Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: internet-of-things-in-utility
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Internet Of Things (IoT) in the utility sector, covering market dynamics, trends, opportunities, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include market sizes, growth rates, regional analyses, and the impact of technological advancements.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
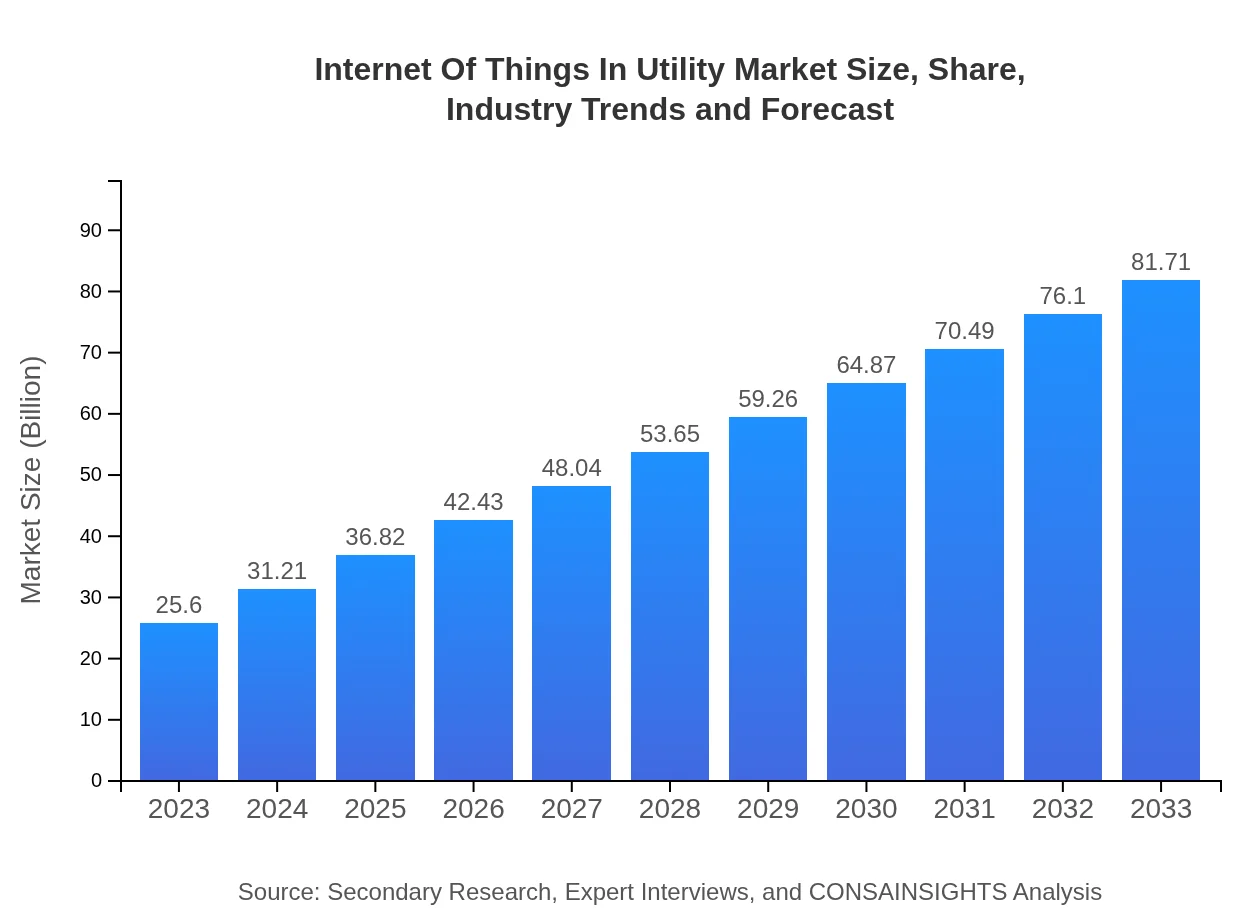
| 2023 Market Size | $25.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 11.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $81.71 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, General Electric, IBM, Cisco Systems, Oracle Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Overview
Customize Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Internet Of Things In Utility market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Internet Of Things In Utility's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Internet Of Things In Utility
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Internet Of Things In Utility market in 2023?
Internet Of Things In Utility Industry Analysis
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report:
Europe leads the market with an initial size of USD 7.89 billion in 2023, forecasted to reach USD 25.18 billion by 2033. Strict regulations for carbon emissions and increasing investments in renewable energy technologies are significant factors driving IoT adoption in utilities across the EU.Asia Pacific Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness a market size of USD 5.02 billion, expanding to USD 16.01 billion by 2033, achieving a significant growth rate. Countries like China and India are heavily investing in smart grid infrastructure and sustainable energy solutions, thereby boosting the adoption of IoT technologies in utilities.North America Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report:
The North American market is anticipated to grow from USD 8.79 billion in 2023 to USD 28.06 billion by 2033, representing robust growth driven by advancements in technology and a strong focus on infrastructure enhancement. The United States and Canada are setting benchmarks in smart utility solutions, notably in energy efficiency and grid modernization.South America Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report:
The South American market is smaller in comparison, standing at USD 1.51 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to USD 4.83 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to increasing urbanization and investment in sustainable energy projects, particularly in Brazil and Chile, recognized as leaders in the adoption of energy-efficient solutions.Middle East & Africa Internet Of Things In Utility Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region's market size is expected to rise from USD 2.39 billion in 2023 to USD 7.63 billion by 2033. The growing interest in sustainable energy and smart infrastructure projects, particularly in the UAE and South Africa, is expected to strengthen the IoT footprint in utilities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
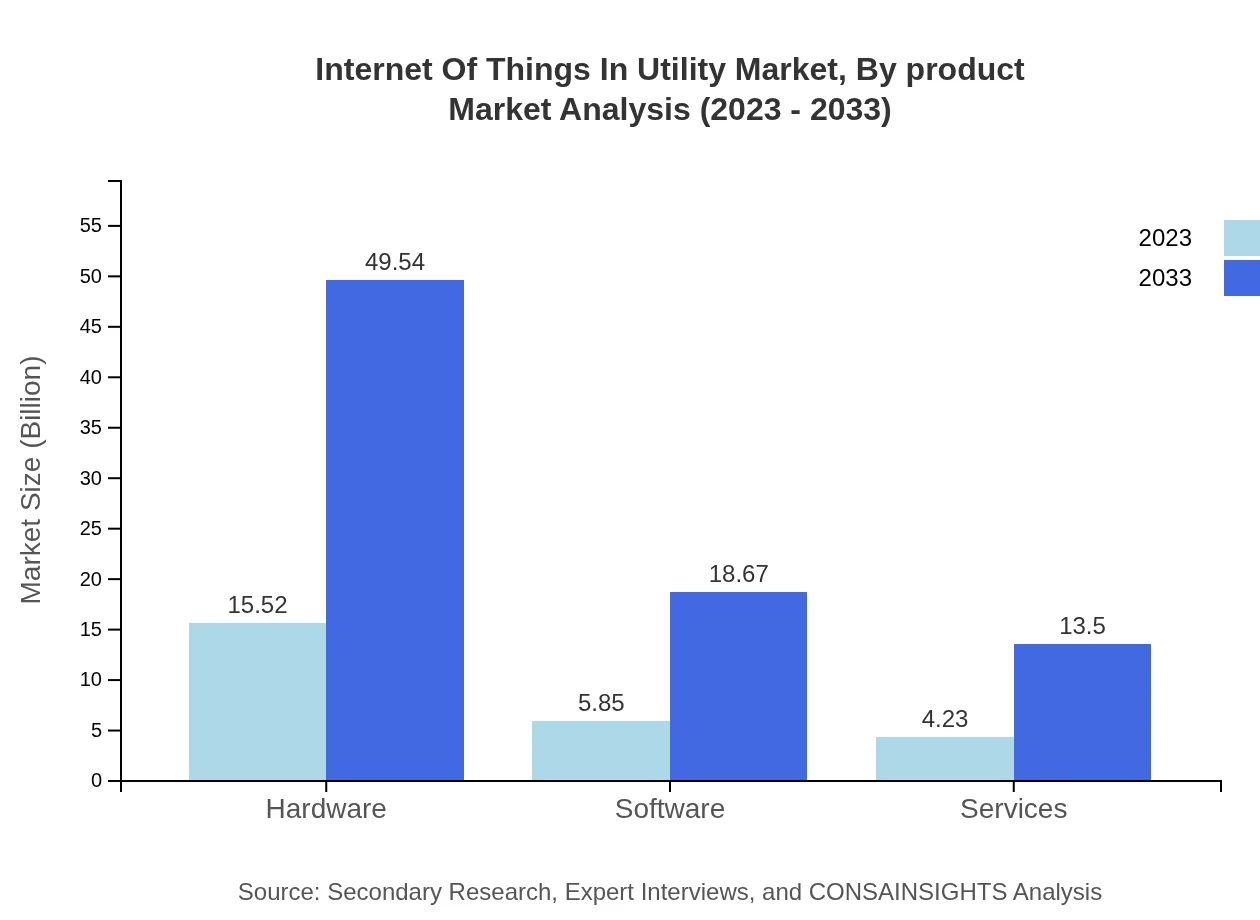
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Analysis By Product
In the product segment, the hardware market is projected to increase from USD 15.52 billion in 2023 to USD 49.54 billion by 2033, securing a dominant market share of 60.63%. Software solutions are expected to see growth from USD 5.85 billion to USD 18.67 billion, while service offerings are set to rise from USD 4.23 billion to USD 13.50 billion.
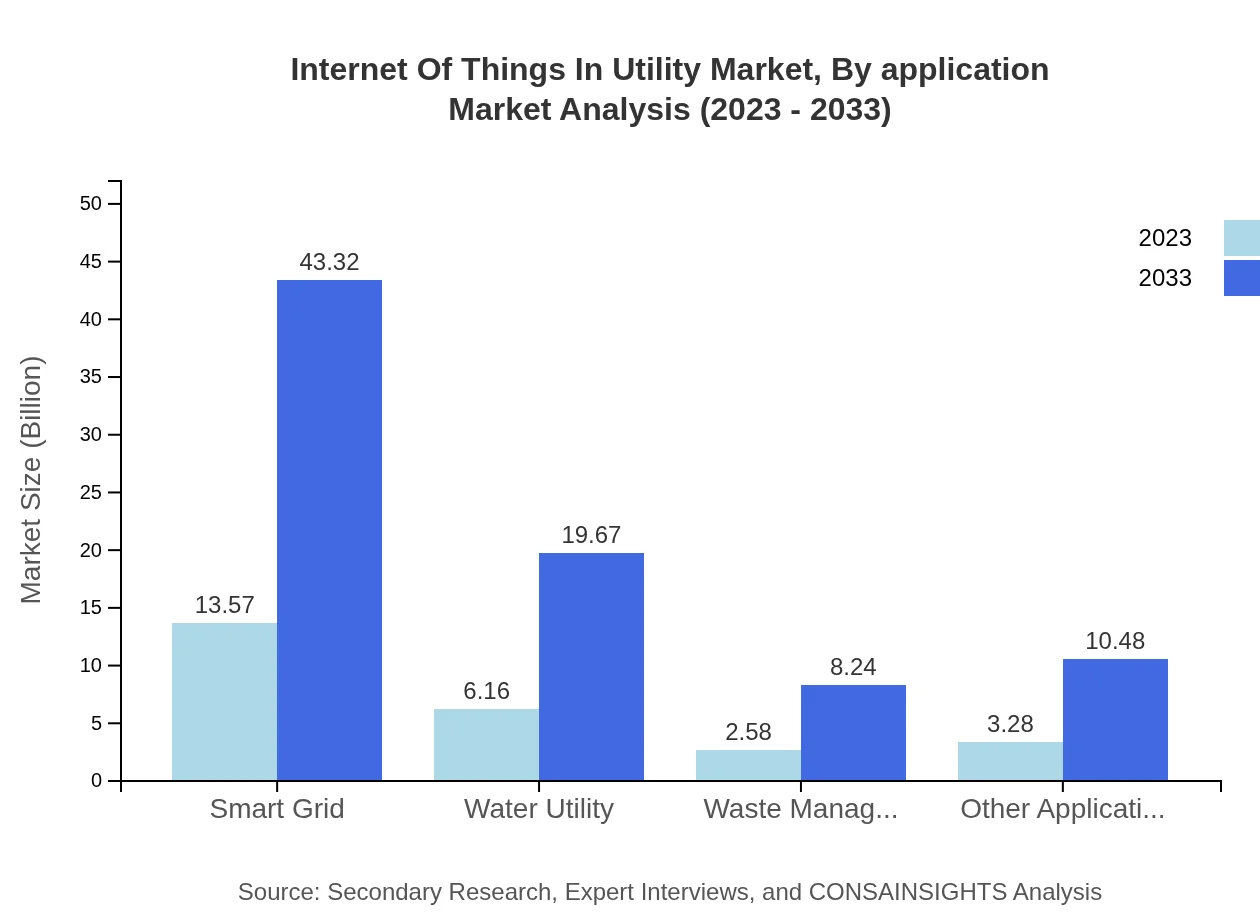
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Analysis By Application
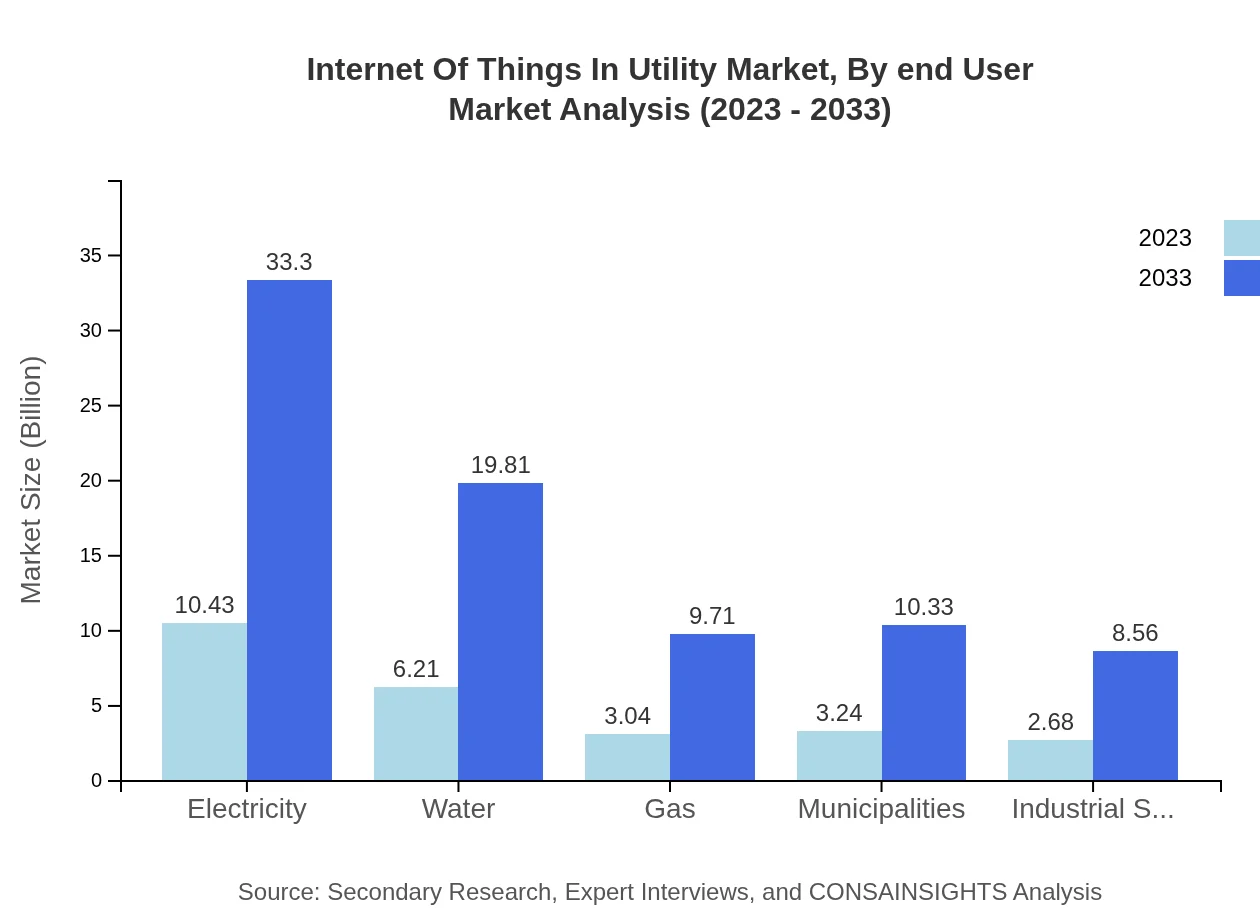
For application segments, electricity management will dominate with a market jump from USD 10.43 billion to USD 33.30 billion by 2033, while water utilities will grow from USD 6.21 billion to USD 19.81 billion. Gas management shows a promising increase, alongside municipalities focusing on IoT to optimize services.
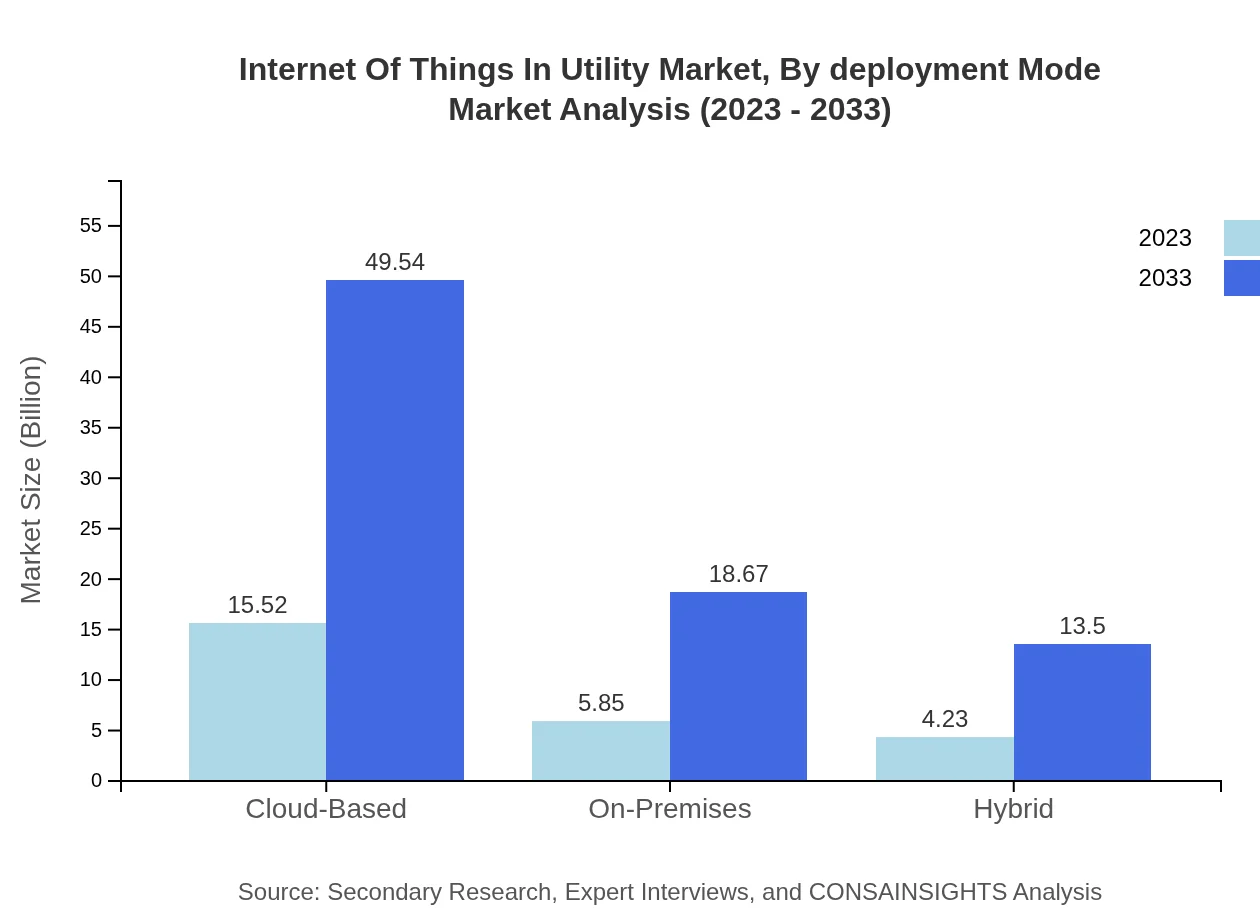
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
Cloud-based deployment is significantly prevalent, expanding from USD 15.52 billion to USD 49.54 billion, representing 60.63% market share. On-premises and hybrid models are also growing, driven by organizations seeking flexibility in their IoT solutions.
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment is burgeoning, with utility providers being the primary adopters of IoT technologies. The industrial sector is also witnessing increased adoption of IoT solutions to enhance energy efficiency and operational performance.
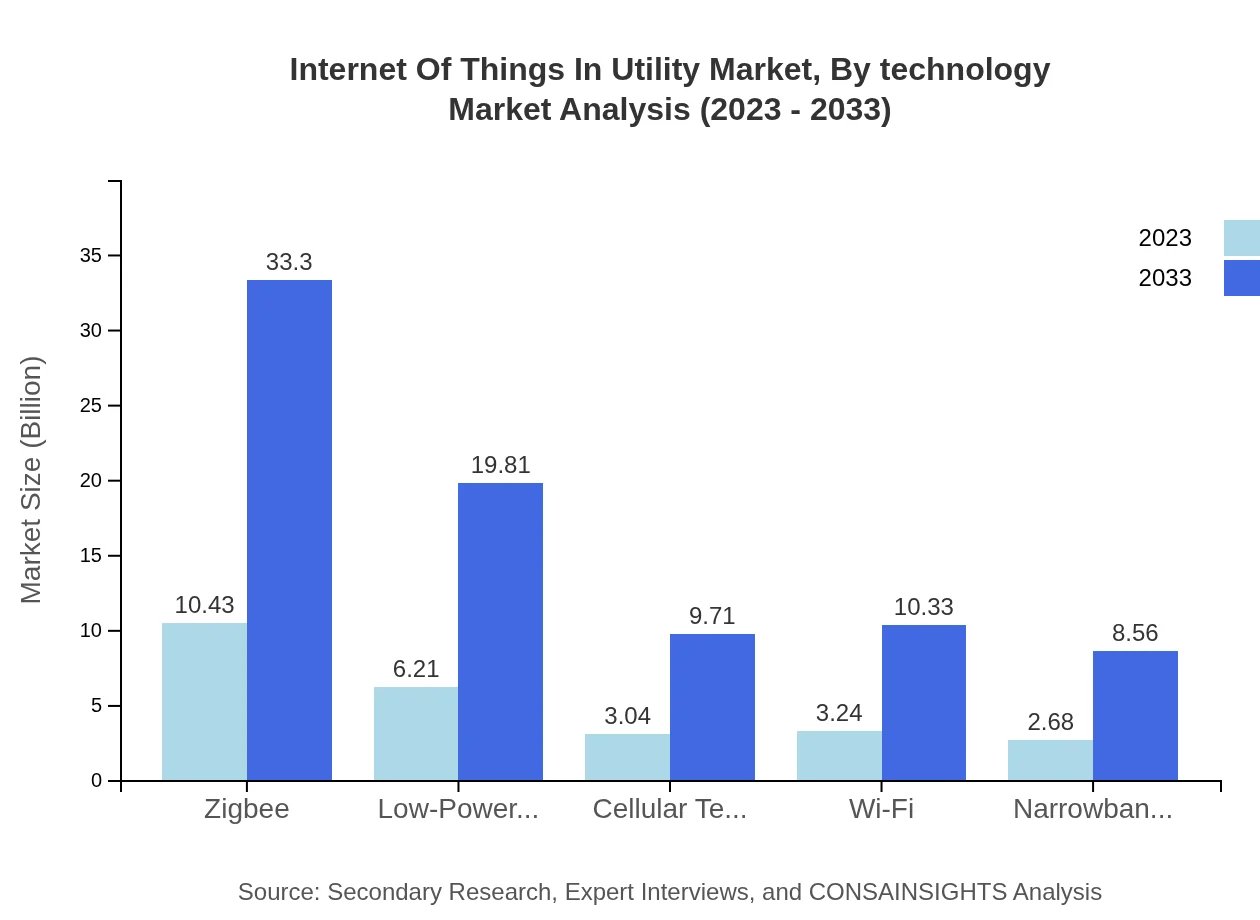
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Analysis By Technology
Key technologies driving the IoT market in utilities include Smart Grids, Zigbee, LPWAN, and NB-IoT. Smart Grids specifically are projected to grow from USD 13.57 billion in 2023 to USD 43.32 billion in 2033, highlighting technological advancements in electricity distribution management.
Internet Of Things In Utility Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Internet Of Things In Utility Industry
Siemens AG:
A leader in automation and digitalization, Siemens provides cutting-edge solutions for smart grids and energy management.General Electric:
General Electric plays a pivotal role in IoT innovations, offering integrated solutions to optimize energy distribution and consumption.IBM:
IBM leverages its AI and cloud computing capabilities to enhance utility operations through data-driven insights and IoT technology.Cisco Systems:
Cisco offers networking solutions crucial for enabling IoT connectivity in the utility sector while enhancing cybersecurity frameworks.Oracle Corporation:
Oracle provides IoT cloud applications tailored for the utility sector, focusing on data management and analytics.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of internet Of Things In Utility?
The Internet of Things in Utility market is projected to grow from $25.6 billion in 2023 to significant heights by 2033, with a CAGR of 11.8%. This growth underscores the increasing integration of smart technologies in utility management.
What are the key market players or companies in this internet Of Things In Utility industry?
Key players in the IoT in utility sector include major companies like Siemens, Schneider Electric, GE, Oracle, and IBM. These companies are innovating and leading development in smart grid technology, energy management, and analytics to enhance efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the internet Of Things In Utility industry?
The growth of the IoT in utilities is driven by advancements in smart infrastructure, demand for energy efficiency, government mandates for sustainability, and increased consumer demand for smart services. Additionally, cost reductions in IoT technology boost adoption.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the internet Of Things In Utility?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the Internet of Things in Utility market, projected to rise from $8.79 billion in 2023 to $28.06 billion by 2033. Europe follows closely, with substantial growth driven by renewable energy initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the internet Of Things In Utility industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the Internet of Things in Utility industry, tailored to meet specific research needs, including detailed segmentation and analysis according to client requirements, ensuring relevant insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this internet Of Things In Utility market research project?
From the IoT in Utility market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports, market forecasts, segmented data analysis, competitive landscape assessments, and insights into emerging trends and technologies shaping the industry.
What are the market trends of internet Of Things In Utility?
Key trends in the IoT in utility market include the increasing deployment of smart meters, enhanced data analytics for operational efficiency, growing adoption of renewable energy sources, and the rise of grid modernization initiatives.