Greenhouse Produce Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: greenhouse-produce
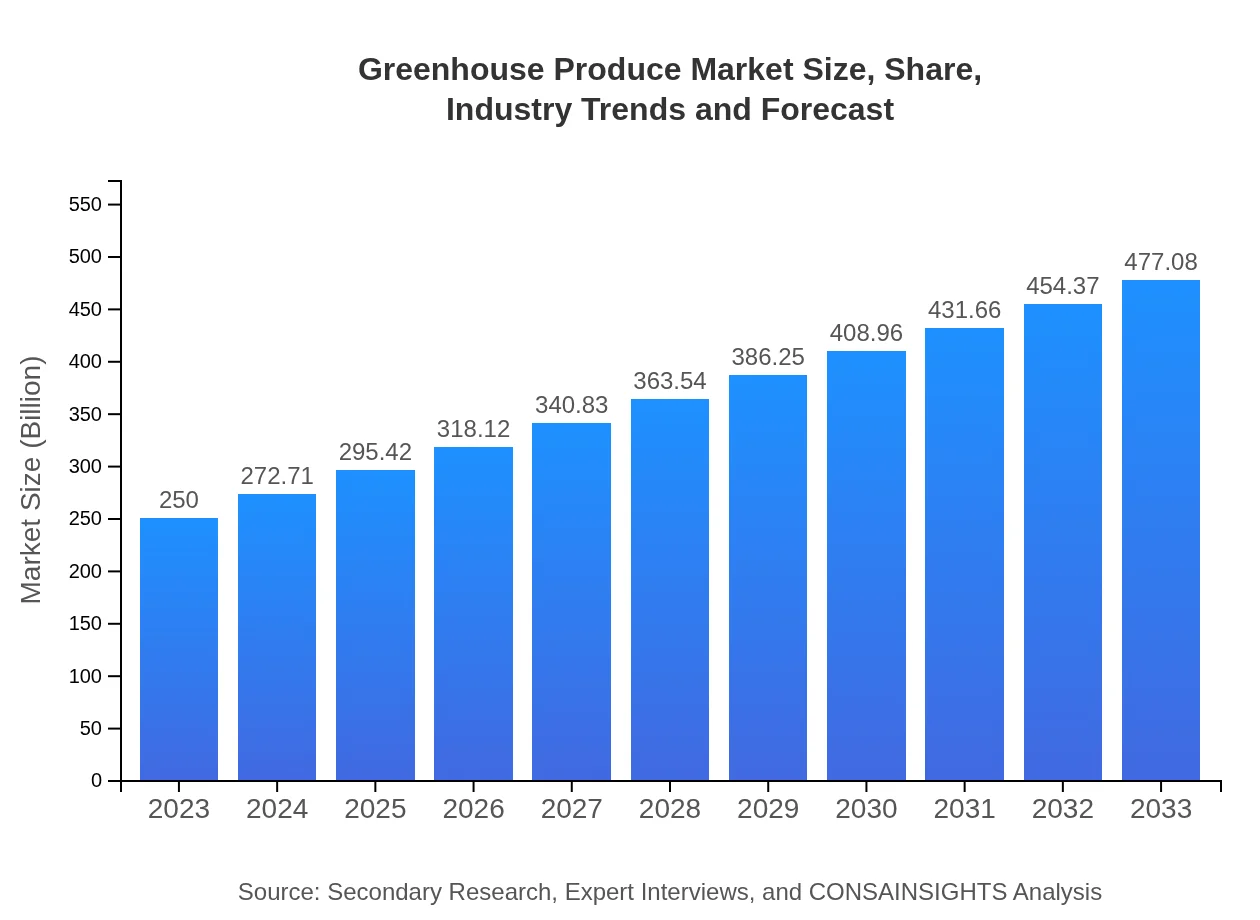
Greenhouse Produce Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the greenhouse produce market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market size, growth trends, segmentation, and regional insights, coupled with an evaluation of technological advancements and key players in the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $250.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $477.08 Billion |
| Top Companies | Netafim, Royal Brinkman, Valoya, BrightFarms, Sundrop Farms |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Greenhouse Produce Market Overview
Customize Greenhouse Produce Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Greenhouse Produce market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Greenhouse Produce's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Greenhouse Produce
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Greenhouse Produce Market in 2023?
Greenhouse Produce Industry Analysis
Greenhouse Produce Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Greenhouse Produce Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Greenhouse Produce Market Report:
Europe represents a substantial segment, with a market size of $74.30 billion in 2023 anticipated to grow to $141.79 billion by 2033. European nations are increasingly adopting sustainable agricultural practices, supported by government policies that encourage greenhouse farming.Asia Pacific Greenhouse Produce Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing significant growth, with a market size of $46.50 billion in 2023, projected to reach $88.74 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and the need for food security in densely populated countries such as China and India.North America Greenhouse Produce Market Report:
North America is the largest market, projected to escalate from $94.50 billion in 2023 to $180.34 billion in 2033. Demand for organic produce, combined with technological advancements in greenhouse farming, drives this growth, particularly in the U.S. and Canada.South America Greenhouse Produce Market Report:
The South American market for greenhouse produce stands at $10.55 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow to $20.13 billion by 2033. The region is leveraging its agricultural capabilities to enhance food production for both domestic consumption and export, capitalizing on favorable climatic conditions.Middle East & Africa Greenhouse Produce Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the greenhouse produce market is expanding from $24.15 billion in 2023 to $46.09 billion by 2033. The region is investing in advanced irrigation technologies and greenhouse facilities to combat food scarcity and improve agricultural productivity.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
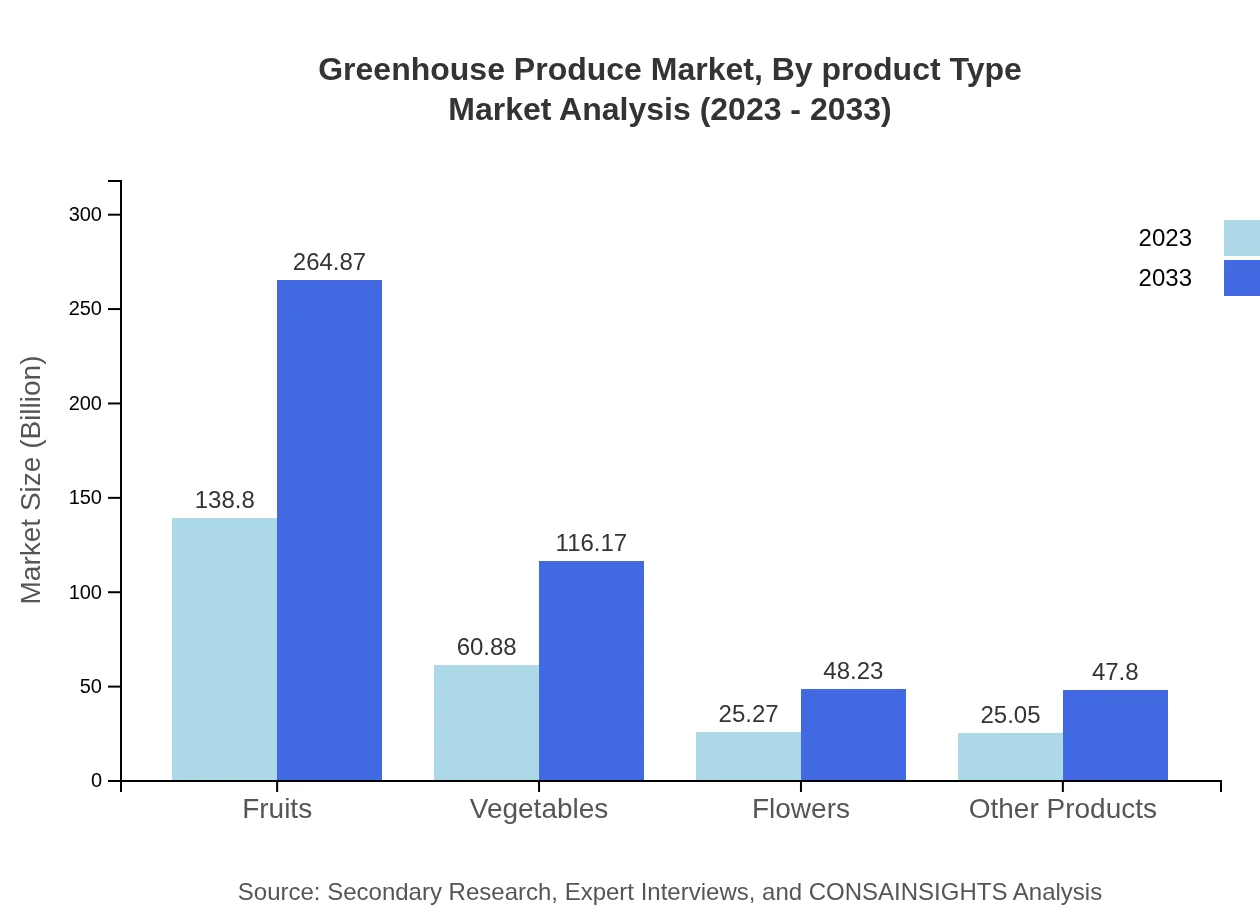
Greenhouse Produce Market Analysis By Product Type
In 2023, the greenhouse produce market by product type indicates that fruits dominate with a size of $138.80 billion, expected to grow to $264.87 billion by 2033, claiming a 55.52% market share. Vegetables follow with a market of $60.88 billion, growing to $116.17 billion and holding a share of 24.35%. Flowers and seedlings reflect significant segments with $25.27 billion and $214.05 billion, respectively, with projections indicating steady growth in these categories.
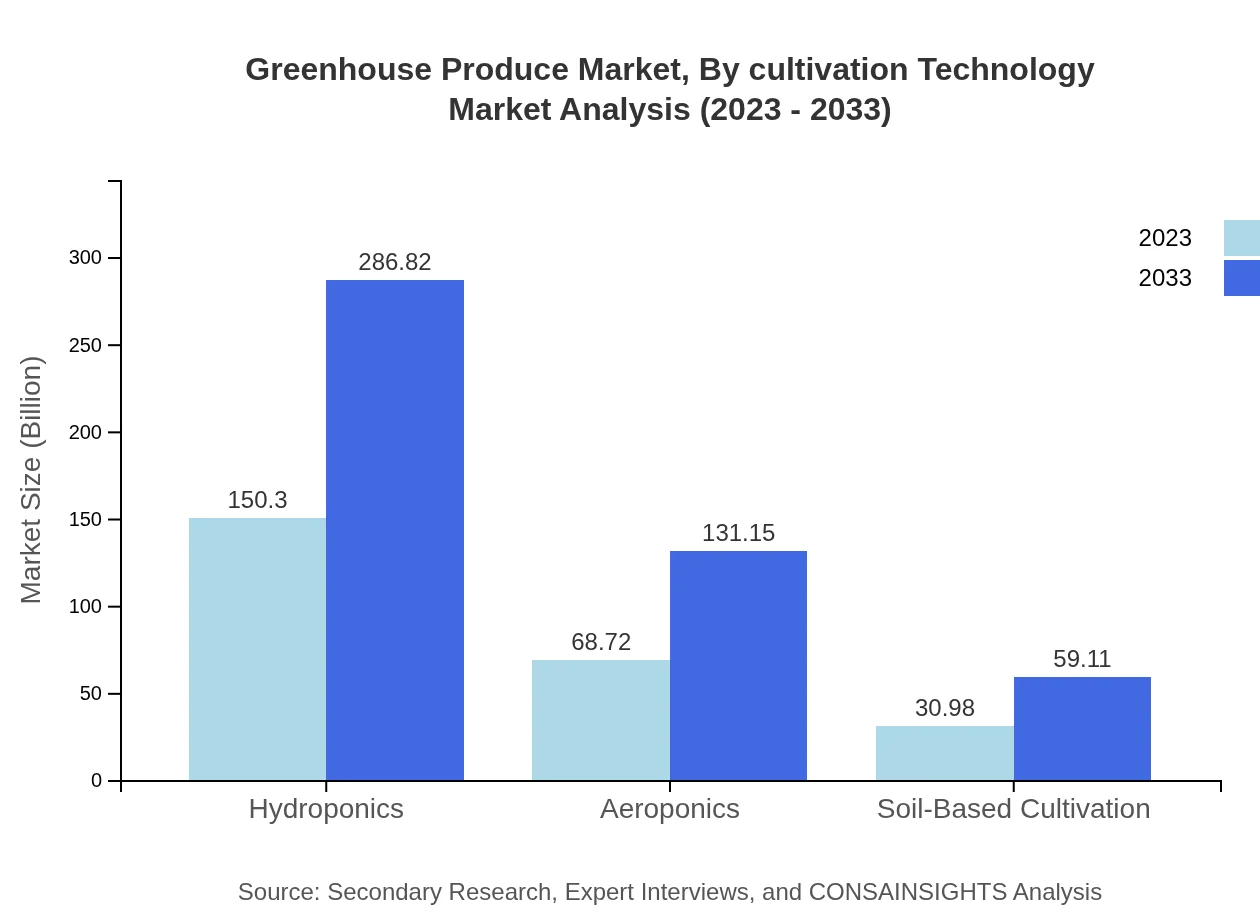
Greenhouse Produce Market Analysis By Cultivation Technology
The cultivation technology segment reveals hydroponics as the largest contributor at $150.30 billion in 2023, growing to $286.82 billion by 2033 with a market share of 60.12%. Aeroponics also shows promising growth, expected to rise from $68.72 billion to $131.15 billion, while soil-based cultivation is consolidating at a smaller scale.
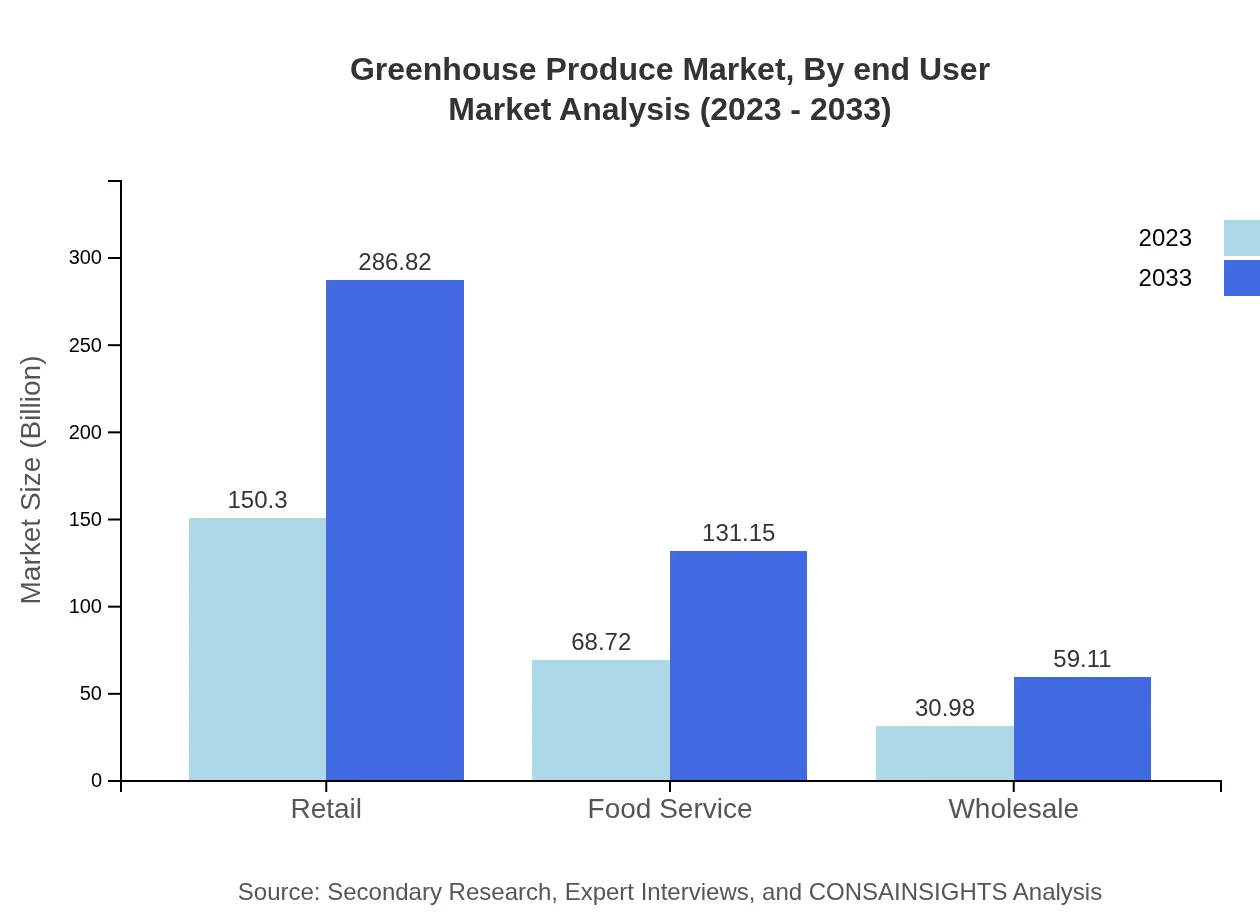
Greenhouse Produce Market Analysis By End User
Retail leads the end-user segment, with a market size of $150.30 billion in 2023 growing to $286.82 billion by 2033, corresponding to a share of 60.12%. The food service sector, witnessing parallel growth from a market of $68.72 billion to $131.15 billion, shows the trend towards integrating fresh produce into dining experiences.
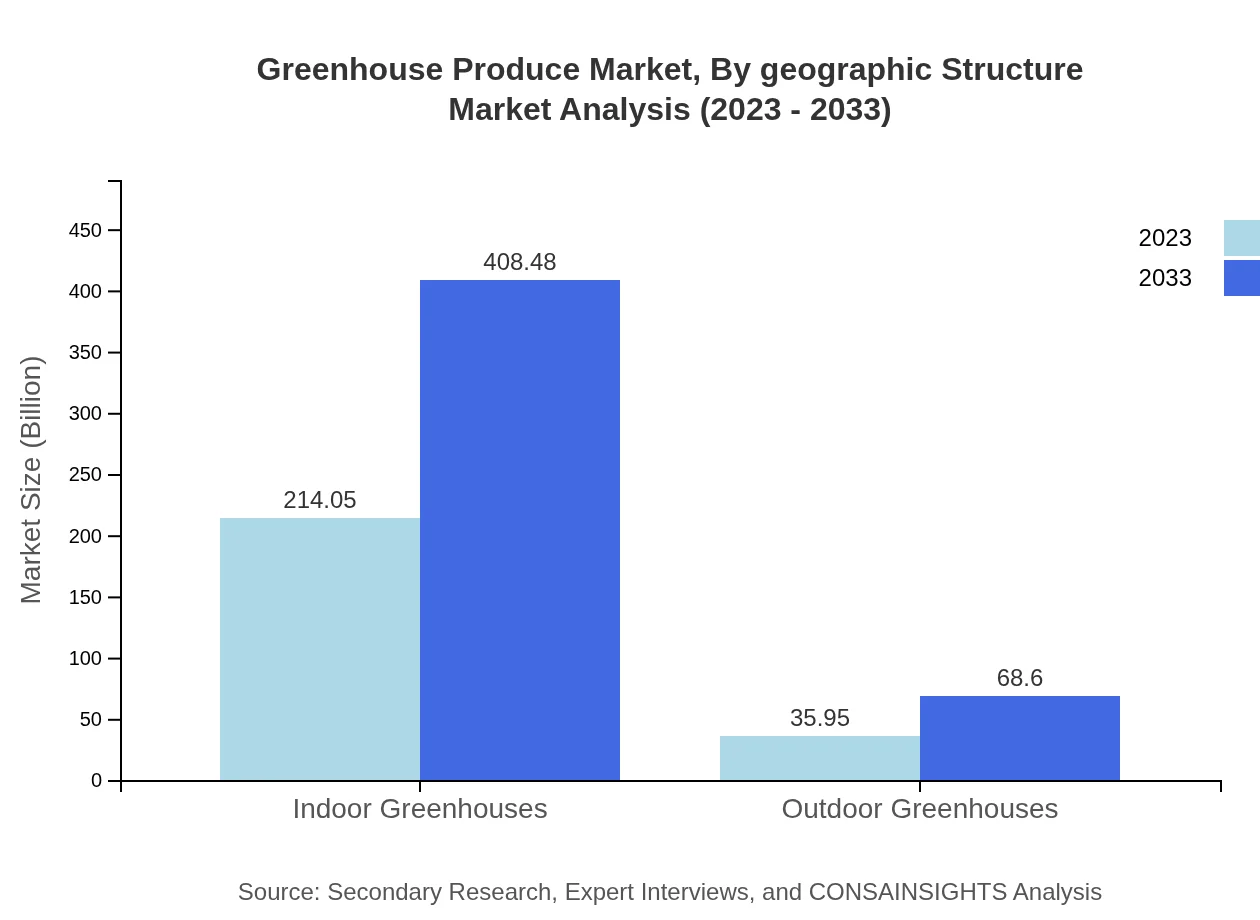
Greenhouse Produce Market Analysis By Geographic Structure
This segment evaluates the geographical distribution, highlighting North America as the strongest, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. Each region’s specific dynamics, varying infrastructural developments, demand for fresh produce, and government policies significantly influence market behaviors and opportunities.
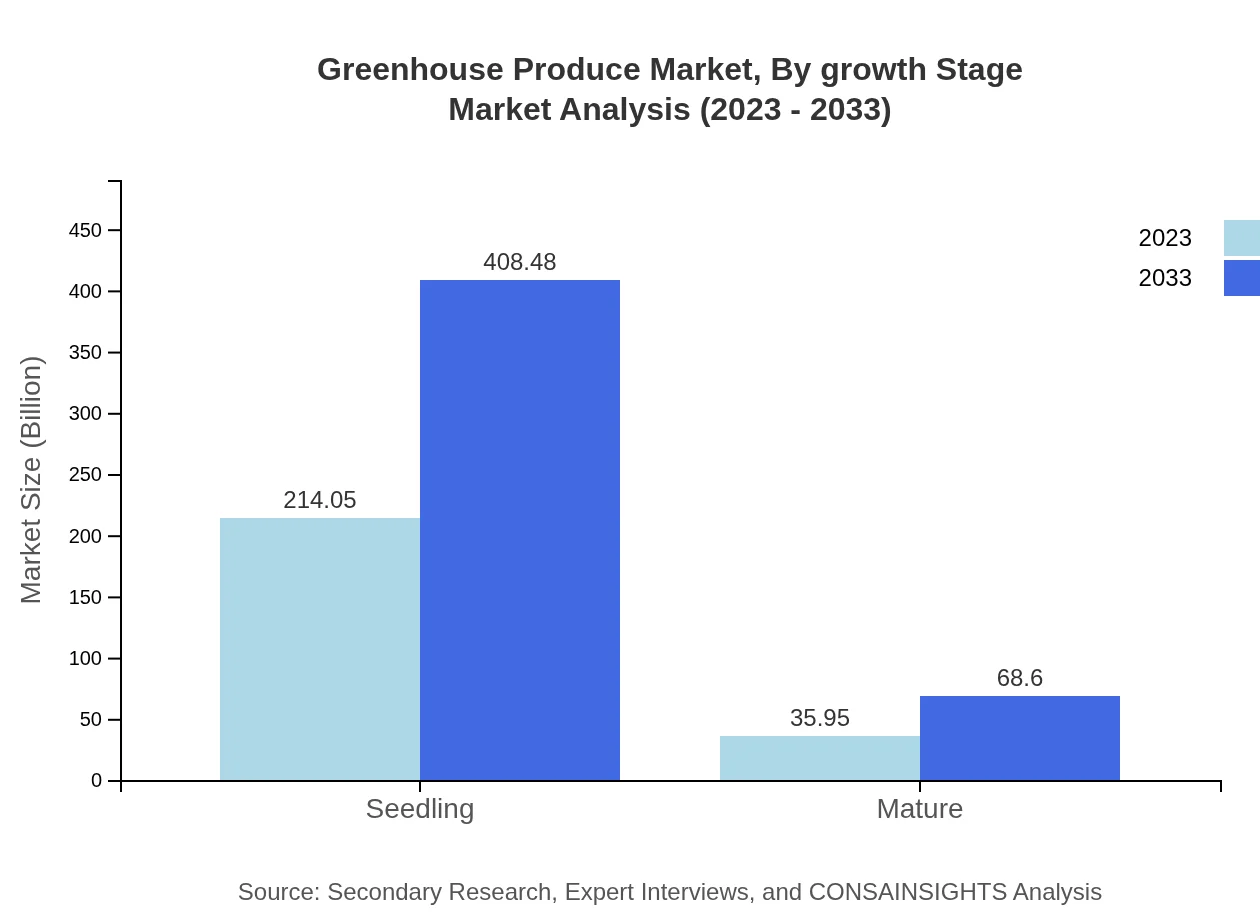
Greenhouse Produce Market Analysis By Growth Stage
This segment assesses greenhouse production stages from seedling to mature plants. Seedlings represent the majority stake at $214.05 billion growing to $408.48 billion by 2033. Mature plants signify a critical market with a share of 14.38%, indicating a balanced approach in producing both young and fully grown produce.
Greenhouse Produce Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Greenhouse Produce Industry
Netafim:
A pioneering company in greenhouse irrigation systems, Netafim specializes in drip irrigation solutions tailored for optimal water efficiency.Royal Brinkman:
Royal Brinkman is a global provider of products and solutions for greenhouse horticulture, focusing on technological innovations to enhance crop yields.Valoya:
Valoya is at the forefront of LED lighting solutions for greenhouses, improving photosynthetic efficiency and energy savings.BrightFarms:
A leader in building and operating greenhouse farms, BrightFarms focuses on sustainable farming practices to supply local fresh produce.Sundrop Farms:
Specializing in solar-thermal greenhouses, Sundrop Farms leverages renewable energy to support sustainable food production.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of greenhouse Produce?
The greenhouse produce market size is projected to reach $250 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 6.5% from its current size in 2023.
What are the key market players or companies in this greenhouse Produce industry?
Key players in the greenhouse produce industry include major agri-tech firms, seed companies, and retailers specializing in hydroponics and climate-controlled farming solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the greenhouse Produce industry?
Growth is driven by rising global food demand, advancements in greenhouse technology, sustainable practices, and an increasing preference for fresh produce.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the greenhouse Produce?
North America is the fastest-growing region, with market size growing from $94.50 million in 2023 to $180.34 million by 2033, showing tremendous investment in agricultural technology.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the greenhouse Produce industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific requirements of stakeholders in the greenhouse-produce sector, ensuring relevant insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this greenhouse Produce market research project?
Expect comprehensive reports including market analysis, forecasts, segment breakdowns, and insights into competitive landscapes within the greenhouse produce market.
What are the market trends of greenhouse Produce?
Current trends include increased adoption of indoor farming, sustainability practices, precision agriculture technologies, and the rising popularity of organic and locally sourced products.