High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: high-altitude-pseudo-satellites
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the High Altitude Pseudo Satellites market, covering key aspects such as market size, segmentation, regional insights, leading players, and future trends for the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
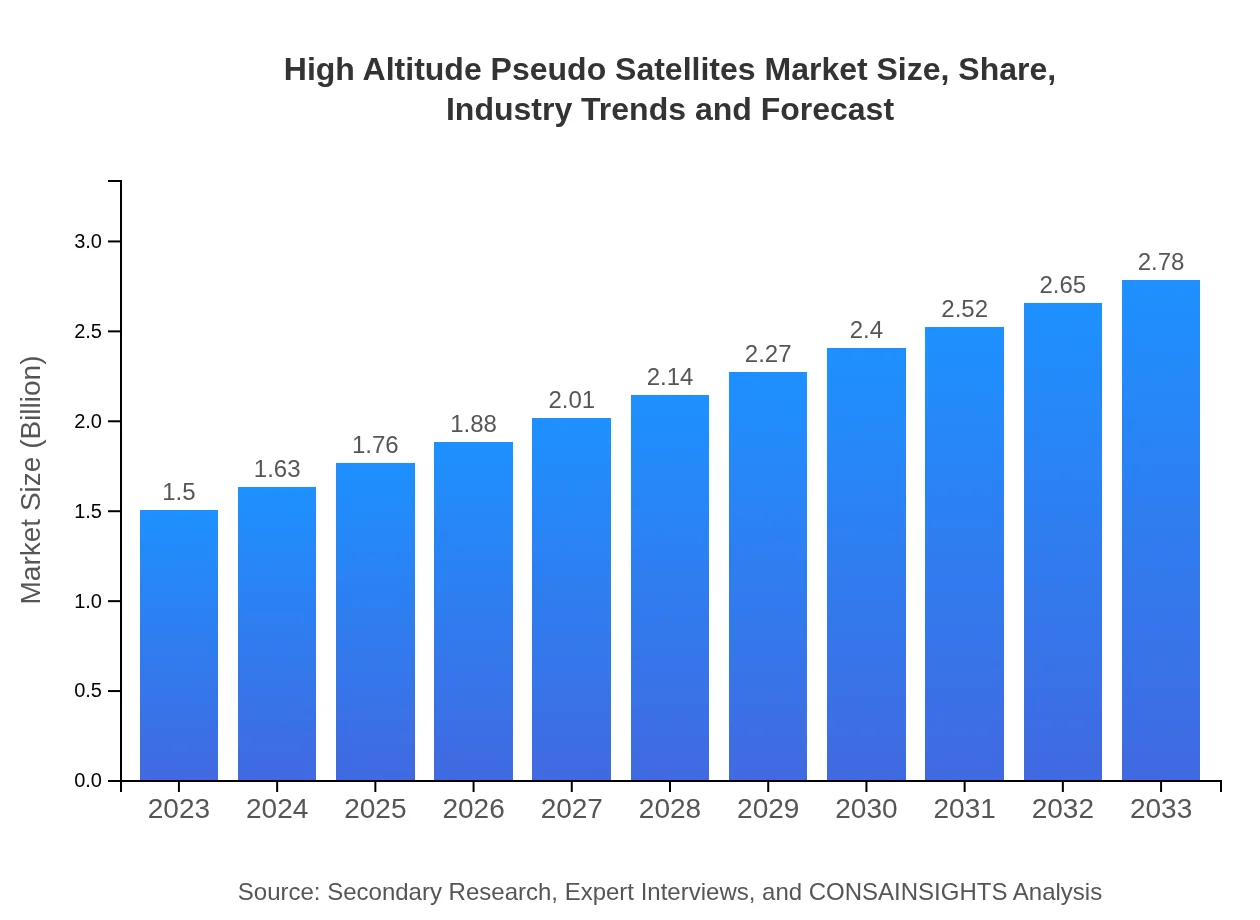
| 2023 Market Size | $1.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $2.78 Billion |
| Top Companies | Airbus, Lockheed Martin, Aerial Technologies, Thales Group |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Overview
Customize High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand High Altitude Pseudo Satellites's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in High Altitude Pseudo Satellites
What is the Market Size & CAGR of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites market in 2023?
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Industry Analysis
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report:
The European market stands at $450 million in 2023, expected to grow to $830 million by 2033. Regulatory support for telecommunications and environmental monitoring initiatives contributes to market expansion in this region.Asia Pacific High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market was valued at $280 million in 2023 and is expected to grow to $510 million by 2033. The growing focus on military modernization and increasing telecommunications needs in developing countries are major growth drivers.North America High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report:
North America is the largest market, valued at $550 million in 2023, and projected to grow to $1.02 billion by 2033. The presence of key players and significant government spending on defense and surveillance technologies are primary growth factors.South America High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report:
South America represents a smaller market, with a size of $80 million in 2023, projected to reach $150 million by 2033. Increased investment in connectivity infrastructure is expected to boost market growth in this region.Middle East & Africa High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market was valued at $140 million in 2023 and is anticipated to grow to $260 million by 2033. The demand for improved communication and surveillance capabilities, driven by regional security challenges, is a primary driver.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
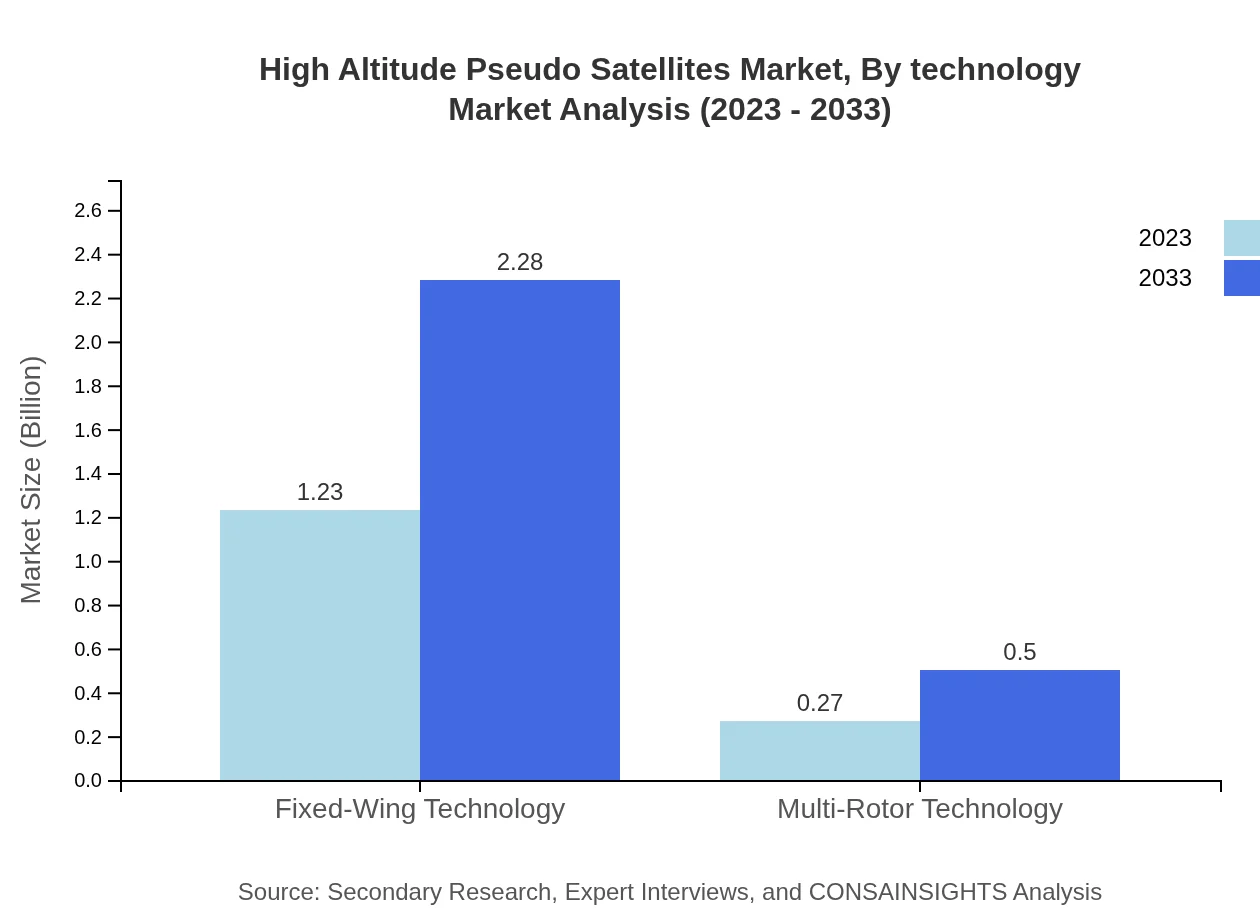
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment includes Fixed-Wing and Multi-Rotor technologies. Fixed-Wing technology leads the market with a size of $1.23 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $2.28 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, Multi-Rotor technology is expected to contribute significantly, with a market size of $270 million in 2023, growing to $500 million by 2033.
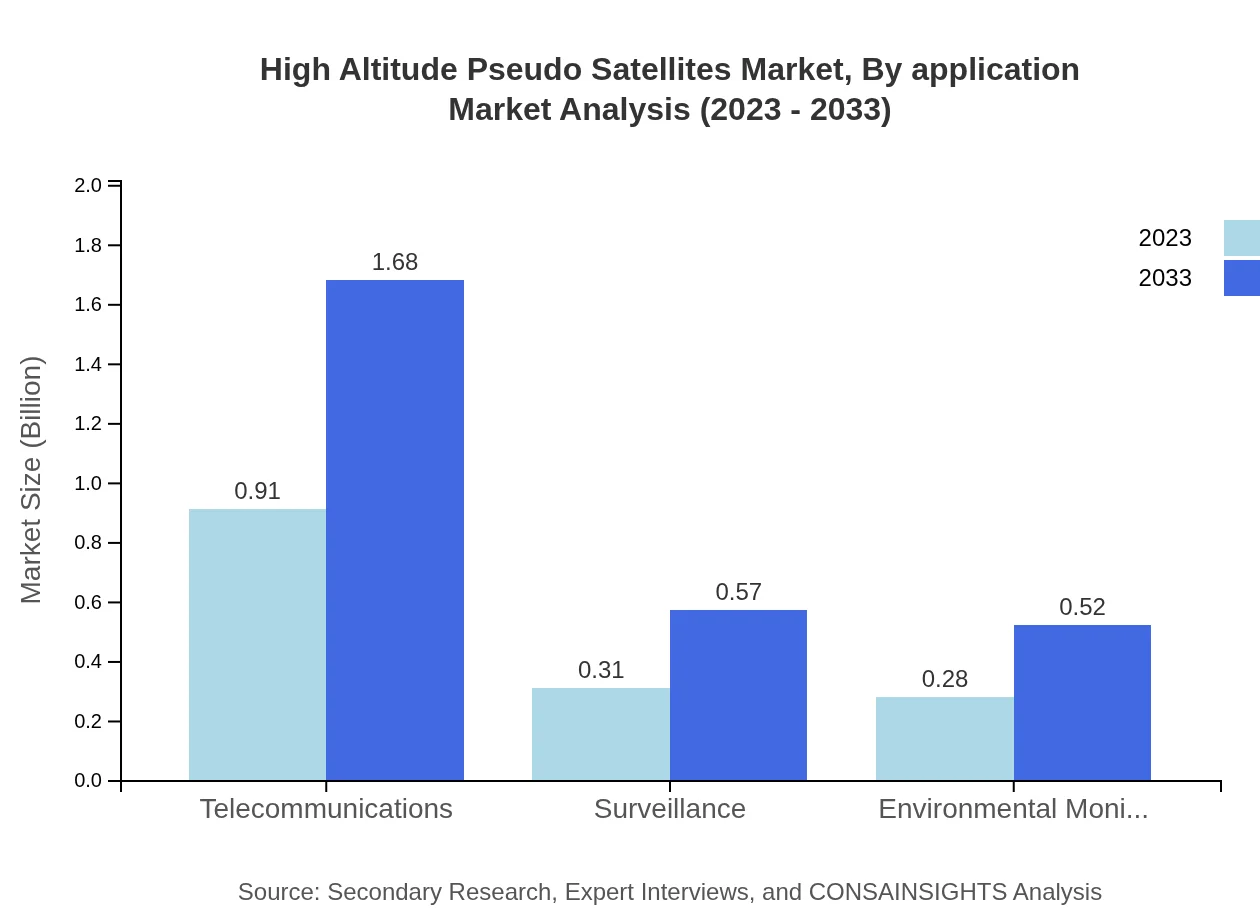
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Analysis By Application
Telecommunications is the dominant application segment, with a market size of $910 million in 2023, escalating to $1.68 billion by 2033. Defense-related applications also hold a substantial share, currently at $760 million and projected to reach $1.40 billion by 2033.
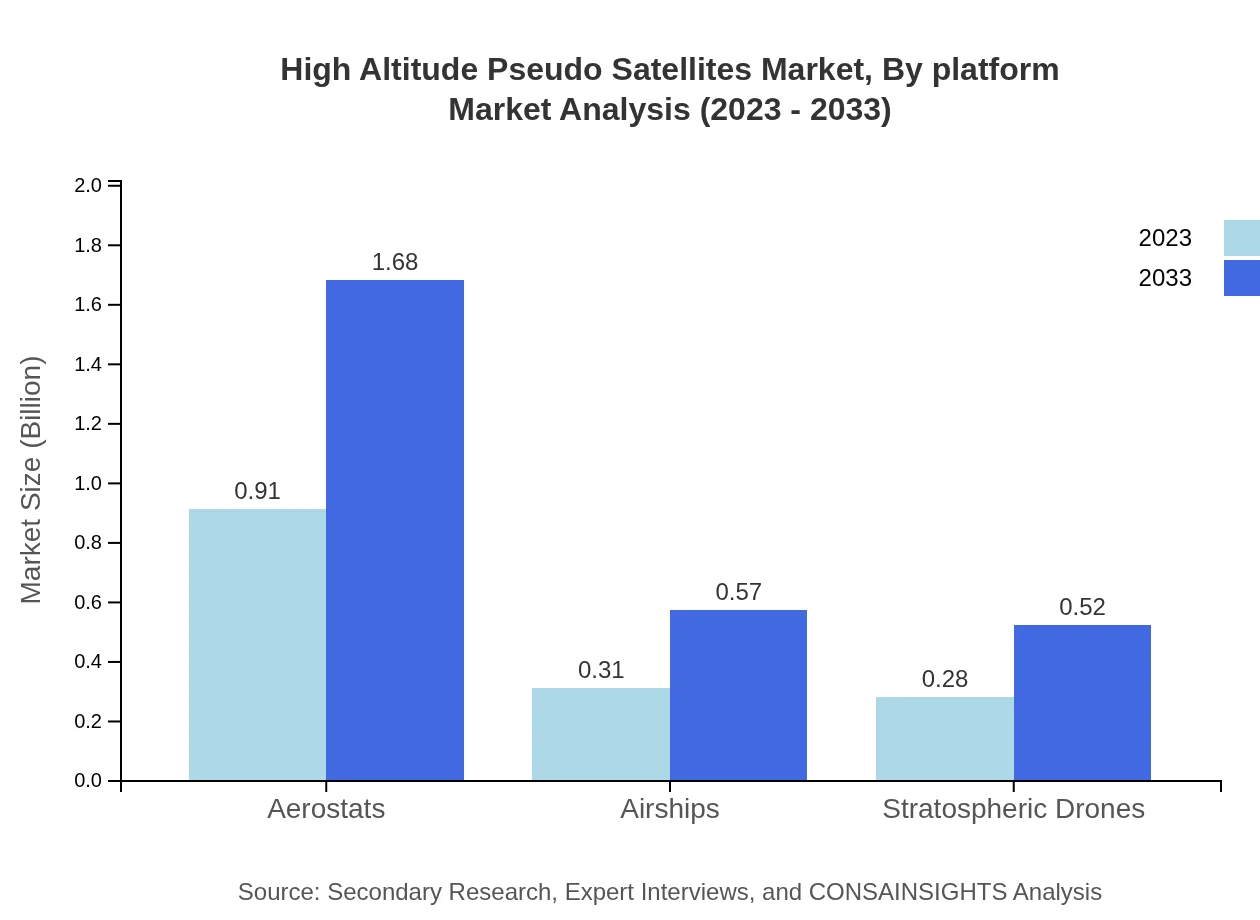
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Analysis By Platform
Platforms include Aerostats, Airships, and Drones. Aerostats currently dominate this market with a valuation of $910 million, expected to grow to $1.68 billion by 2033. Airships follow with expected growth from $310 million to $570 million, while Stratospheric Drones are projected to rise from $280 million to $520 million in the same period.
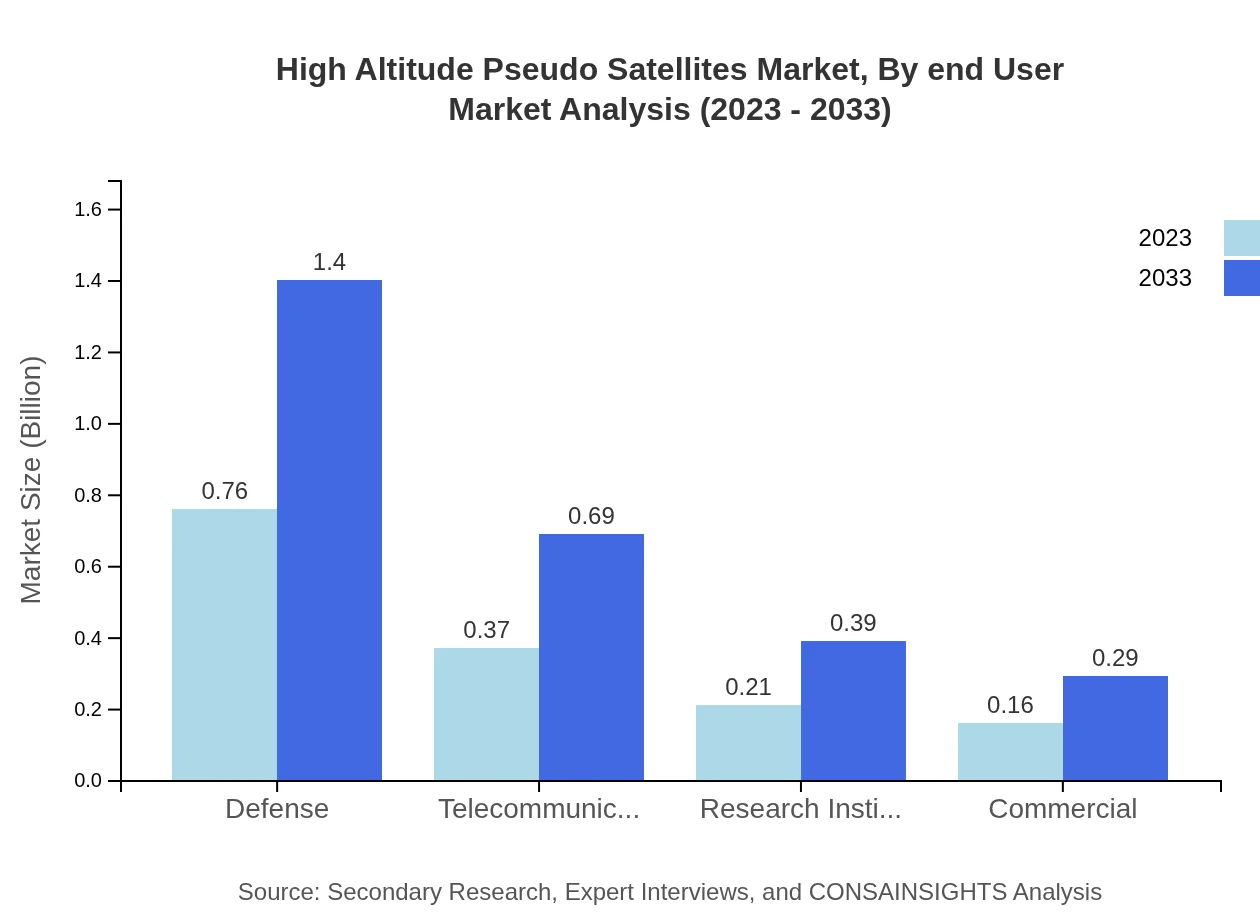
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Analysis By End User
End-user applications include commercial companies, defense agencies, and research institutions. The defense sector takes up a significant market share of 50.54% in 2023. Research institutions account for 14.06% of the market, with a growth trajectory expected to keep pace with defense applications as more research projects integrate HAPS technology.
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in High Altitude Pseudo Satellites Industry
Airbus:
Airbus is a leader in aerospace and defense and has developed HAPS technology aimed at providing connectivity and environmental monitoring.Lockheed Martin:
Lockheed Martin offers advanced HAPS solutions primarily for defense purposes, integrating cutting-edge technology in platforms.Aerial Technologies:
Aerial Technologies specializes in innovative drone-based HAPS, focusing on telecommunications and surveillance applications.Thales Group:
Thales Group provides comprehensive HAPS solutions, particularly in defense and surveillance, leveraging their extensive aerospace expertise.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of high Altitude Pseudo Satellites?
The global high-altitude pseudo-satellites market is projected to reach approximately $1.5 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023. This growth is driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for various applications.
What are the key market players or companies in this high Altitude Pseudo Satellites industry?
Key players in the high-altitude pseudo-satellites market include companies specializing in aerospace technology, telecommunications, defense technologies, and research institutions. These organizations are focused on developing innovative solutions and products to enhance capabilities in surveillance and telecommunications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the high Altitude Pseudo Satellites industry?
The growth of the high-altitude pseudo-satellites market is driven by several factors, including the rising need for persistent surveillance, expanded telecommunications coverage, and advancements in aeronautical technologies. Furthermore, initiatives to enhance environmental monitoring systems contribute significantly to market growth.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the high Altitude Pseudo Satellites?
North America is recognized as the fastest-growing region for high-altitude pseudo-satellites, projected to increase its market size from $0.55 billion in 2023 to $1.02 billion by 2033, due to strong investments in defense and telecommunications.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the high Altitude Pseudo Satellites industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific requirements in the high-altitude pseudo-satellites industry, enabling clients to access insights beneficial for strategic decision-making and investment planning.
What deliverables can I expect from this high Altitude Pseudo Satellites market research project?
From the high-altitude pseudo-satellites market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market size, forecasts, competitive analysis, detailed regional insights, and potential growth opportunities that are clearly actionable for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of high Altitude Pseudo Satellites?
Emerging trends in the high-altitude pseudo-satellites market include increasing reliance on defense applications, enhancements in fixed-wing technology, and greater collaboration between private and public sectors, fostering innovative solutions in telecommunications and environmental monitoring.