Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: greenhouse-horticulture
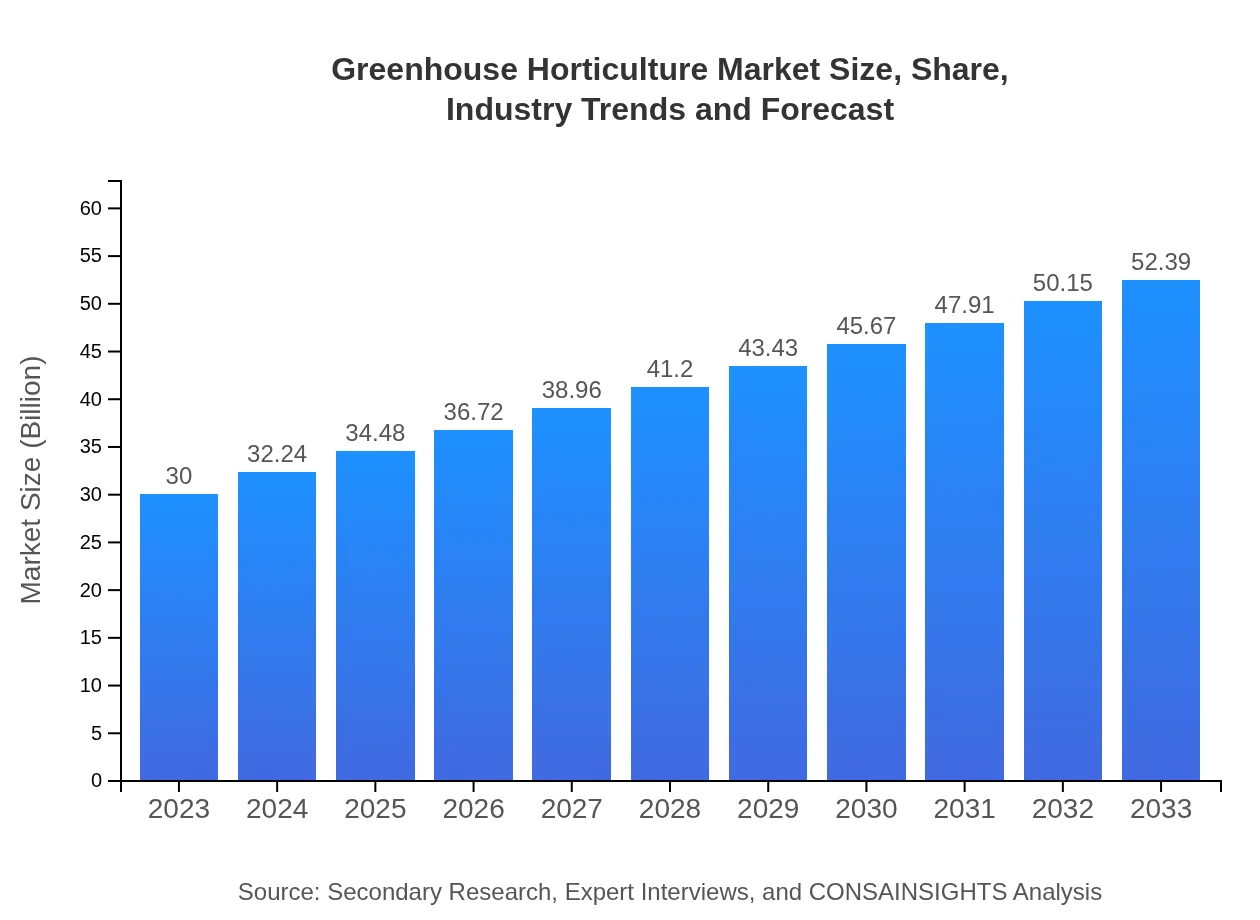
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Greenhouse Horticulture market from 2023 to 2033, including market size, growth forecasts, regional insights, key players, and technological advancements impacting the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $30.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.6% |
| 2033 Market Size | $52.39 Billion |
| Top Companies | Netafim, Hort Americas, Rivulis Irrigation, Sakata Seed Corporation, Stahl Greenhouses |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Overview
Customize Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Greenhouse Horticulture market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Greenhouse Horticulture's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Greenhouse Horticulture
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Greenhouse Horticulture market in 2023?
Greenhouse Horticulture Industry Analysis
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report:
Europe's market is significant, with a value of $9.83 billion in 2023 projected to grow to $17.16 billion by 2033. The region leads in greenhouse technology and sustainable practices due to stringent agricultural policies.Asia Pacific Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Greenhouse Horticulture market was valued at $5.69 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $9.93 billion by 2033, showcasing a strong growth opportunity due to increasing agricultural demand and innovations in agricultural technologies.North America Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report:
North America holds a market value of $10.20 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $17.82 billion by 2033. The surge is fueled by advanced farming technology adoption and an increasing focus on sustainability in agriculture.South America Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report:
The South American market is valued at $2.71 billion in 2023, growing to $4.73 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by rising investments in agricultural infrastructure and the increasing preference for locally sourced produce.Middle East & Africa Greenhouse Horticulture Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is valued at $1.57 billion in 2023, anticipated to rise to $2.75 billion by 2033. The region is leveraging greenhouse technologies to address food security issues.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
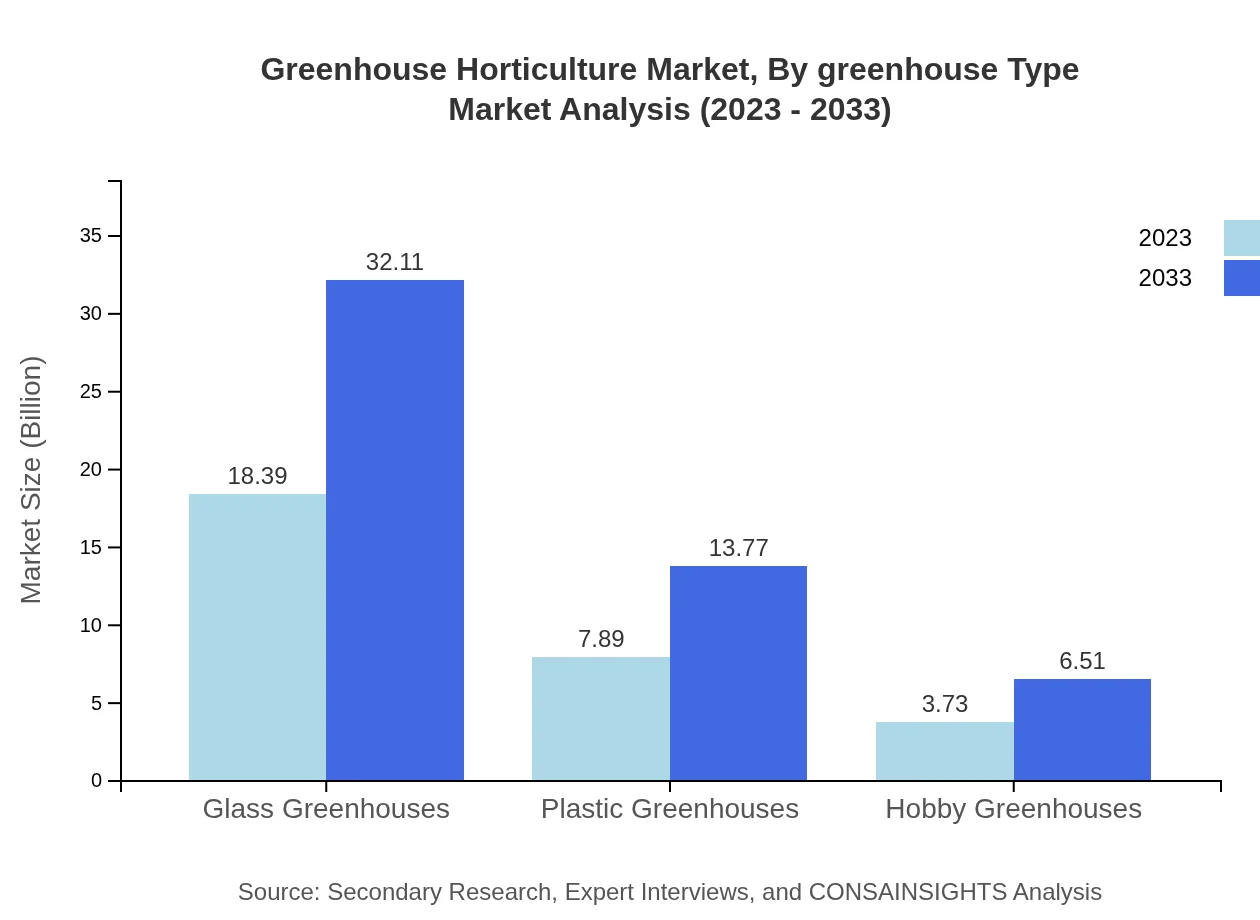
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Analysis By Greenhouse Type
The greenhouse types include glass, plastic, and hobby greenhouses, with glass greenhouses dominating in both size and market share at $18.39 billion (61.29%) in 2023. Plastic greenhouses account for $7.89 billion (26.29%) and hobby greenhouses for $3.73 billion (12.42%). This structure shows that commercial growers favor glass for its durability and efficiency.
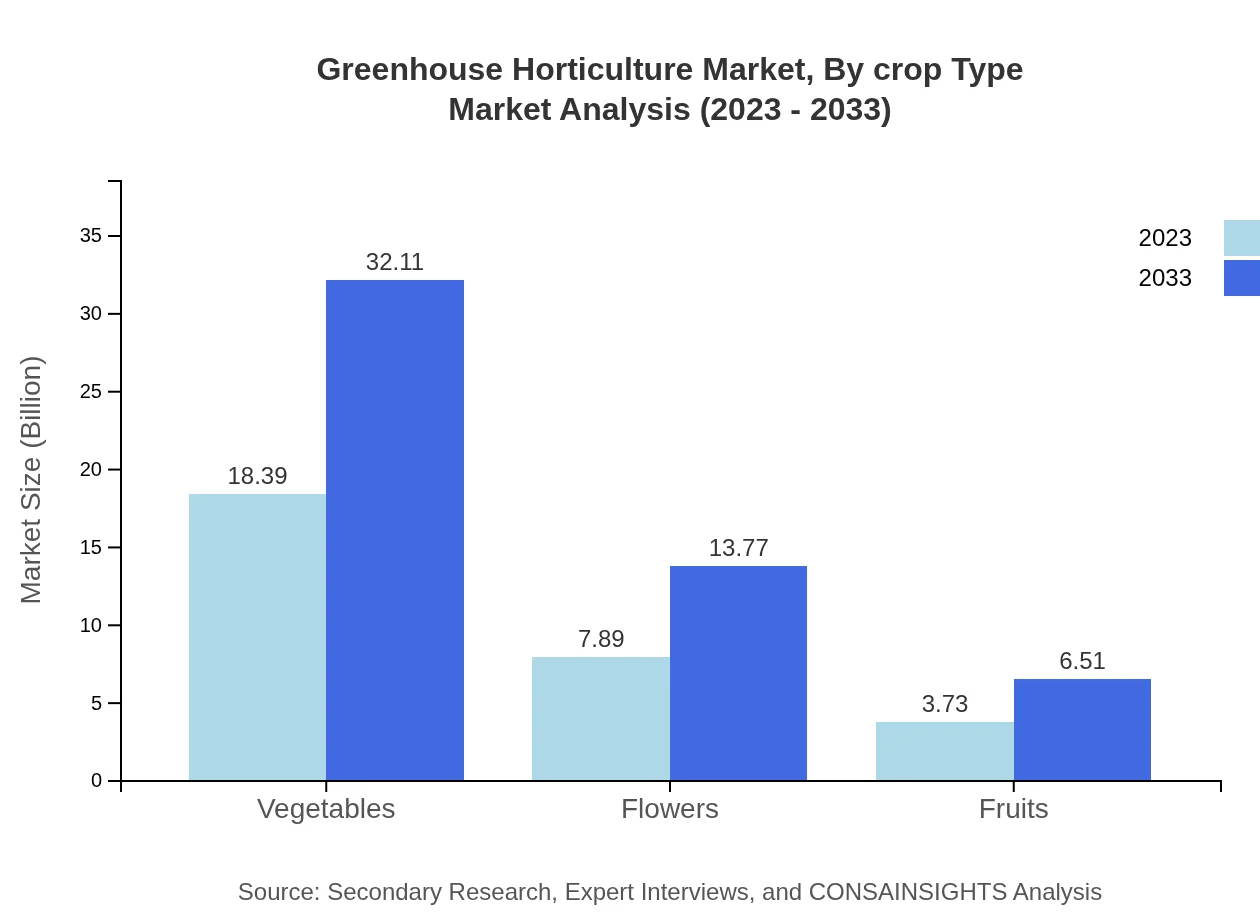
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Analysis By Crop Type
The major crop types include vegetables, fruits, and flowers. Vegetables, valued at $18.39 billion (61.29%) in 2023, lead the market due to steady consumer demand. Flower segment is $7.89 billion (26.29%), while fruits are at $3.73 billion (12.42%). These value segments indicate strong consumer trends towards fresh produce availability.
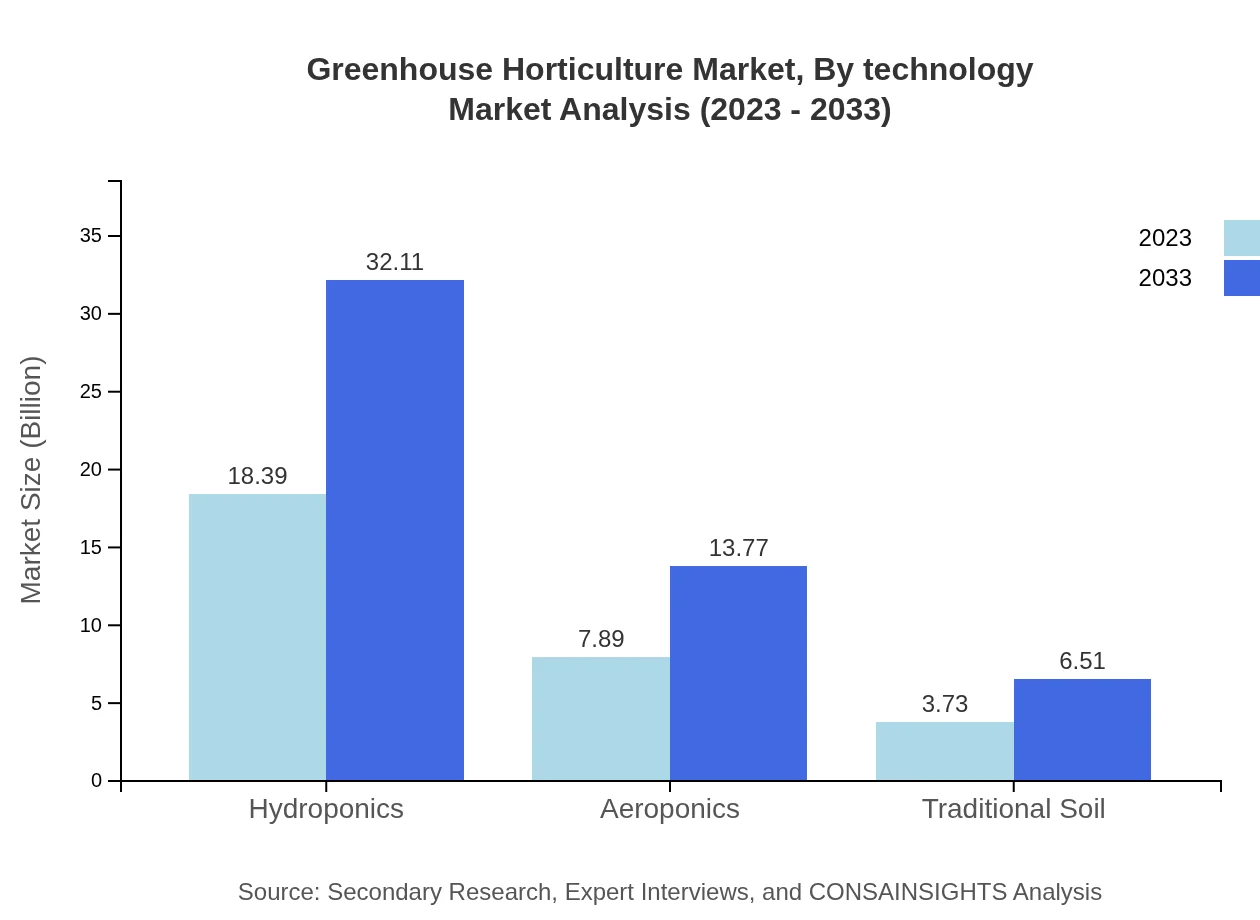
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Analysis By Technology
Technology adoption includes hydroponics valued at $18.39 billion (61.29%) in 2023, and aeroponics at $7.89 billion (26.29%), both indicating a shift towards more sustainable growing practices. Traditional soil setups retain a share of $3.73 billion (12.42%), reflecting a gradual change in growing technology preference among growers.
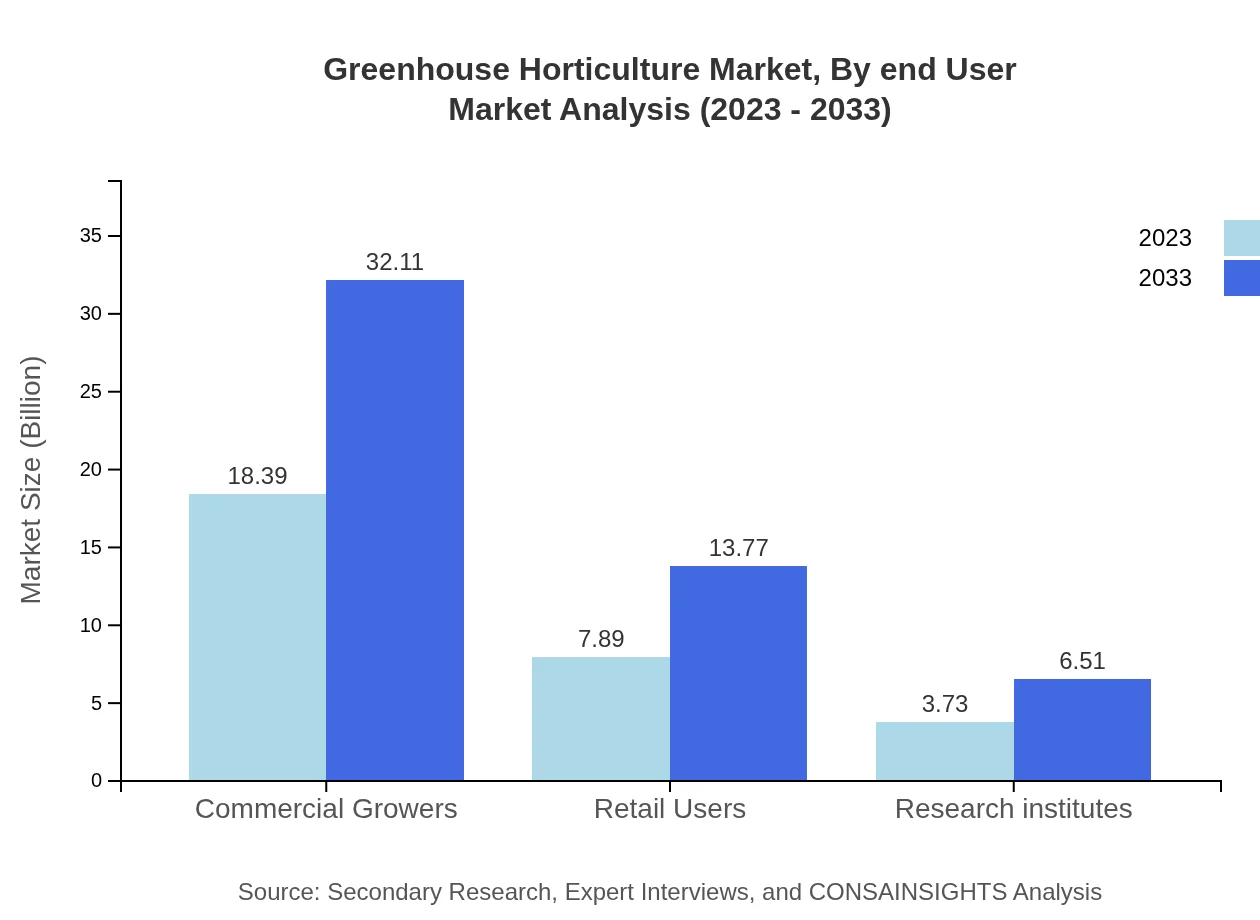
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segmentation includes commercial growers, retail users, and research institutes, with commercial growers commanding a market size of $18.39 billion (61.29%) in 2023. This underscores the dominant role of commercial scale operations in driving greenhouse horticulture, whereas retail users and research institutes follow with $7.89 billion (26.29%) and $3.73 billion (12.42%), respectively.
Greenhouse Horticulture Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Greenhouse Horticulture Industry
Netafim:
A leader in drip and micro-irrigation solutions for greenhouse horticulture, known for its innovative water-saving technologies.Hort Americas:
Focuses on providing advanced horticultural technology and solutions including LED lighting and climate control systems.Rivulis Irrigation:
Specializes in delivering irrigation products and solutions which enhance greenhouse productivity and water efficiency.Sakata Seed Corporation:
A major player in the seed industry, providing high-quality seeds for flower and vegetable cultivation in greenhouse settings.Stahl Greenhouses:
Provides custom design and construction of greenhouses tailored for various horticultural applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of greenhouse Horticulture?
The global greenhouse horticulture market is projected to grow from $30 billion in 2023 to $52.4 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 5.6% over the forecast period.
What are the key market players or companies in this greenhouse Horticulture industry?
Key players in the greenhouse-horticulture industry include major agricultural companies, seed suppliers, technology providers, and distributors. These companies are leveraging innovative technologies to enhance crop yields and meet the growing demand for fresh produce.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the greenhouse Horticulture industry?
Growth in the greenhouse-horticulture industry is mainly driven by increasing demand for fresh vegetables and fruits, advancements in greenhouse technology, and the rising trend of sustainable agricultural practices among growers.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the greenhouse Horticulture market?
The fastest-growing region in the greenhouse-horticulture market is Europe, projected to rise from $9.83 billion in 2023 to $17.16 billion by 2033, reflecting robust investment in advanced horticulture techniques.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the greenhouse Horticulture industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs in the greenhouse-horticulture industry, ensuring comprehensive insights based on the latest market trends and forecasts.
What deliverables can I expect from this greenhouse Horticulture market research project?
Deliverables from the greenhouse-horticulture market research project include a detailed report, executive summaries, data visualizations, segmented analysis, and strategic recommendations for business growth and market entry.
What are the market trends of greenhouse Horticulture?
Current trends in the greenhouse-horticulture market include the adoption of hydroponic and aeroponic systems, increasing use of automation and smart technology in greenhouse management, and a focus on sustainability and organic produce.