Healthcare Edi Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: healthcare-edi
Healthcare Edi Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Healthcare EDI market from 2023 to 2033, providing insights into market size, growth trends, regional dynamics, industry challenges, and emerging technologies that influence this rapidly evolving sector.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
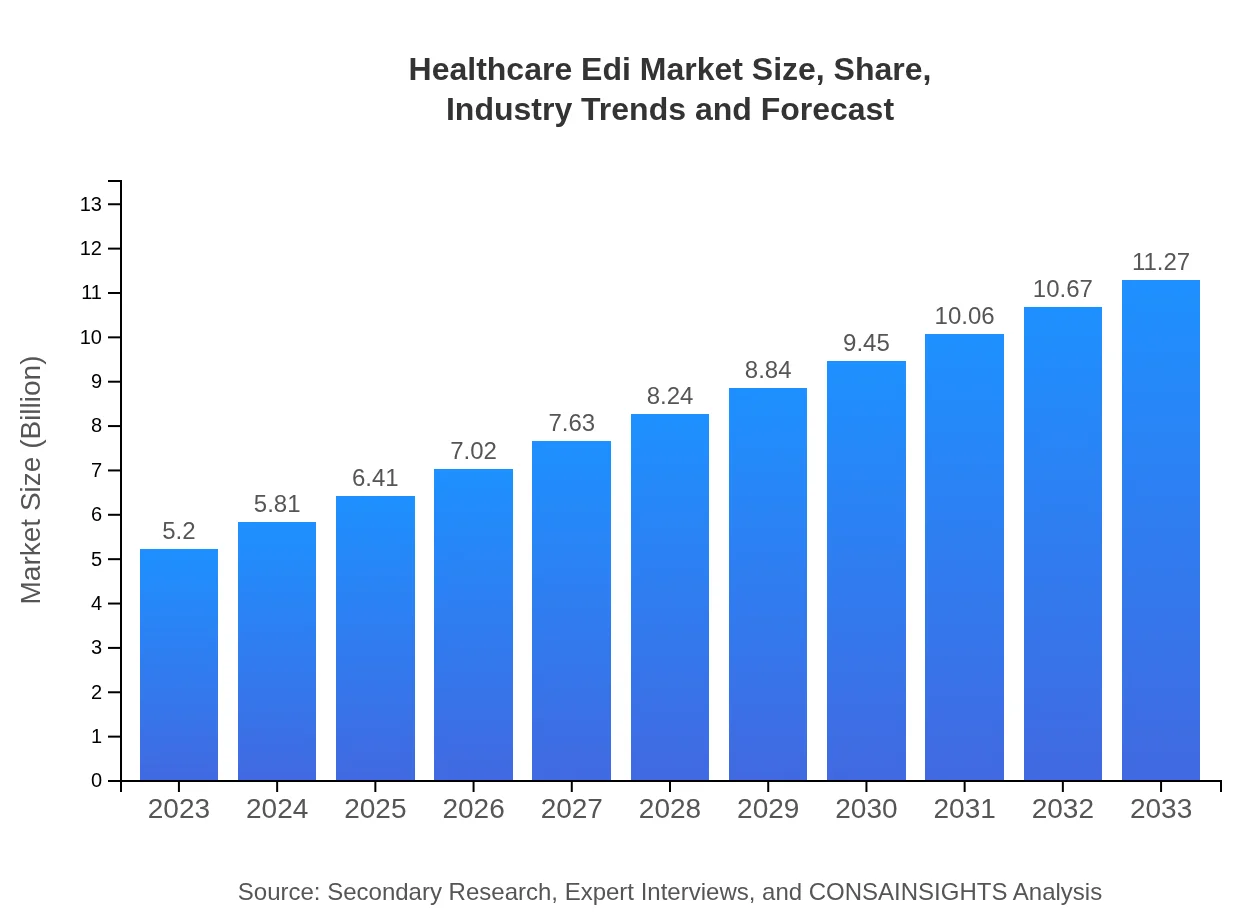
| 2023 Market Size | $5.20 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $11.27 Billion |
| Top Companies | McKesson Corporation, Cerner Corporation, Epic Systems Corporation, Informatica, NextGen Healthcare |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Healthcare Edi Market Overview
Customize Healthcare Edi Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Healthcare Edi market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Healthcare Edi's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Healthcare Edi
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Healthcare Edi market in 2023?
Healthcare Edi Industry Analysis
Healthcare Edi Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Healthcare Edi Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Healthcare Edi Market Report:
Europe's Healthcare EDI market is poised for significant growth, from $1.60 billion in 2023 to approximately $3.47 billion in 2033, driven by healthcare reform initiatives and a focus on interoperability standards.Asia Pacific Healthcare Edi Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as a key player in the Healthcare EDI market, showing a market size of $0.92 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $2.00 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing healthcare spending and a shift towards digitization in healthcare processes.North America Healthcare Edi Market Report:
North America leads the market with a size of $1.93 billion in 2023, anticipated to reach $4.17 billion by 2033. The region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, high technological adoption, and stringent regulatory requirements promoting EDI usage.South America Healthcare Edi Market Report:
In South America, the Healthcare EDI market is estimated at $0.05 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand to $0.10 billion by 2033. Growth is supported by increasing government initiatives aimed at enhancing healthcare data management and patient care.Middle East & Africa Healthcare Edi Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa regions are also witnessing growth, with a current market size of $0.70 billion expected to rise to $1.52 billion by 2033. The increasing focus on improving healthcare systems and data security protocols is fueling this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Healthcare Edi Market Analysis By Type
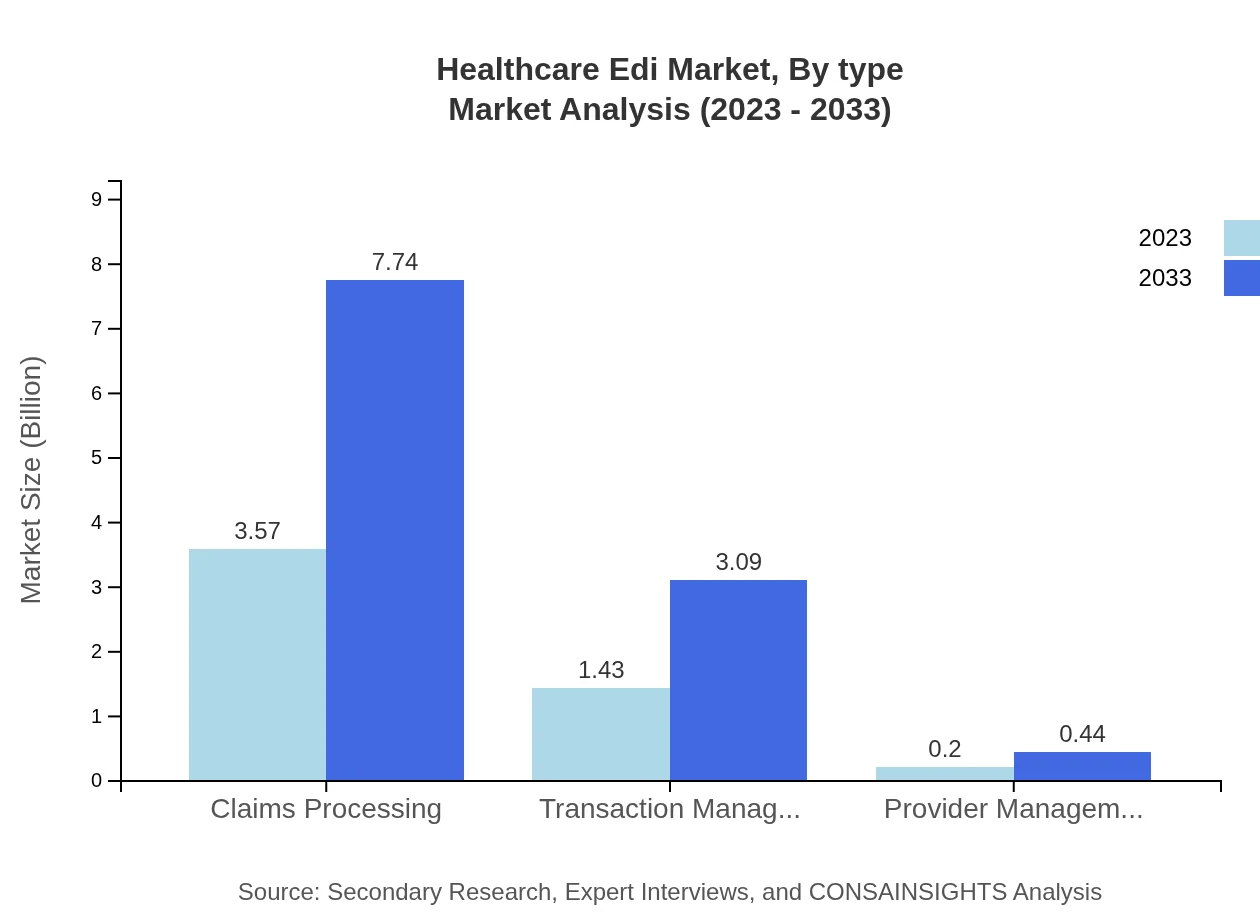
In the Healthcare EDI market, the claims processing segment leads with a market size of $3.57 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $7.74 billion by 2033, capturing a significant share of 68.65%. Transaction management follows with $1.43 billion, projected to increase to $3.09 billion. Provider management, though smaller, plays a crucial role in managing relationships with healthcare professionals, reflecting growing emphasis on the quality of care through discrete market segments.
Healthcare Edi Market Analysis By Application
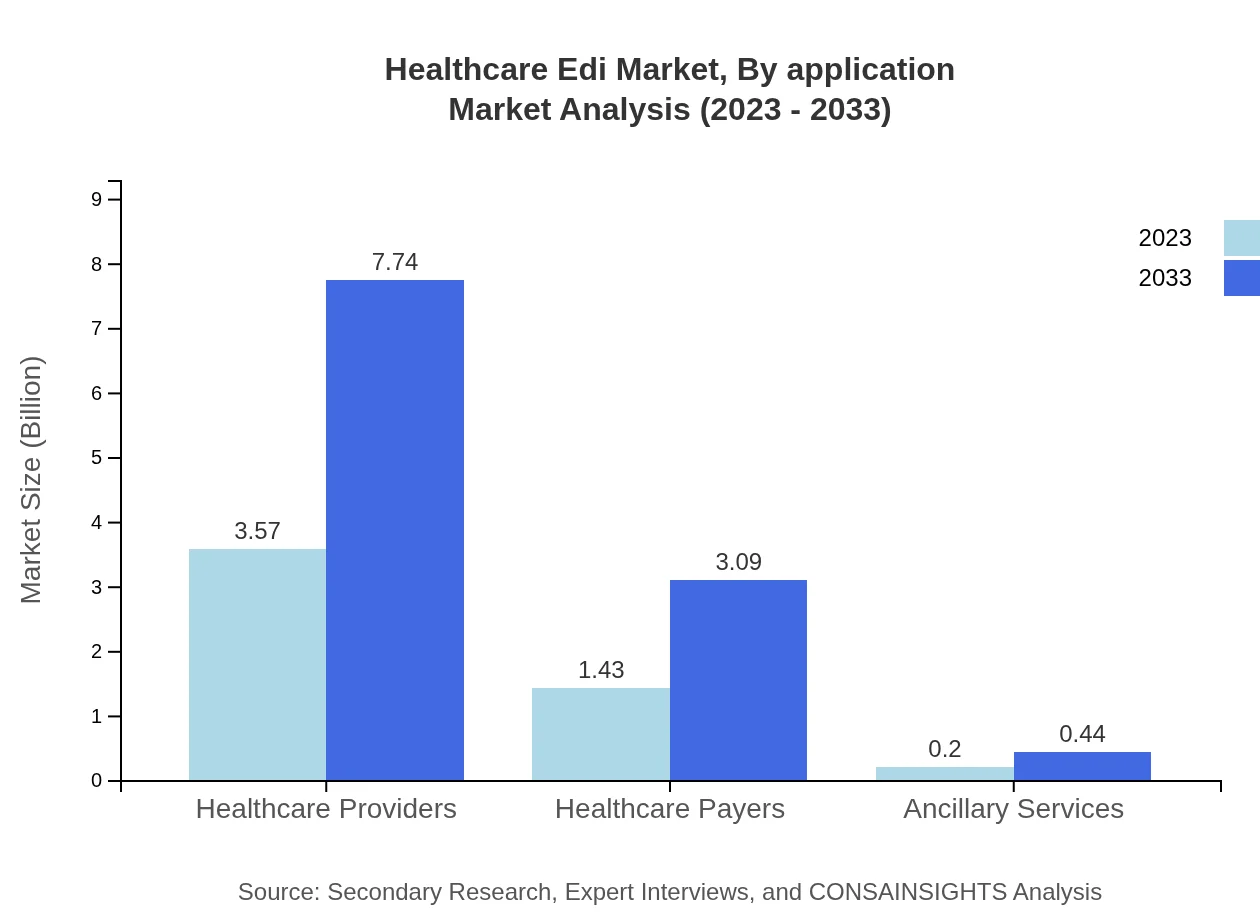
The applications segment of the Healthcare EDI market is driven by healthcare providers and payers, with the providers’ share growing significantly due to the need for streamlined billing and patient information management. Healthcare payers contribute significantly due to requirements for secure transactions and data accuracy in claims processing. Ancillary services also hold potential for growth as organizations seek integrated solutions.
Healthcare Edi Market Analysis By End User
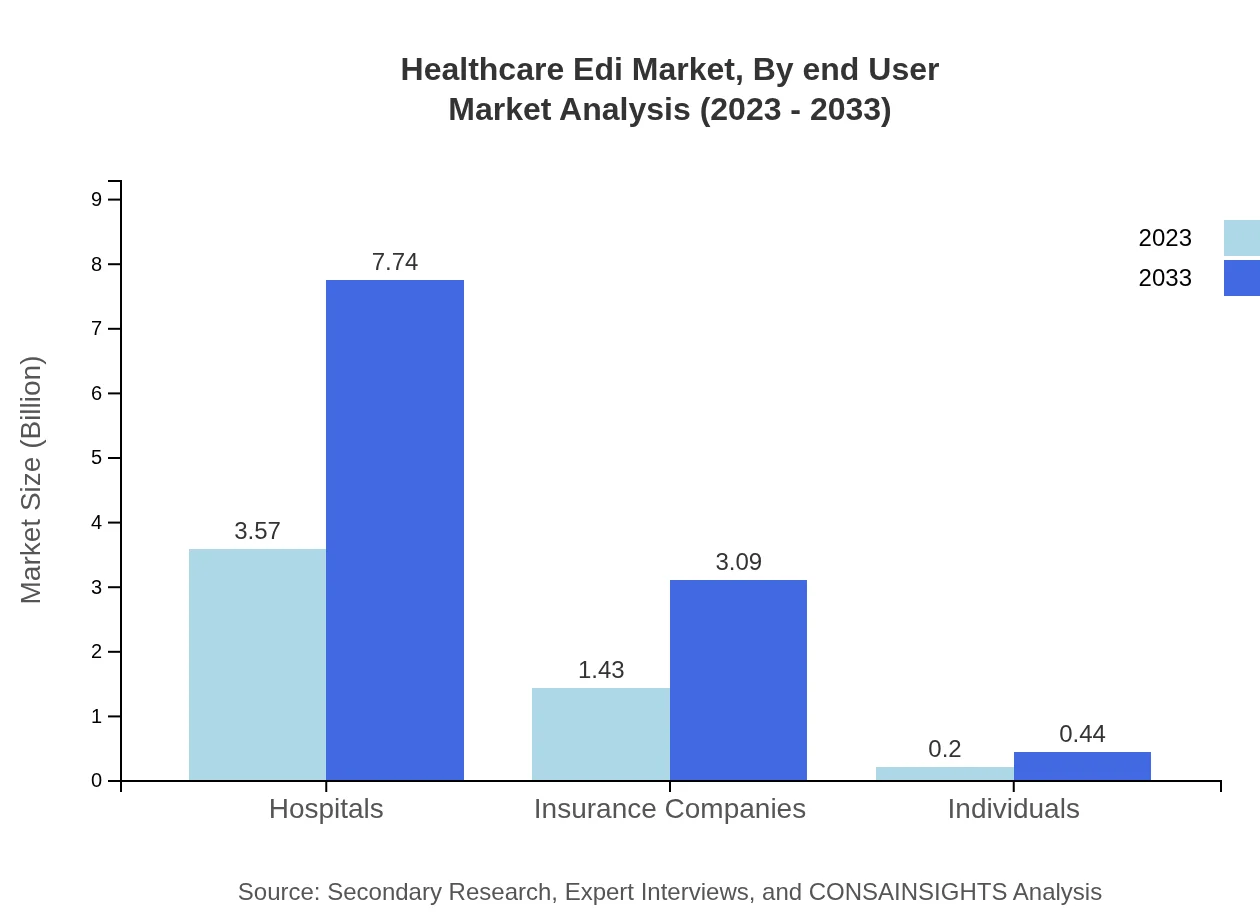
Healthcare providers accounted for the largest portion of the market with significant investments in EDI solutions aimed at improving operational efficiencies. Conversely, insurance companies are increasingly adopting EDI to facilitate secure communication with providers, enhance claim accuracy, and improve customer satisfaction through timely reimbursements.
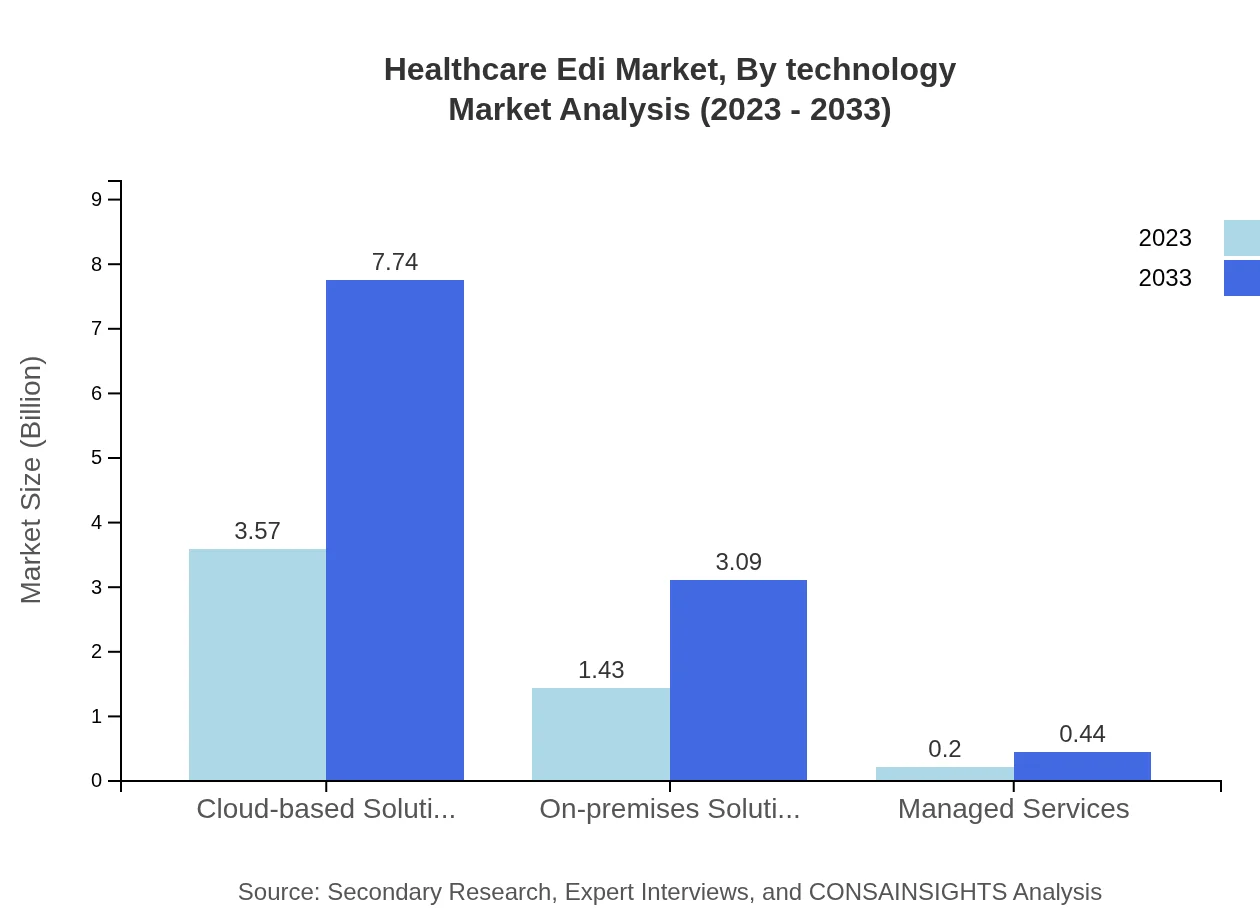
Healthcare Edi Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment of Healthcare EDI is heavily influenced by the rise of cloud-based solutions, which dominated the market due to their flexibility and cost-efficiency. On-premises solutions retain a share but are less favored due to higher maintenance costs. Managed services are growing in response to the demand for outsourced IT solutions, allowing organizations to focus on core competencies.
Healthcare Edi Market Analysis By Regulatory
Regulatory compliance is integral to the Healthcare EDI market, with HIPAA and other mandates driving adoption. The need for compliance with state and federal regulations ensures that healthcare organizations implement EDI solutions, thereby fostering growth within this segment. This trend is likely to continue, especially as regulators emphasize data security and patient privacy.
Healthcare Edi Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Healthcare Edi Industry
McKesson Corporation:
A leading healthcare company offering a wide range of EDI solutions designed to streamline healthcare operations and facilitate efficient data exchange.Cerner Corporation:
Known for providing integrated EDI solutions that enhance healthcare management, Cerner's technology aligns closely with regulatory requirements.Epic Systems Corporation:
Focusing on EDI implementations within electronic health record systems, Epic Systems is pivotal in improving interoperability in healthcare.Informatica:
Offers data integration solutions that include EDI capabilities, helping healthcare companies manage vast amounts of patient data effectively.NextGen Healthcare:
Provides cloud-based EDI solutions that are instrumental in helping practices improve their operational efficiencies.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of healthcare Edi?
The global Healthcare EDI market is projected to grow from $5.2 billion in 2023 to an estimated market size by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 7.8%. This growth signifies the increasing adoption of electronic data interchange in healthcare.
What are the key market players or companies in the healthcare Edi industry?
Key players in the Healthcare EDI market include prominent companies like Optum, Change Healthcare, and Cerner Corporation, which contribute significantly to technological advancements and service offerings in electronic data interchange solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the healthcare Edi industry?
The growth of the Healthcare EDI industry is driven by factors such as enhanced efficiency in claims processing, increasing demand for interoperability, and regulatory requirements mandating electronic transactions across healthcare organizations.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the healthcare Edi?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for Healthcare EDI, anticipated to expand from $0.92 billion in 2023 to $2.00 billion by 2033. Growth is driven by rising healthcare expenditures and digital transformation in evolving economies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the healthcare Edi industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients in the Healthcare EDI sector, enabling organizations to gain relevant insights and make informed business decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this healthcare Edi market research project?
Deliverables from the Healthcare EDI market research project include comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth projections, competitive analysis, and segmentation insights, tailored to meet organizational needs for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of healthcare Edi?
Current trends in the Healthcare EDI market include a shift towards cloud-based solutions, increased integration of AI and machine learning for data analytics, and an emphasis on regulatory compliance to enhance operational efficiencies.