Industrial Sugar Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: industrial-sugar
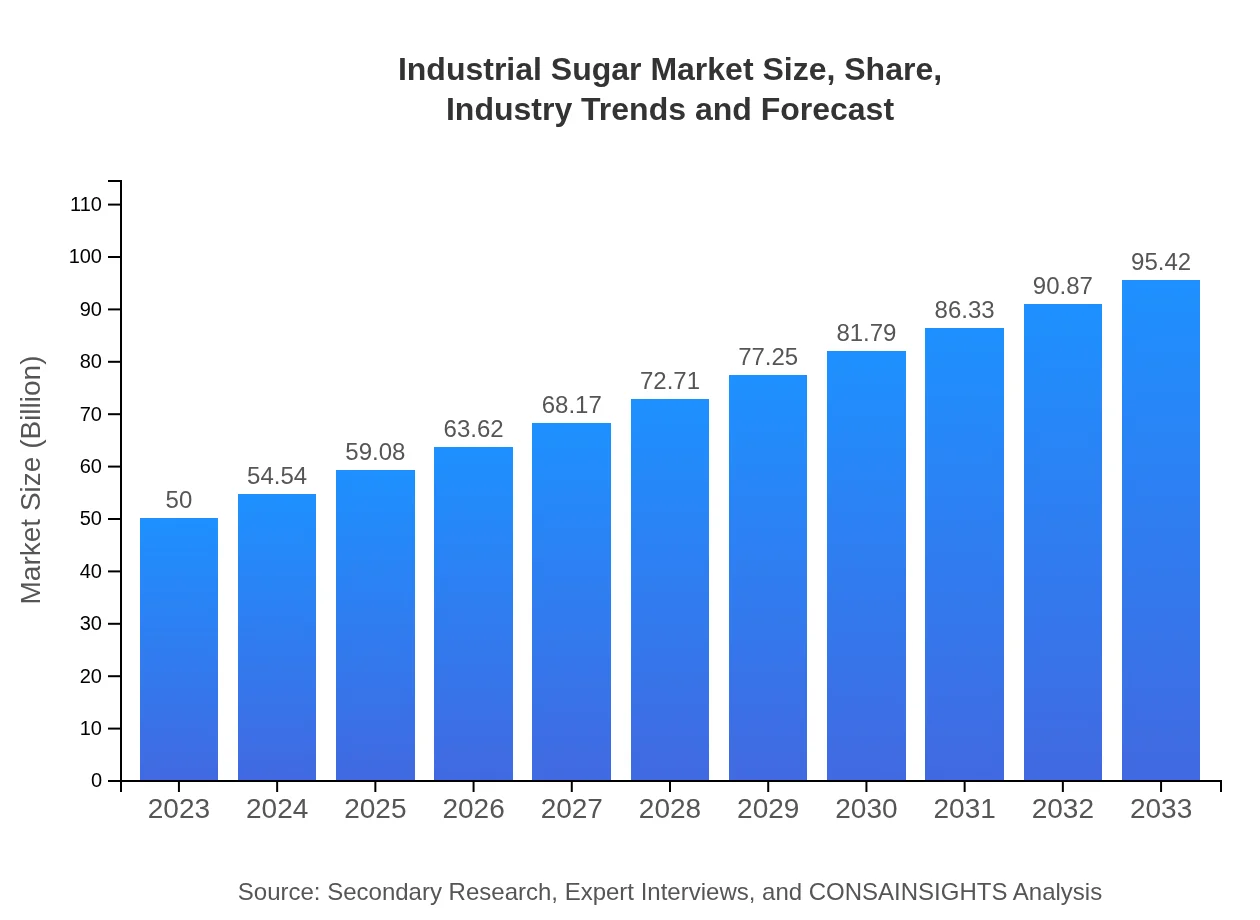
Industrial Sugar Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive report delves into the Industrial Sugar market, providing insights on market size, trends, growth forecast, and regional analysis from 2023 to 2033. It aims to equip stakeholders with essential data for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $95.42 Billion |
| Top Companies | Wilmar International Limited, Cargill, Incorporated, American Sugar Refining, Inc., Tereos SCA, Südzucker AG |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Industrial Sugar Market Overview
Customize Industrial Sugar Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Industrial Sugar market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Industrial Sugar's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Industrial Sugar
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Industrial Sugar Market in 2023?
Industrial Sugar Industry Analysis
Industrial Sugar Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industrial Sugar Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Industrial Sugar Market Report:
Europe's market is projected to expand from $14.00 billion in 2023 to $26.72 billion by 2033, supported by stringent regulations on food labeling and a rising preference for natural sweeteners, prompting major food manufacturers to reformulate products.Asia Pacific Industrial Sugar Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Industrial Sugar market is set to grow from $9.55 billion in 2023 to $18.22 billion by 2033, driven by increasing consumption in emerging economies like India and China, where the demand for processed and convenience foods is rising rapidly.North America Industrial Sugar Market Report:
The North American Industrial Sugar market is the largest globally, expected to grow from $18.95 billion in 2023 to $36.15 billion by 2033. Rising demand for clean label products and innovations in food technology are key growth factors, alongside the booming beverage industry.South America Industrial Sugar Market Report:
The South American market, valued at $2.21 billion in 2023, shows significant growth potential, reaching $4.21 billion by 2033. The region's rich agricultural base and shifting consumer preferences towards organic and sustainable sugar products will drive this increase.Middle East & Africa Industrial Sugar Market Report:
This region shows robust growth from $5.30 billion in 2023 to $10.11 billion by 2033 as urbanization and changing lifestyles contribute to rising demand. Increasing investments in agriculture and infrastructure will further support market expansion.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
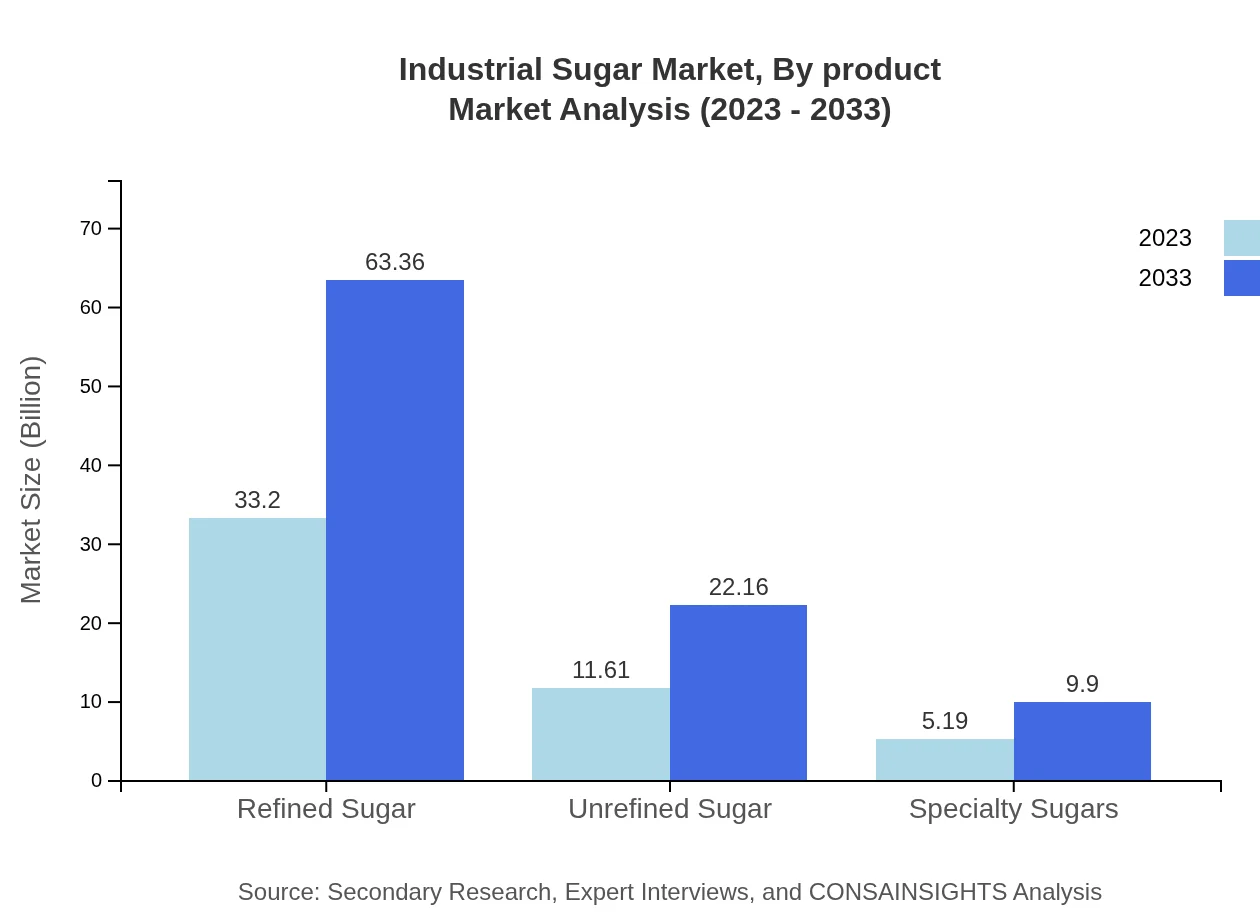
Industrial Sugar Market Analysis By Product
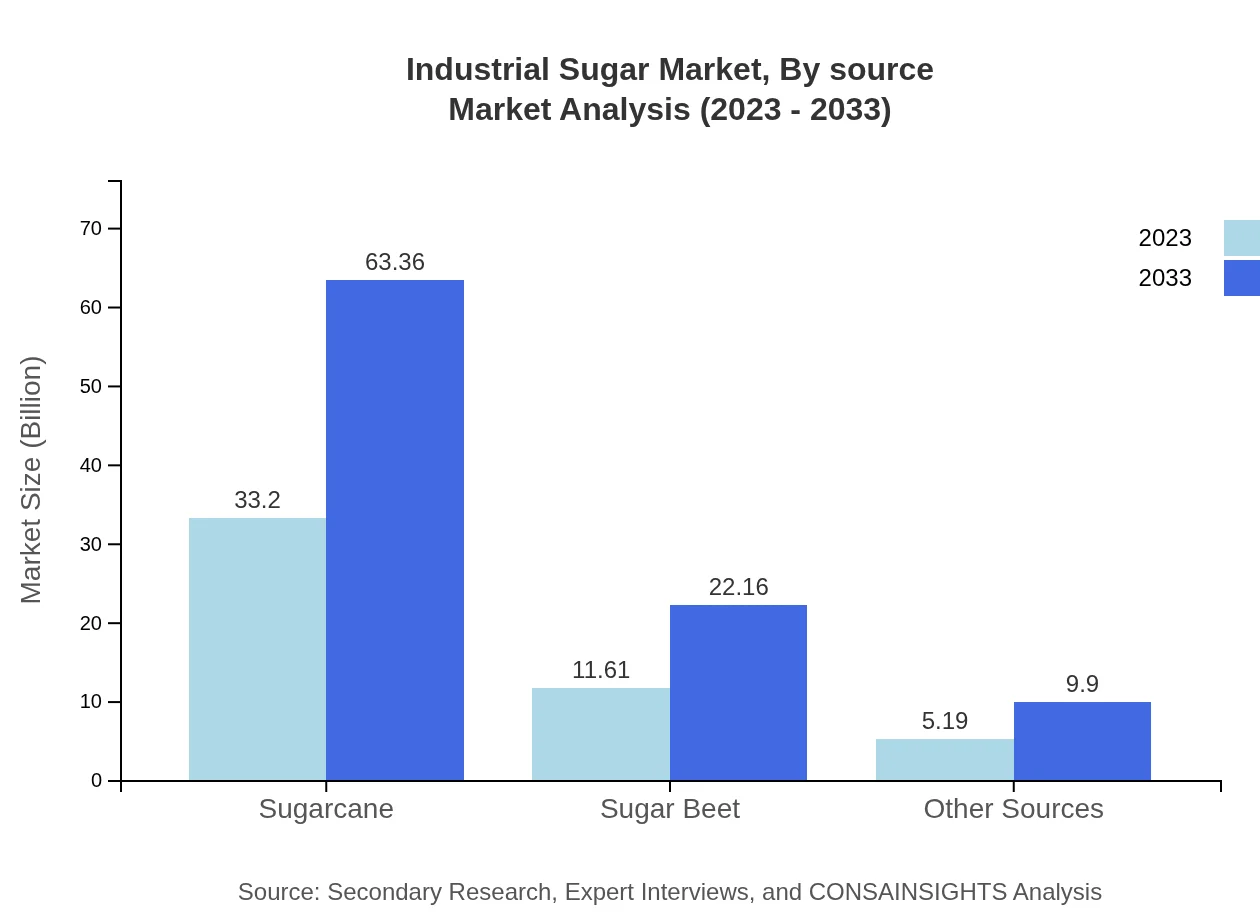
The sector is significantly dominated by Sugarcane, with the market size projected to grow from $33.20 billion in 2023 to $63.36 billion by 2033, retaining a market share of 66.4%. Sugar Beet is another significant segment, anticipated to expand from $11.61 billion in 2023 to $22.16 billion by 2033, capturing 23.22% market share. Other sources contribute significantly with growth from $5.19 billion to $9.90 billion, maintaining a 10.38% share.
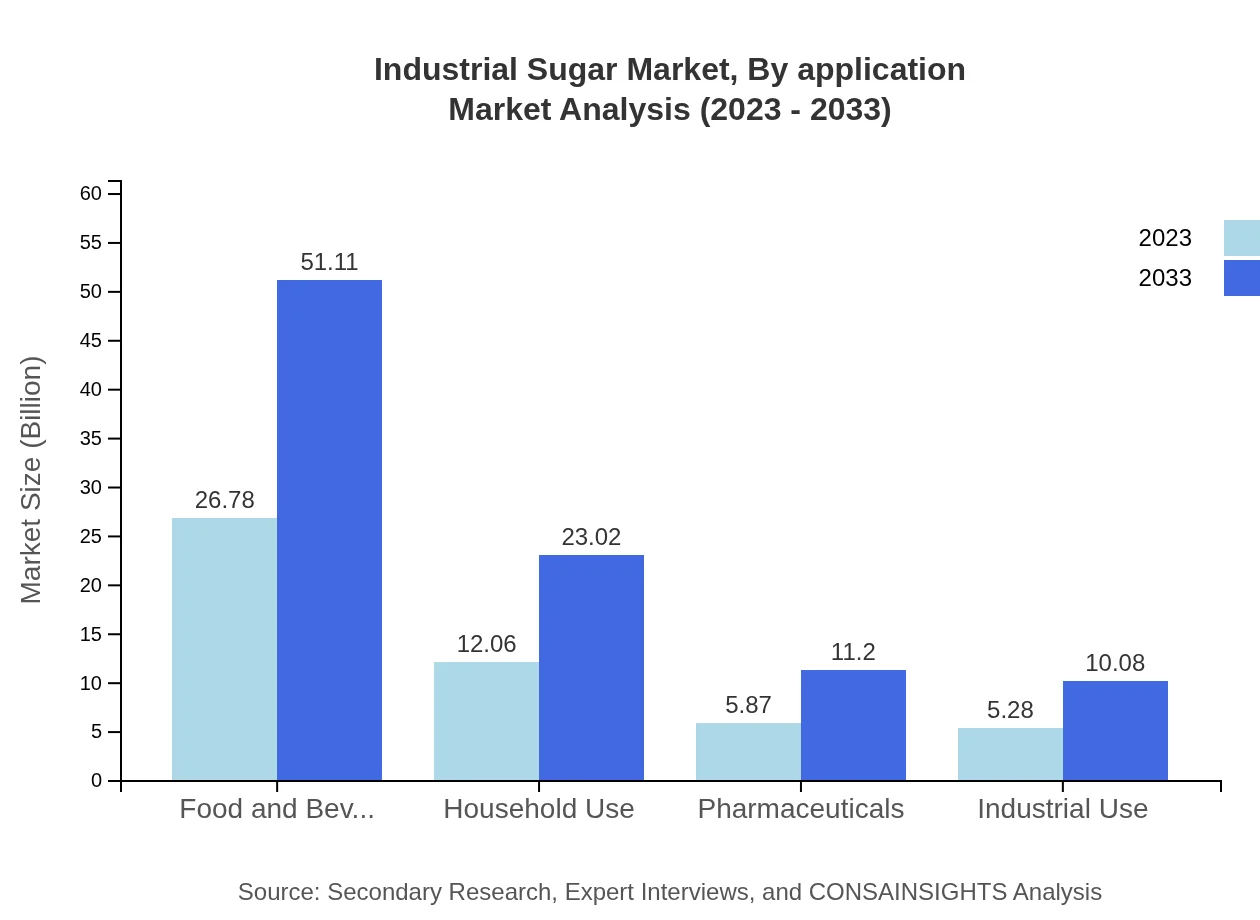
Industrial Sugar Market Analysis By Application
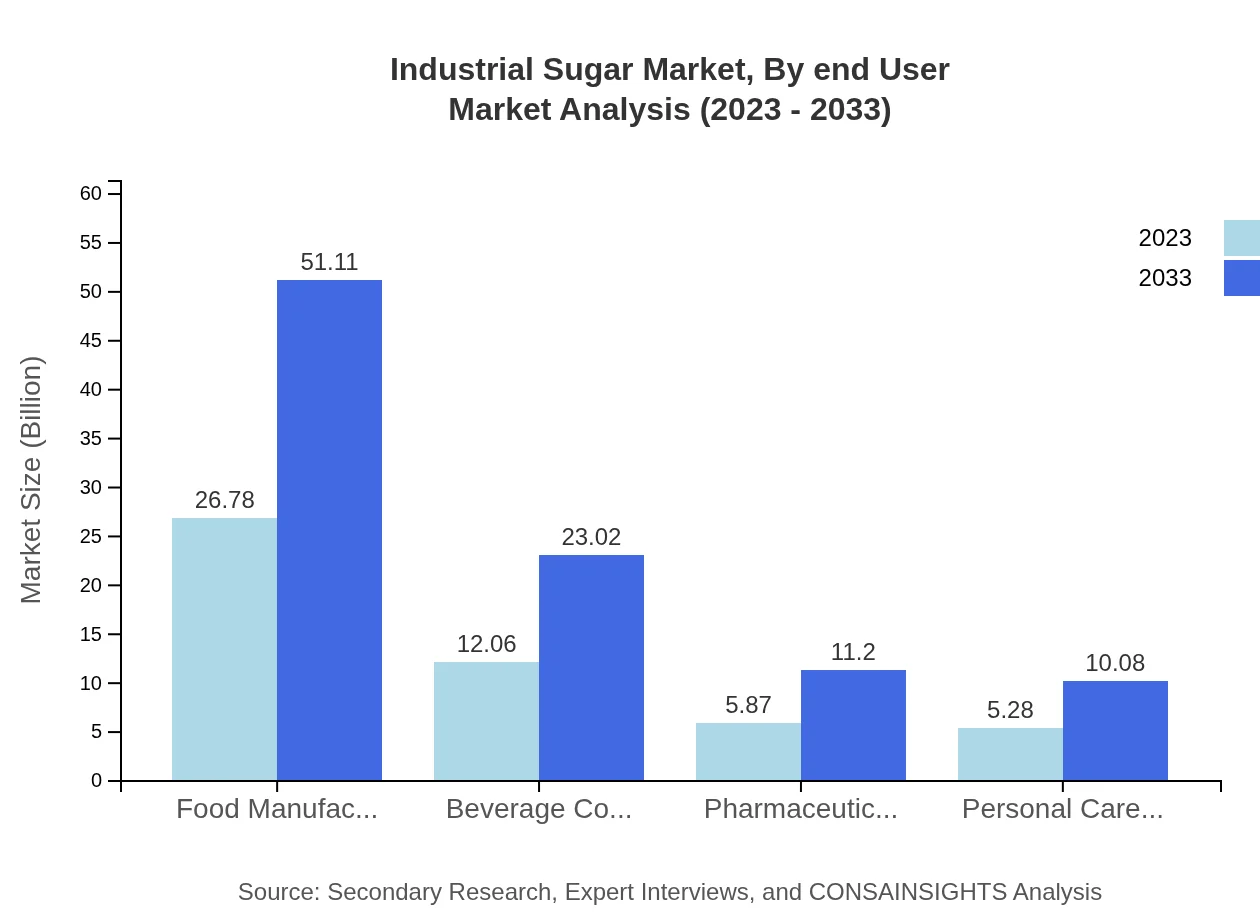
The Food and Beverage sector leads the Industrial Sugar market, representing a revenue increase from $26.78 billion in 2023 to $51.11 billion by 2033, showing a 53.57% share. Beverage companies alone see growth from $12.06 billion to $23.02 billion. The pharmaceutical sector is also crucial, expanding from $5.87 billion to $11.20 billion, facilitating innovations in drug development.
Industrial Sugar Market Analysis By Source
Sugarcane and Sugar Beet continue to dominate the sourcing segment. Innovations and sustainable practices in sourcing are increasingly gaining traction, supporting health and environmental awareness. Projections indicate that the sustainability segment will reflect growth, reinforcing the shift towards eco-friendly sugar production methods.
Industrial Sugar Market Analysis By End User
Increased sugar utilization in the food and beverage industry correlates with the overall market growth. The Pharmaceutical industry's reliance on pure sugar for medicinal purposes further solidifies its need. Additionally, personal care industries are recognizing the benefits of sugar in formulations, contributing to the anticipated growth.
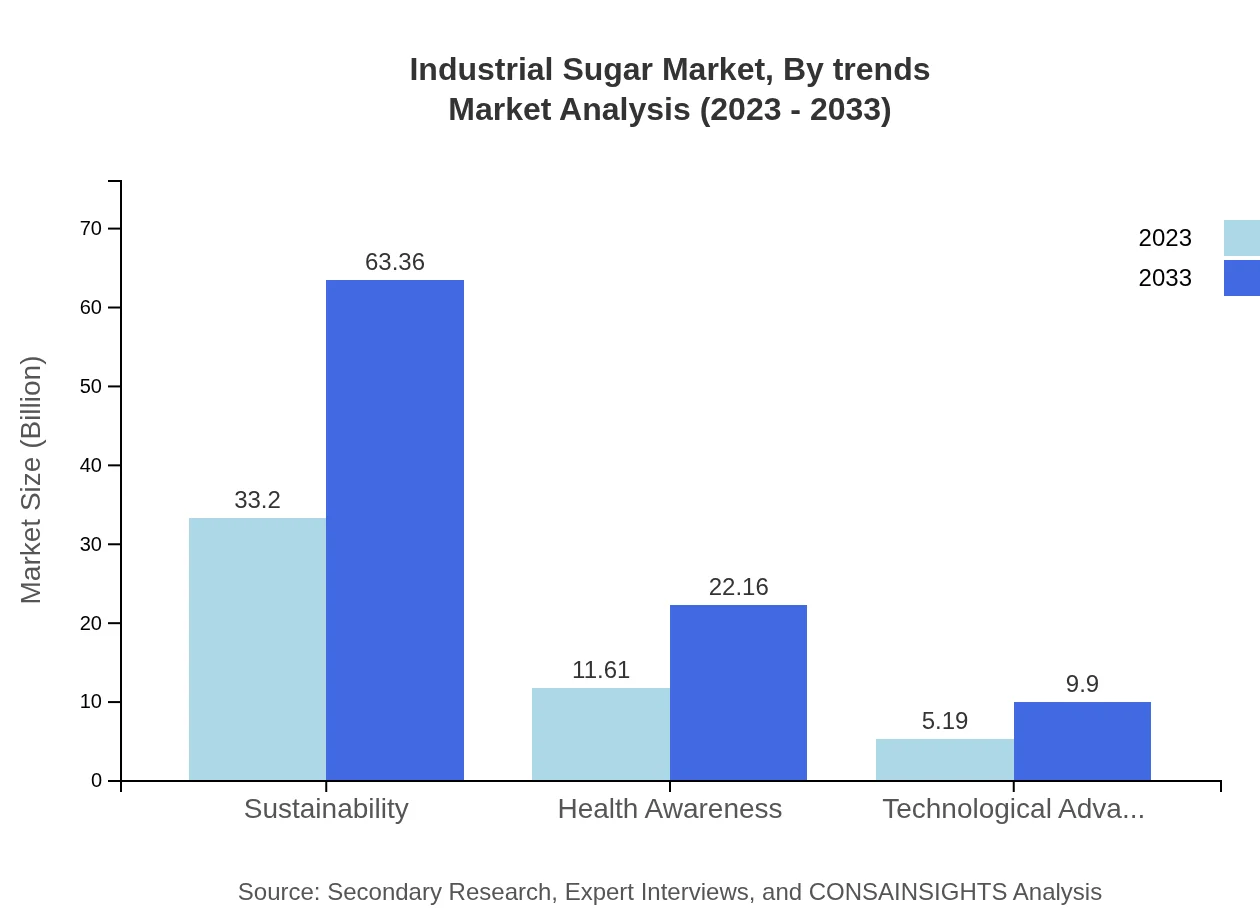
Industrial Sugar Market Analysis By Trends
Notable trends influencing the market include a shift towards organic sugar products, heightened health awareness, and advancements in refining technology. There is growing consumer interest in the sustainability of sugar sources, leading to innovations aimed at reducing environmental impacts during production and refining.
Industrial Sugar Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Industrial Sugar Industry
Wilmar International Limited:
A leading global agribusiness group, Wilmar produces and processes sugar and operates across the entire value chain, ensuring a significant position in the Industrial Sugar market.Cargill, Incorporated:
Cargill is a prominent player in the sugar industry, recognized for its substantial investments in refining processes and extensive product offerings across food and industrial applications.American Sugar Refining, Inc.:
With a consistent reputation for quality, American Sugar Refining specializes in refining sugar products, catering to various end-user markets including food processing and distribution.Tereos SCA:
A French multinational known for its integrated sugar production and agricultural expertise, Tereos is pivotal in driving sustainable practices in sugar sourcing and processing.Südzucker AG:
As one of the largest sugar producers in Europe, Südzucker plays a crucial role in the market due to its diversified product range and emphasis on sustainability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of industrial sugar?
The industrial sugar market size is projected to reach approximately $50 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from its current size.
What are the key market players or companies in the industrial sugar industry?
Key players in the industrial sugar market include notable companies such as Archer Daniels Midland, Cargill, and Tate & Lyle, among others. These companies play significant roles in production, distribution, and innovation within the sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the industrial sugar industry?
Drivers of growth in the industrial sugar market include increased demand in food and beverage sectors, innovations in agriculture, and rising consumer focus on health and sustainability, significantly influencing market dynamics.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the industrial sugar market?
The fastest-growing region in the industrial sugar market is projected to be North America, with market size increasing from $18.95 billion in 2023 to $36.15 billion in 2033, indicating a robust growth trajectory.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the industrial sugar industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the industrial sugar industry, allowing clients to gain targeted insights relevant to their business objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this industrial sugar market research project?
Deliverables from the industrial sugar market research project typically include detailed reports, market forecasts, strategic recommendations, and segment analyses to aid in strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of industrial sugar?
Current trends in the industrial sugar market highlight a shift towards sustainability, technological advancements in production processes, and a rising preference for healthier sugar alternatives among consumers.