Gnss Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: gnss
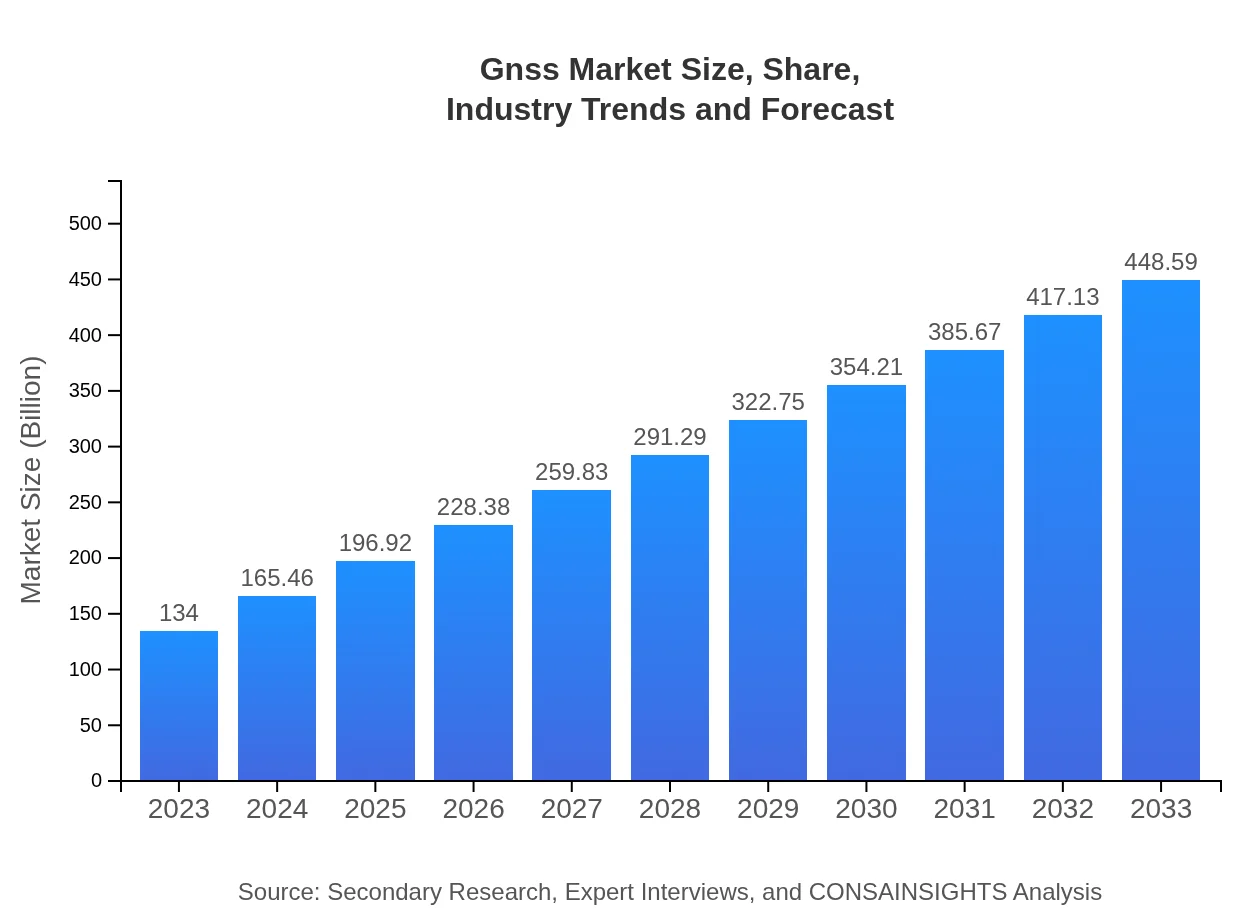
Gnss Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) market, covering market size, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It highlights regional performance, industry insights, and profiles of leading companies, providing valuable data for stakeholders to make informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $134.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $448.59 Billion |
| Top Companies | Trimble Inc., Garmin Ltd., Hexagon AB |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
GNSS Market Overview
Customize Gnss Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Gnss market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Gnss's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Gnss
What is the Market Size & CAGR of GNSS market in 2023 and 2033?
GNSS Industry Analysis
GNSS Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
GNSS Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Gnss Market Report:
The European GNSS market is projected to grow from $39.24 billion in 2023 to $131.35 billion by 2033. The adoption of GNSS technologies in various sectors, including transportation and agriculture, alongside favorable government policies supporting satellite technology, will continue to propel the market.Asia Pacific Gnss Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to witness substantial growth, with the market projected to expand from $25.22 billion in 2023 to $84.42 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization and increased investments in urban infrastructure are driving demand for GNSS technologies, especially in countries like China and India.North America Gnss Market Report:
North America holds the largest GNSS market share, projected to increase from $49.93 billion in 2023 to $167.14 billion by 2033. The presence of advanced technological infrastructure and significant investment in autonomous vehicles primarily drive this growth.South America Gnss Market Report:
In South America, the GNSS market is expected to grow from $1.84 billion in 2023 to $6.15 billion by 2033. Although the market is smaller compared to other regions, rising mobile device penetration and an increasing focus on agriculture applications are notable growth factors.Middle East & Africa Gnss Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to expand from $17.78 billion in 2023 to $59.53 billion by 2033. Increased demand for GNSS in defense and transportation sectors, particularly in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, will stimulate growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
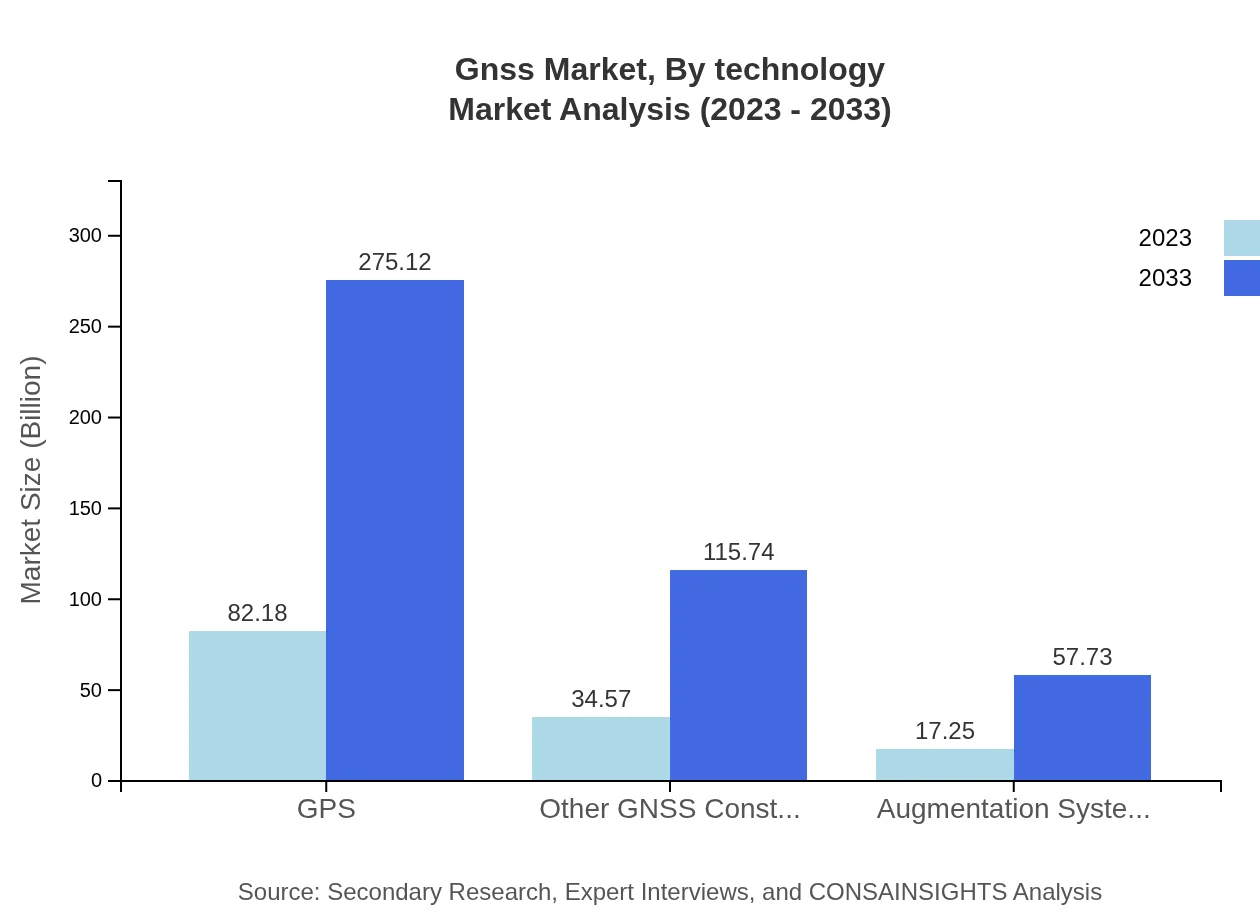
Gnss Market Analysis By Technology
The GNSS market is significantly impacted by technology segments, with GPS leading the market, expected to grow from $82.18 billion in 2023 to $275.12 billion by 2033. Other constellations such as GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou also see increased adoption, courtesy of improved accuracy and coverage.
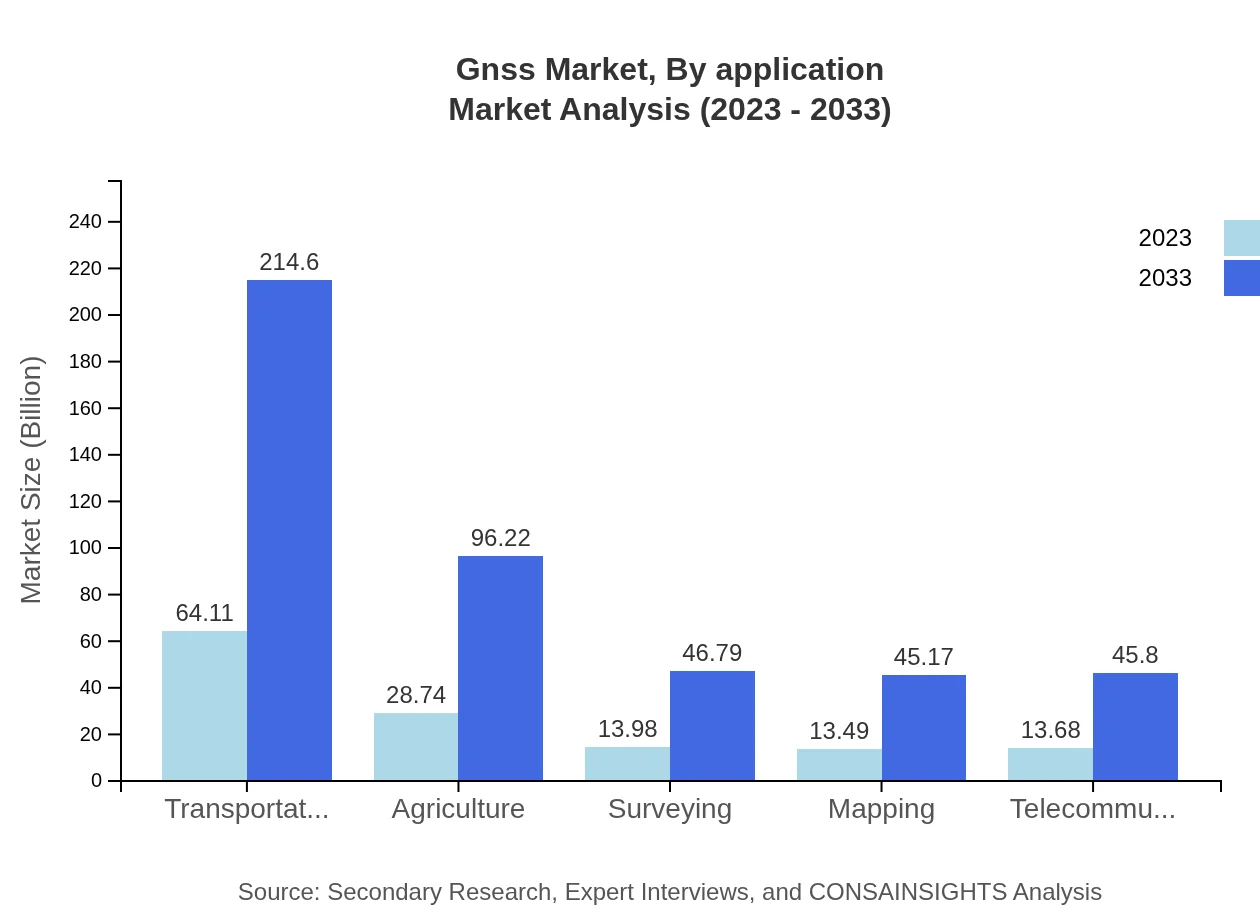
Gnss Market Analysis By Application
Applications in the GNSS market encompass transportation, agriculture, surveying, telecommunications, and mapping. The transportation sector is particularly noteworthy, projected to expand from $64.11 billion in 2023 to $214.60 billion by 2033, reflecting the burgeoning demand for autonomous driving technologies.
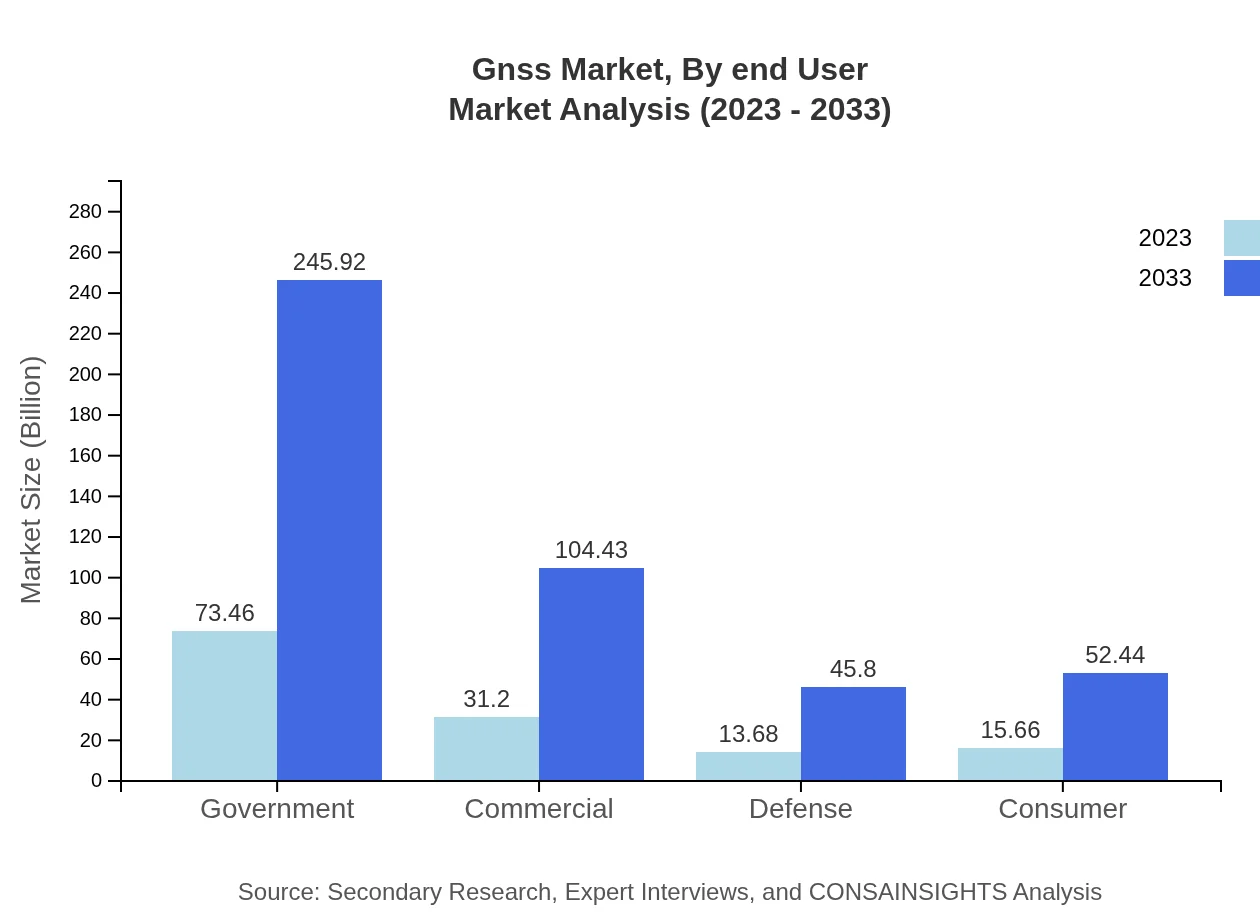
Gnss Market Analysis By End User
End-users include government, commercial, defense, and consumer sectors, with the government segment expanding from $73.46 billion in 2023 to $245.92 billion by 2033. The consumer segment is also significant, expected to increase from $15.66 billion to $52.44 billion during the same period, driven by demand for navigation in smartphones.
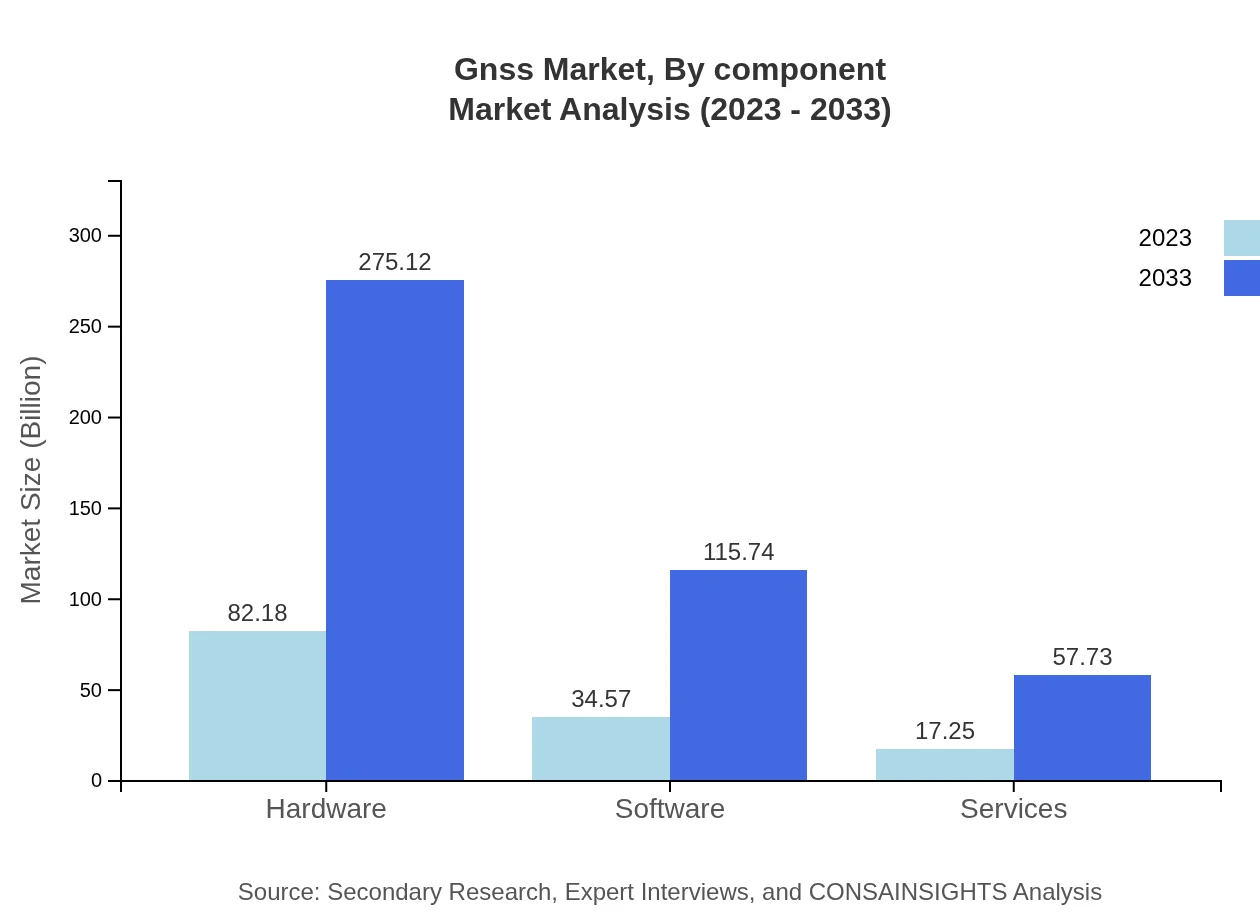
Gnss Market Analysis By Component
The GNSS market is divided into hardware, software, and services. Hardware leads the segment with a market size growing from $82.18 billion in 2023 to $275.12 billion by 2033. Services which facilitate system integration and maintenance support are also witnessing increased demand.
GNSS Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in GNSS Industry
Trimble Inc.:
A leader in positioning solutions, Trimble offers advanced GPS technology for various industries, including construction, agriculture, and transportation.Garmin Ltd.:
A prominent player in consumer electronics, Garmin develops GPS navigation and wearable technology, catering to both general users and professionals.Hexagon AB:
Hexagon specializes in measurement technologies and software solutions, leveraging GNSS capabilities for defense, automotive, and integrated surveying applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of GNSS?
The global GNSS market size is projected to reach $134 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.3% from 2023. The market encompasses diverse segments including government applications and hardware solutions, significantly impacting the forecasted growth.
What are the key market players or companies in the GNSS industry?
Key players in the GNSS industry include major technology companies and defense contractors. They are focused on innovation in GNSS technology and often collaborate on global standards and infrastructure development, driving competition and market evolution.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the GNSS industry?
Factors driving GNSS market growth include increasing demand for accurate location data in transportation and agriculture, rising adoption of IoT devices, and advancements in GNSS technology. These trends enhance efficiency and safety across various sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the GNSS market?
The North American region is the fastest-growing in the GNSS market, expected to expand from $49.93 billion in 2023 to $167.14 billion by 2033. Its robust technology infrastructure and early adoption of GNSS applications fuel this growth.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the GNSS industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored for the GNSS industry. Clients can receive insights specific to their needs, including market segments, growth forecasts, and competitive analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this GNSS market research project?
Deliverables from the GNSS market research project include comprehensive reports, market trends analysis, segment performance insights, competitive landscapes, and forecasts up to 2033, allowing for informed decision-making.
What are the market trends of GNSS?
Market trends in the GNSS sector indicate a shift towards enhanced accuracy systems, increased integration in autonomous vehicles, and growth in consumer applications. These trends suggest a dynamic evolution within the GNSS landscape.