Humanoids Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: humanoids
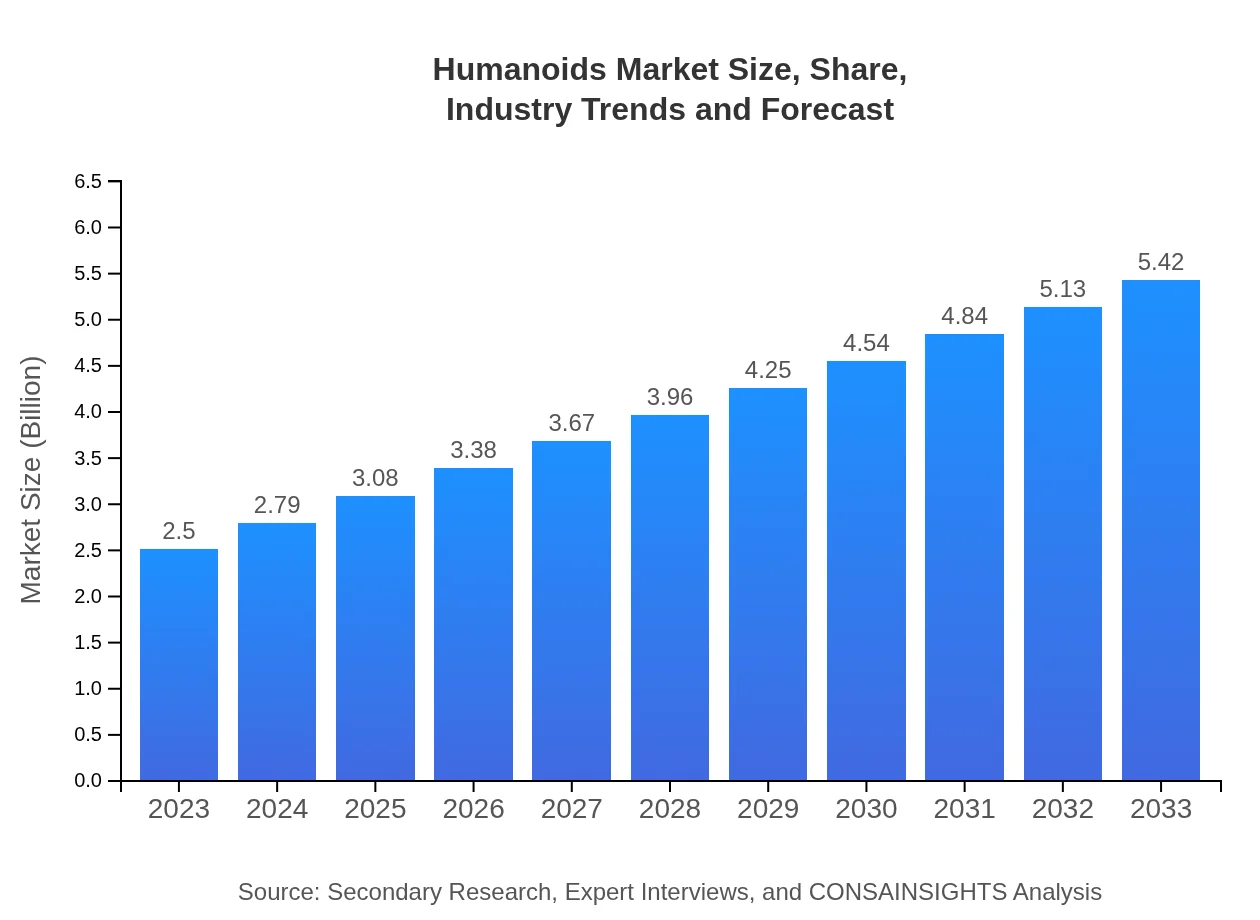
Humanoids Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the humanoids market, covering key insights and data up to the forecast year 2033. It includes market sizing, trends, segment analysis, and regional insights to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $2.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $5.42 Billion |
| Top Companies | Boston Dynamics, SoftBank Robotics, Hanson Robotics, ABB Robotics |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Humanoids Market Overview
Customize Humanoids Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Humanoids market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Humanoids's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Humanoids
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Humanoids market in 2023?
Humanoids Industry Analysis
Humanoids Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Humanoids Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Humanoids Market Report:
Europe's humanoids market is anticipated to expand from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $1.31 billion by 2033, with significant developments in the UK and Germany focusing on humanoid integration in industries like healthcare and education.Asia Pacific Humanoids Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the humanoids market is forecasted to grow from $0.48 billion in 2023 to $1.04 billion by 2033, driven by increasing automation and a growing technology adoption rate, particularly in China and Japan.North America Humanoids Market Report:
North America leads the humanoids market, with a value of approximately $0.94 billion in 2023, projected to double to $2.03 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by advances in AI technology and a high adoption rate in healthcare and manufacturing.South America Humanoids Market Report:
The South American humanoids market is expected to rise from $0.24 billion in 2023 to $0.53 billion by 2033, as countries like Brazil and Argentina begin investing in robotic solutions to enhance service delivery in diverse sectors.Middle East & Africa Humanoids Market Report:
The market in the Middle East and Africa is gradually emerging, expanding from $0.24 billion in 2023 to $0.52 billion by 2033, as governments and organizations invest in technology to improve service efficiency and customer experiences.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
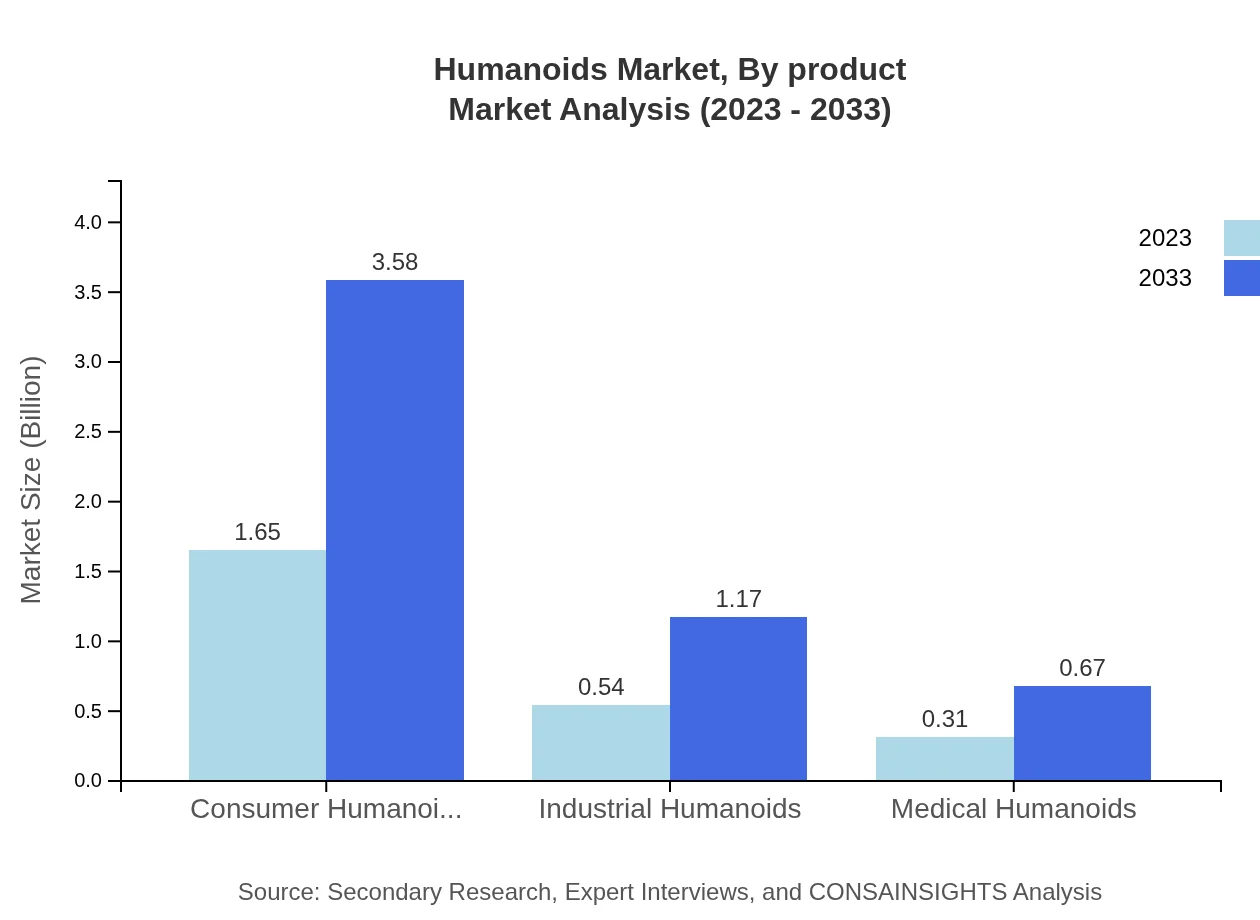
Humanoids Market Analysis By Product
The humanoids market is divided into consumer humanoids, industrial humanoids, and medical humanoids. Consumer humanoids represented $1.65 billion in 2023 and are set to grow to $3.58 billion by 2033. Industrial humanoids, currently at $0.54 billion, will rise to $1.17 billion, while medical humanoids are expected to increase from $0.31 billion to $0.67 billion in the same time frame, reflecting their growing importance in medical settings.
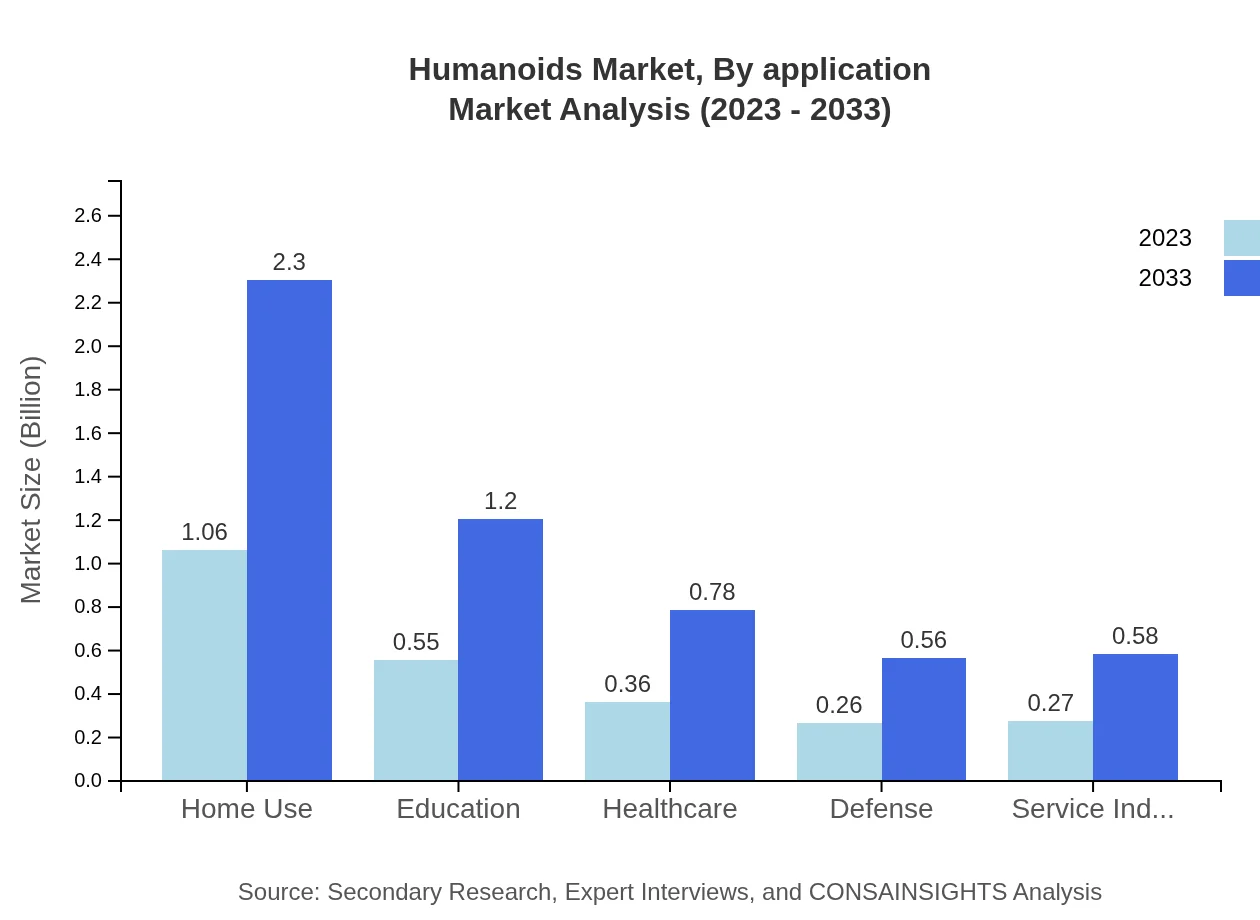
Humanoids Market Analysis By Application
Applications range widely across sectors such as retail, hospitality, healthcare, and education. Humanoids aimed at retail generated $1.06 billion in 2023, expected to double by 2033. In healthcare, the segment exhibits a growing trend as healthcare providers deploy humanoids for patient interaction and care, estimated to grow from $0.31 billion to $0.67 billion by 2033.
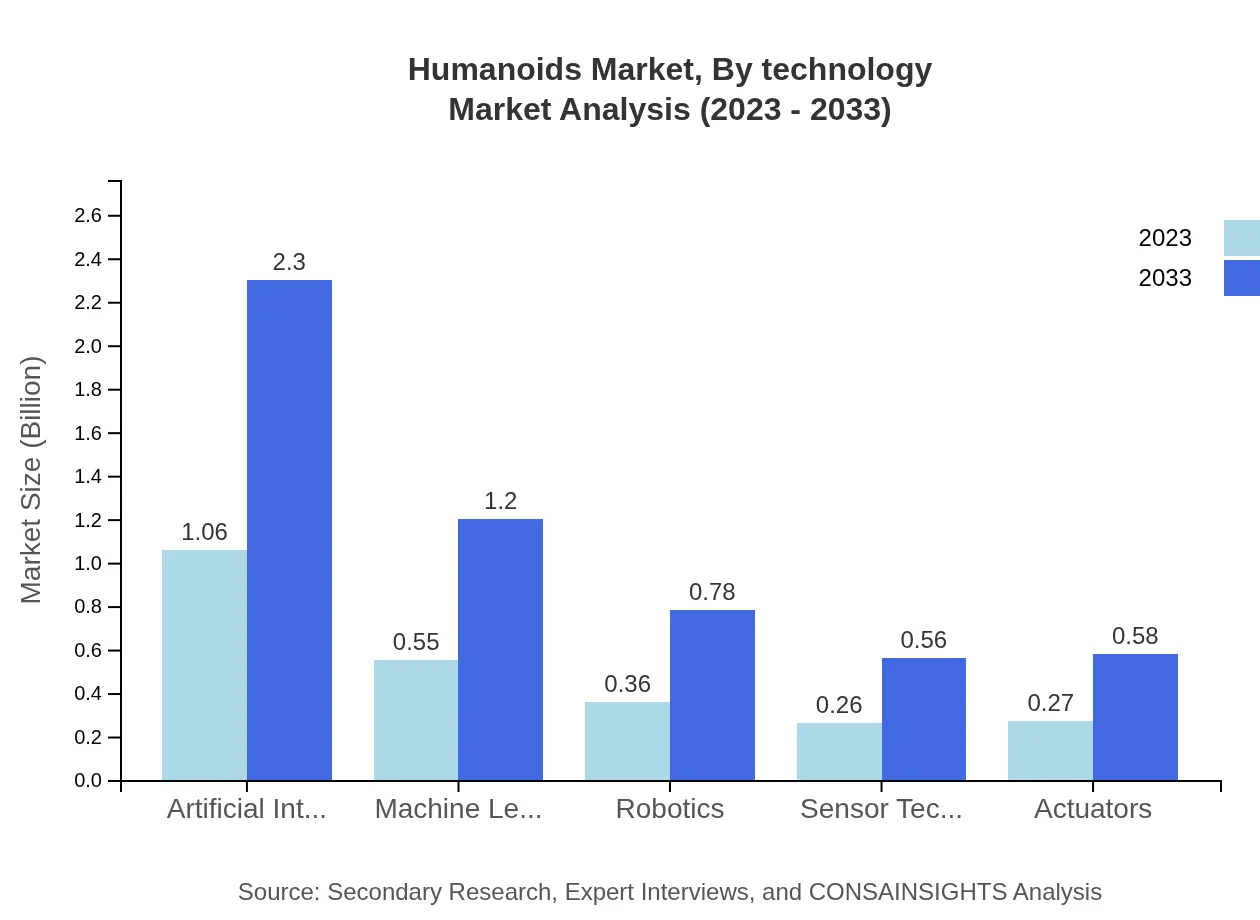
Humanoids Market Analysis By Technology
Technologies powering humanoids include Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Sensor Technology, and Actuators. The AI segment of the humanoids market was valued at $1.06 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $2.30 billion by 2033. Robotics technology is also critical, with a significant market share projected to enhance humanoid capabilities further in various applications.
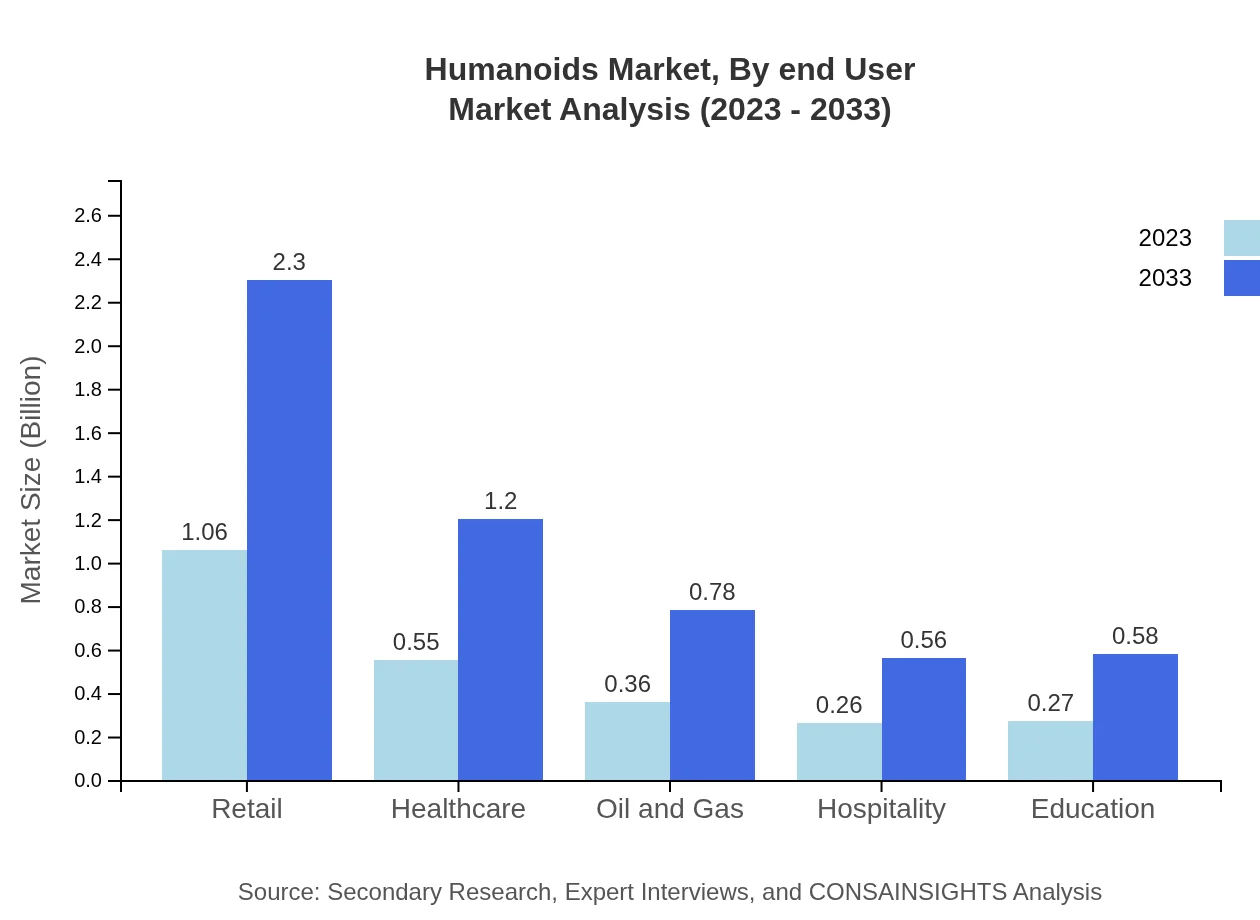
Humanoids Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries include healthcare, retail, education, and hospitality. The healthcare sector is expected to hold a significant share of the humanoids market, growing from $0.55 billion to $1.20 billion by 2033, reflecting the increased reliance on technology for patient care and medical assistance.
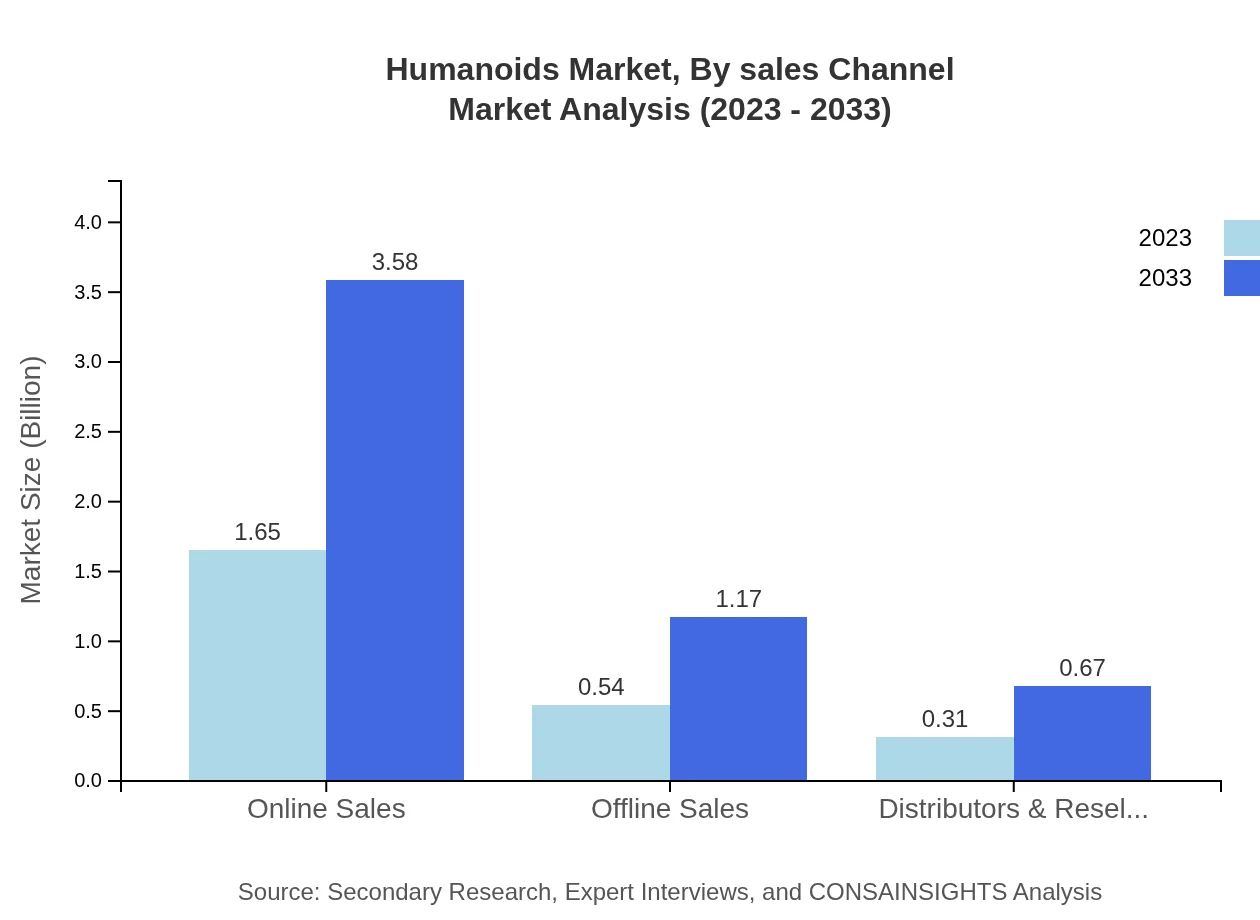
Humanoids Market Analysis By Sales Channel
Sales channels for humanoids primarily include online and offline sales, with online sales generating $1.65 billion in 2023. This segment is projected to grow to $3.58 billion by 2033, demonstrating a shift toward e-commerce in technology products. Offline sales, while significant, will see moderation curbing growth as digital platforms become the preferred choice.
Humanoids Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Humanoids Industry
Boston Dynamics:
Boston Dynamics is known for its advanced robotic solutions. Its humanoid robot, Atlas, showcases cutting-edge capabilities in movement and interaction, setting a benchmark for the industry.SoftBank Robotics:
SoftBank Robotics focuses on developing humanoids like Pepper, which is used in consumer engagement and customer service settings, driving growth in the humanoids market.Hanson Robotics:
Hanson Robotics is recognized for creating lifelike humanoids, such as Sophia, which emphasizes social interaction and emotional AI applications.ABB Robotics:
ABB Robotics partners with various sectors to deliver humanoid solutions that improve efficiency and productivity, especially in manufacturing areas.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of humanoids?
The global humanoids market is valued at $2.5 billion in 2023, with a robust CAGR of 7.8%. Projections estimate market growth, leading to significant advancements and investments by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this humanoids industry?
Key players in the humanoid market include industry leaders like SoftBank Robotics, Honda, and Boston Dynamics. These companies drive innovation through advanced technologies, AI integration, and robotics development, catering to various sectors.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the humanoids industry?
Growth in the humanoids industry is driven by increased automation demand, advancements in AI, and enhanced human-robot interaction. Additionally, applications in sectors like healthcare, retail, and education are expanding opportunities.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the humanoids?
The fastest-growing region for humanoids is North America, projected to grow from $0.94 billion in 2023 to $2.03 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia-Pacific are also witnessing notable expansions.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the humanoids industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights specializes in providing tailored market reports for the humanoids industry, ensuring that businesses receive comprehensive insights that meet their specific needs and objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this humanoids market research project?
Deliverables from the humanoids market research project include detailed market analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and insights on regional trends and consumer behavior.
What are the market trends of humanoids?
Market trends for humanoids indicate a shift towards increased AI integration, enhanced user experience design, and diversification across industries like healthcare, retail, and tourism. Consumer humanoids are expected to dominate market share.