Hydroponics Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: hydroponics
Hydroponics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Hydroponics market from 2023 to 2033, examining key insights, market dynamics, and forecasts. It covers aspects such as market size, trends, segmentation, and analysis across major regions and technologies in the hydroponics industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
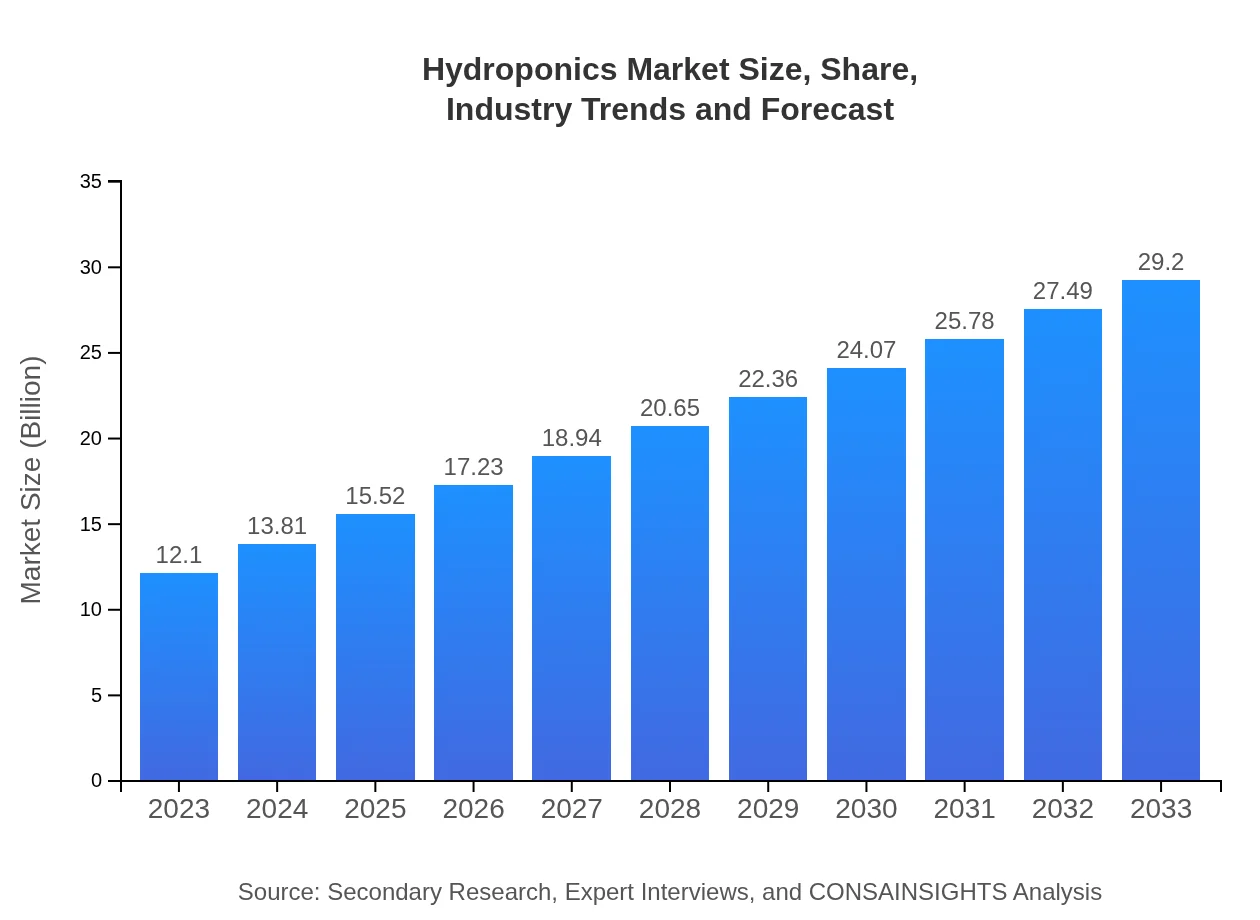
| 2023 Market Size | $12.10 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.9% |
| 2033 Market Size | $29.20 Billion |
| Top Companies | Netafim, AeroFarms, Greener Roots, Valoya, Signify |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Hydroponics Market Overview
Customize Hydroponics Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Hydroponics market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Hydroponics's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Hydroponics
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Hydroponics market in 2023?
Hydroponics Industry Analysis
Hydroponics Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Hydroponics Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Hydroponics Market Report:
The European hydroponics market size is projected to increase from USD 3.56 billion in 2023 to USD 8.59 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by regulatory support for sustainable farming practices and increasing concern over food quality and traceability.Asia Pacific Hydroponics Market Report:
The Asia Pacific hydroponics market was valued at USD 2.35 billion in 2023, growing to USD 5.67 billion by 2033. Countries such as Japan, China, and India are leading the way with innovations in urban farming practices and increased investments in food technology.North America Hydroponics Market Report:
North America represents one of the largest markets for hydroponics, estimated to grow from USD 4.32 billion in 2023 to USD 10.42 billion by 2033. The United States leads this growth through technological innovations and large-scale commercial hydroponic farms catering to organic produce demands.South America Hydroponics Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to rise from USD 0.66 billion in 2023 to USD 1.59 billion by 2033. Brazil is emerging as a key player, leveraging hydroponics to combat challenges in conventional agriculture and promote sustainability.Middle East & Africa Hydroponics Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa hydroponics market is expected to grow from USD 1.21 billion in 2023 to USD 2.93 billion by 2033. The region's push for food security and sustainable agriculture has led to increased interest in hydroponic systems in arid climates.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
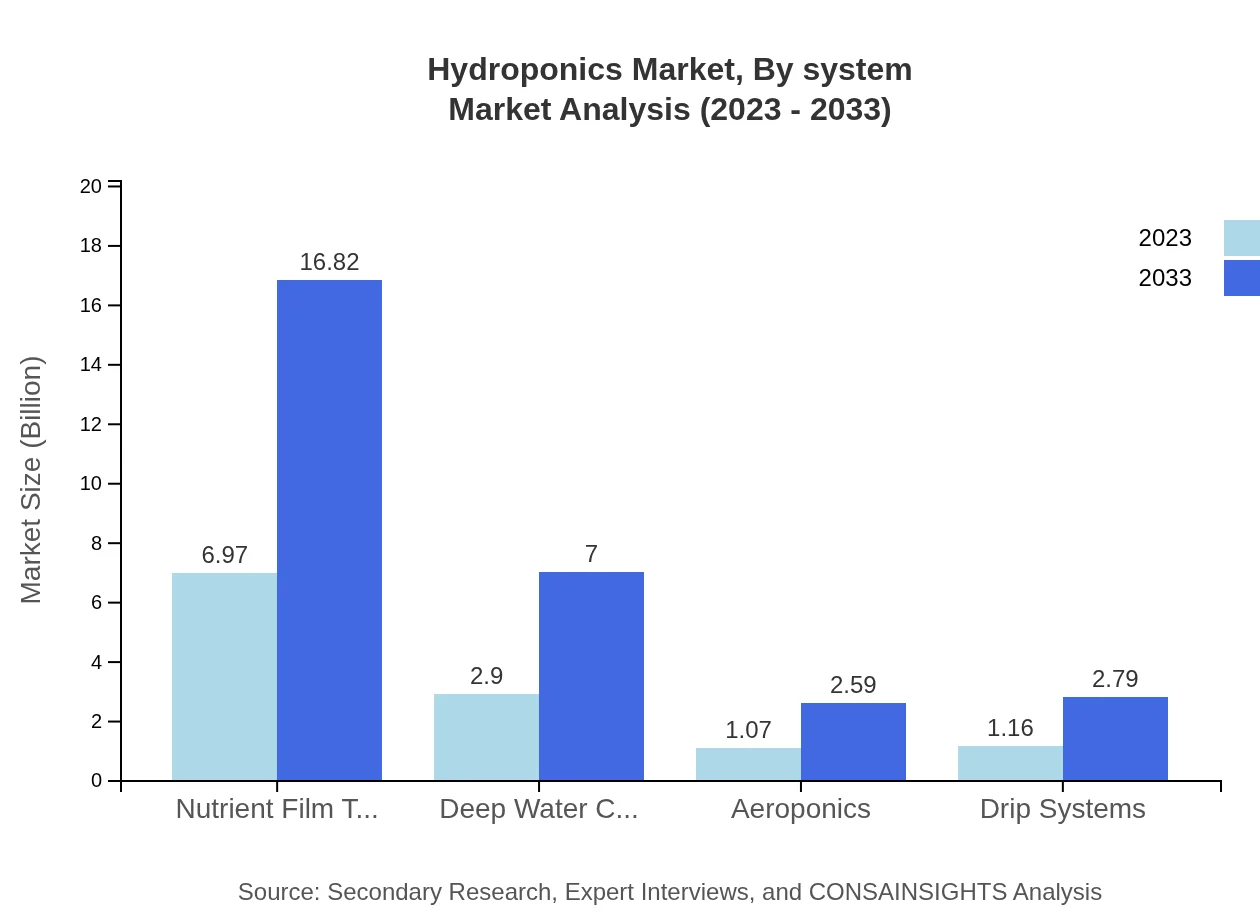
Hydroponics Market Analysis By System
The integration of various hydroponic systems showcases varying market sizes and shares. The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) leads with a market size expected to rise from USD 6.97 billion in 2023 to USD 16.82 billion by 2033, while Deep Water Culture (DWC) and Aeroponics are projected at USD 2.90 billion to USD 7.00 billion and USD 1.07 billion to USD 2.59 billion, respectively. This segmentation emphasizes the dominant positions of NFT and DWC in commercial hydroponics.
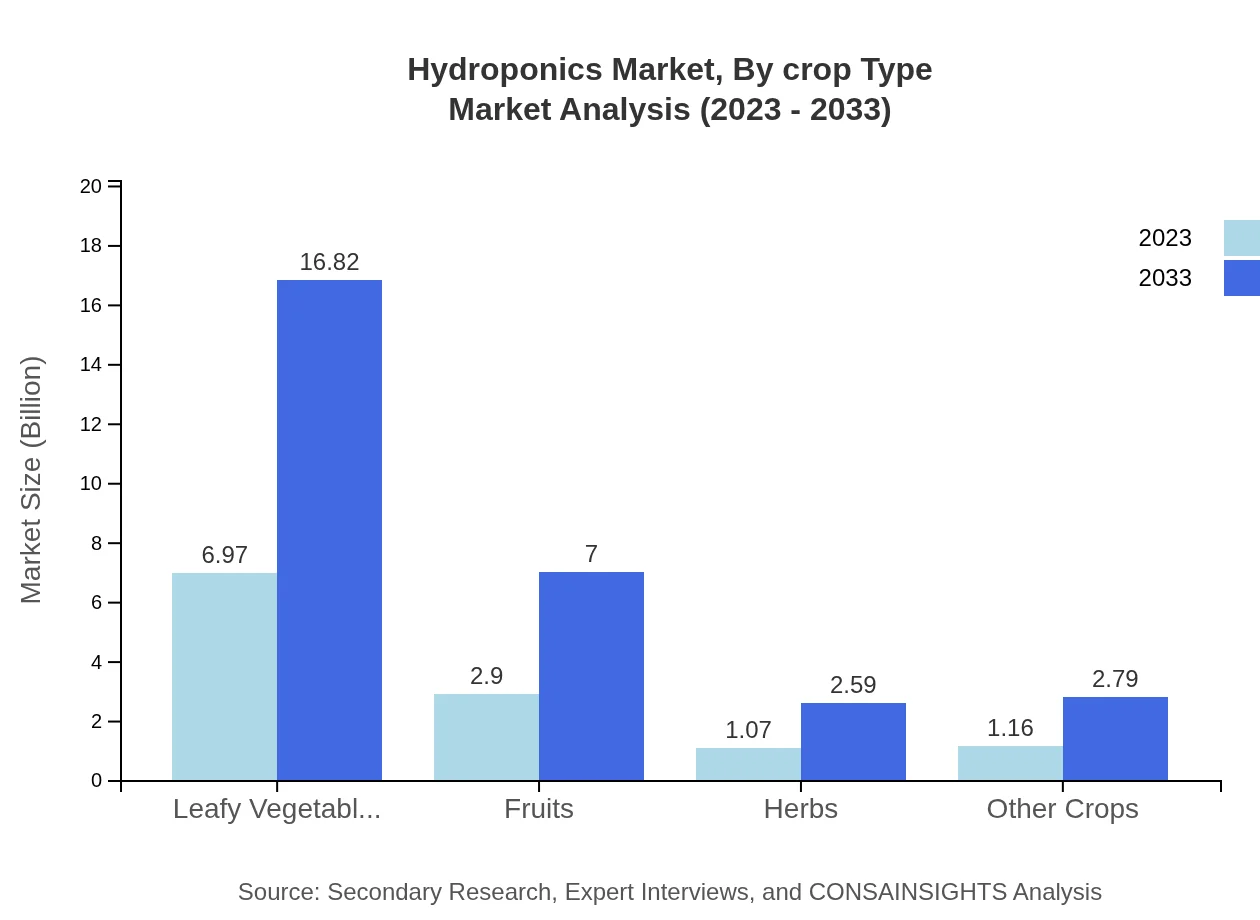
Hydroponics Market Analysis By Crop Type
In the crop type segmentation, leafy vegetables share the largest market size expected to increase from USD 6.97 billion to USD 16.82 billion, predominantly due to consumer demand for fresh and organic produce. Fruits represent a significant segment as well, mapping out growth from USD 2.90 billion to USD 7.00 billion, along with herbs and other crops contributing to market diversity and revenue growth.
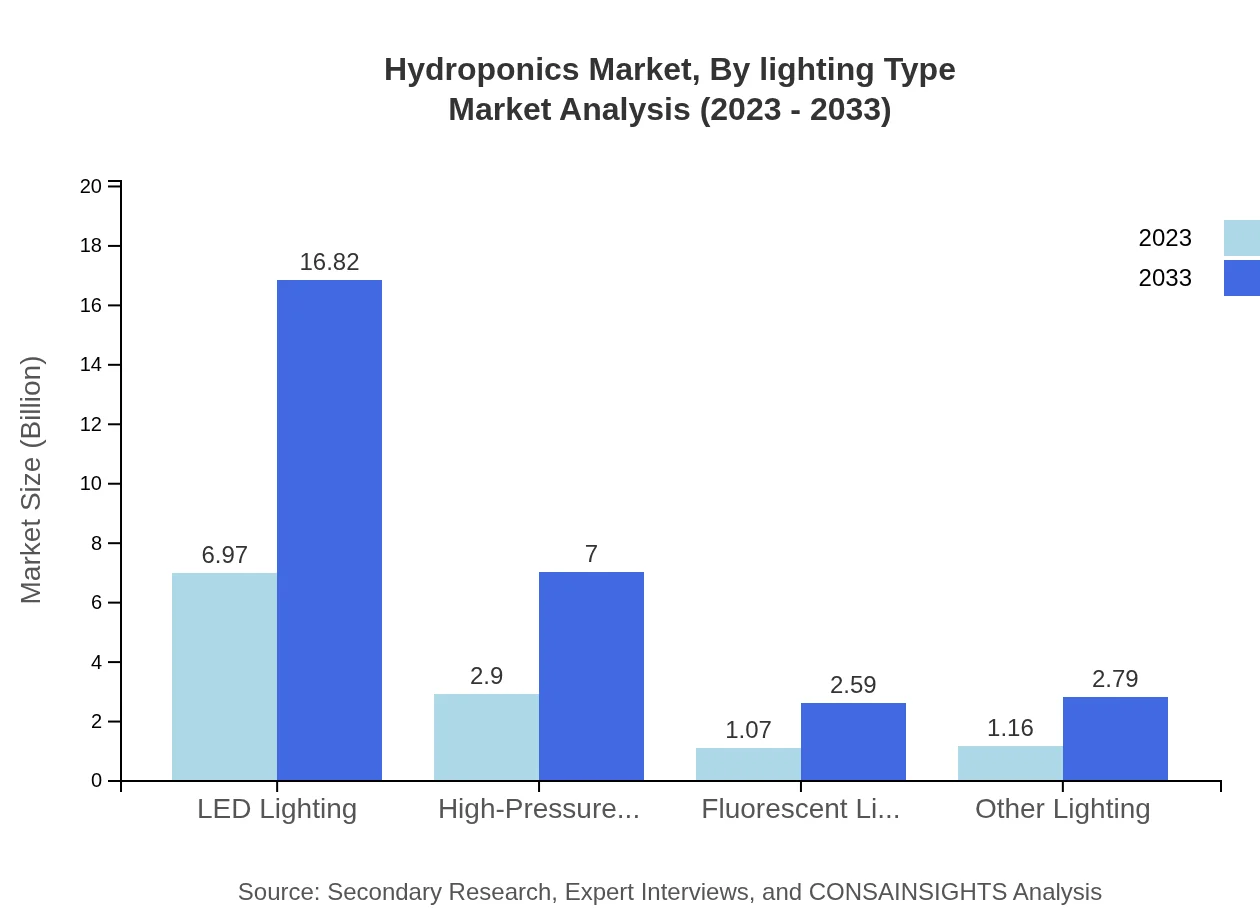
Hydroponics Market Analysis By Lighting Type
Lighting types play a crucial role in optimizing photosynthesis in hydroponics. LED lighting dominates with a market size anticipated to expand from USD 6.97 billion in 2023 to USD 16.82 billion by 2033 due to energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to other lighting options like High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) and fluorescent lighting, which demonstrate respective markets of USD 2.90 billion and USD 1.07 billion in the same forecast period.
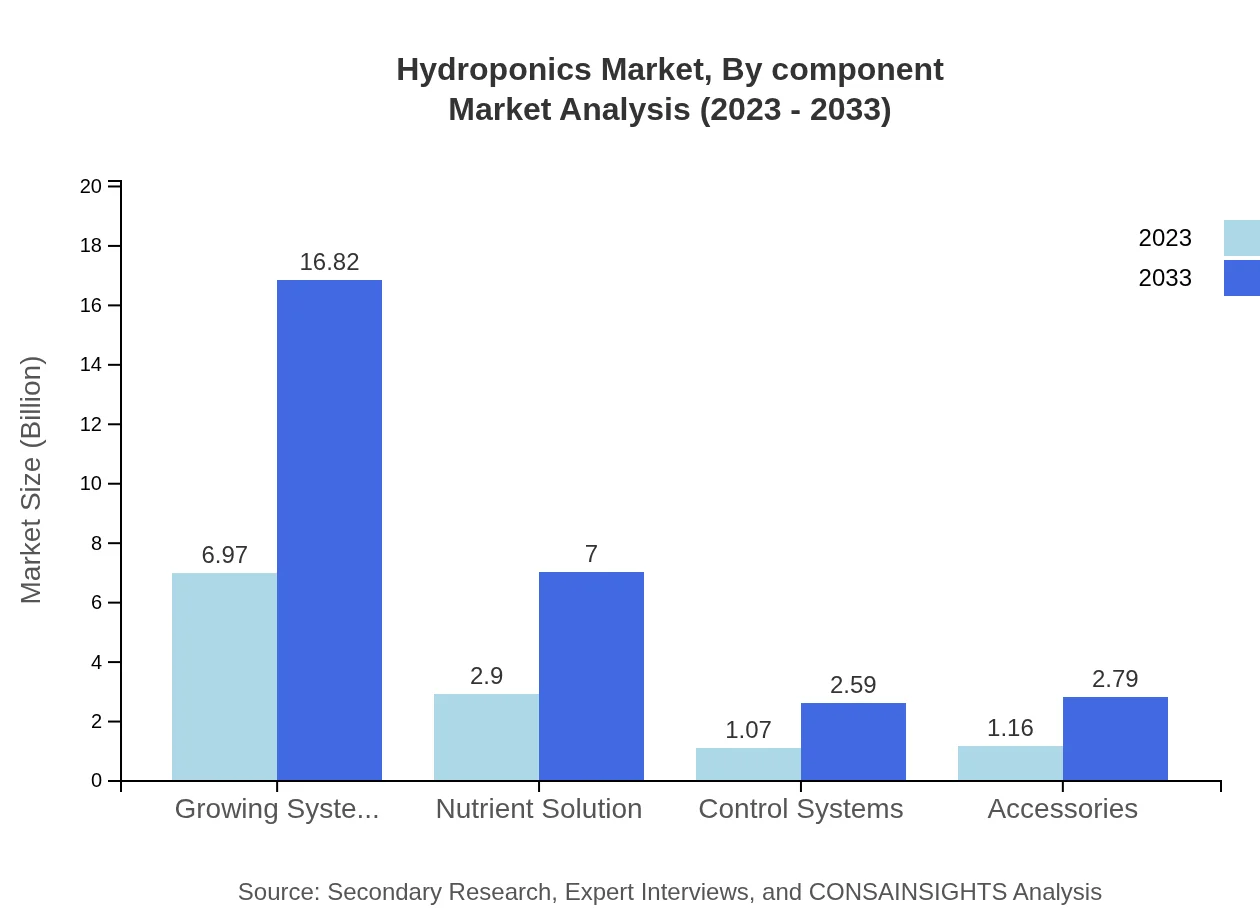
Hydroponics Market Analysis By Component
The components segment includes nutrient solutions, control systems, and accessories. For example, nutrient solutions alone are expected to grow from USD 2.90 billion in 2023 to USD 7.00 billion by 2033, representing crucial inputs for effective plant growth. Control systems and accessories also hold significant shares, indicating the comprehensive nature of hydroponic operations that integrate multiple technological solutions.
Hydroponics Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Hydroponics Industry
Netafim:
A leader in drip irrigation technology, Netafim plays a vital role in hydroponic system development, providing solutions that optimize resource use in agricultural practices.AeroFarms:
AeroFarms is a pioneer in vertical farming and hydroponics, leveraging innovative technologies to produce leafy greens while minimizing water usage and maximizing yield efficiency.Greener Roots:
Specializing in hydroponics systems for homes and communities, Greener Roots contributes by making sustainable agriculture accessible for smaller scale growers.Valoya:
Valoya specializes in LED grow lights specifically designed for indoor growing, enhancing growth efficiency and produce quality in hydroponics.Signify:
A global leader in lighting products, Signify's horticulture offerings incorporate advanced technology to optimize growth conditions in hydroponics.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of hydroponics?
The global hydroponics market is valued at approximately $12.1 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 8.9% over the next decade, reflecting strong growth driven by increasing demand for sustainable agricultural solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in the hydroponics industry?
Key players in the hydroponics industry include companies like AeroFarms, Freight Farms, and BrightFarms, all of which focus on innovative systems and technologies to optimize hydroponic practices for food production.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the hydroponics industry?
The hydroponics industry is primarily driven by urbanization, increasing demand for local and sustainable food sources, and technological advancements that enhance the efficiency and yields of hydroponic systems.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the hydroponics market?
The fastest-growing region in the hydroponics market is Europe, expected to grow from $3.56 billion in 2023 to $8.59 billion by 2033, driven by favorable policies and increasing adoption of urban farming.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the hydroponics industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the hydroponics industry, allowing businesses to get insights that directly align with their strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this hydroponics market research project?
From the hydroponics market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports, detailed market analysis, insights into key trends, and data segmented by region and product type.
What are the market trends of hydroponics?
Current hydroponics market trends include increasing investment in automation technologies, growing consumer preference for organic produce, and the rise of vertical farming techniques to maximize space utilization.