Industrial-3d Printing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: industrial-3d-printing
Industrial-3d Printing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides an in-depth analysis of the Industrial-3D Printing sector, including market size, trends, segmentation, regional insights, and forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
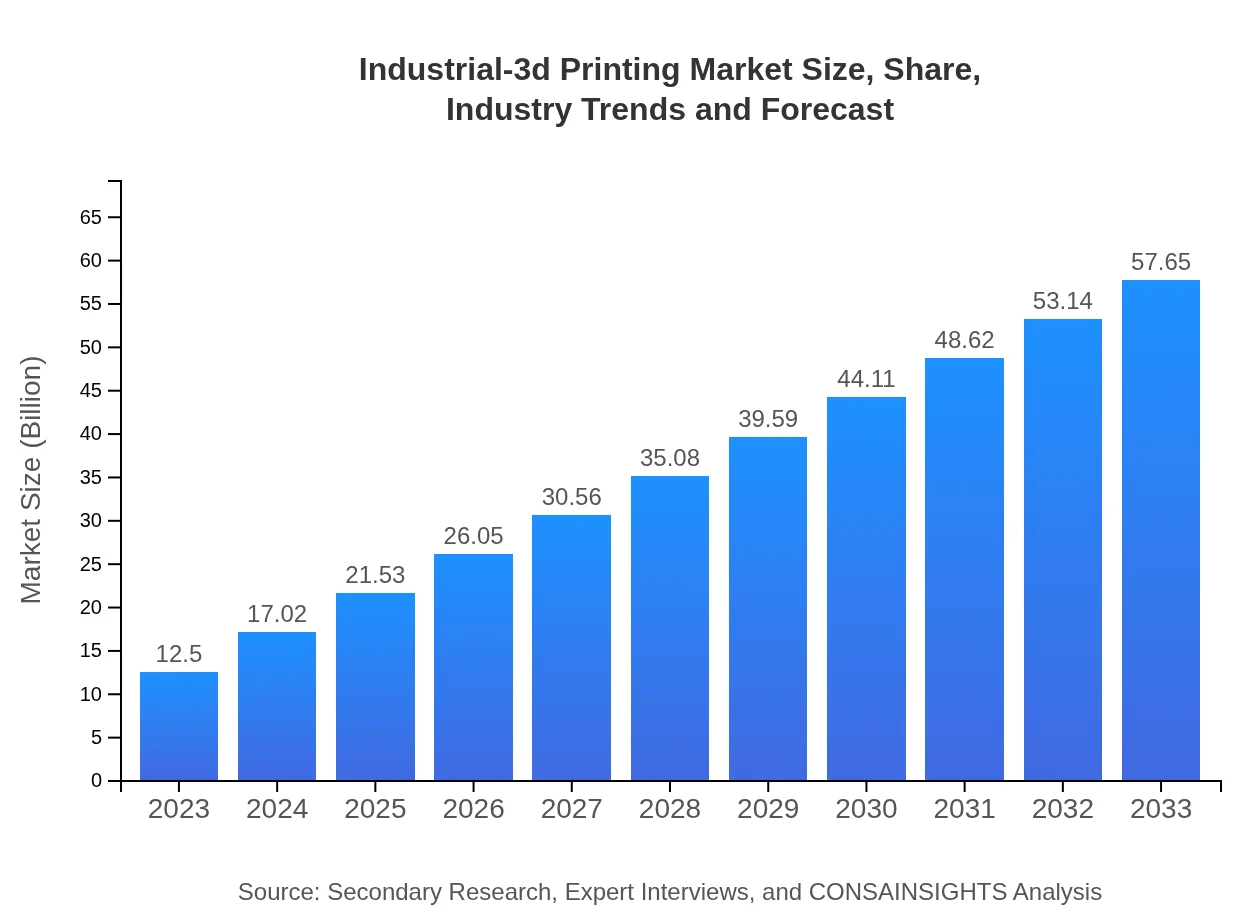
| 2023 Market Size | $12.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 15.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $57.65 Billion |
| Top Companies | Stratasys, 3D Systems, EOS GmbH, Siemens AG, HP Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Industrial-3D Printing Market Overview
Customize Industrial-3d Printing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Industrial-3d Printing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Industrial-3d Printing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Industrial-3d Printing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Industrial-3D Printing market in 2023?
Industrial-3D Printing Industry Analysis
Industrial-3D Printing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industrial-3D Printing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Industrial-3d Printing Market Report:
Europe's market is forecasted to expand from $3.07 billion in 2023 to $14.18 billion by 2033. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are at the forefront of technological advancements in 3D printing, contributing to a robust industrial base.Asia Pacific Industrial-3d Printing Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness significant market growth, with a projected size of $11.49 billion by 2033, up from $2.49 billion in 2023. Key advancements in technology and rising demand for personalized manufacturing in countries like China, Japan, and India are major contributors to this growth.North America Industrial-3d Printing Market Report:
North America will continue to be a leader in the Industrial-3D Printing market, projected to surge from $4.82 billion in 2023 to $22.24 billion by 2033. The region’s strong automotive and aerospace sectors are significant drivers of growth.South America Industrial-3d Printing Market Report:
In South America, the market is anticipated to grow from $1.17 billion in 2023 to $5.40 billion by 2033. The adoption of sustainable manufacturing practices and government initiatives promoting technology innovations will drive this increase.Middle East & Africa Industrial-3d Printing Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to grow from $0.94 billion in 2023 to $4.35 billion by 2033. Investments in modernization and diversification of economies are expected to enhance the adoption of industrial 3D printing technologies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
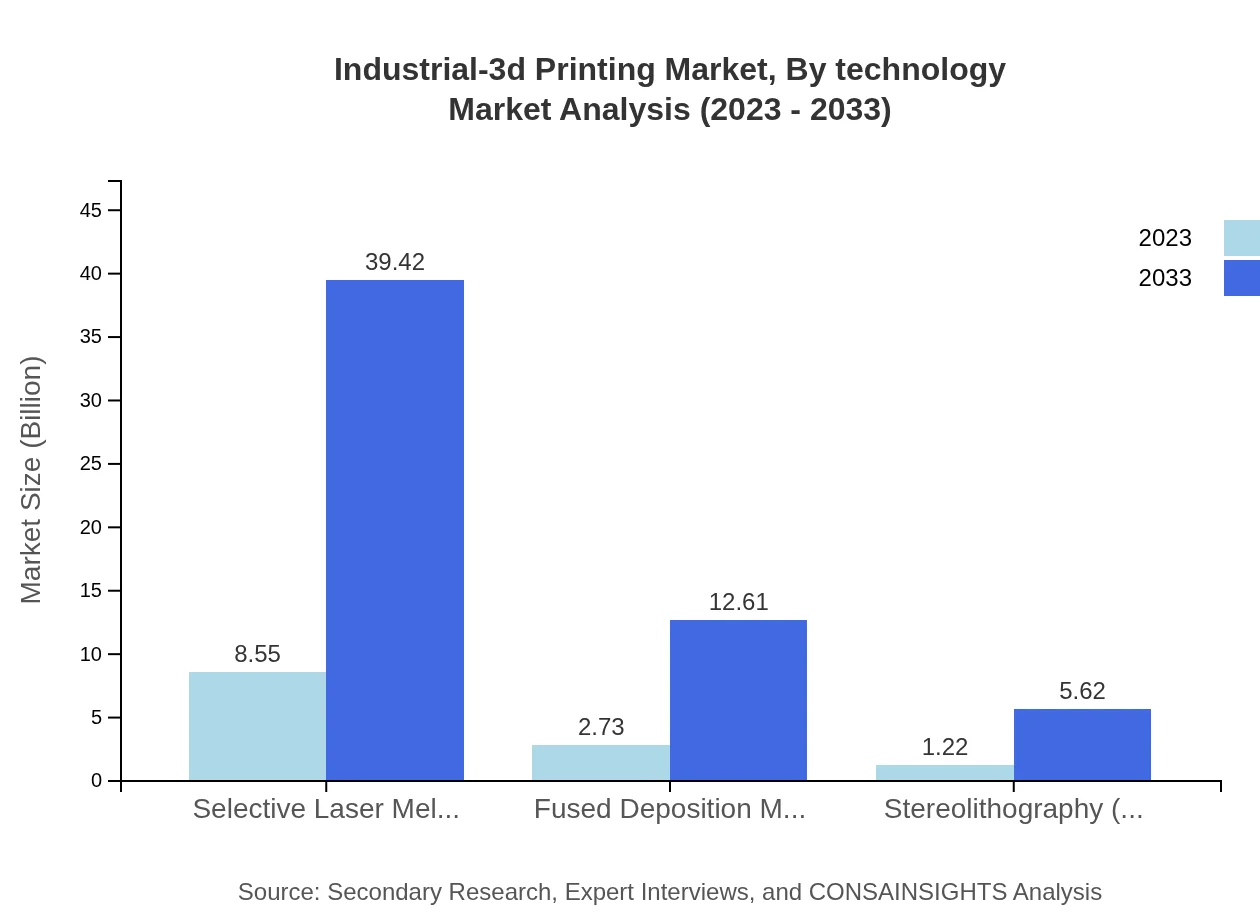
Industrial-3d Printing Market Analysis By Technology
In terms of technology, the Industrial-3D Printing market predominantly utilizes Selective Laser Melting (SLM), accounting for a market size of $8.55 billion in 2023, projected to reach $39.42 billion by 2033, thus representing a market share of 68.38%. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) follow with substantial contributions, serving various industries like automotive and healthcare.
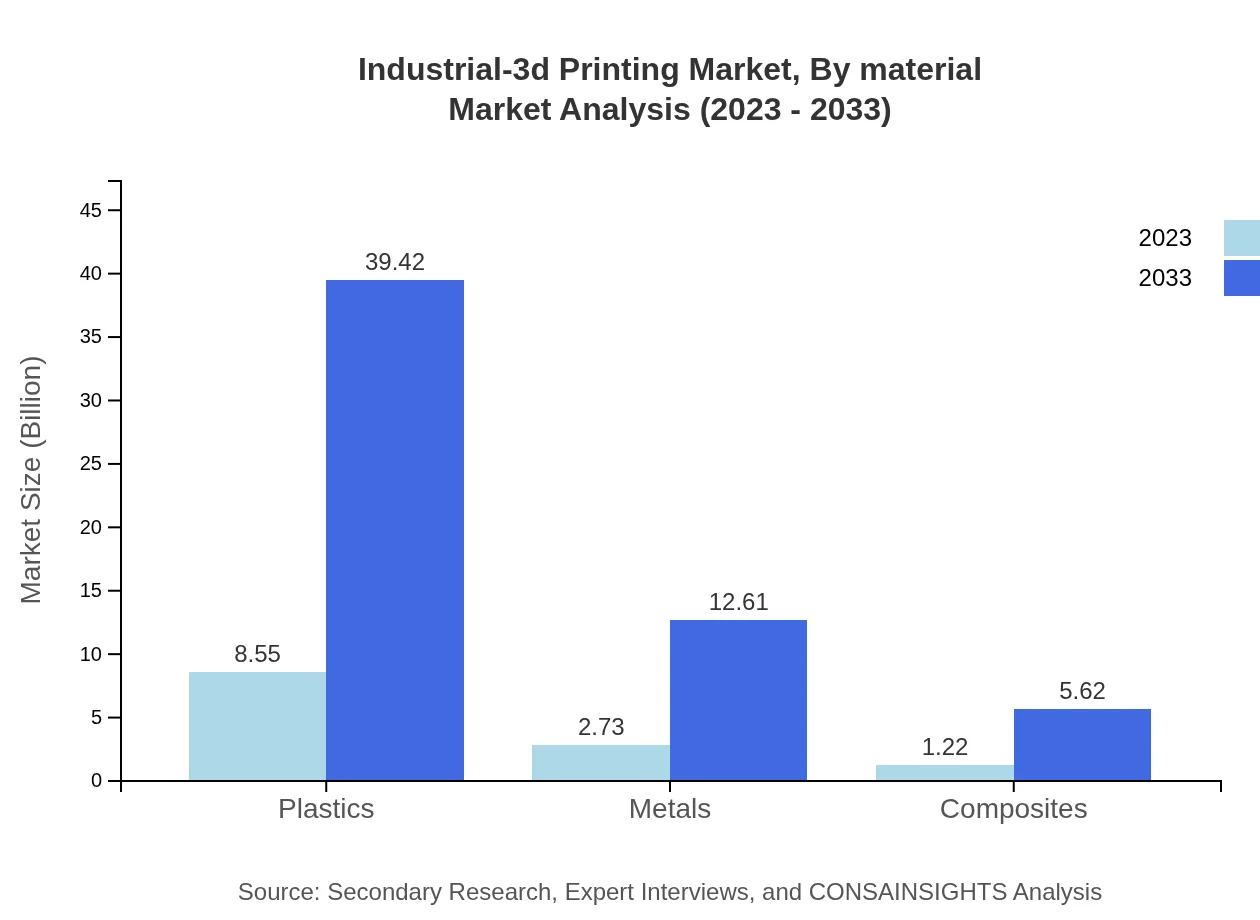
Industrial-3d Printing Market Analysis By Material
Plastics dominate the material segment, comprising a market size of $8.55 billion in 2023, likely to grow to $39.42 billion by 2033 (68.38% market share). Metals and composites also play a significant role, with notable growth in applications across high-stakes industries such as aerospace and medical devices.
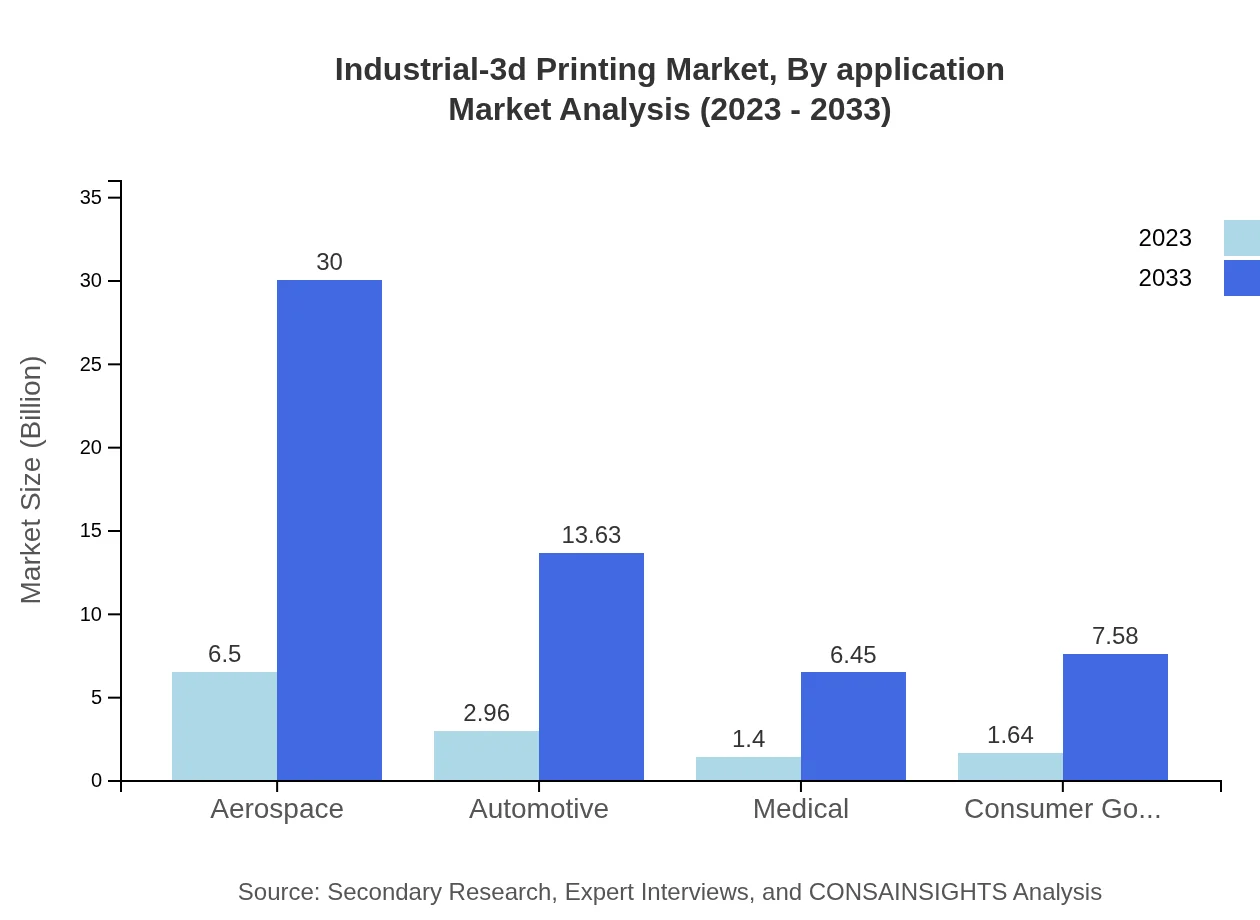
Industrial-3d Printing Market Analysis By Application
The aerospace sector is a leading application area for Industrial-3D Printing, with a size of $6.50 billion in 2023 anticipated to expand to $30.00 billion within a decade (52.03% share). The healthcare sector follows with $2.96 billion in 2023, predicted to reach $13.63 billion (23.64% share) by 2033, reflecting the industry's substantial growth in custom prosthetics.
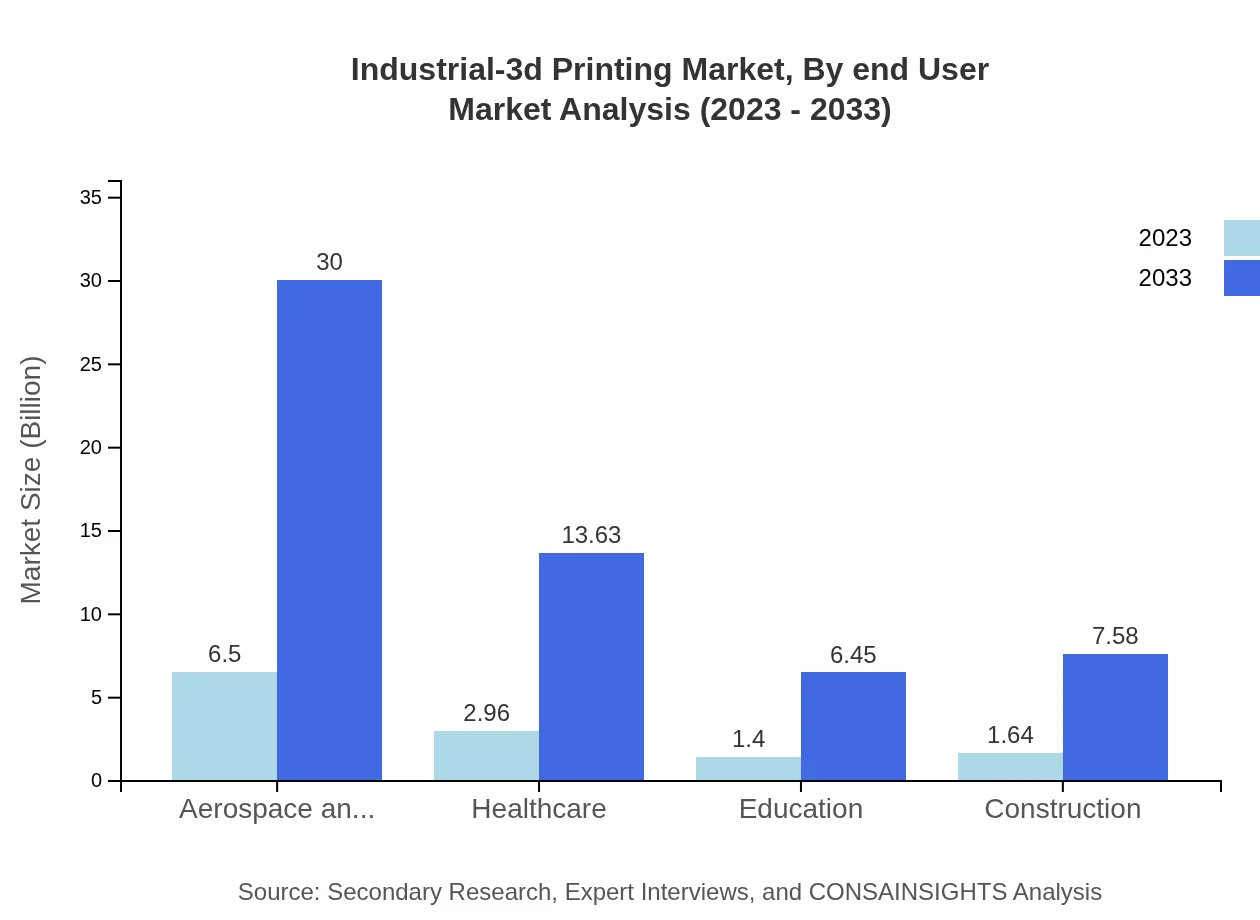
Industrial-3d Printing Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries for 3D printing include automotive, medical, and consumer goods. The automotive sector, with a market size of $2.96 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $13.63 billion by 2033, while consumer goods will also see substantial growth from $1.64 billion to $7.58 billion during the same period.
Industrial-3D Printing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Industrial-3D Printing Industry
Stratasys:
Stratasys is a leading global provider of 3D printing solutions, offering innovative products that cater to various sectors, including aerospace and automotive.3D Systems:
3D Systems is recognized for its broad portfolio of 3D printing technologies and digital manufacturing solutions, impacting industries such as healthcare and consumer goods.EOS GmbH:
EOS is a pioneer of industrial 3D printing technology, focusing on metal and polymer materials. Its innovative solutions cater to numerous manufacturing needs.Siemens AG:
Siemens is leveraging additive manufacturing to enhance production processes and is heavily invested in the development of digital manufacturing technologies.HP Inc.:
HP is a major player in the 3D printing market, known for its multi-jet fusion technology which offers advantages in speed and efficiency.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of industrial-3d Printing?
The industrial 3D printing market is projected to reach USD 12.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 15.7%. This growth highlights increasing demand across various sectors including aerospace, healthcare, and automotive.
What are the key market players or companies in this industrial-3d Printing industry?
Key players in the industrial 3D printing market include Stratasys, 3D Systems, and EOS, among others. These companies are significant in driving innovation and expanding manufacturing capabilities within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the industrial-3d Printing industry?
Growth in the industrial 3D printing industry is primarily driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for custom products, and a shift towards on-demand manufacturing, which reduces waste and improves efficiency.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the industrial-3d Printing?
North America is the fastest-growing region in industrial 3D printing, with the market expected to expand from USD 4.82 billion in 2023 to USD 22.24 billion by 2033, reflecting a robust demand in various manufacturing segments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the industrial-3d Printing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the industrial 3D printing industry. This allows businesses to access insights that are relevant to their unique operational contexts.
What deliverables can I expect from this industrial-3d Printing market research project?
Expect comprehensive reports featuring market size, growth projections, competitor analysis, key trends, and regional profiles. Deliverables will include detailed charts, graphs, and actionable insights to guide strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of industrial-3d Printing?
Current trends in industrial 3D printing include increasing integration of AI and machine learning, expansion into healthcare applications, enhanced materials usage, and growing interest in sustainable manufacturing practices.