High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: high-fructose-corn-syrup
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report covers the comprehensive analysis of the High Fructose Corn Syrup market from 2023 to 2033, including market size, growth rates, trends, technological impacts, and geographic insights.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
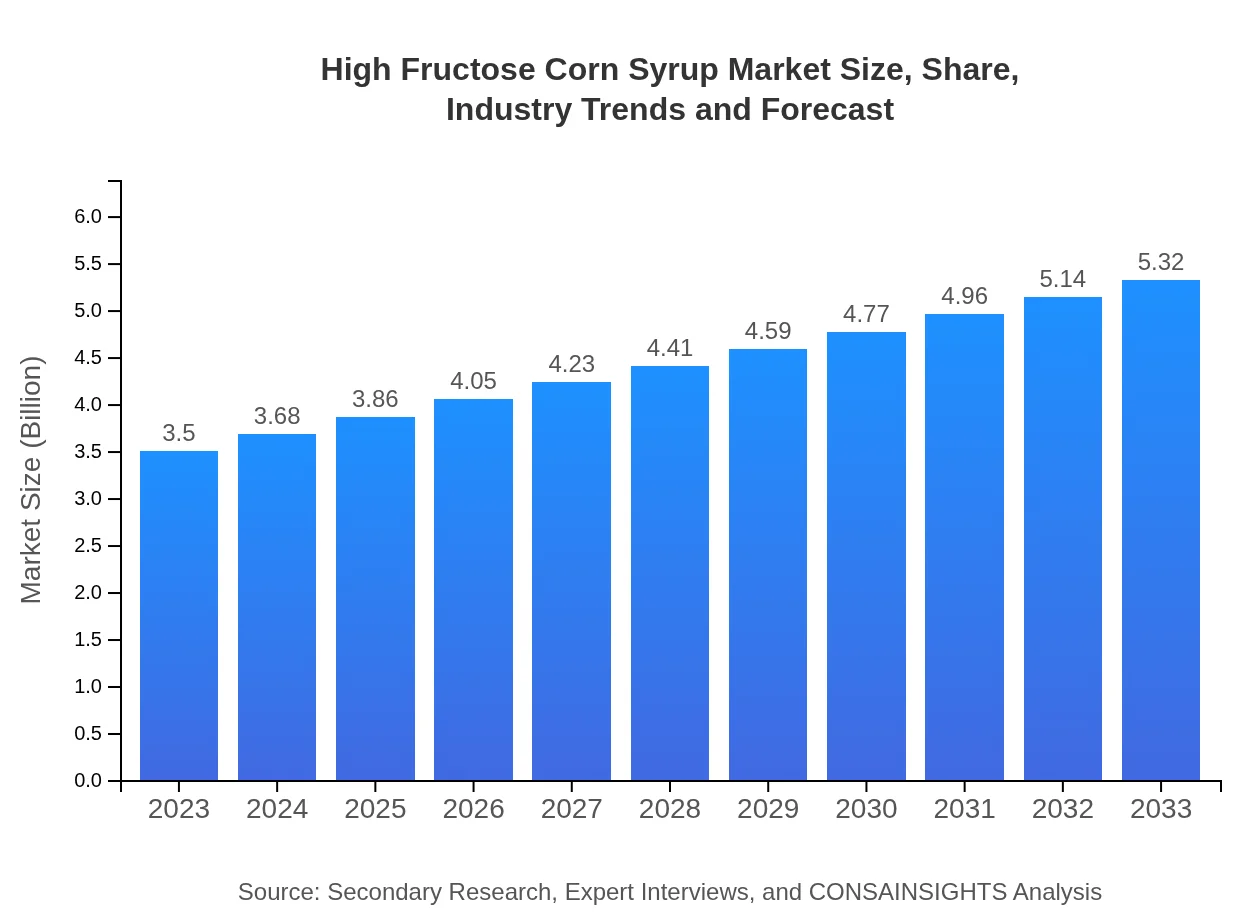
| 2023 Market Size | $3.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $5.32 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill Inc., ADM (Archer Daniels Midland Company), Tate & Lyle, Ingredion Incorporated, Corn Products International |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Overview
Customize High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of High Fructose Corn Syrup market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand High Fructose Corn Syrup's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in High Fructose Corn Syrup
What is the Market Size & CAGR of High Fructose Corn Syrup market in 2023?
High Fructose Corn Syrup Industry Analysis
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report:
In Europe, the HFCS market is anticipated to grow from $1.00 billion in 2023 to $1.52 billion by 2033. Consumer preferences shifting towards low-calorie sweeteners amid strict regulations drive innovations in product formulation, influencing market dynamics.Asia Pacific High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report:
The Asia Pacific market for HFCS is projected to grow from $0.75 billion in 2023 to $1.14 billion by 2033, reflecting an increased demand from growing economies. Key drivers include rising disposable incomes and the expanding beverage sector, alongside urbanization which shifts dietary preferences.North America High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report:
North America dominates the HFCS market, projected to rise from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $1.83 billion by 2033. This market is primarily driven by the demand from food and beverage manufacturers, while ongoing debates about health impacts steer evolving consumer choices.South America High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report:
Latin America shows steady growth in the HFCS market, increasing from $0.34 billion in 2023 to $0.52 billion in 2033. The growth is propelled by the increasing prevalence of soft drinks and processed foods, with local manufacturers seeking competitive advantages through cost-effective ingredients.Middle East & Africa High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa markets are smaller but show promising growth, with values increasing from $0.21 billion in 2023 to $0.32 billion by 2033. Increased urbanization and Western-style eating habits contribute to this upward growth trajectory.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
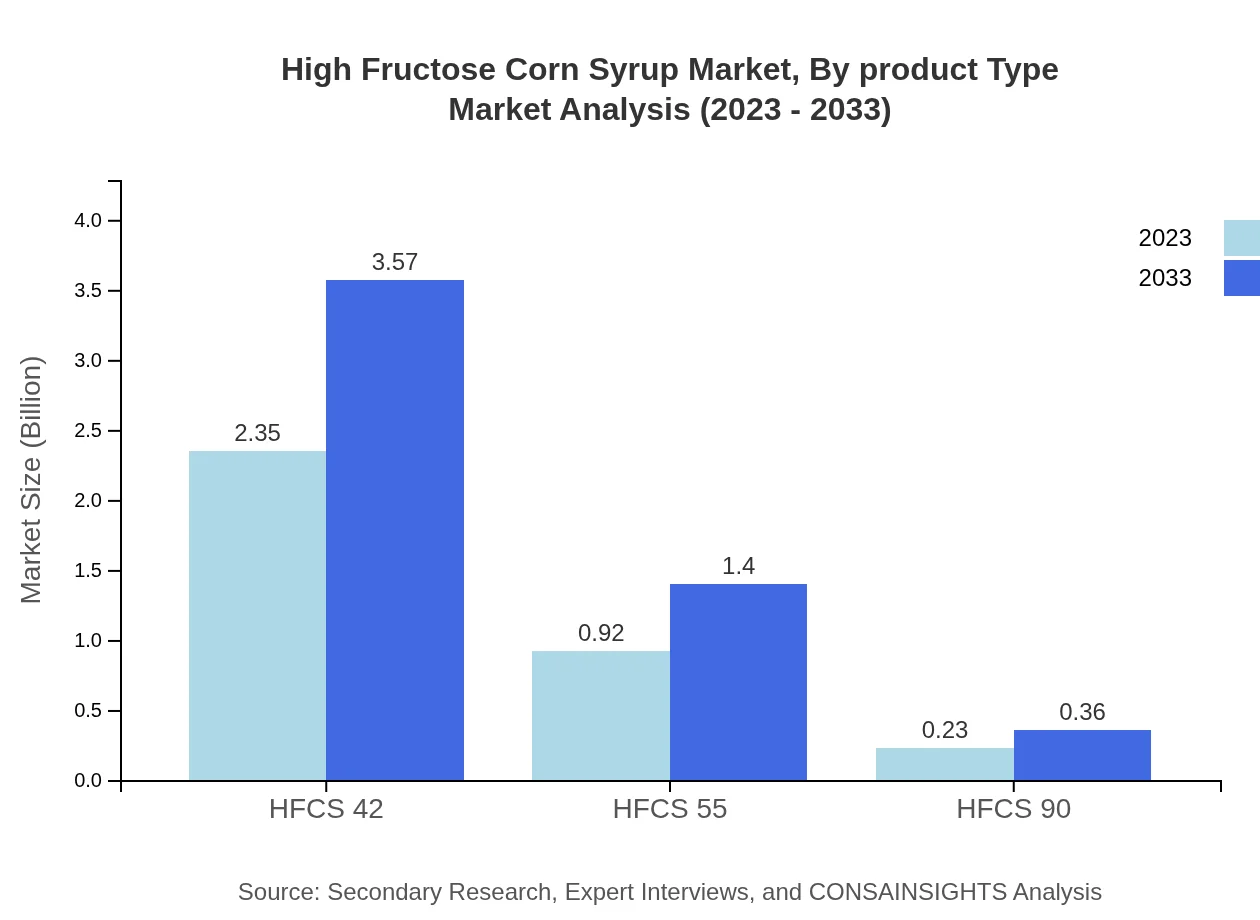
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Analysis By Product Type
The HFCS market is largely available in two types: Liquid HFCS and Powdered HFCS. Liquid HFCS is expected to grow from $3.06 billion in 2023 to $4.66 billion by 2033, accounting for 87.51% of the market share. Powdered HFCS, while smaller, also shows growth potential, from $0.44 billion in 2023 to $0.66 billion in 2033, with a market share of 12.49%.
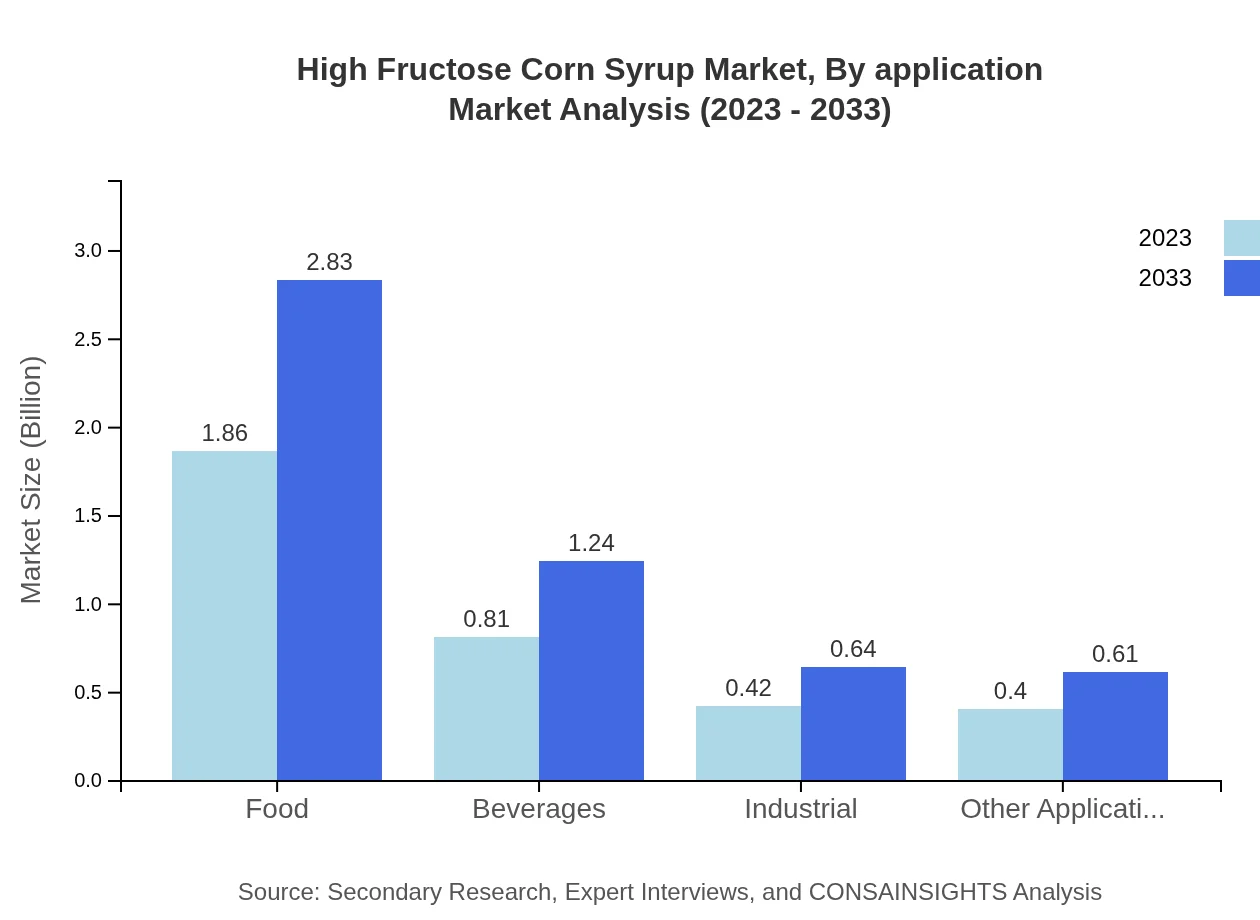
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Analysis By Application
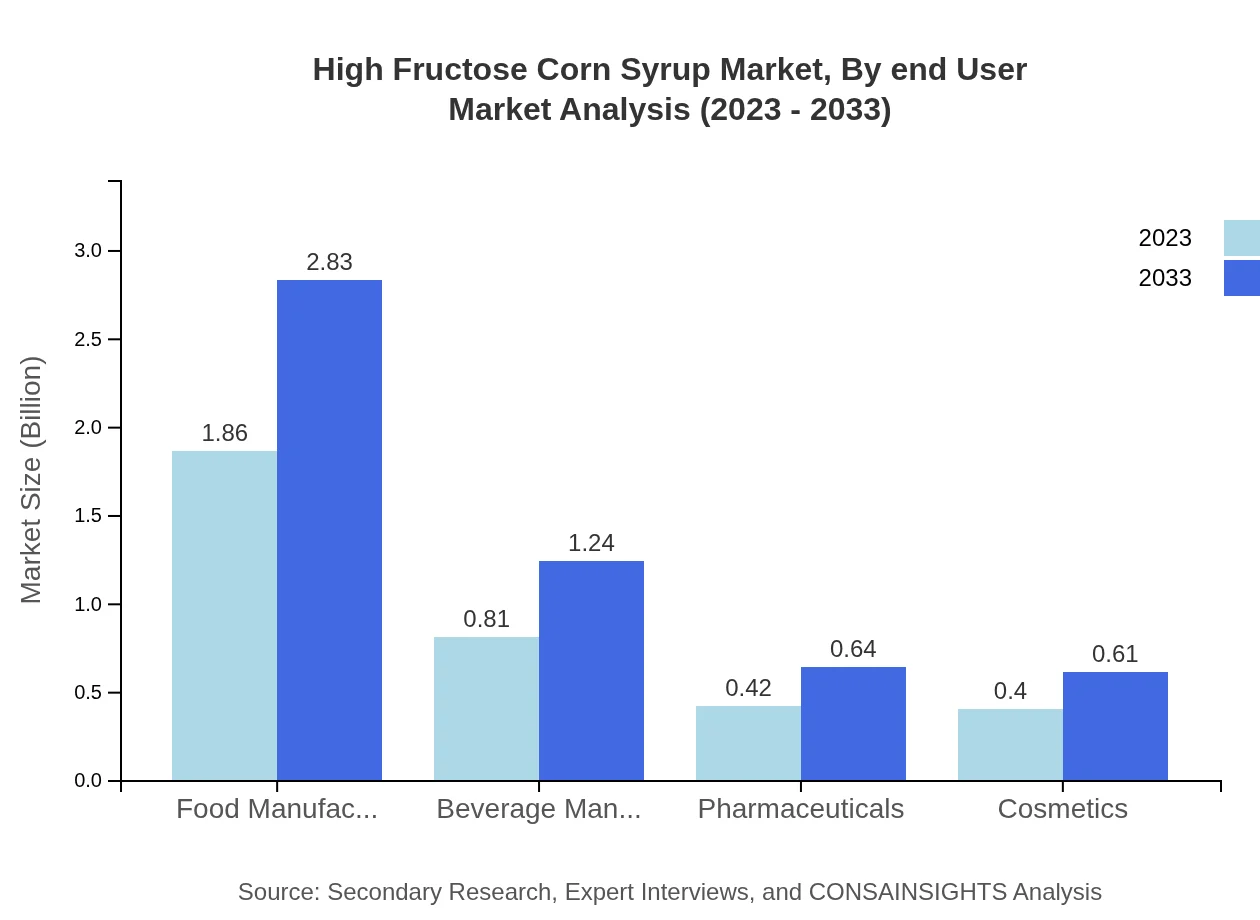
Applications for HFCS are segmented into Food and Beverage Manufacturers, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, and Industrial. Food Manufacturers dominate with $1.86 billion growing to $2.83 billion (53.25%), followed closely by Beverage Manufacturers at $0.81 billion to $1.24 billion (23.24%). Pharmaceuticals constitute 12.02% and cosmetics 11.49%, underscoring diverse usage.
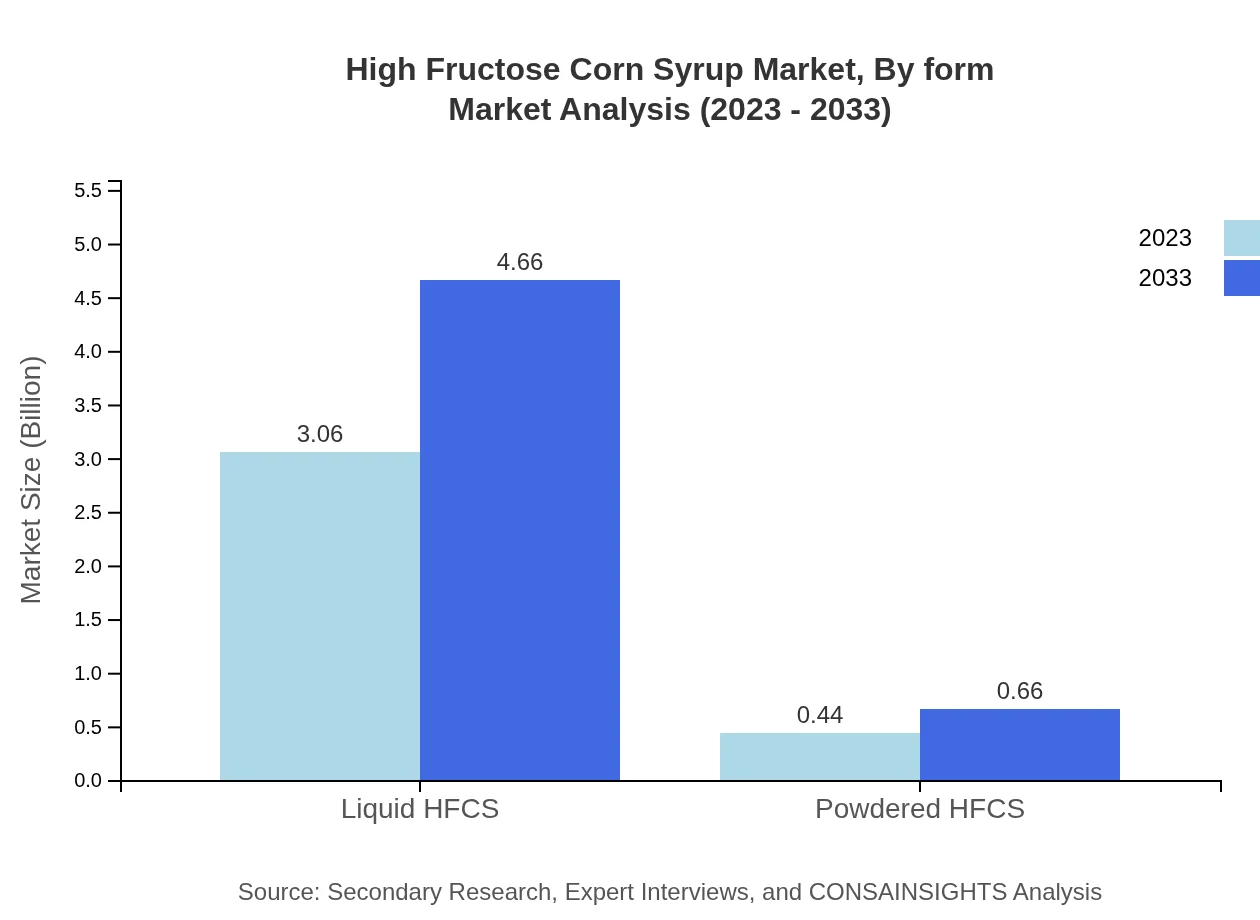
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Analysis By Form
HFCS is primarily available in liquid and powdered forms, with liquid forms preferred due to ease of use in manufacturing processes. This category generates significant sales, from $3.06 billion to $4.66 billion, while powdered forms play a crucial role in niche applications.
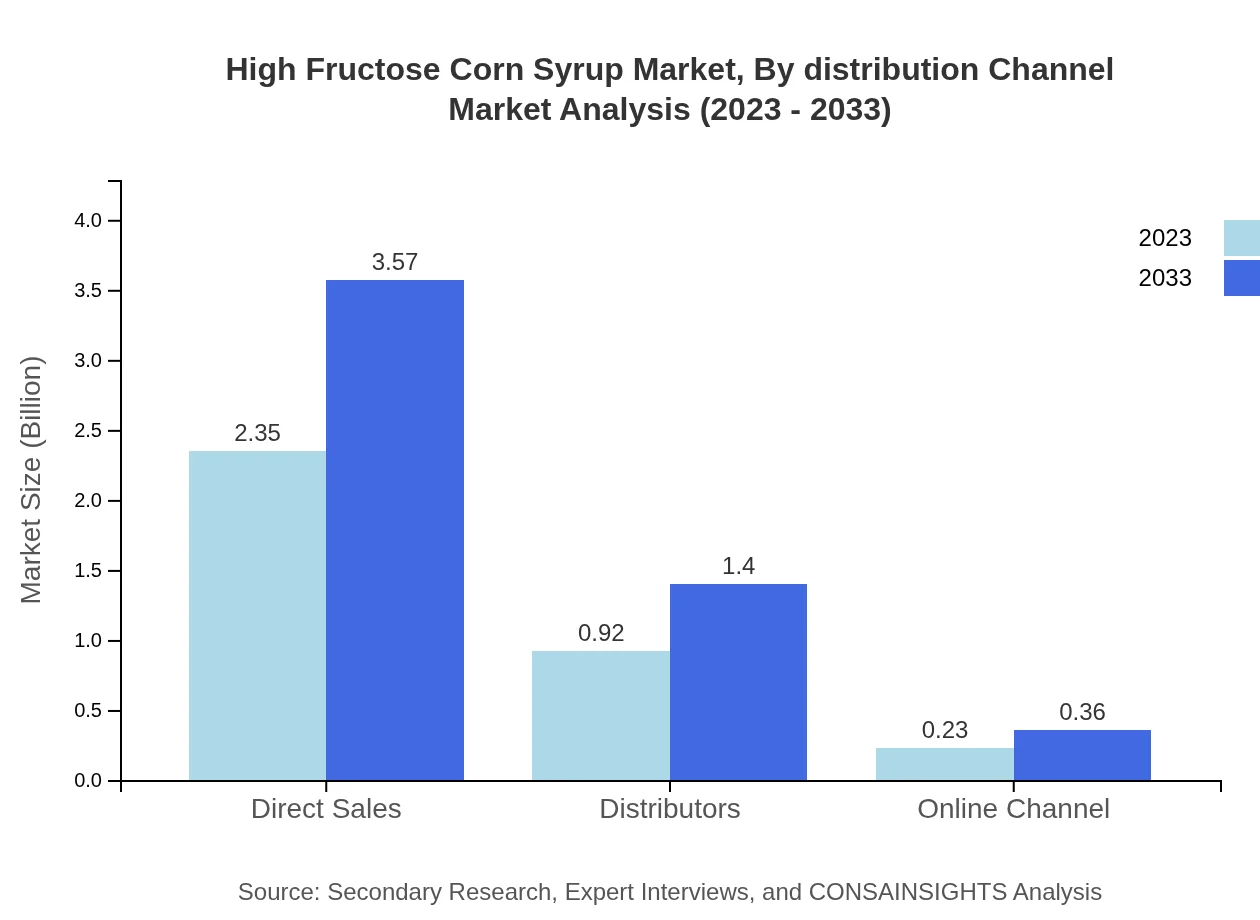
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels for HFCS include Direct Sales, Distributors, and Online Channels. Direct Sales lead the market with $2.35 billion in 2023, maintaining a 67.01% market share. The role of distributors is also crucial, showcasing the necessity of effective distribution frameworks for market reach.
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries for HFCS span Food, Beverages, Industrial applications, and Other segments. Food and Beverages combined make up over 76% of market consumption, highlighting the essential role that HFCS plays in these industries amid shifting consumer preferences toward healthier options.
High Fructose Corn Syrup Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in High Fructose Corn Syrup Industry
Cargill Inc.:
Cargill is a leading producer and marketer of HFCS, recognized for its extensive product portfolio and innovative processing technologies that enhance quality and efficiency.ADM (Archer Daniels Midland Company):
ADM is a global agribusiness leader providing HFCS products, with a commitment to sustainability and advancing agricultural practices that support the food industry's evolving needs.Tate & Lyle:
Tate & Lyle focuses on delivering innovative sweetener solutions, including HFCS, to meet changing consumer demands for healthier ingredients.Ingredion Incorporated:
Ingredion is highly regarded for its specialty ingredients, including HFCS, emphasizing product quality and customer-centric solutions in various applications.Corn Products International:
This company specializes in manufacturing and distributing a variety of sweeteners, including HFCS, and plays a significant role in the global market supply chain.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of high Fructose Corn Syrup?
The high-fructose corn syrup market is valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 4.2% from 2023 to 2033, indicating steady growth driven by demand in various end-use sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in this high Fructose Corn Syrup industry?
Key players in the high-fructose corn syrup industry include major companies such as Archer Daniels Midland Company, Cargill, and Tate & Lyle, all of which play significant roles in production and distribution.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the high Fructose Corn Syrup industry?
Growth in the high-fructose corn syrup market is primarily driven by increased demand from food and beverage manufacturers, rising consumer preference for sweeteners, and the need for cost-effective sugar alternatives.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the high Fructose Corn Syrup?
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing region in the high-fructose corn syrup market, with a projected increase from $0.75 billion in 2023 to $1.14 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the high Fructose Corn Syrup industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the high-fructose corn syrup industry, enabling businesses to gain detailed insights and competitive analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this high Fructose Corn Syrup market research project?
Deliverables from the high-fructose corn syrup market research project include comprehensive reports containing market size, growth forecasts, segment analysis, and competitive landscape insights.
What are the market trends of high Fructose Corn Syrup?
Current trends in the high-fructose corn syrup market include increased usage in food and beverage sectors, innovations in production processes, and a growing consumer focus on healthier alternatives.