Indoor Farming Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: indoor-farming
Indoor Farming Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the indoor farming market, focusing on growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It covers market size, regional insights, segmentation, and trends shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
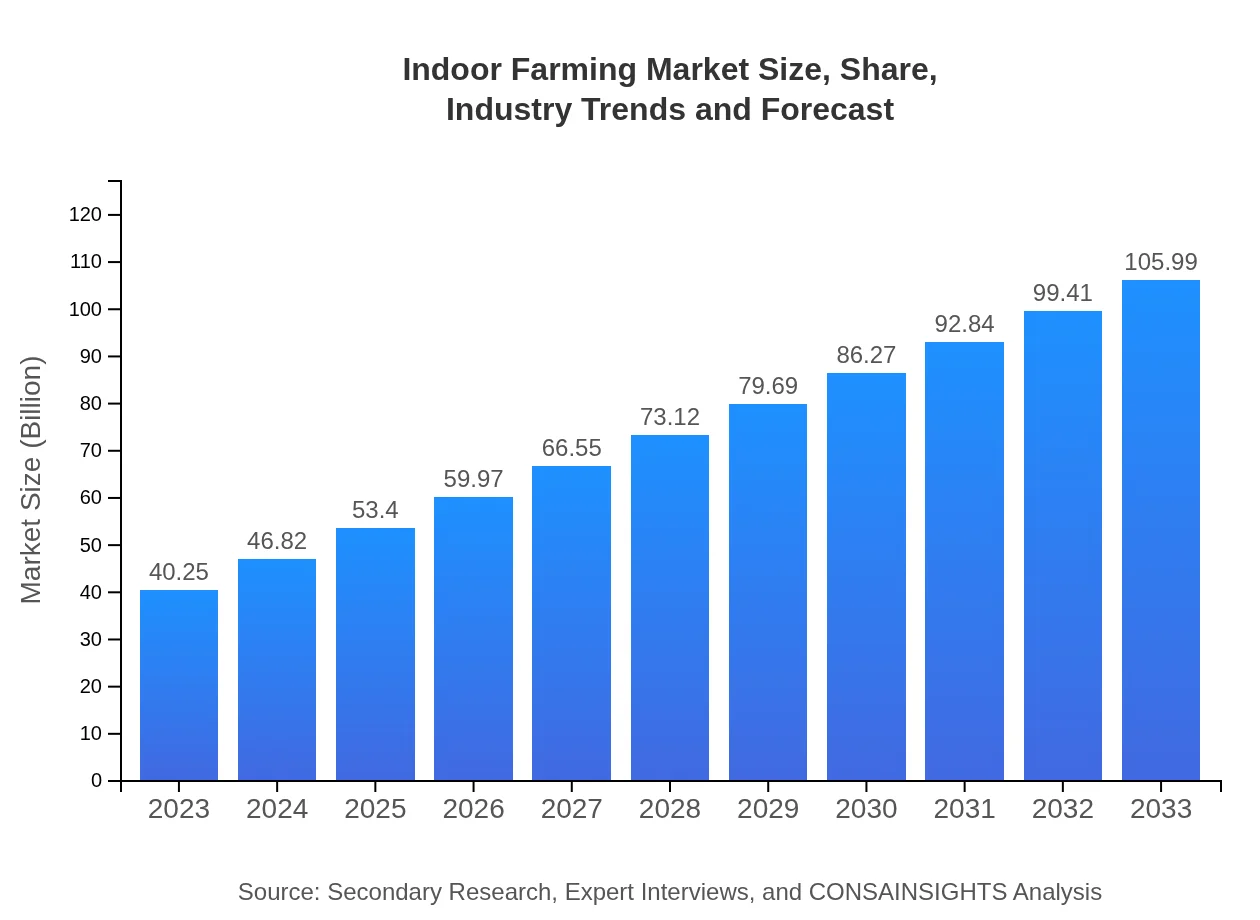
| 2023 Market Size | $40.25 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $105.99 Billion |
| Top Companies | AeroFarms, Gotham Greens, Plenty, Green Spirit Farms |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Indoor Farming Market Overview
Customize Indoor Farming Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Indoor Farming market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Indoor Farming's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Indoor Farming
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Indoor Farming market in 2023?
Indoor Farming Industry Analysis
Indoor Farming Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Indoor Farming Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Indoor Farming Market Report:
The European indoor farming market reached USD 12.99 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 34.21 billion by 2033. Supportive governmental policies promoting urban farming and sustainable agriculture are key drivers in this region.Asia Pacific Indoor Farming Market Report:
The Asia Pacific indoor farming market was valued at approximately USD 7.15 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to grow to USD 18.82 billion by 2033. The region benefits from increasing urbanization trends and a rising emphasis on local food production, particularly in densely populated countries like China and India.North America Indoor Farming Market Report:
North America stands as a leader in the indoor farming market, with a value of USD 15.10 billion in 2023 projected to escalate to USD 39.77 billion by 2033. The region boasts advanced technological adaptations and a strong consumer shift towards sustainable agricultural practices.South America Indoor Farming Market Report:
In South America, the indoor farming market is relatively nascent, valued at USD 0.27 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 0.71 billion by 2033. Growing awareness and initiatives to enhance local food production and food security are expected to drive market growth in this region.Middle East & Africa Indoor Farming Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa indoor farming market, valued at USD 4.74 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow to USD 12.47 billion by 2033. Factors such as limited arable land and the focus on food security drive growth in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
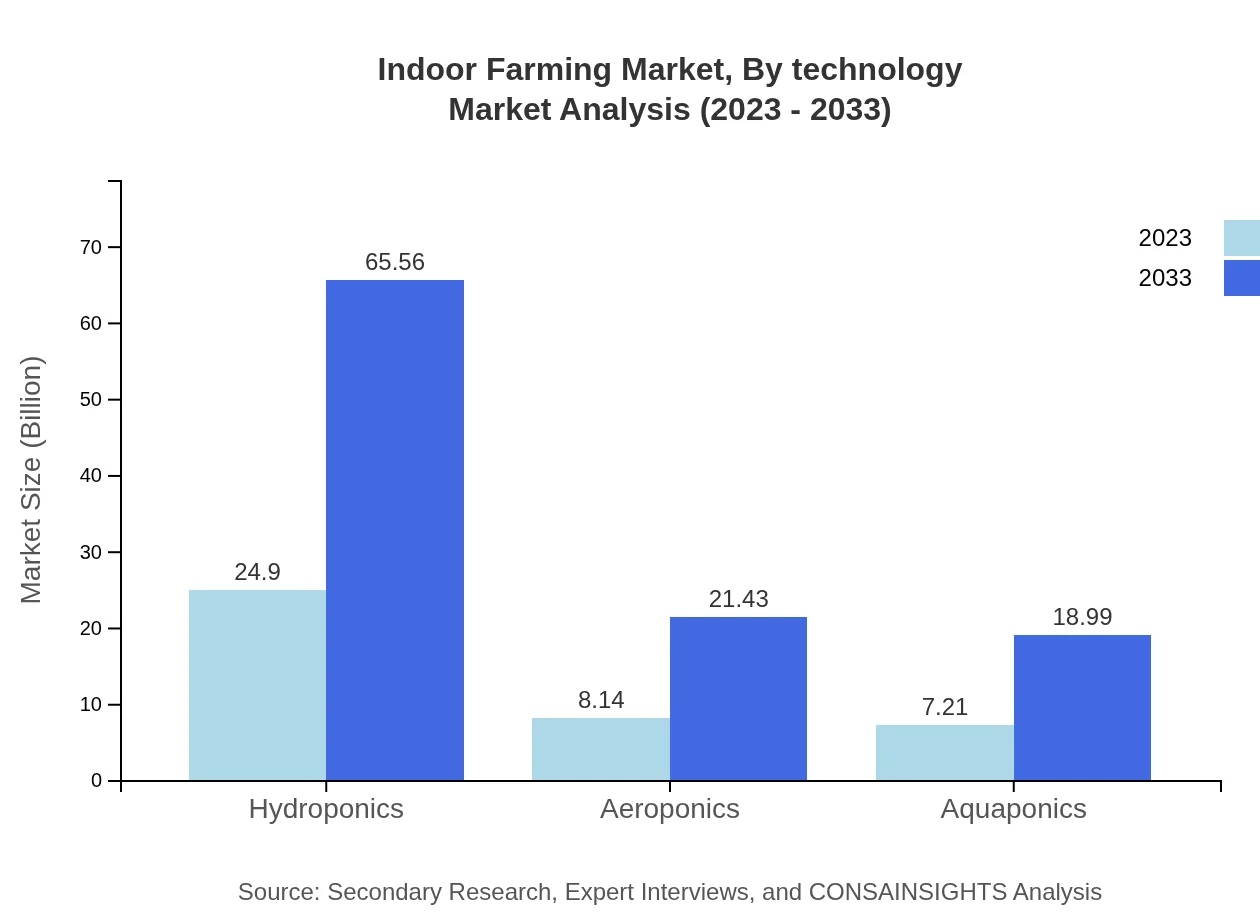
Indoor Farming Market Analysis By Technology
Hydroponics holds a significant market share, valued at USD 24.90 billion in 2023 and projected at USD 65.56 billion by 2033, driven by its effectiveness in water conservation and nutrient delivery. Aeroponics and aquaponics also show promising growth, aligning with sustainable practices. This technological segmentation emphasizes innovations that lead to efficient farming options in urban settings.
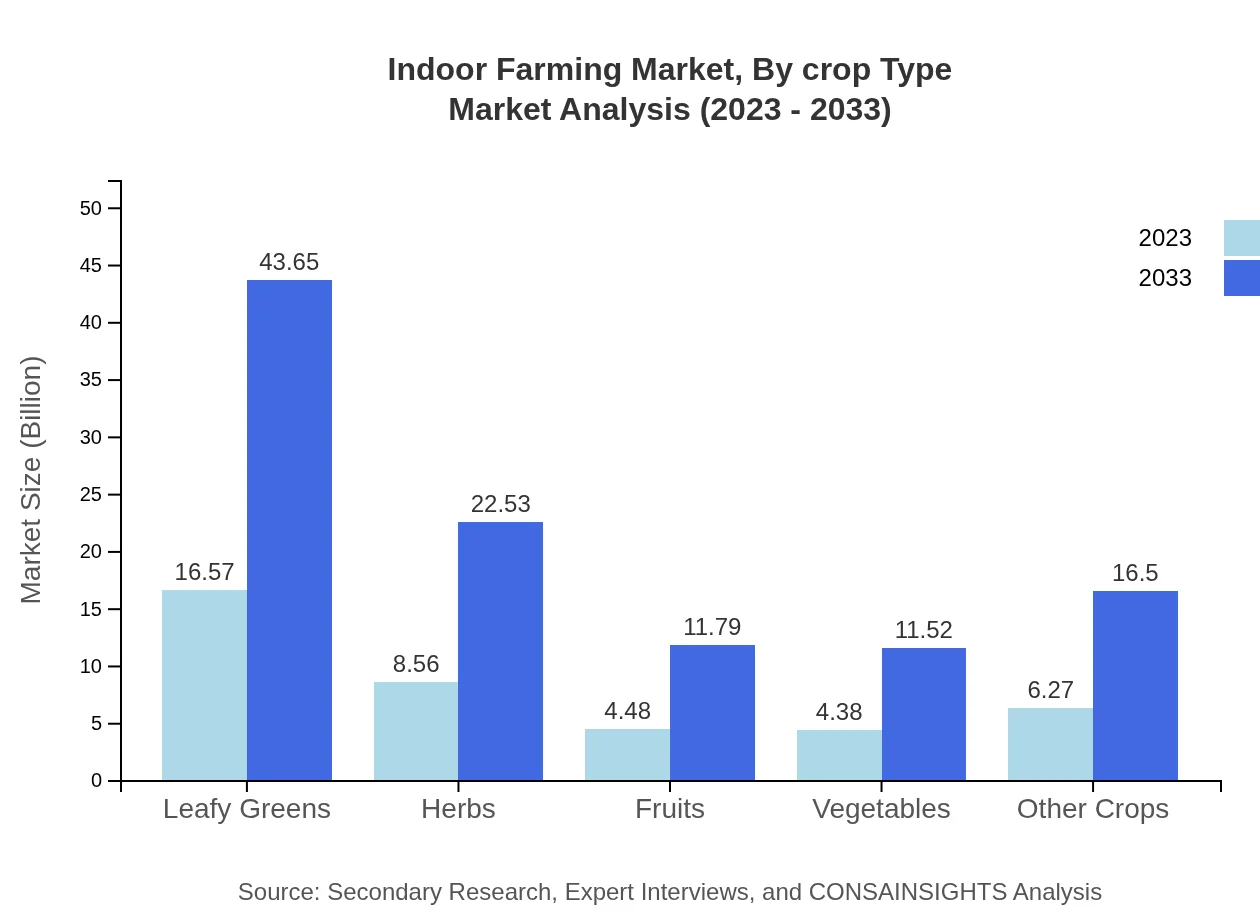
Indoor Farming Market Analysis By Crop Type
Leafy greens dominate the crop segment, valued at USD 16.57 billion in 2023, expected to reach USD 43.65 billion by 2033. Other crops like herbs, fruits, and vegetables also present lucrative opportunities, showing significant demand in both retail sectors and restaurants as consumers seek fresh produce. Each crop type contributes uniquely to market dynamics based on demand preferences.
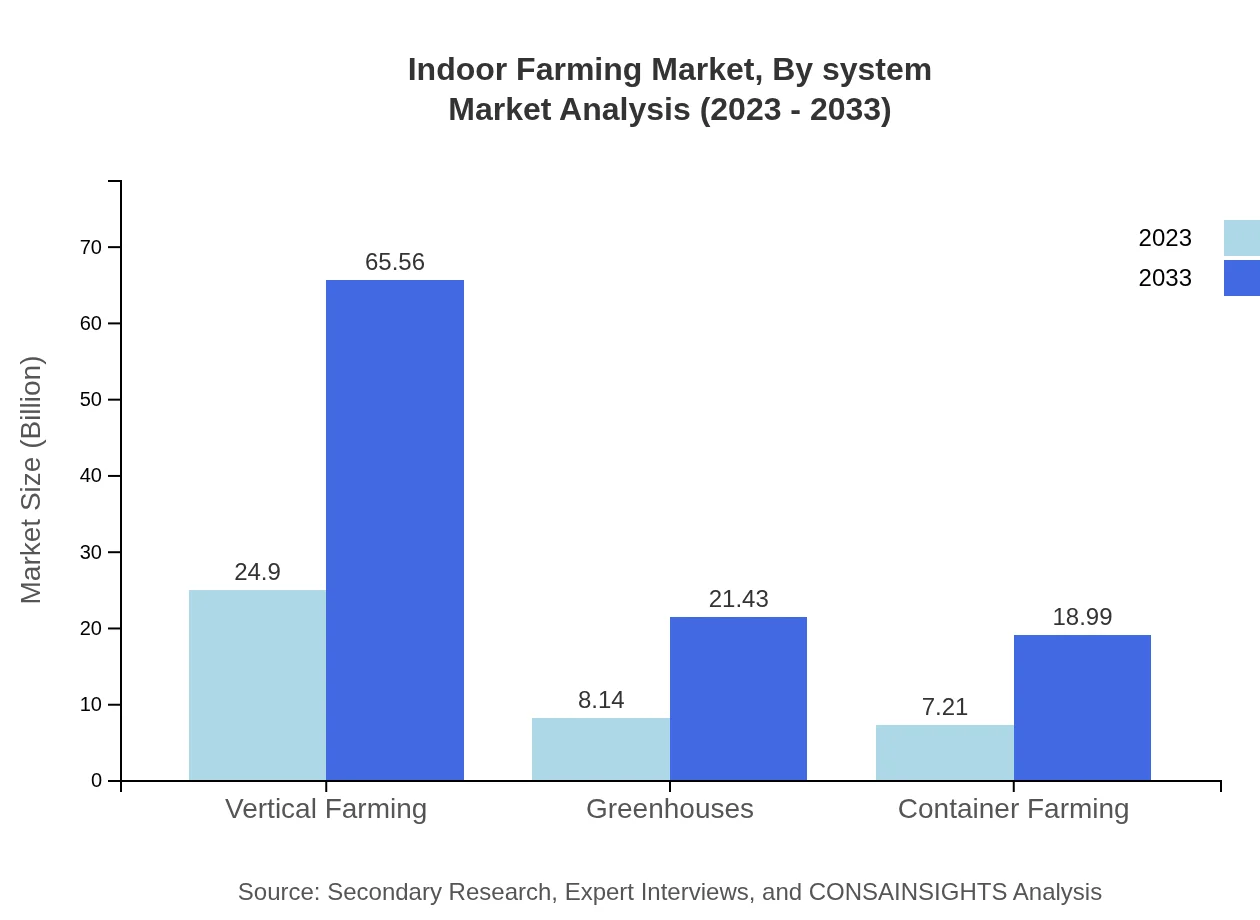
Indoor Farming Market Analysis By System
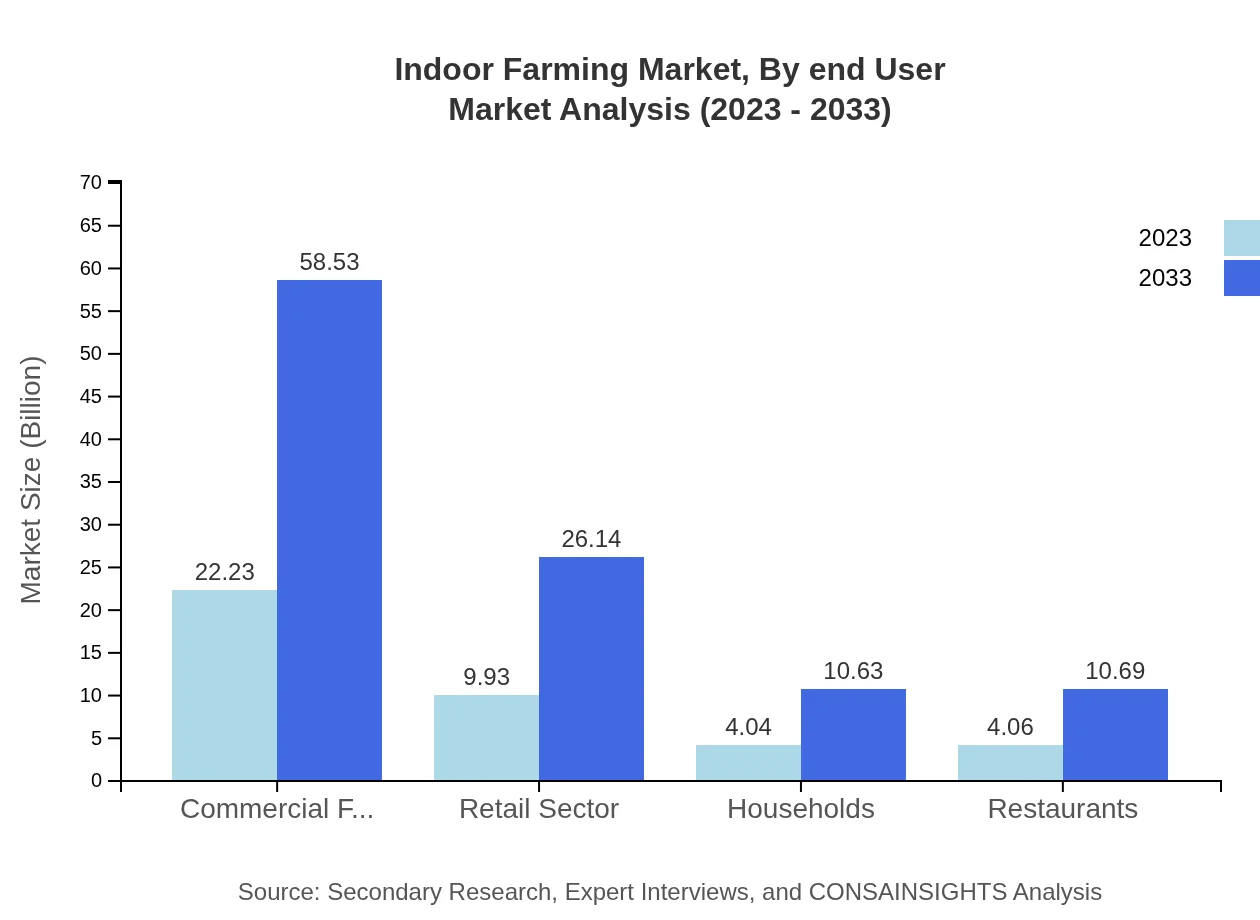
Commercial farmers lead the end-user market, valued at USD 22.23 billion in 2023 with a forecast of USD 58.53 billion by 2033. Other systems such as households and restaurants contribute to growth as urban residential areas adopt indoor farming technologies, expanding into personal and food service market sectors.
Indoor Farming Market Analysis By End User
The retail sector shows robust growth potential, reaching USD 9.93 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to USD 26.14 billion by 2033. This highlights the increasing trend of consumers opting for locally sourced and fresh produce, supporting supermarkets and local markets' integration of indoor-farmed products.
Indoor Farming Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Indoor Farming Industry
AeroFarms:
AeroFarms is a leader in vertical farming technology, utilizing aeroponic systems to grow crops indoors while significantly reducing water and land usage compared to traditional farming.Gotham Greens:
Gotham Greens operates commercial greenhouses across North America, offering locally-grown, pesticide-free produce to urban markets, emphasizing sustainability and community engagement.Plenty:
Plenty focuses on revolutionary indoor farming technologies that enhance productivity and sustainability, delivering fresh fruits and vegetables to urban consumers.Green Spirit Farms:
Green Spirit Farms specializes in vertical farming and greenhouse cultivation, using innovative technologies to provide fresh produce year-round in urban environments.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of indoor Farming?
The indoor farming market is valued at approximately $40.25 billion in 2023, with a projected growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% until 2033. This growth reflects the increasing demand for sustainable farming practices and technology-driven solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in the indoor Farming industry?
Key players in the indoor farming industry include Aerofarms, AppHarvest, and Gotham Greens, which pioneer vertical farming solutions. Additionally, companies like Freight Farms and Plenty focus on container farming to enhance agriculture efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the indoor Farming industry?
Drivers include rising food demand due to population growth, technological advancements in farming practices, and the increasing preference for locally sourced produce. Sustainability concerns also foster innovation in eco-friendly cultivation methods.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the indoor Farming?
North America is the fastest-growing region in indoor farming, with a market size of $15.10 billion in 2023, projected to reach $39.77 billion by 2033, driven by favorable regulations and consumer support for local farming.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the indoor Farming industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the indoor farming sector. Clients can receive insights and analytics relevant to their market strategies and operational decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this indoor Farming market research project?
Expect comprehensive reports including market size, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, and regional insights. The deliverables will provide actionable recommendations to facilitate decision-making in the indoor farming industry.
What are the market trends of indoor Farming?
Current trends include the rise of vertical farming technologies, increasing investment in hydroponics and aquaponics, and growing interest in using artificial intelligence for crop management. Sustainable practices continue to gain traction among consumers.