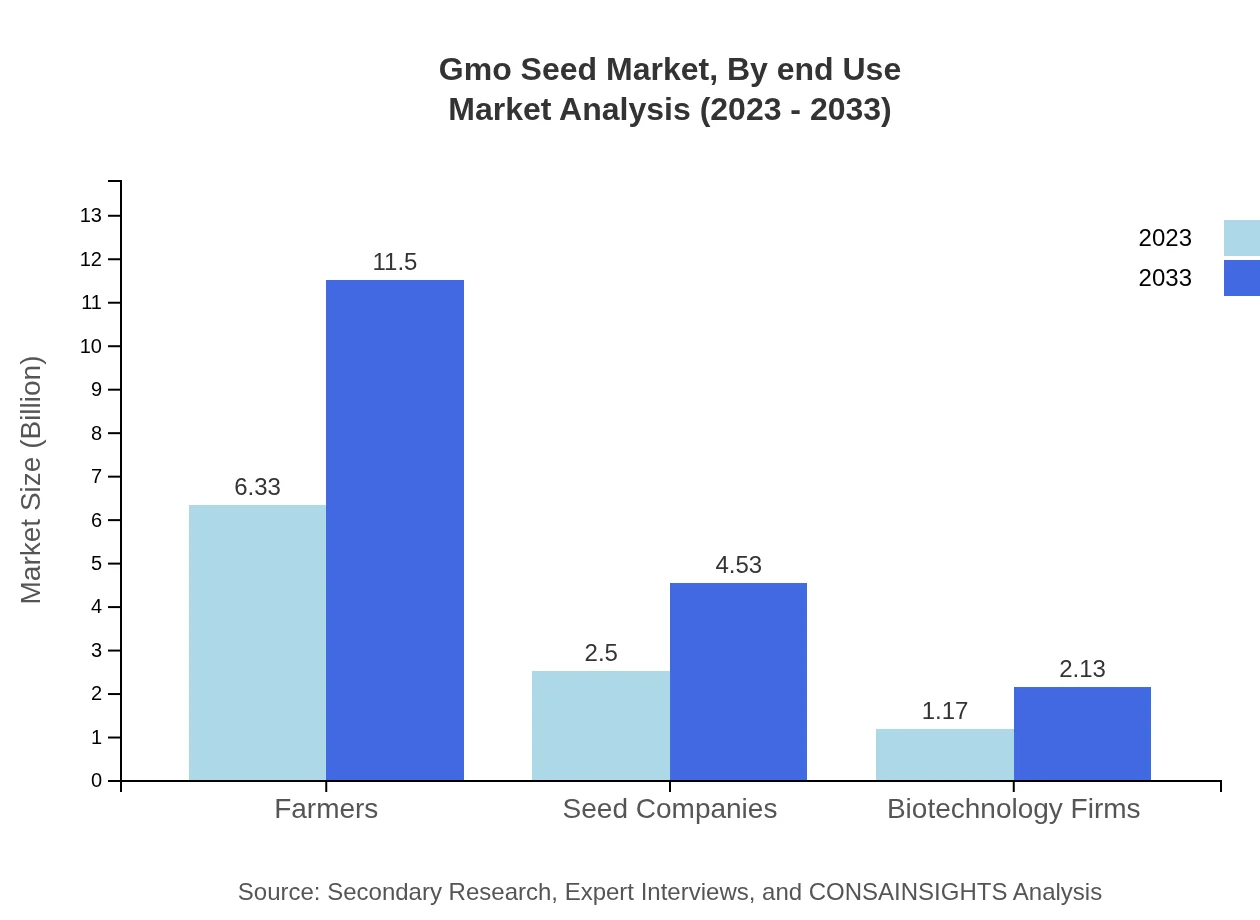
Gmo Seed Market Analysis By End Use
End-use categories such as food and feed highlight the versatile applications of GMO seeds. The escalating need for biofuels contributes significantly, with market dynamics leaning towards sustainable practices, reflecting growing consumer preference for environmentally friendly options.
Gmo Seed Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Gmo Seed Industry
Monsanto:
Monsanto, now part of Bayer, is a leading provider of agricultural products, especially in GMO seeds. Their innovation in biotech solutions has significantly impacted corn and soybean production worldwide.DuPont Pioneer:
A pioneer in agricultural sciences, DuPont offers a vast range of GMO seeds that enhance productivity and sustainability in farming operations globally.Syngenta:
Syngenta focuses on innovation and sustainable agriculture, providing advanced Gmo Seed solutions that help farmers tackle various agricultural challenges.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of GMO seeds?
The global GMO seed market is currently valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 6% leading to significant growth by 2033. This robust market reflects increasing demand for genetically modified crops and their benefits.
What are the key market players or companies in the GMO seed industry?
Major players in the GMO seed industry include key seed companies and biotechnology firms. The market is driven by leading companies that focus on innovative agricultural solutions, enhancing productivity, and addressing global food security challenges.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the GMO seed industry?
Driving factors include the need for increased agricultural productivity, resistance to pests and diseases, and the growing demand for biofuels. Biotechnology advancements and supportive regulations further foster growth in this sector.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the GMO seed market?
The North American GMO seed market is experiencing rapid growth, projected to increase from $3.72 billion in 2023 to $6.76 billion by 2033. Other regions like Europe and Asia Pacific also exhibit notable growth rates.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the GMO seed industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs within the GMO seed industry, providing in-depth insights, regional analysis, and segment data to support strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this GMO seed market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables, including detailed market analysis, segmentation data, regional overviews, competitive landscape insights, and future forecasts to aid in understanding market dynamics and trends.
What are the market trends of GMO seeds?
Current trends in the GMO seed market include a shift towards sustainable practices, increased adoption of precision agriculture, and growing consumer awareness of biotech benefits. Innovations in genetic engineering are also shaping future growth.