Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: greenhouse-gas-monitoring-systems
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems market, covering market conditions, size estimates, technological advancements, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
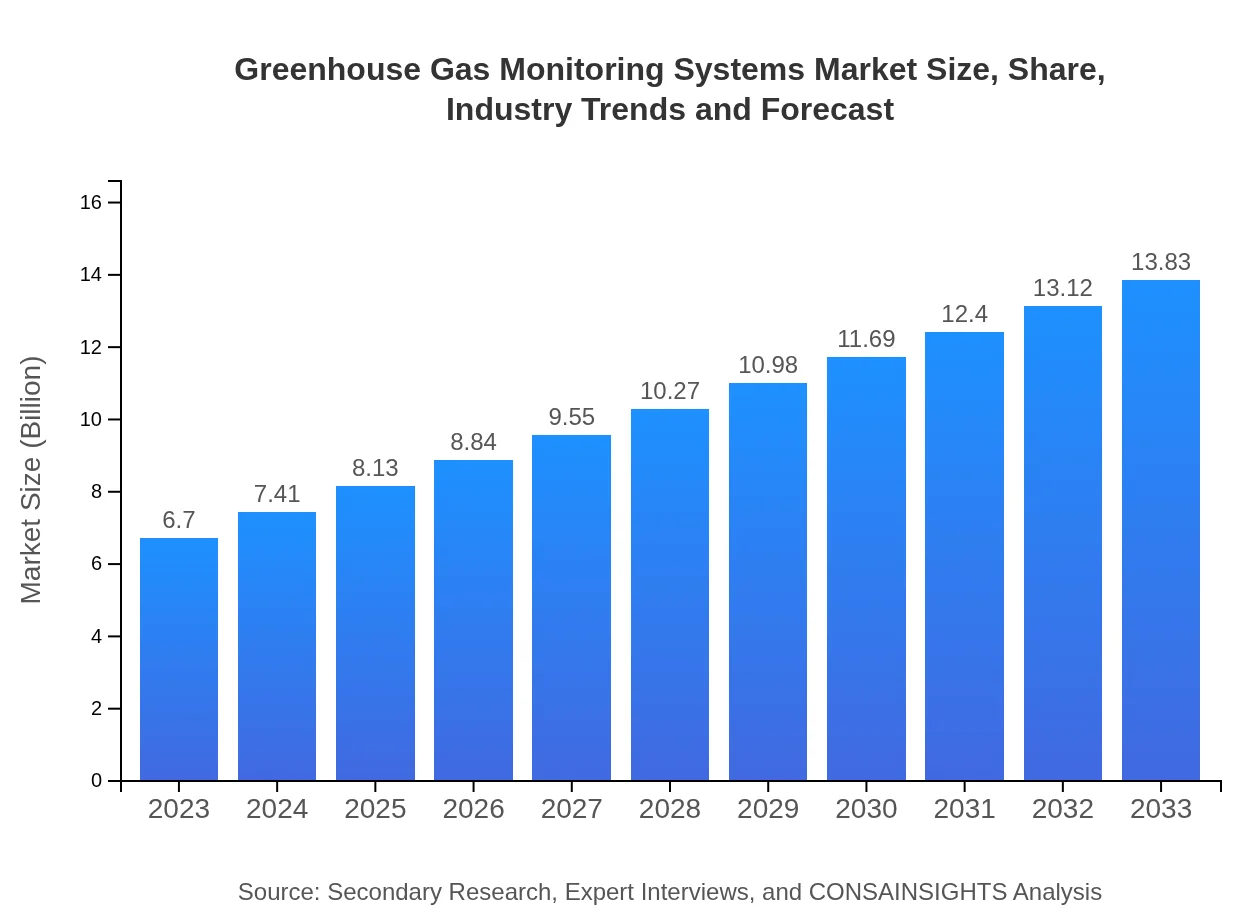
| 2023 Market Size | $6.70 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13.83 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Honeywell International Inc., Ametek, Inc., Teledyne Technologies |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Overview
Customize Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems market in 2023 and 2033?
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Industry Analysis
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report:
Europe is anticipated to experience rapid expansion, soaring from $2.10 billion in 2023 to $4.33 billion in 2033. The region's proactive environmental policies and heightened focus on green technologies play a critical role in this growth.Asia Pacific Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is expected to see a substantial growth trajectory, increasing from $1.25 billion in 2023 to $2.57 billion by 2033. This rise is fueled by rapid industrialization and stringent environmental regulations enforced by governments in nations like China and India.North America Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report:
North America currently holds a significant market share, projected to escalate from $2.53 billion in 2023 to $5.23 billion in 2033. The region is noted for its advanced technological frameworks, offering a variety of innovative solutions for emission monitoring.South America Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report:
In South America, the market is growing gradually, predicted to double from $0.13 billion in 2023 to $0.26 billion in 2033. The increase is attributed to improving governmental policies on emissions and rising awareness of climate change impacts.Middle East & Africa Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is set to grow from $0.70 billion in 2023 to $1.44 billion in 2033, driven by increasing industrial activities and emerging regulatory frameworks targeting greenhouse gas emissions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Analysis By Technology
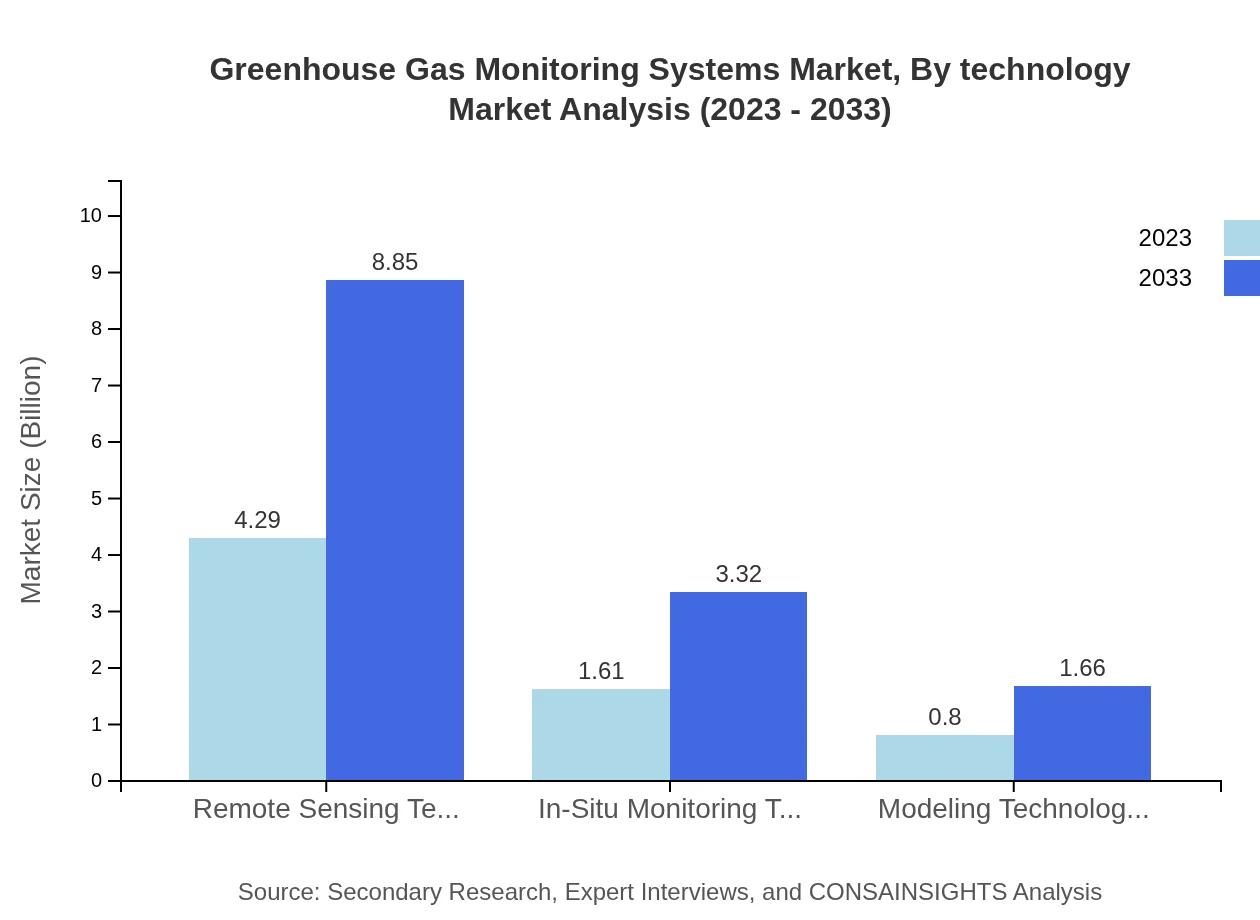
The technological landscape of Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems includes key technologies such as Remote Sensing Technologies and In-Situ Monitoring Technologies. Remote Sensing Technologies dominate the market with a share of 64%, valued at $4.29 billion in 2023 and expected to rise to $8.85 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, In-Situ Monitoring Technologies represent a versatile solution for real-time measurements, growing from $1.61 billion in 2023 to $3.32 billion by 2033.
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Analysis By Gas Type
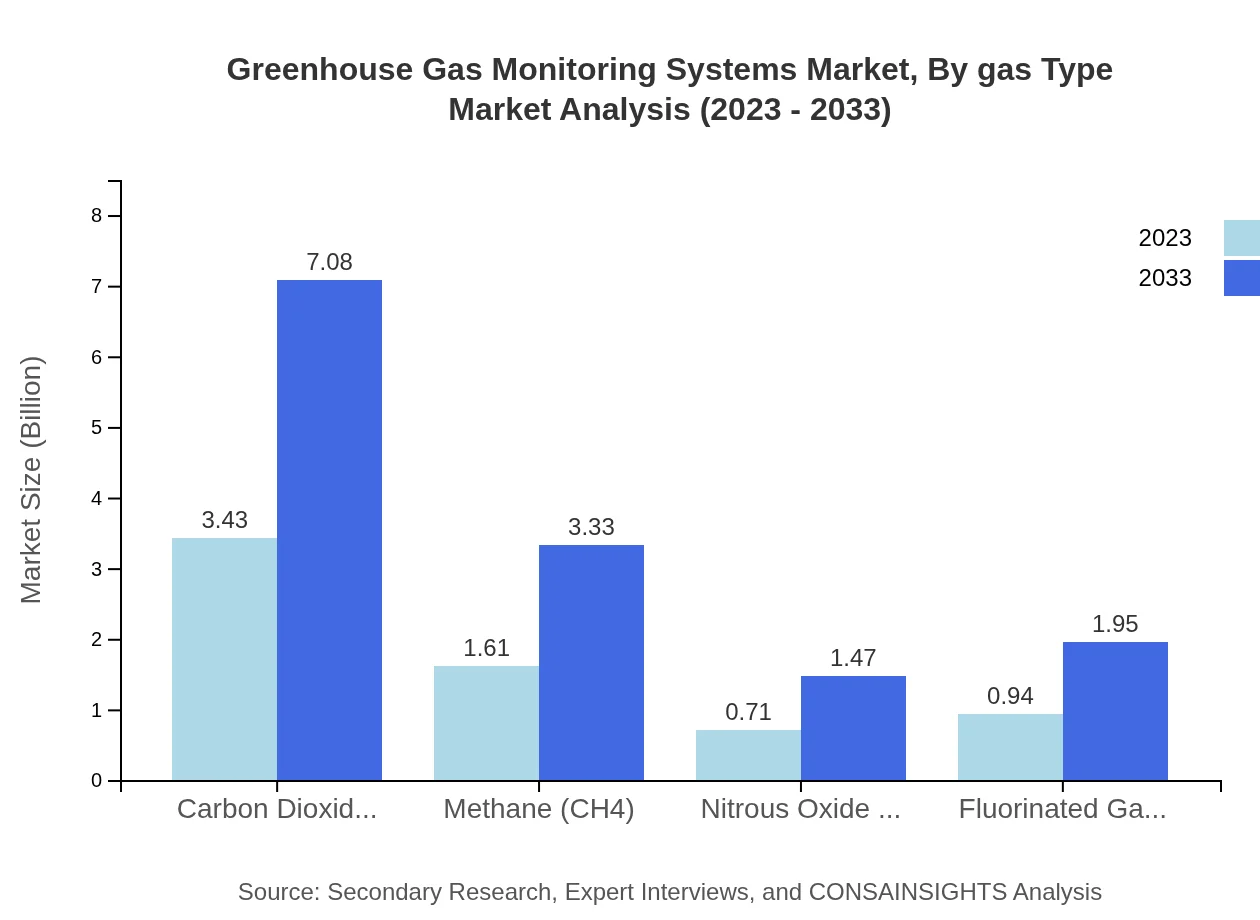
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) currently leads the market with a sizeable share of 51.19%, valued at $3.43 billion in 2023, increasing to $7.08 billion by 2033. Methane (CH4) follows with a market size of $1.61 billion in 2023 and projected growth to $3.33 billion. The significance of Nitrous Oxide (N2O) and Fluorinated Gases has also been noted, growing steadily owing to specific regulatory initiatives.
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Analysis By Application
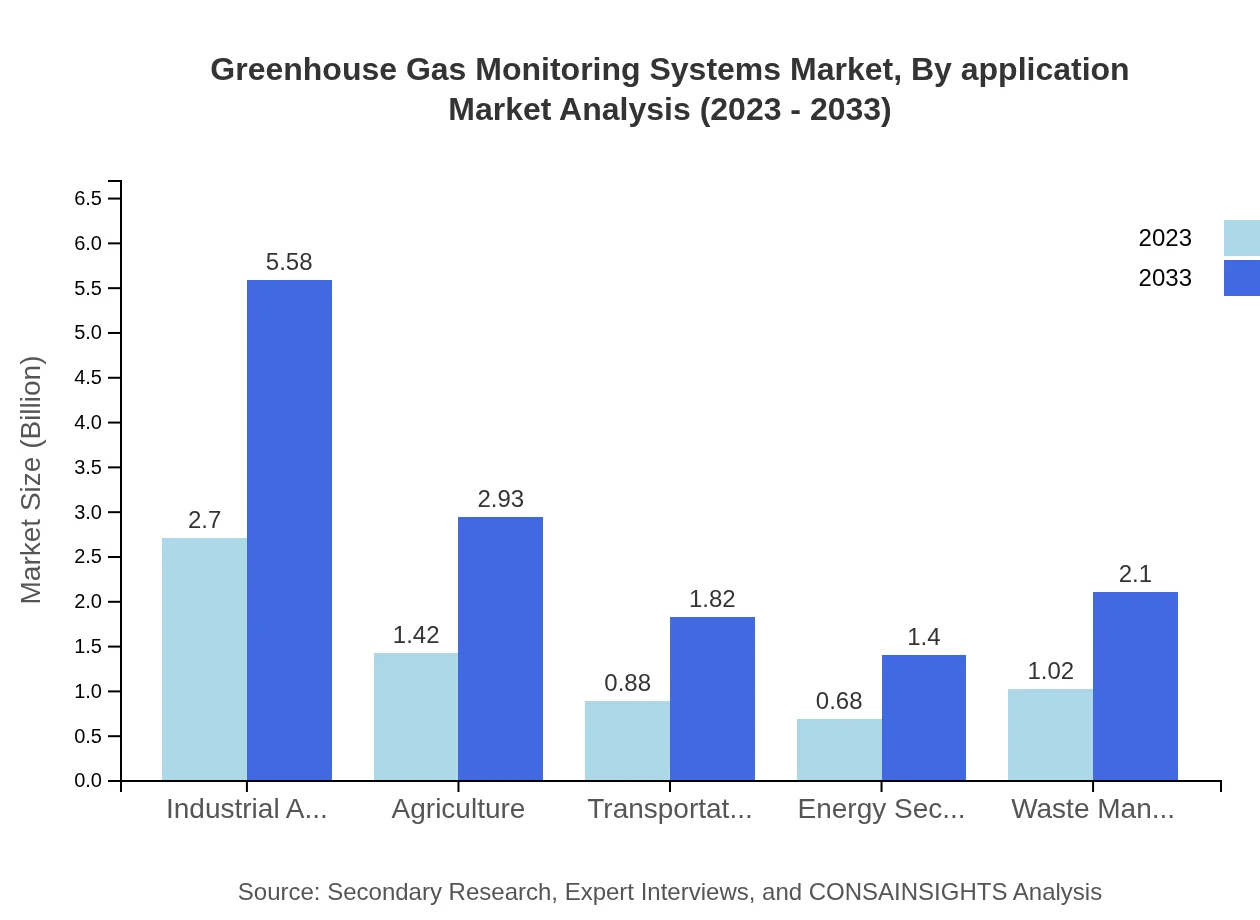
Key applications of monitoring systems include Industrial, Agriculture, Transportation, Energy Sector, and Waste Management. The Industrial Applications segment accounts for the largest share at 40.35% in 2023, valued at $2.70 billion, and anticipated to grow to $5.58 billion by 2033. Other applications are also gaining traction as regulations tighten and industries seek effective emissions tracking.
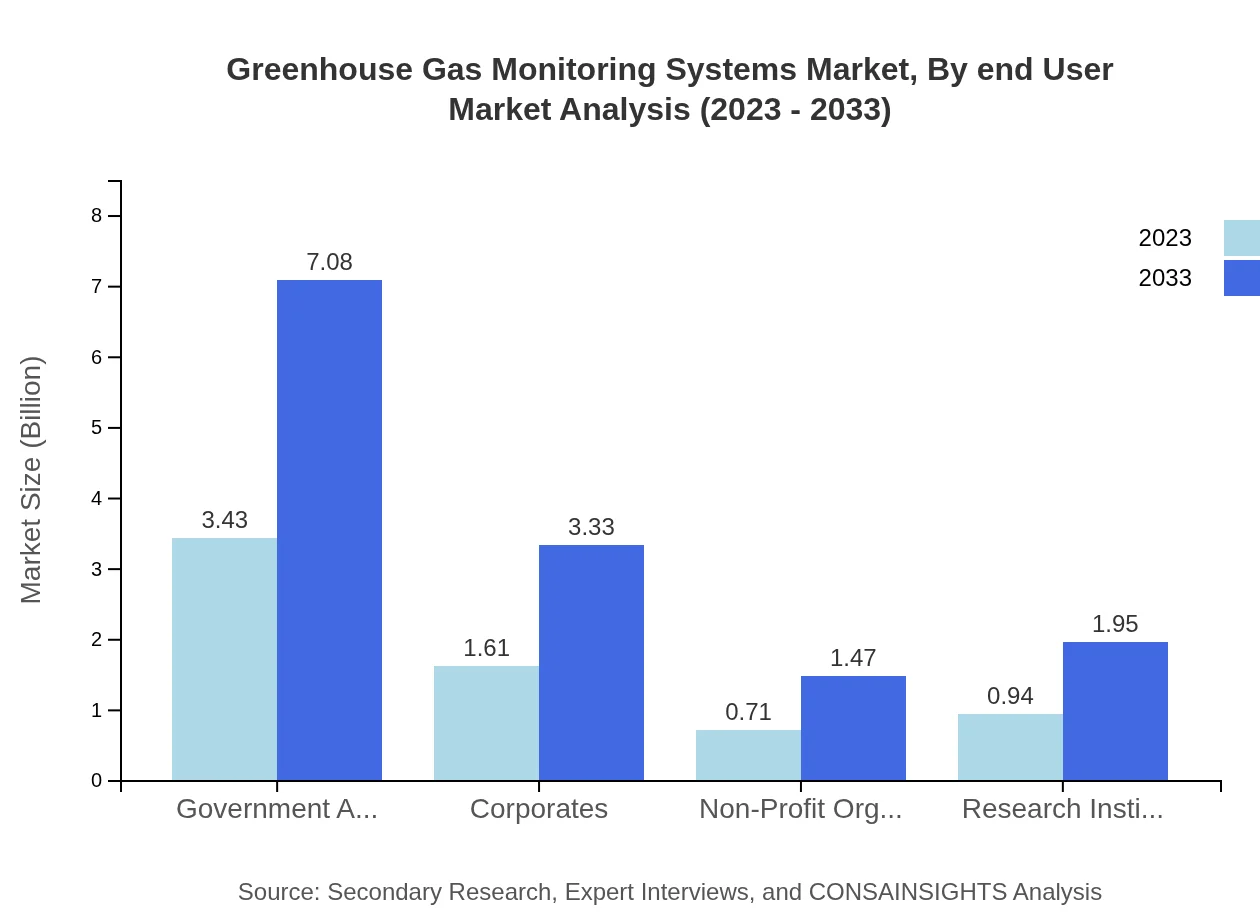
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Analysis By End User
End-user segmentation includes Government Agencies, Corporates, Non-Profit Organizations, and Research Institutions. Government Agencies represent the largest market size at $3.43 billion in 2023, projected to reach $7.08 billion by 2033. Corporates follow with a current market value of $1.61 billion, expected to grow to $3.33 billion as organizations increasingly prioritize sustainability measures.
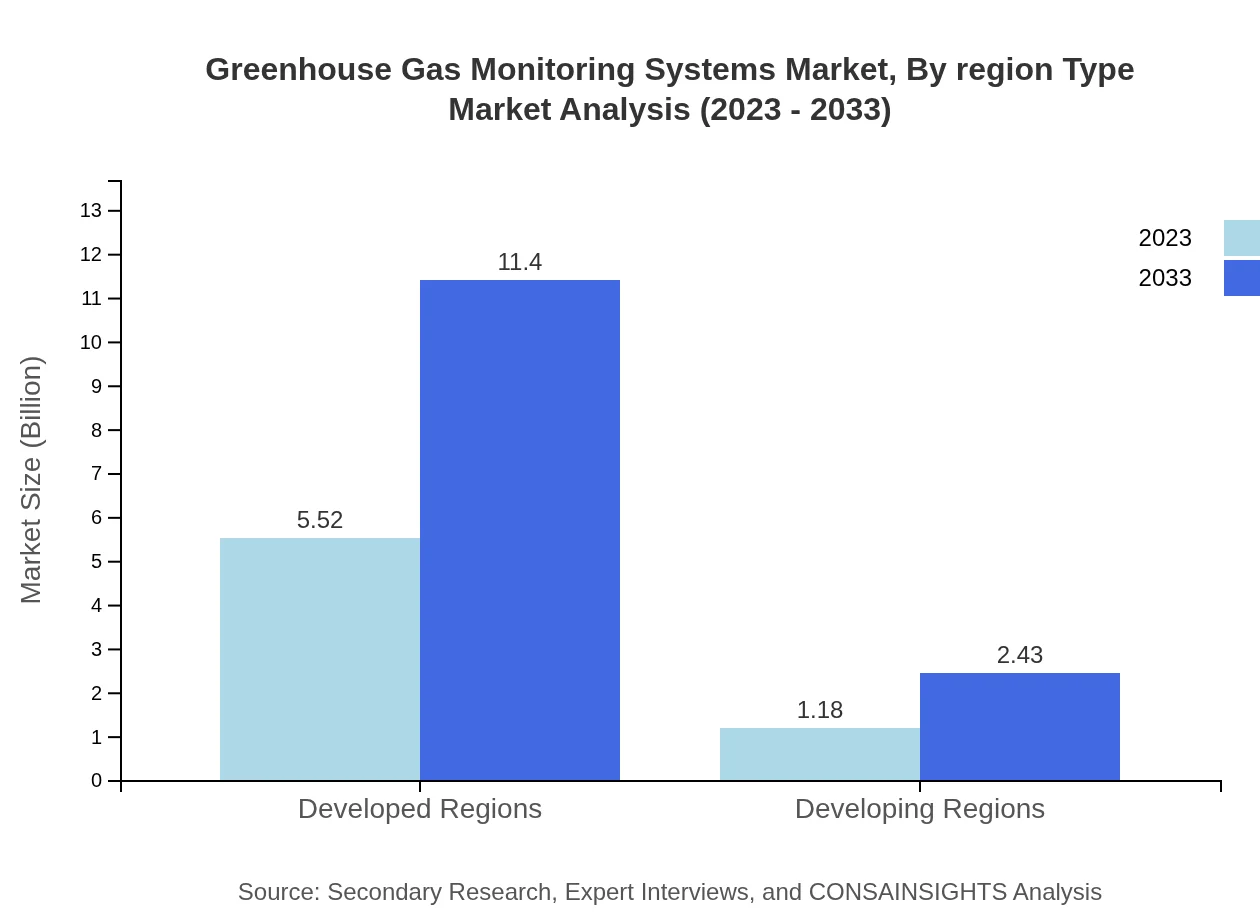
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Analysis By Region Type
The market is heavily represented in developed regions, comprising a dominant share of 82.44% in 2023 at $5.52 billion, with growth anticipated to reach $11.40 billion by 2033. In contrast, developing regions, which represent 17.56% of the market, are projected to grow from $1.18 billion in 2023 to $2.43 billion by 2033, indicating strengthened investments in environmental monitoring.
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a leading technology corporation known for its innovative solutions in industrial automation and electrification, contributing extensively to the monitoring systems with advanced sensor technologies.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell provides integrated solutions for achieving environmental compliance, offering a diverse range of greenhouse gas monitoring instruments that enhance the accuracy of emissions data.Ametek, Inc.:
Ametek specializes in analytical instrumentation focused on environmental monitoring, delivering state-of-the-art equipment for various greenhouse gases.Teledyne Technologies:
Teledyne Technologies develops advanced monitoring technologies, including gas detection systems crucial for ensuring compliance with emissions regulations worldwide.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems?
The greenhouse gas monitoring systems market is currently valued at approximately $6.7 billion with an expected CAGR of 7.3% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing global focus on emissions monitoring and climate change mitigation.
What are the key market players or companies in this greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems industry?
Key players in the greenhouse gas monitoring systems market include established firms in environmental science and technology, such as Aeroqual Ltd., Teledyne Technologies Inc., and Siemens AG, who drive innovation and market penetration.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems industry?
Growth in the greenhouse gas monitoring systems industry is driven by regulatory mandates for emissions tracking, advancements in sensor technology, and heightened corporate responsibility towards sustainability and environmental performance.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems?
Europe is the fastest-growing region in the greenhouse gas monitoring systems market, expanding from $2.10 billion in 2023 to $4.33 billion by 2033, propelled by stringent environmental regulations and policy initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights provides customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the greenhouse gas monitoring systems industry, enabling stakeholders to gain insights pertinent to their business strategies.
What deliverables can I expect from this greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems market research project?
Deliverables from this research project include detailed market analysis, segmented data reports on technology adoption and regional insights, and actionable recommendations for market entry and competitive positioning.
What are the market trends of greenhouse Gas Monitoring Systems?
Current market trends include the increasing adoption of remote sensing technologies, a shift towards real-time data analytics, and a growing emphasis on compliance with international emission standards and corporate sustainability goals.