Industry-4-0 Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: industry-4-0
Industry-4-0 Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the Industry 4.0 market, including market size forecasts, growth trends, regional insights, and technology advancements from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
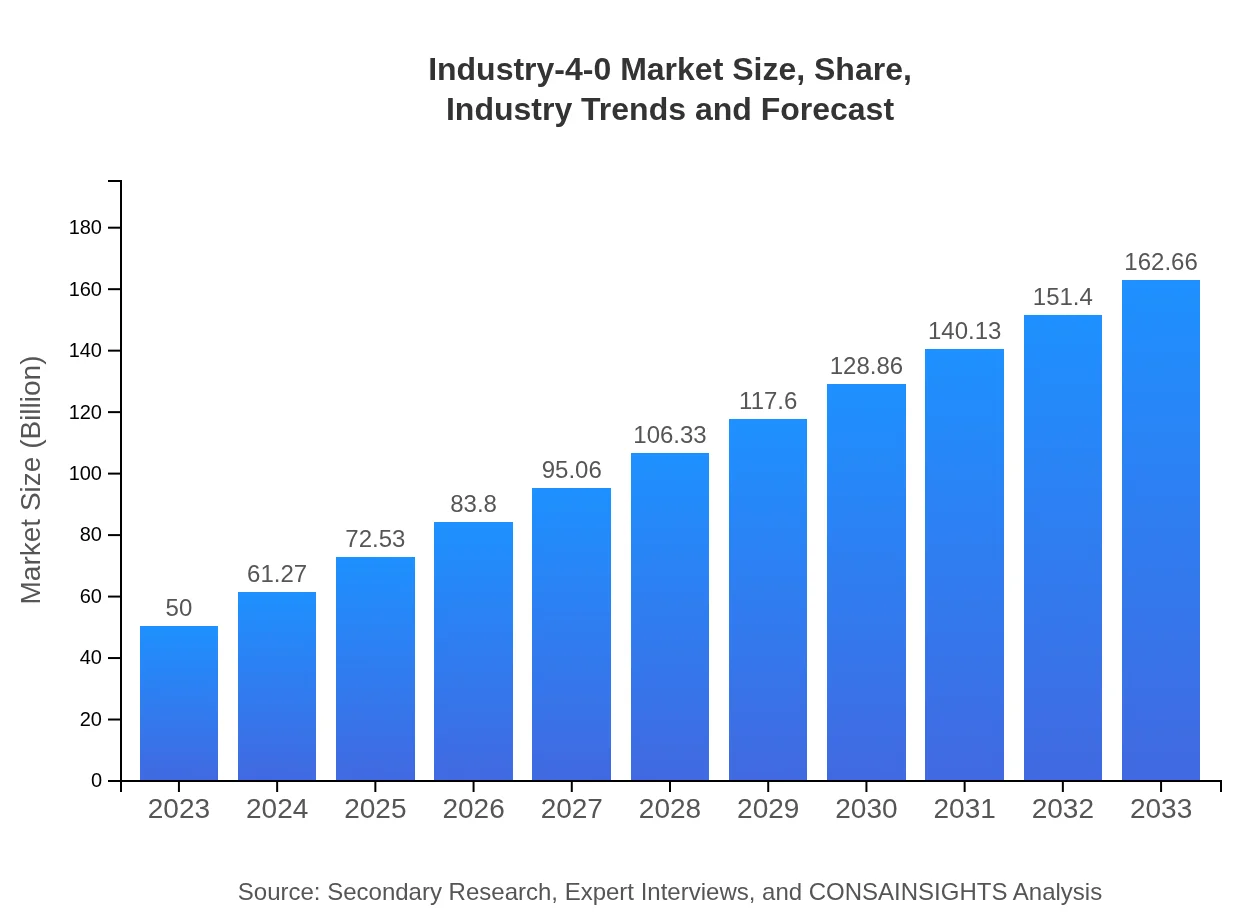
| 2023 Market Size | $50.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12% |
| 2033 Market Size | $162.66 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, General Electric, ABB Ltd., Rockwell Automation |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Industry-4-0 Market Overview
Customize Industry-4-0 Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Industry-4-0 market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Industry-4-0's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Industry-4-0
What is the Market Size & CAGR of the Industry-4-0 market in 2023?
Industry-4-0 Industry Analysis
Industry-4-0 Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
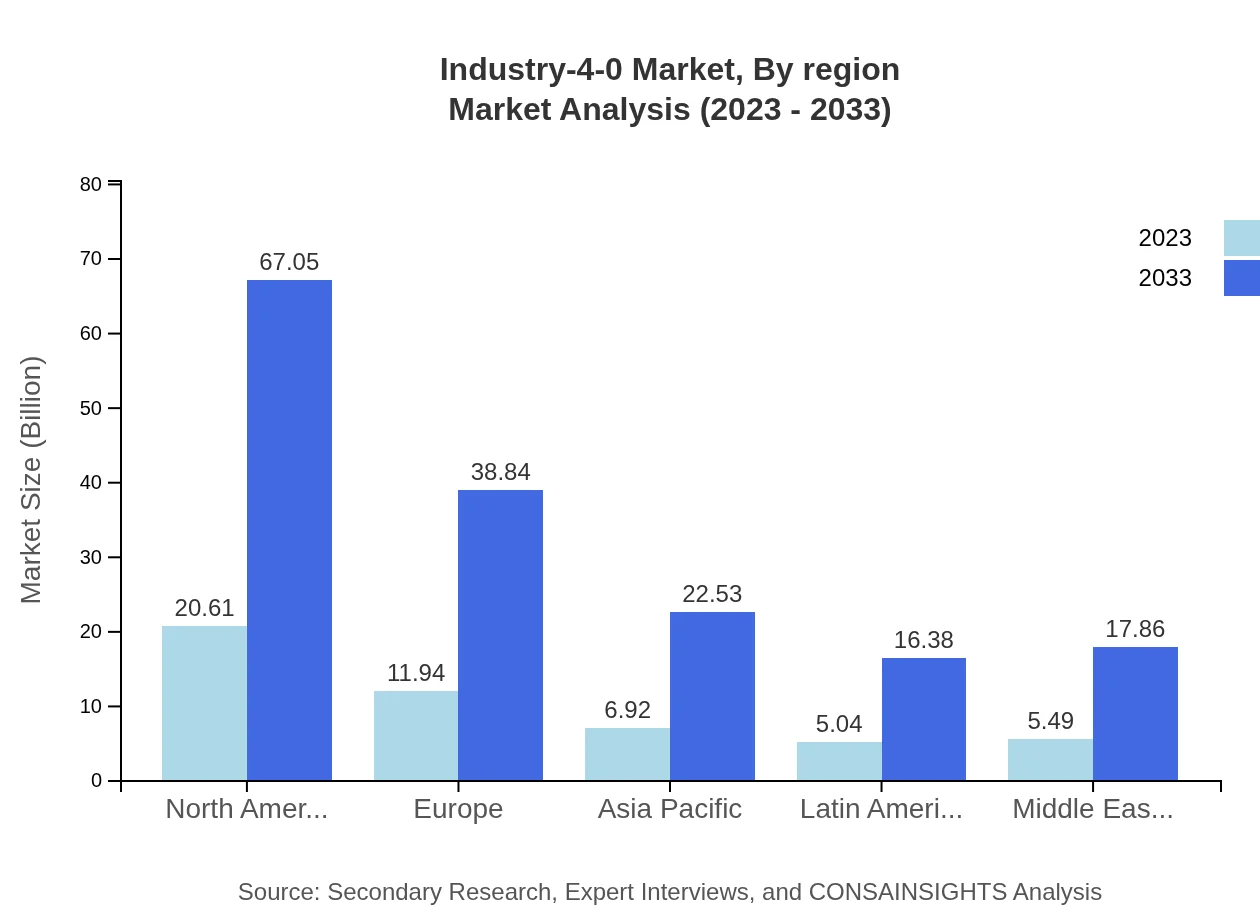
Industry-4-0 Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Industry-4-0 Market Report:
Europe, beginning at a market size of $12.27 billion in 2023, shows a forecasted growth to $39.90 billion by 2033, supported by stringent regulations on energy efficiency and a concerted push towards sustainable practices.Asia Pacific Industry-4-0 Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region, with a market size of $10.96 billion in 2023, is projected to rise to $35.64 billion by 2033, implying a robust growth trajectory driven by rising manufacturing sectors in China and India, as well as increasing investments in smart technologies.North America Industry-4-0 Market Report:
The North American market, valued at $16.81 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $54.69 billion in 2033. This growth reflects the strong demand for automation technologies in sectors such as manufacturing and logistics, coupled with the rising emphasis on sustainability involving innovative technologies.South America Industry-4-0 Market Report:
In South America, the Industry 4.0 market size was $4.43 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $14.43 billion by 2033. The growth is bolstered by expanding economic initiatives aimed at digitizing local industries.Middle East & Africa Industry-4-0 Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market, starting at $5.54 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to $18.01 billion by 2033. Investment in smart cities and infrastructure developments is a crucial factor driving this growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Industry-4-0 Market Analysis By Technology
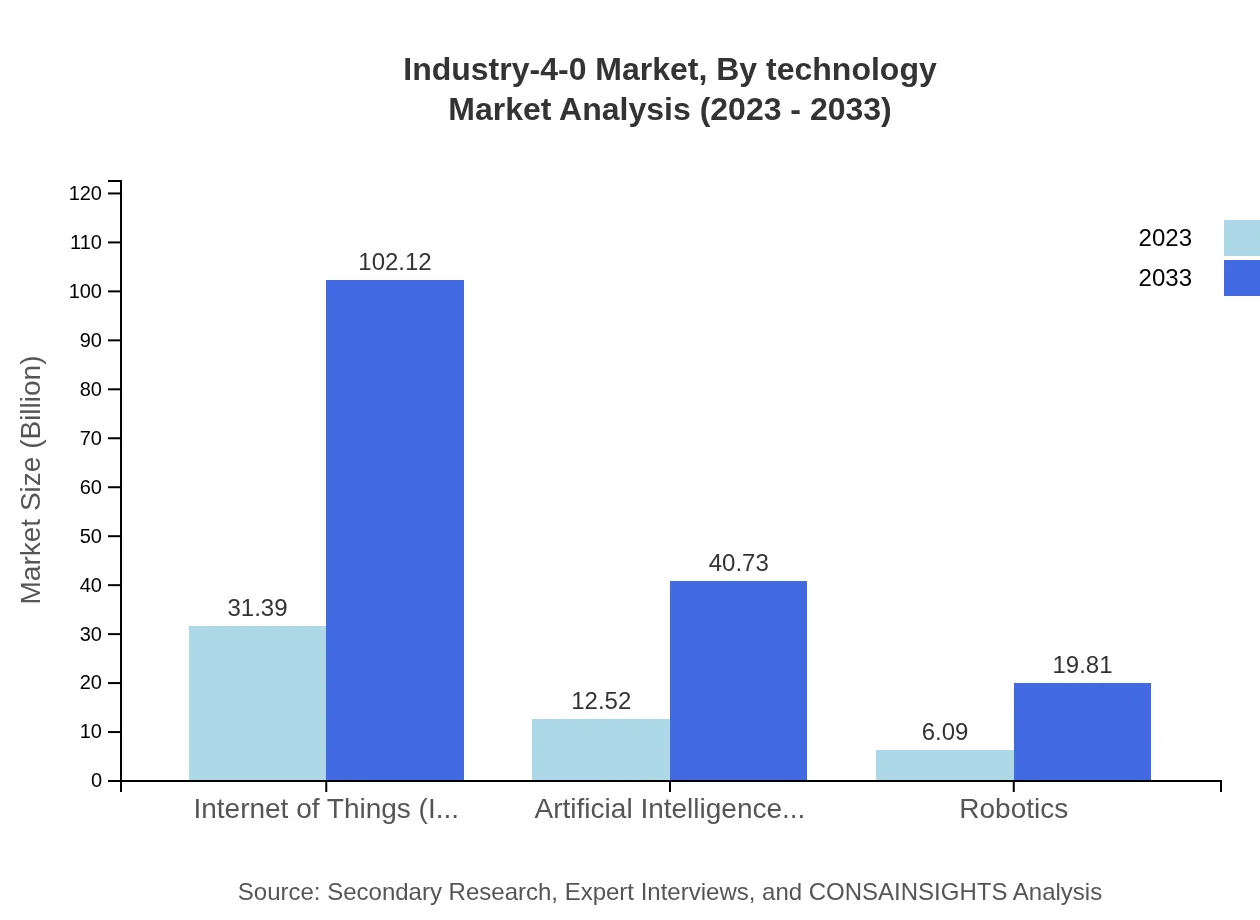
The technology segment of the Industry 4.0 market includes critical components such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotics, Smart Manufacturing, and Predictive Maintenance. IoT dominates the segment with a market size of $31.39 billion in 2023, growing to $102.12 billion by 2033, driven by the need for interconnected machinery.
Industry-4-0 Market Analysis By Application
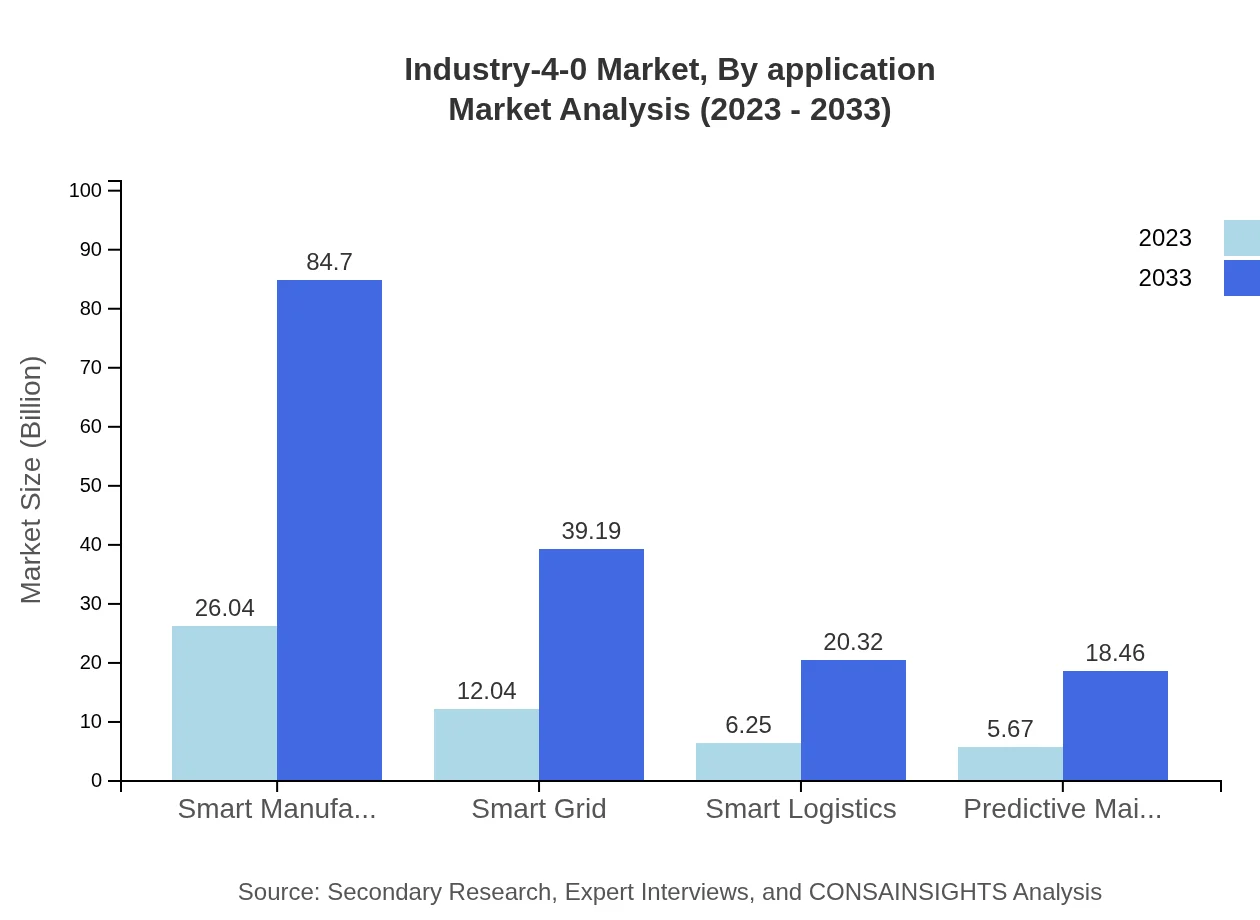
Applications of Industry 4.0 technology encompass diverse sectors like Manufacturing, Healthcare, Logistics, and Energy. Manufacturing holds the largest share, increasing from $26.04 billion in 2023 to $84.70 billion in 2033. The healthcare segment is also significant, predicting growth from $12.04 billion to $39.19 billion during the same period as enhanced operational efficiency becomes crucial.
Industry-4-0 Market Analysis By End User
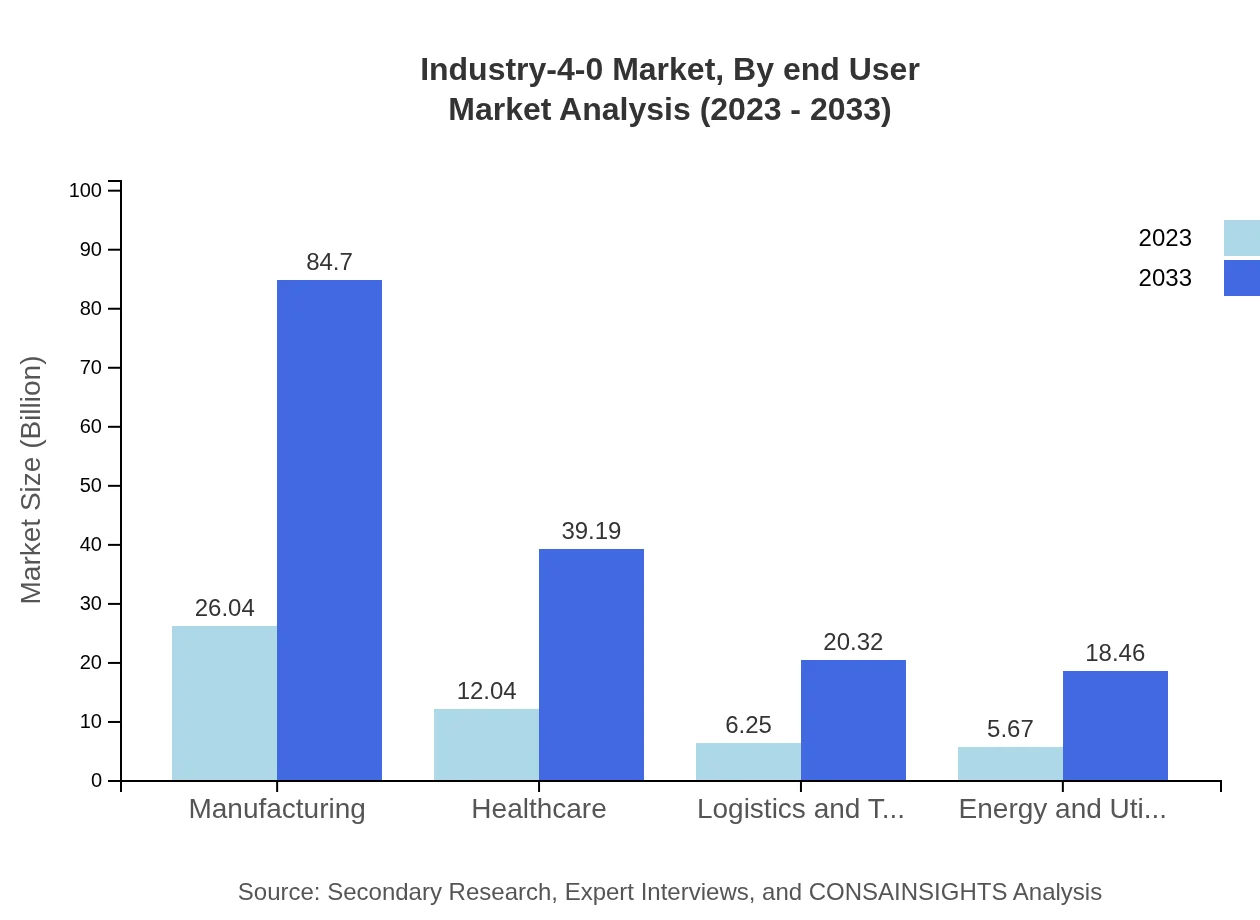
End-users of Industry 4.0 technologies span various industries including Manufacturing, Healthcare, Energy, and Utilities. The manufacturing sector is the largest consumer, expected to firmly retain its position owing to the push for smart manufacturing practices and automation.
Industry-4-0 Market Analysis By Region
Regionally, North America leads with significant investments and innovations in technology, followed closely by Europe. While Asia-Pacific is rapidly growing, South America and the Middle East & Africa present emerging markets that are gradually adopting Industry 4.0 solutions.
Industry-4-0 Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in the Industry-4-0 Industry
Siemens AG:
A major player in digital industries, Siemens provides automation and digitalization solutions to various sectors, significantly contributing to the advancement of Industry 4.0.General Electric:
Known for its innovative technologies, GE is implementing Industrial Internet solutions to enhance operational efficiencies across multiple industries.ABB Ltd.:
ABB is a leader in electrification and automation, providing integrated digital solutions that help customers achieve significant productivity gains.Rockwell Automation:
Focusing on innovative automation and software solutions, Rockwell empowers industries to leverage data-driven insights for better decision-making.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Industry 4.0?
The global Industry 4.0 market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023, with an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%. Projections suggest that this market will continue to grow significantly, highlighting the increasing integration of advanced technologies in manufacturing and services.
What are the key market players or companies in the Industry 4.0 industry?
Key players in the Industry 4.0 market include major technology firms, manufacturers, and software developers focusing on the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, and robotics. Companies such as Siemens, GE, and ABB are pivotal in driving innovation and market expansion.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Industry 4.0 industry?
Growth in the Industry 4.0 sector is largely driven by advancements in IoT, AI, and big data analytics, along with rising demand for automation and smart manufacturing solutions. Additionally, increasing investments in digital transformation are fostering Industry 4.0 adoption across various sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Industry 4.0?
Among global regions, North America currently leads the Industry 4.0 market, with a size of $16.81 billion in 2023, projected to reach $54.69 billion by 2033. Europe follows closely, showcasing rapid growth fueled by technological innovation and industrial automation.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the Industry 4.0 industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the Industry 4.0 sector. Clients can benefit from detailed analyses, insights, and forecasts that address unique market dynamics and regional trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this Industry 4.0 market research project?
From the Industry 4.0 market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market size analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape, regional breakdowns, and segment-specific insights, all aimed at guiding strategic decisions.
What are the market trends of Industry 4.0?
Current market trends in Industry 4.0 include the rapid adoption of smart manufacturing technologies, increased emphasis on predictive maintenance, and advancements in the IoT and AI sectors. Additionally, sustainability initiatives are shaping strategies as companies strive for efficient resource utilization.