Higher Education Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: higher-education
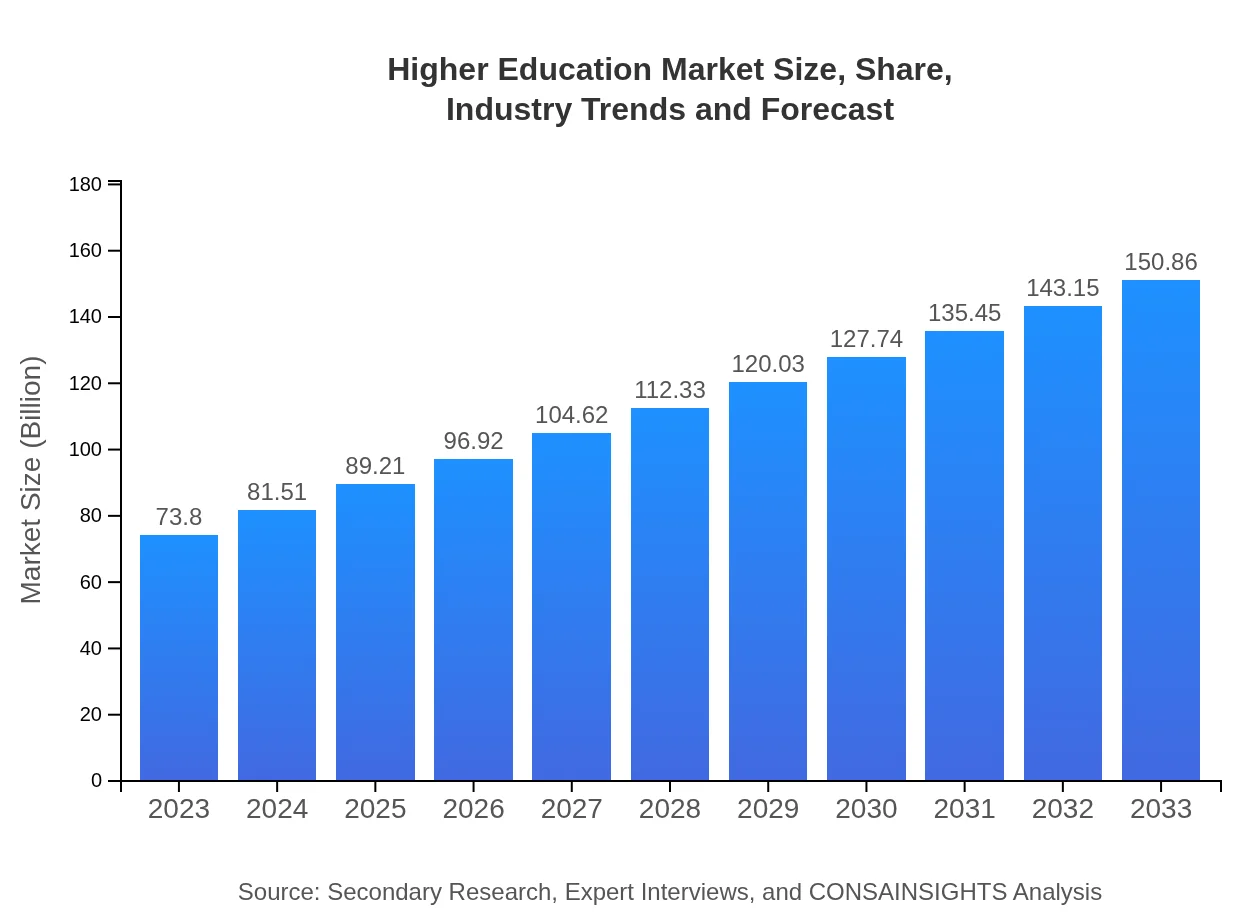
Higher Education Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Higher Education market, focusing on trends, forecast data, and detailed regional insights. Covering the period from 2023 to 2033, this document aids stakeholders in understanding market dynamics and future opportunities.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $73.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $150.86 Billion |
| Top Companies | University of Phoenix, DeVry University, Coursera, Khan Academy |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Higher Education Market Overview
Customize Higher Education Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Higher Education market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Higher Education's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Higher Education
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Higher Education market in 2023?
Higher Education Industry Analysis
Higher Education Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Higher Education Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Higher Education Market Report:
Europe's market is projected to increase from $24.21 billion in 2023 to $49.48 billion by 2033, as institutions increasingly adopt digital tools and internationalize programs to attract a global student base.Asia Pacific Higher Education Market Report:
The Higher Education market in Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow from $13.14 billion in 2023 to $26.87 billion by 2033, driven by rising student populations, investments in educational infrastructure, and increasing accessibility of online platforms.North America Higher Education Market Report:
The North American Higher Education market is expected to expand from $26.89 billion in 2023 to $54.97 billion by 2033, bolstered by a high demand for both traditional and online educational offerings, coupled with a diverse mix of private and public institutions.South America Higher Education Market Report:
In South America, the market size is projected to decline from $-0.63 billion in 2023 to $-1.28 billion by 2033, indicating significant challenges such as economic instability and reduced government funding impacting enrollment numbers.Middle East & Africa Higher Education Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are expected to witness growth from $10.18 billion in 2023 to $20.82 billion by 2033, as governments prioritize education with enhanced funding and expansion of online learning opportunities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
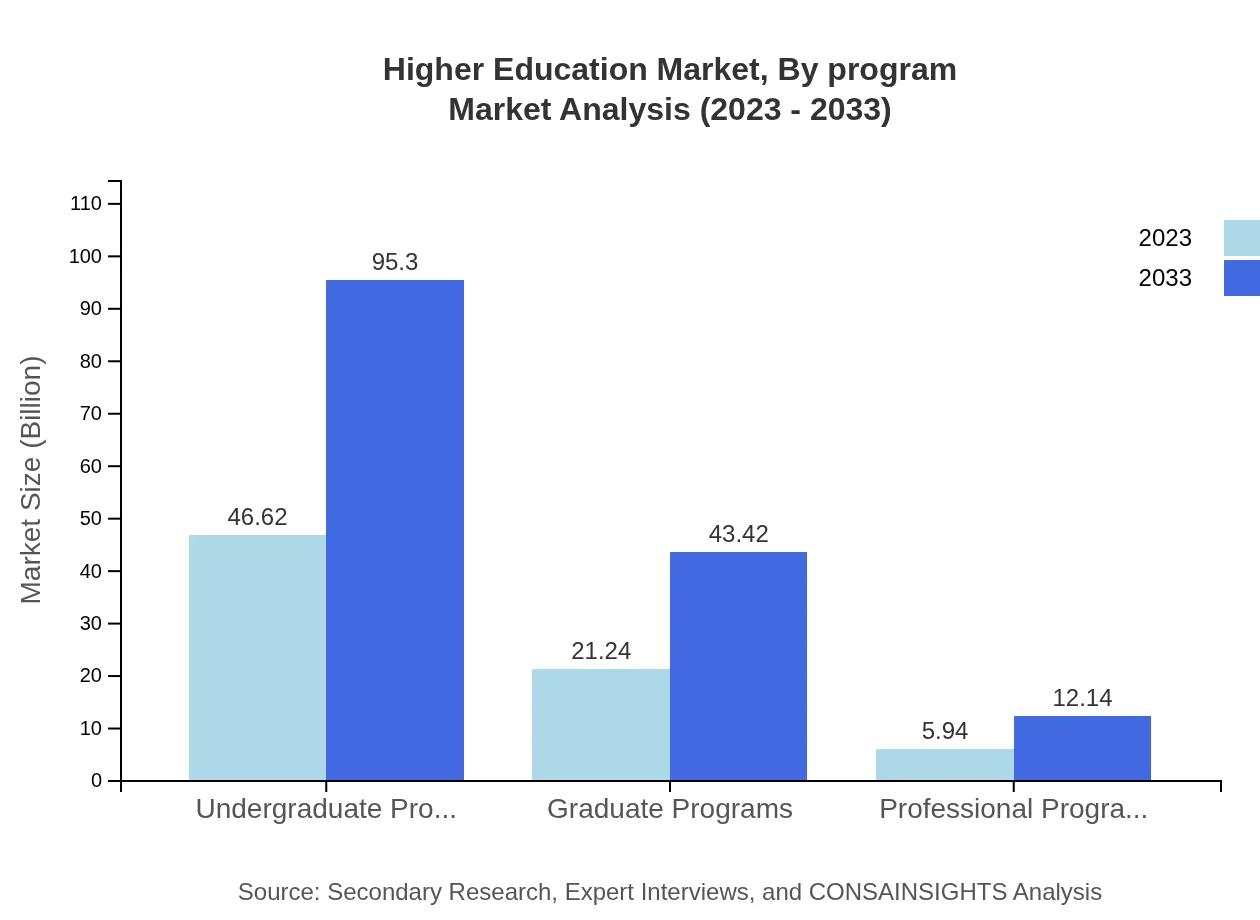
Higher Education Market Analysis By Program
Undergraduate programs, occupying a significant share, are projected to rise from $46.62 billion in 2023 to $95.30 billion by 2033, maintaining a steady market share of 63.17%. Graduate programs are also expected to see significant growth from $21.24 billion to $43.42 billion, with a share of 28.78%.
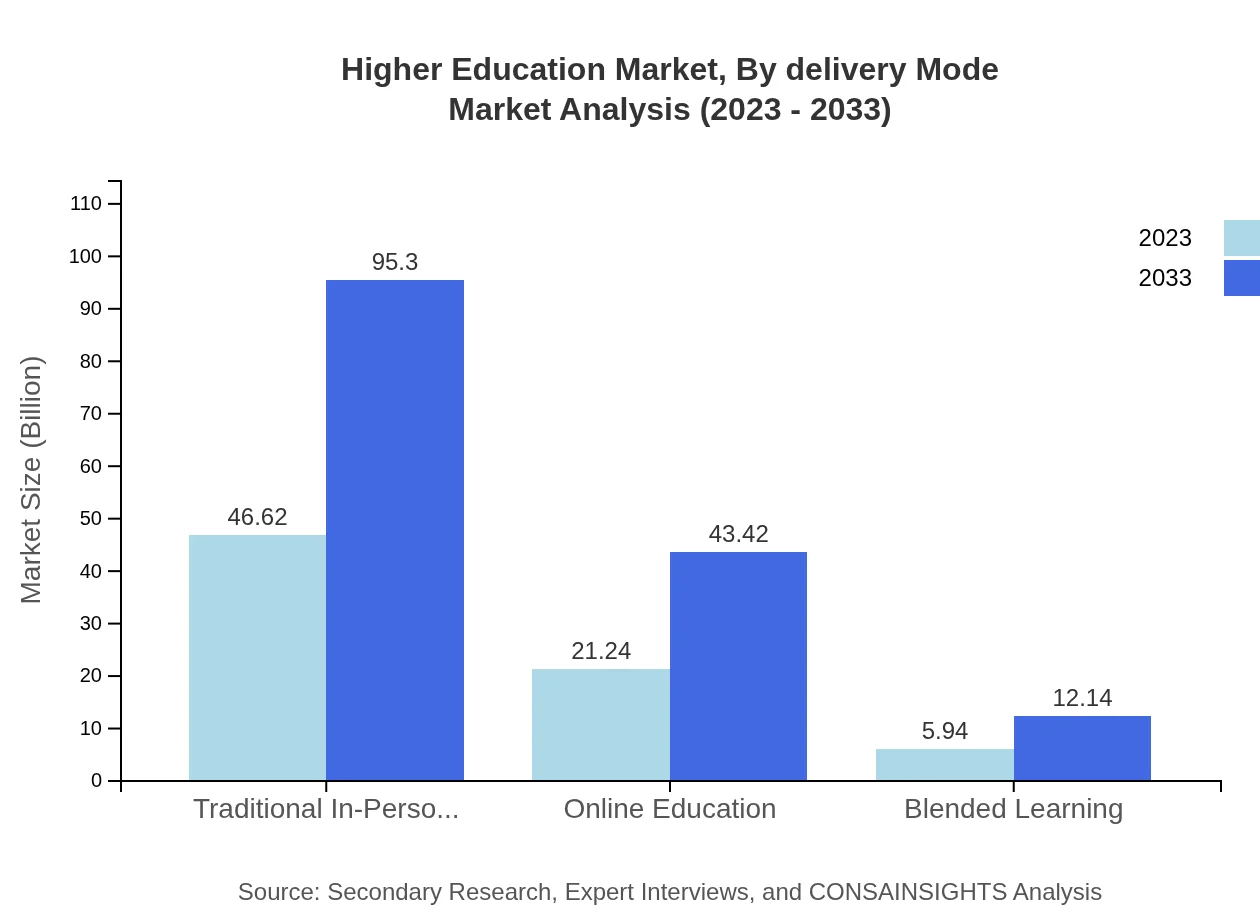
Higher Education Market Analysis By Delivery Mode
The market offers various delivery modes such as Traditional In-Person Education, Online Education, and Blended Learning. Traditional In-Person Education is projected to grow significantly from $46.62 billion to $95.30 billion by 2033. Online Education, currently at $21.24 billion, is set to expand to $43.42 billion, showcasing a growing acceptance of digital learning methods.
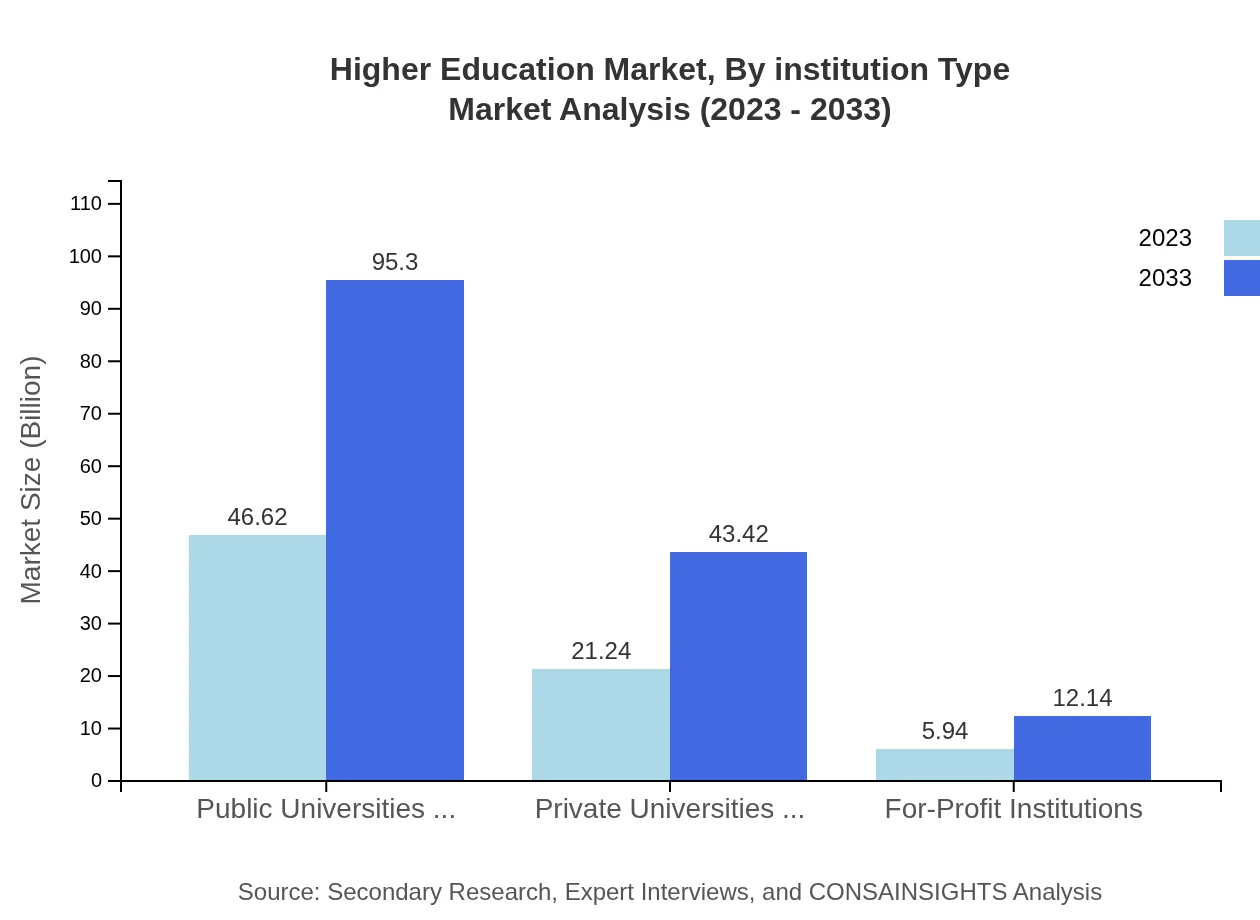
Higher Education Market Analysis By Institution Type
Public Universities and Colleges dominate the market, with the size expected to reach $46.62 billion in 2023 and climb to $95.30 billion by 2033. Conversely, Private Universities, which are largely driven by tuition revenue and specialized programs, will show an upward trajectory, growing from $21.24 billion to $43.42 billion.
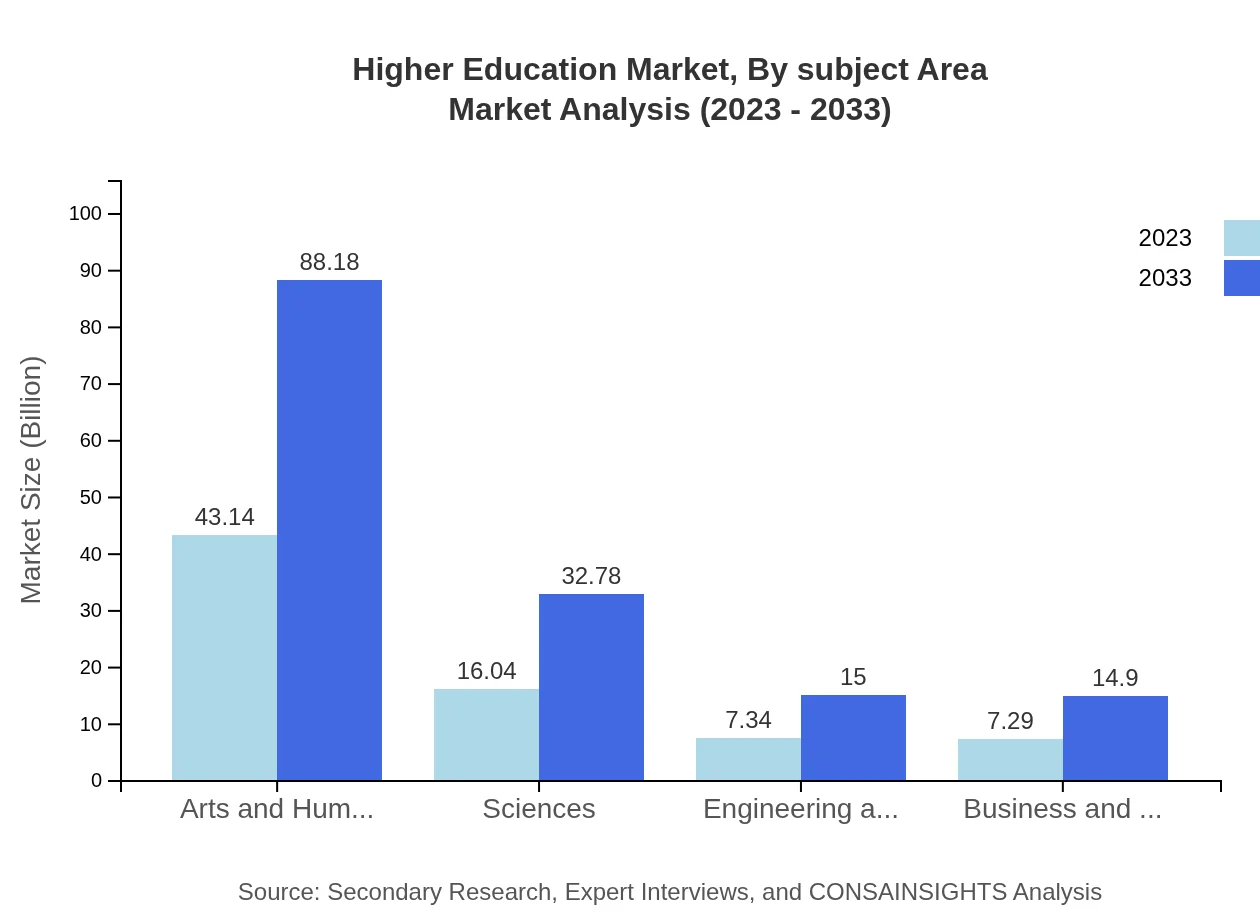
Higher Education Market Analysis By Subject Area
Significant areas include Arts and Humanities, Sciences, Engineering and Technology, and Business and Management. Arts and Humanities will expand from $43.14 billion to $88.18 billion, while Engineering and Technology is expected to grow from $7.34 billion to $15.00 billion by 2033.
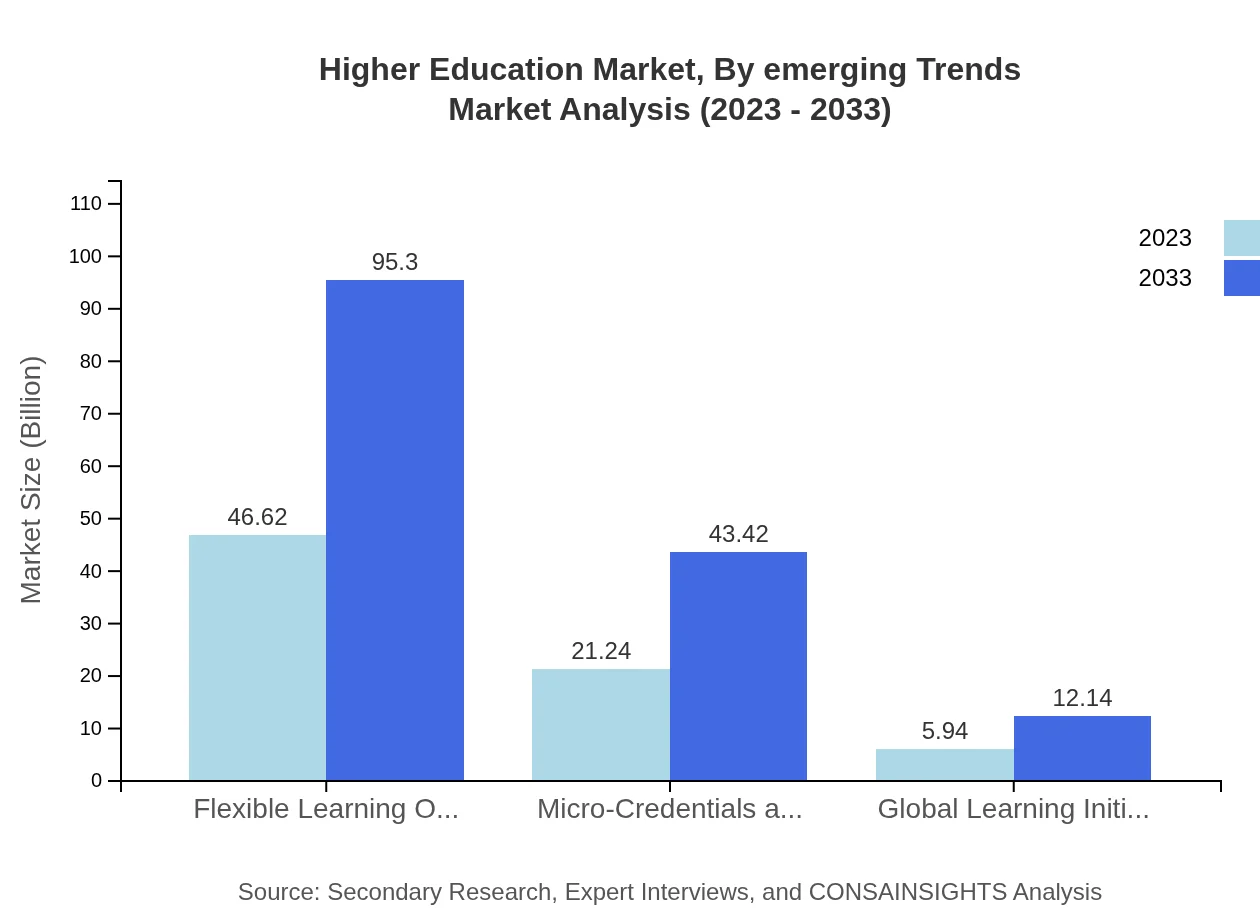
Higher Education Market Analysis By Emerging Trends
Emerging trends include micro-credentials and flexible learning options. Micro-credentials are forecasted to grow from $21.24 billion to $43.42 billion as individuals seek targeted skill enhancement, while flexible learning options will expand significantly, driven by demand for personalized education experiences.
Higher Education Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Higher Education Industry
University of Phoenix:
Known for pioneering online education, University of Phoenix offers a diverse range of programs and has a strong focus on serving adult learners.DeVry University:
DeVry University specializes in career-oriented education and has embraced technology to enhance the learning experience across its programs.Coursera:
As a leader in online learning and partnerships with universities, Coursera provides various courses and degrees designed to make education accessible worldwide.Khan Academy:
A non-profit educational organization, Khan Academy offers free online resources and courses aimed at promoting learning in a range of subjects.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of higher Education?
The global higher education market is projected to reach approximately $73.8 billion by 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. This growth trajectory indicates increasing investment and innovation in educational institutions and programs.
What are the key market players or companies in the higher Education industry?
Key players in the higher education sector include prominent universities, online education platforms, and education technology companies. Major institutions and networks drive innovation, partnerships, and improved educational offerings, while startups focus on technology-driven learning solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the higher education industry?
Growth in the higher education sector is primarily driven by rising demand for skilled professionals, increased online learning adoption, innovations in educational technologies, demographic changes, and government investments in education systems globally.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the higher education market?
The fastest-growing region in the higher education market is North America, projected to expand from $26.89 billion in 2023 to an estimated $54.97 billion by 2033, indicating a strong commitment to educational advancements and infrastructure.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the higher education industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the higher education industry, allowing clients to tailor insights based on specific needs, geographical focus, or market segments to facilitate informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this higher education market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive deliverables, including market analysis reports, trend insights, regional breakdowns, segment performance data, competitive landscape assessments, and actionable recommendations tailored to their specific needs.
What are the market trends of higher education?
Key trends in the higher education market include increased online and flexible learning options, growing importance of micro-credentials, emphasis on technology-enhanced learning environments, and a shift towards personalized learning experiences.