Industrial Radiography Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: industrial-radiography
Industrial Radiography Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Industrial Radiography market, including market size, growth trends, regional insights, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It encompasses detailed segments based on technology, application, and end-user industries, offering valuable data for stakeholders and decision-makers.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
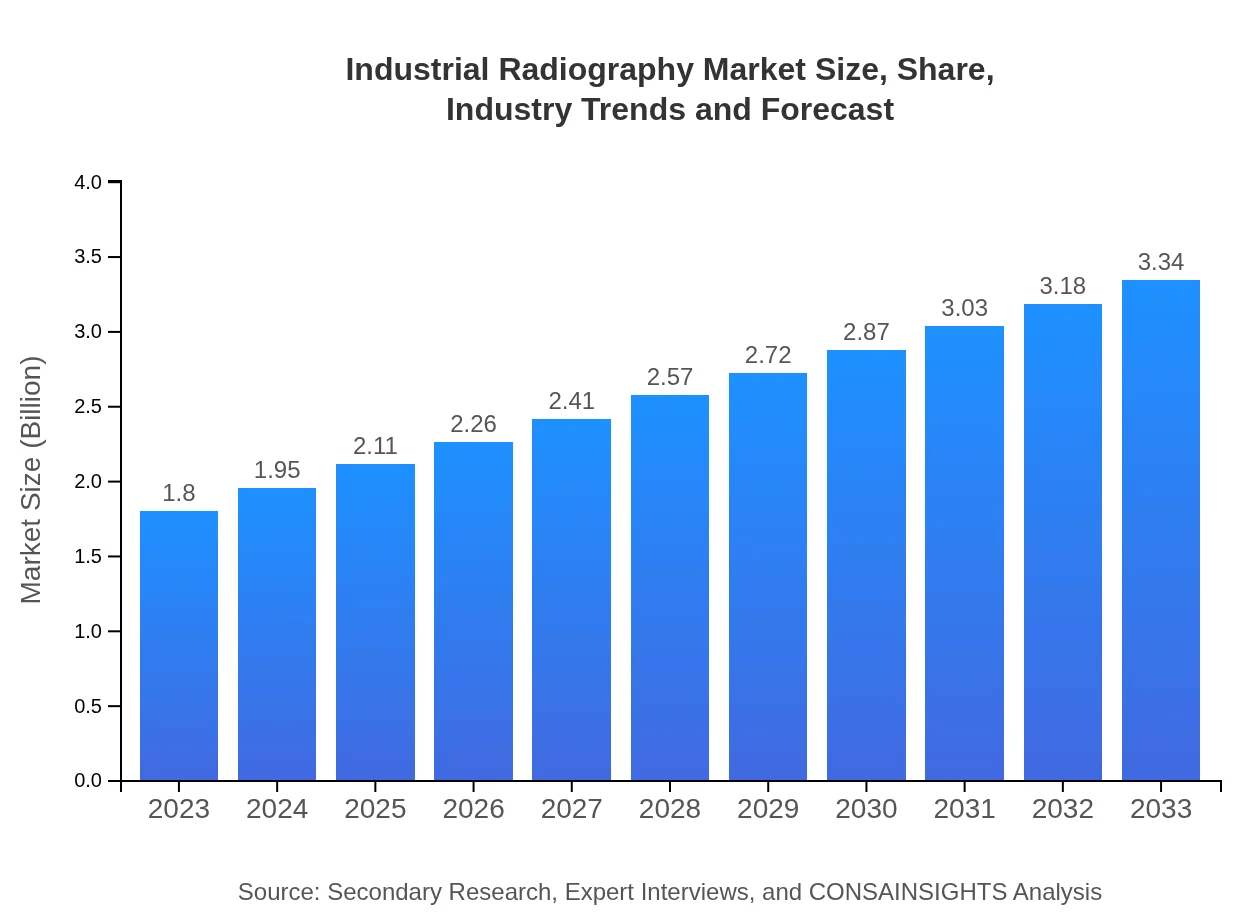
| 2023 Market Size | $1.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $3.34 Billion |
| Top Companies | GE Inspection Technologies, Olympus Corporation, Nikon Metrology, Mistras Group, Siemens AG |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Industrial Radiography Market Overview
Customize Industrial Radiography Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Industrial Radiography market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Industrial Radiography's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Industrial Radiography
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Industrial Radiography market in 2023?
Industrial Radiography Industry Analysis
Industrial Radiography Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industrial Radiography Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Industrial Radiography Market Report:
Europe's Industrial Radiography market is expected to expand from $0.44 billion in 2023 to $0.81 billion by 2033. Initiatives aimed at enhancing manufacturing operations and ensuring compliance with stringent safety standards are propelling growth. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK lead in technological advancements, and increasing R&D investments focused on industrial applications.Asia Pacific Industrial Radiography Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to experience robust growth in the Industrial Radiography market, with a market size increasing from $0.36 billion in 2023 to approximately $0.68 billion by 2033. Rapid industrialization and increasing investments in infrastructure projects, particularly in countries like China and India, are driving this growth. Additionally, government initiatives aimed at enhancing manufacturing capabilities and ensuring quality control are expected to further boost demand for radiographic testing.North America Industrial Radiography Market Report:
The North American market for Industrial Radiography is projected to grow significantly from $0.64 billion in 2023 to about $1.18 billion by 2033. The strong push toward regulatory compliance, coupled with the presence of major players in the region, is driving investments in non-destructive testing technologies. The U.S. and Canada are the primary markets, where aerospace and defense sectors greatly influence radiographic testing services.South America Industrial Radiography Market Report:
In South America, the Industrial Radiography market is anticipated to grow from $0.14 billion in 2023 to $0.25 billion by 2033. The growth is largely attributed to the expansion of the oil and gas sector and the increasing need for safety inspections and quality assurance in industrial processes. Market players are expected to focus on enhancing service offerings in this region to cater to the evolving needs of various industries.Middle East & Africa Industrial Radiography Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region is forecasted to grow from $0.22 billion in 2023 to $0.41 billion by 2033. Growth in this region is fueled by rising oil and gas exploration activities, necessitating effective inspection technologies to ensure safety and operational continuity. Furthermore, increasing infrastructure development projects in the UAE and Saudi Arabia contribute to the expected market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
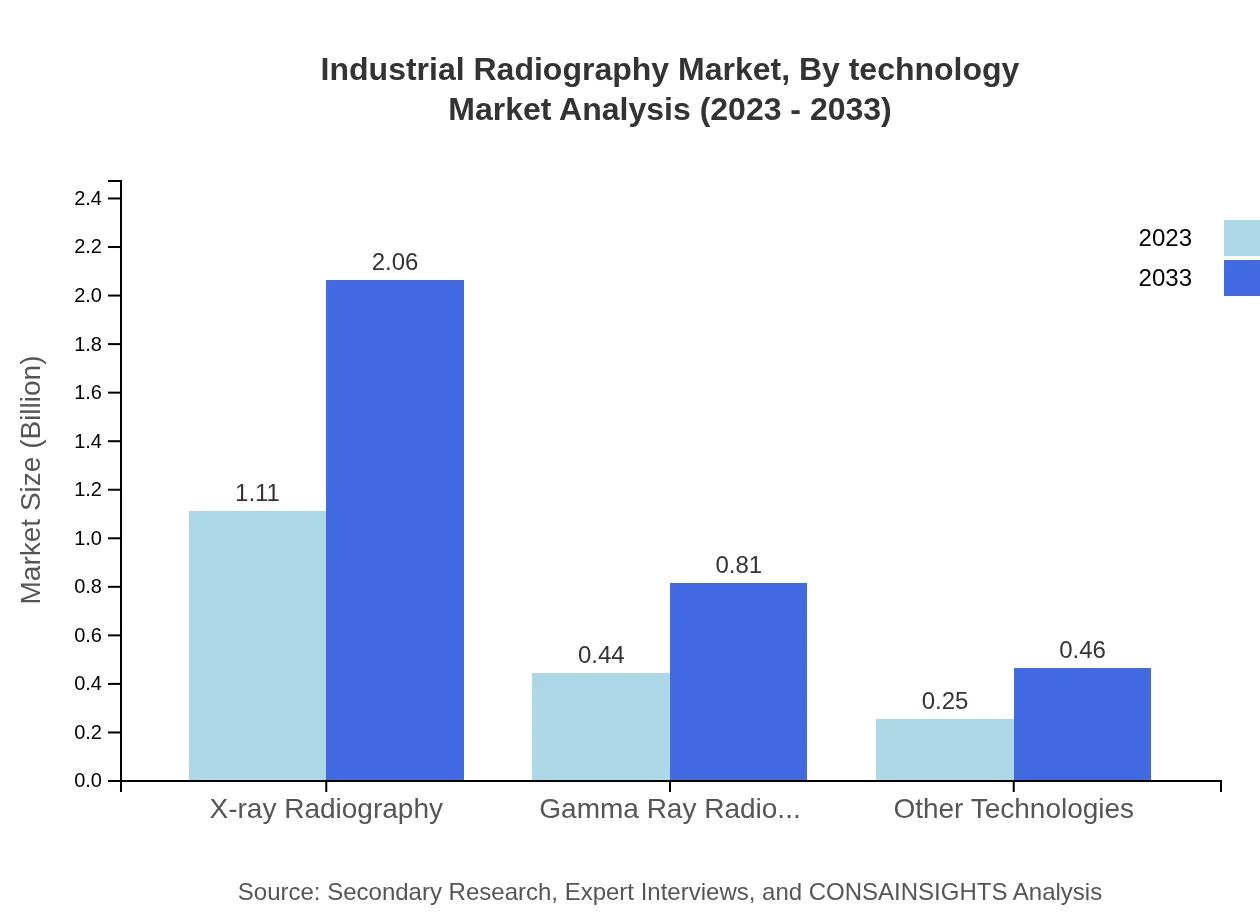
Industrial Radiography Market Analysis By Technology
X-ray radiography is the leader in technology segment, with a market size expected to rise from $1.11 billion in 2023 to $2.06 billion in 2033, capturing 61.76% market share. Gamma-ray radiography follows with a size increase from $0.44 billion to $0.81 billion, representing 24.39% market share. Other technologies, including digital and automated techniques, are also gaining traction as industries seek efficiency and accuracy.
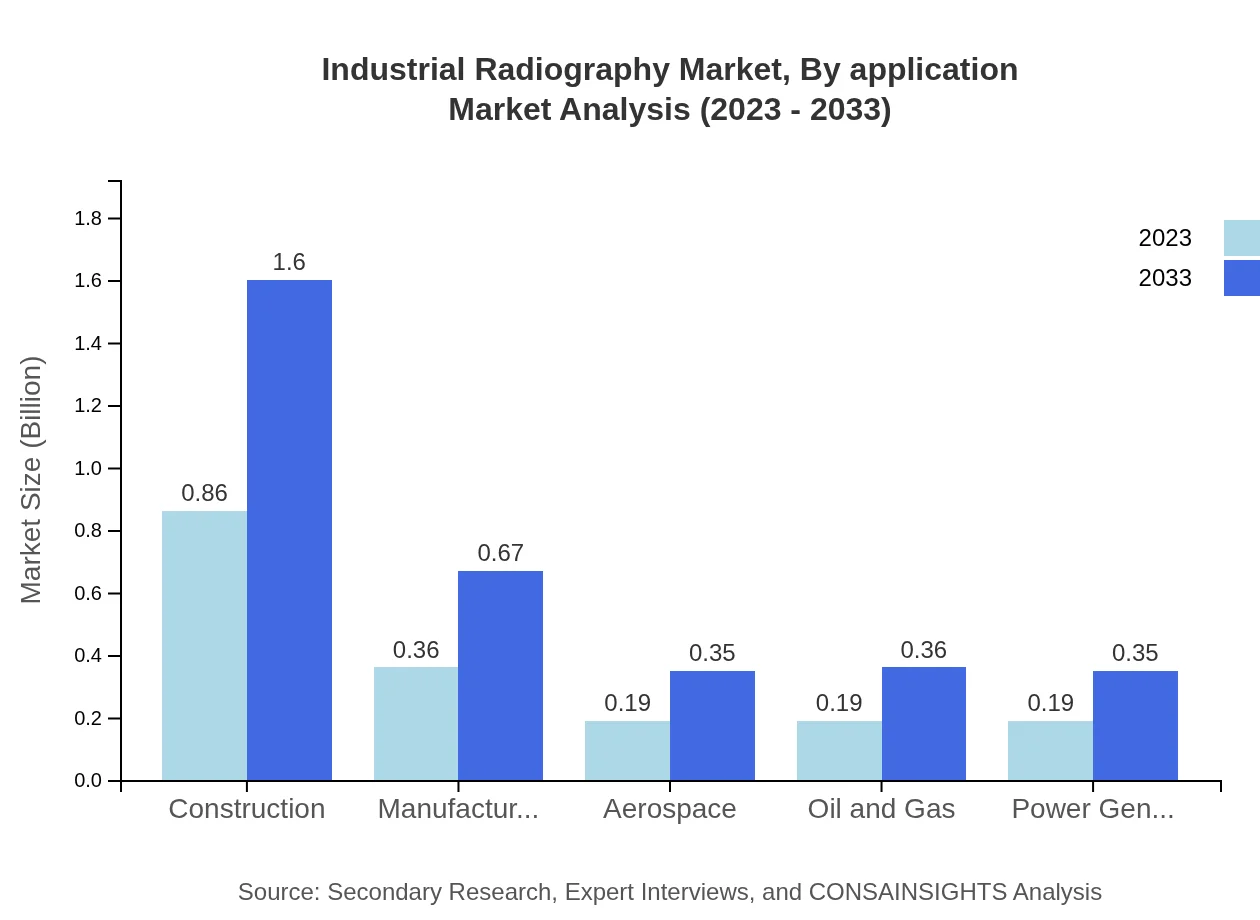
Industrial Radiography Market Analysis By Application
The applications for industrial radiography include sectors like the energy and power industry, which is projected to grow from $0.86 billion in 2023 to $1.60 billion by 2033, commanding a significant share of 47.86%. The aerospace and defense sector is also significant, with a market size increase from $0.36 billion to $0.67 billion, claiming 20.16% market share.
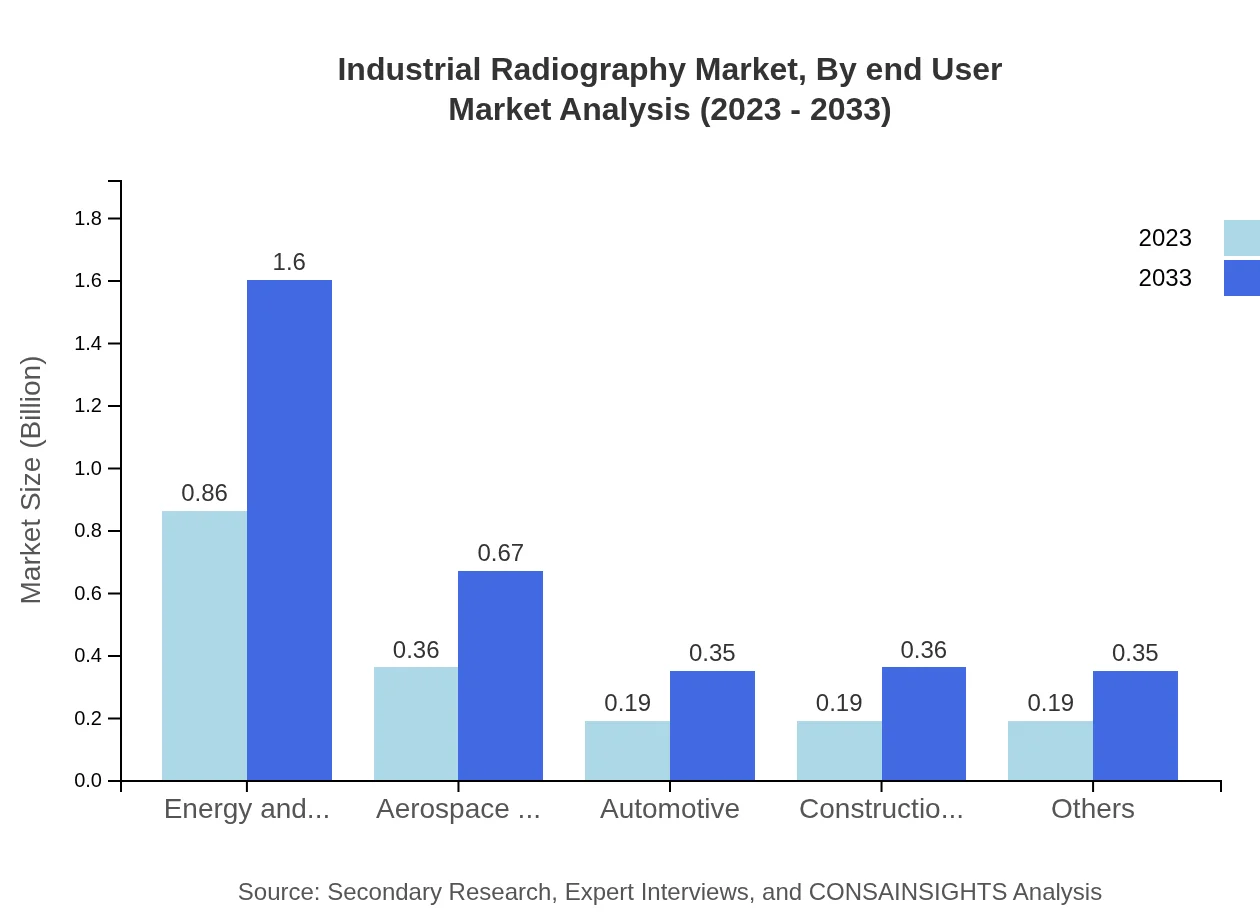
Industrial Radiography Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment highlights manufacturing as a key area, with growth projected from $0.36 billion in 2023 to $0.67 billion by 2033, reflecting a market share of 20.16%. Other notable end-users include automotive and construction, with similar growth trajectories due to rising safety regulations and quality assurance mandates.
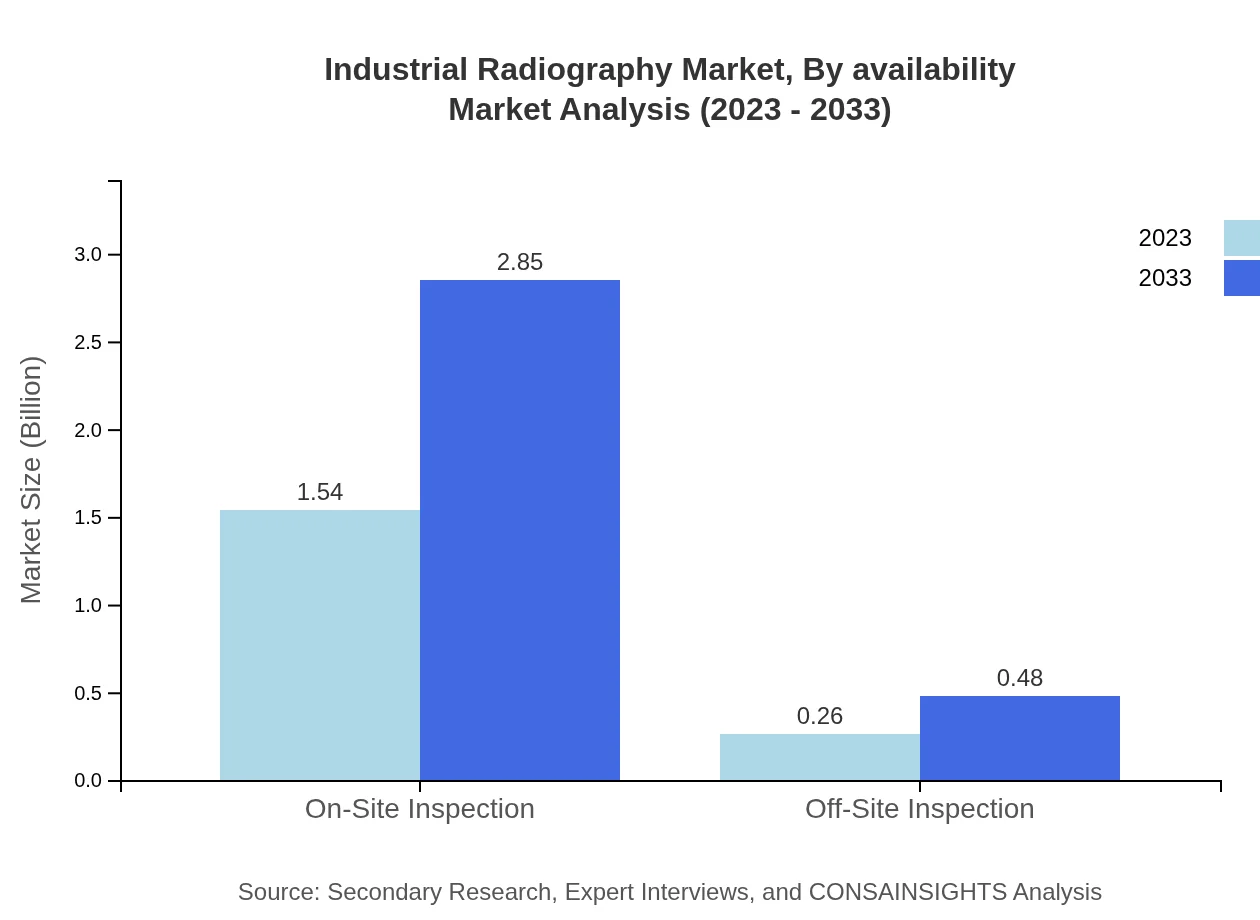
Industrial Radiography Market Analysis By Availability
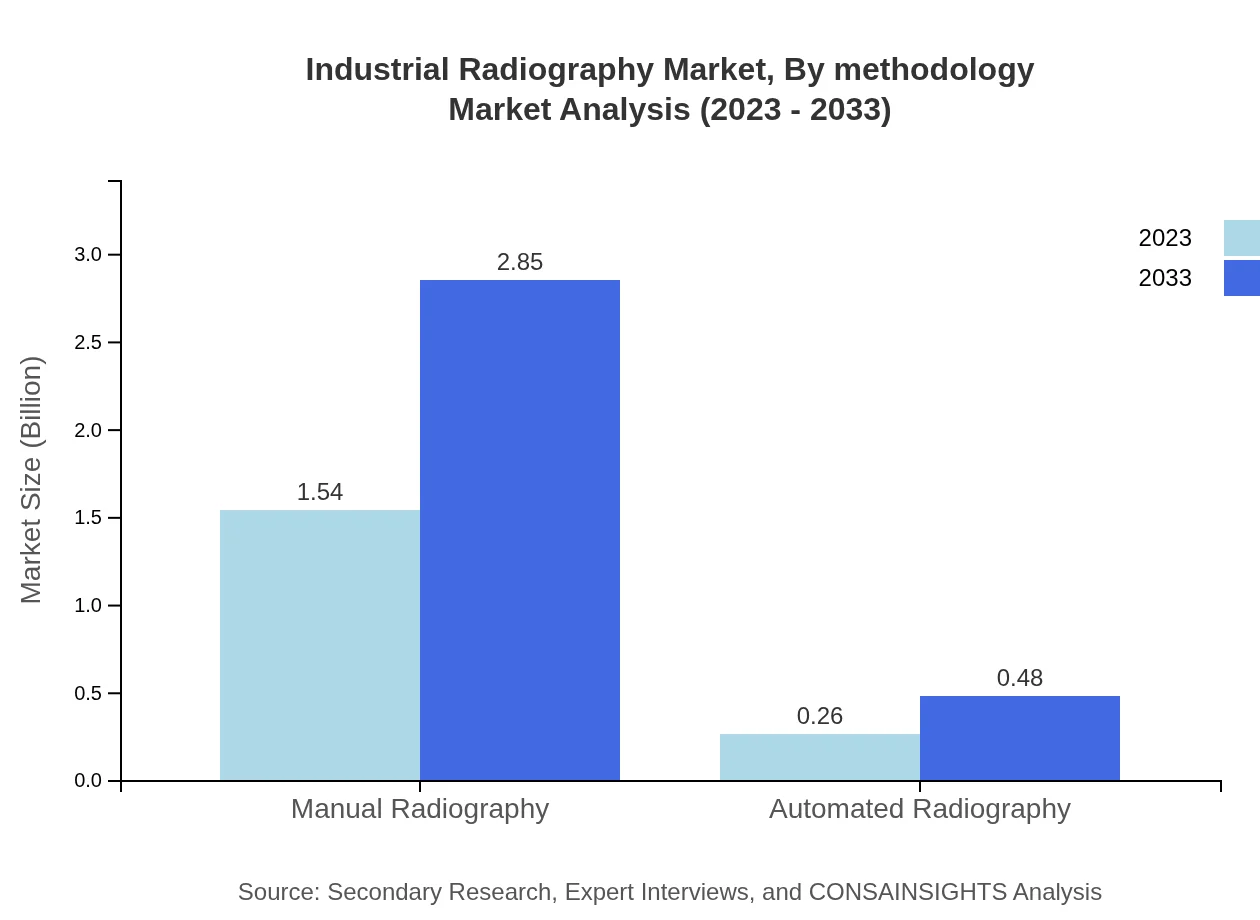
The availability segment shows that manual radiography currently holds a dominant position, expected to grow from $1.54 billion to $2.85 billion by 2033, with a share of 85.48%. Automated methods, while smaller, are gaining popularity and are projected to grow from $0.26 billion to $0.48 billion.
Industrial Radiography Market Analysis By Methodology
Inspection methodologies like on-site inspections are gaining traction, reflecting the industry trend toward immediate assessment processes, projected to grow significantly in market size over the next decade. Off-site inspection methods, while less widespread, signify evolving models of service delivery in industrial radiography.
Industrial Radiography Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Industrial Radiography Industry
GE Inspection Technologies:
A leading provider of industrial inspection technologies focused on advanced non-destructive testing solutions and innovative inspection methods.Olympus Corporation:
A global company known for its imaging technologies and non-destructive testing solutions, focusing on both industrial applications and personnel safety.Nikon Metrology:
Offers industrial microscope and radiography solutions, catering to quality assurance in manufacturing sectors, enhancing inspection accuracy.Mistras Group:
Specializes in asset protection solutions, offering numerous NDT services including industrial radiography to ensure operational safety.Siemens AG:
Provides a broad portfolio of industrial services, focusing on high-technology solutions, including radiography for various industrial applications.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of industrial radiography?
The industrial radiography market is valued at $1.8 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 6.2%, indicating significant growth potential over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in this industrial radiography industry?
Key players in the industrial radiography sector include major companies specializing in radiographic equipment, inspection services, and imaging technologies, driving innovation and competition within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the industrial radiography industry?
Growth drivers include increased industrial inspections, safety regulations, technological advancements in imaging, and a rising demand in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and construction for quality assurance.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the industrial radiography?
North America is identified as the fastest-growing region, expanding from $0.64 billion in 2023 to $1.18 billion by 2033, driven by extensive industrial activities and technological adoption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the industrial radiography industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs, ensuring comprehensive insights across various segments within the industrial radiography industry.
What deliverables can I expect from this industrial radiography market research project?
Expected deliverables include detailed market analysis, segmentation insights, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and tailored recommendations for strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of industrial radiography?
Current trends include the adoption of automation in radiographic inspections, advancements in digital imaging technologies, and a shift towards more environmentally sustainable practices within the industrial radiography sector.