Iot In Energy Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: iot-in-energy
Iot In Energy Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the IoT in Energy market from 2023 to 2033, including market trends, size forecasts, regional insights, and industry analysis. It highlights key growth opportunities and challenges influencing the market dynamics.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
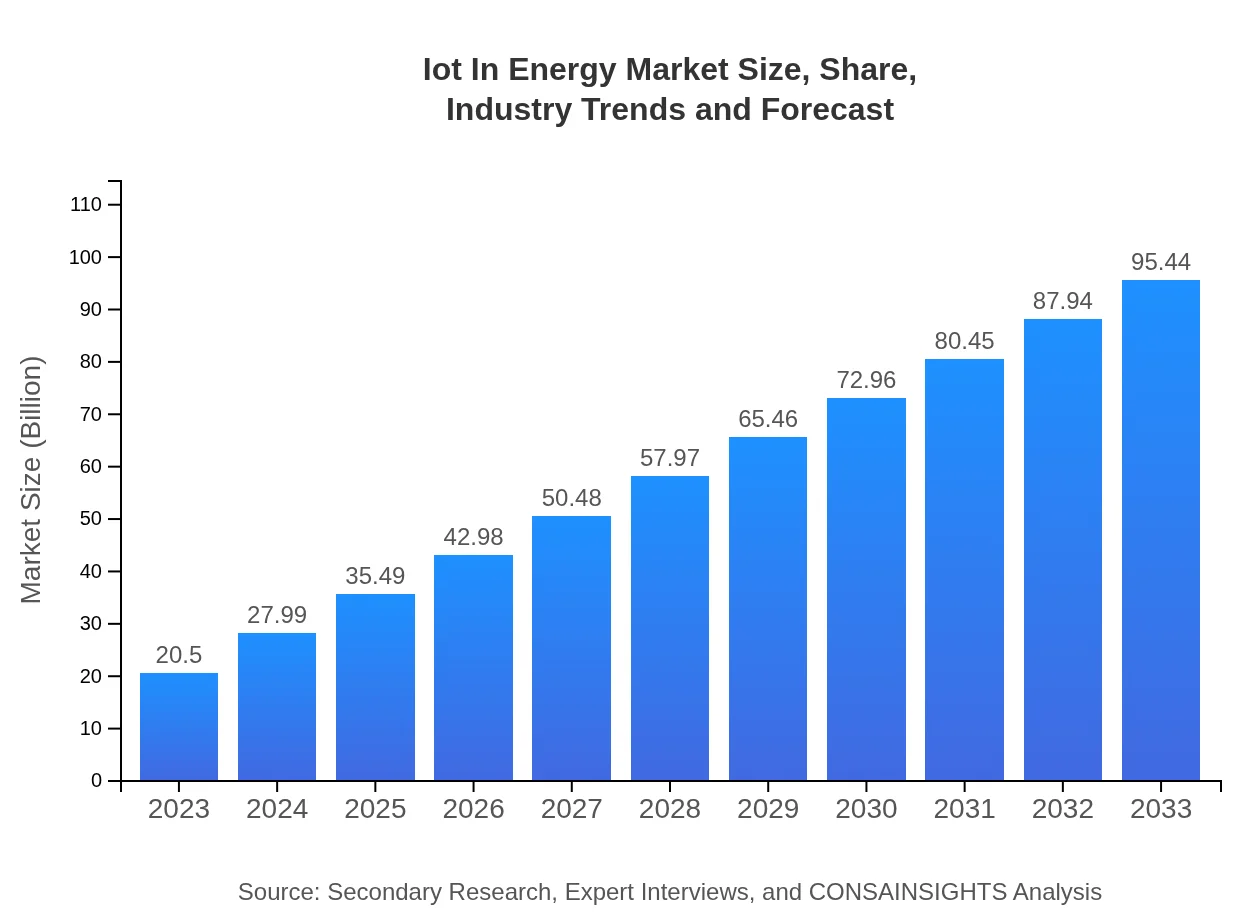
| 2023 Market Size | $20.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 15.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $95.44 Billion |
| Top Companies | IBM, Siemens , Schneider Electric, Cisco |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
IoT In Energy Market Overview
Customize Iot In Energy Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Iot In Energy market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Iot In Energy's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Iot In Energy
What is the Market Size & CAGR of IoT In Energy market in 2023?
IoT In Energy Industry Analysis
IoT In Energy Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
IoT In Energy Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Iot In Energy Market Report:
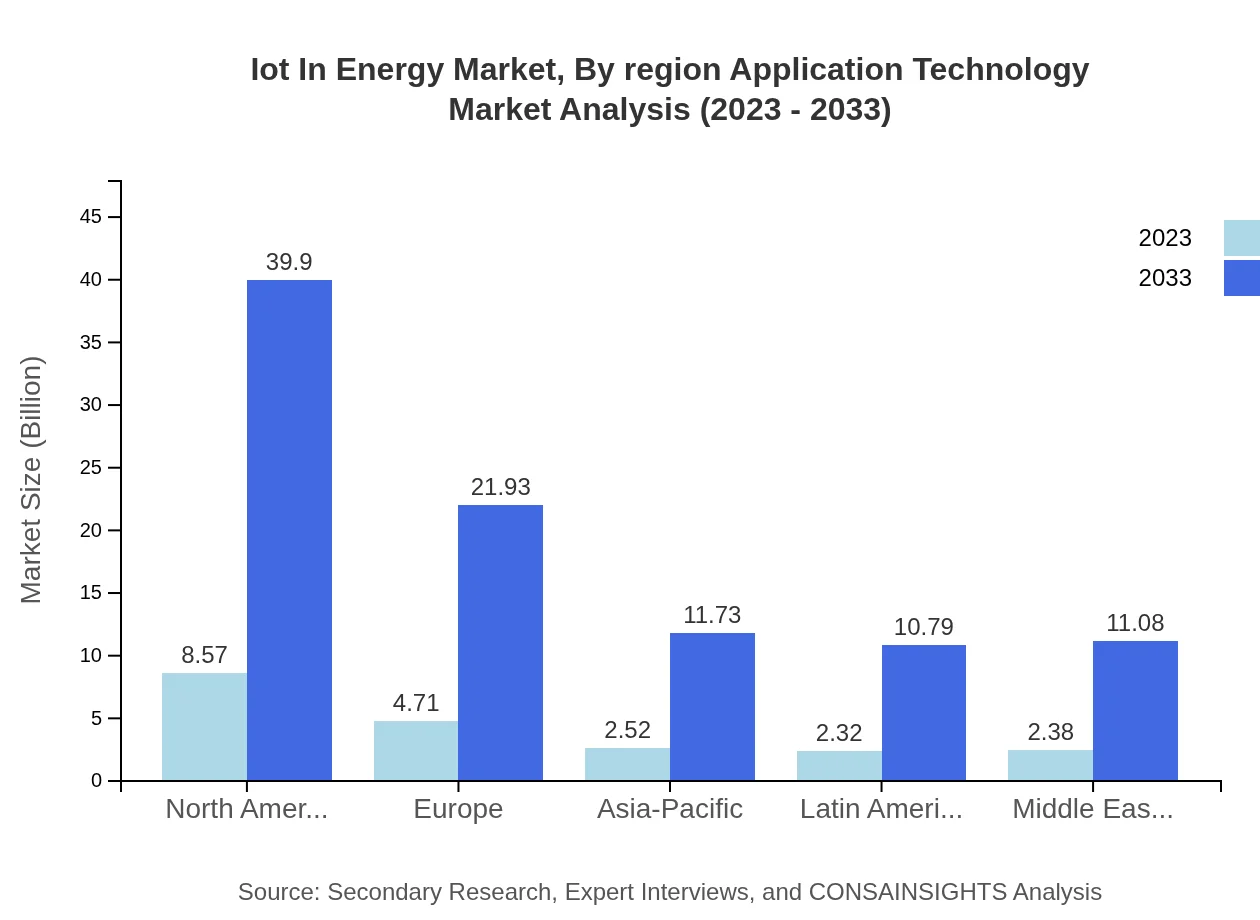
The European IoT in Energy market, starting at $7.07 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $32.93 billion by 2033, is driven by stringent energy regulations and a strong commitment to reducing carbon emissions. The region is a frontrunner in adopting green energy technologies.Asia Pacific Iot In Energy Market Report:
In Asia Pacific, the IoT in Energy market is expected to grow from $3.78 billion in 2023 to $17.62 billion by 2033, reflecting the region's rapid industrialization and emphasis on smart city initiatives. Government policies focused on sustainable energy and investments in smart infrastructure are set to further accelerate this growth.North America Iot In Energy Market Report:
North America will experience significant growth, increasing from $6.85 billion in 2023 to $31.88 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to a robust focus on renewable energy systems, advancements in smart grid technologies, and initiatives geared towards energy optimization.South America Iot In Energy Market Report:
The South American market for IoT in Energy, starting at $1.06 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $4.92 billion by 2033, benefits from increasing investments in renewable energy sources and the need for energy efficiency. Countries are adopting IoT solutions to address energy challenges and enhance their grids.Middle East & Africa Iot In Energy Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are forecasted to see their IoT in Energy market expand from $1.74 billion in 2023 to $8.10 billion by 2033, propelled by investments in infrastructure and energy management solutions aimed at improving the efficiency of existing resources.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
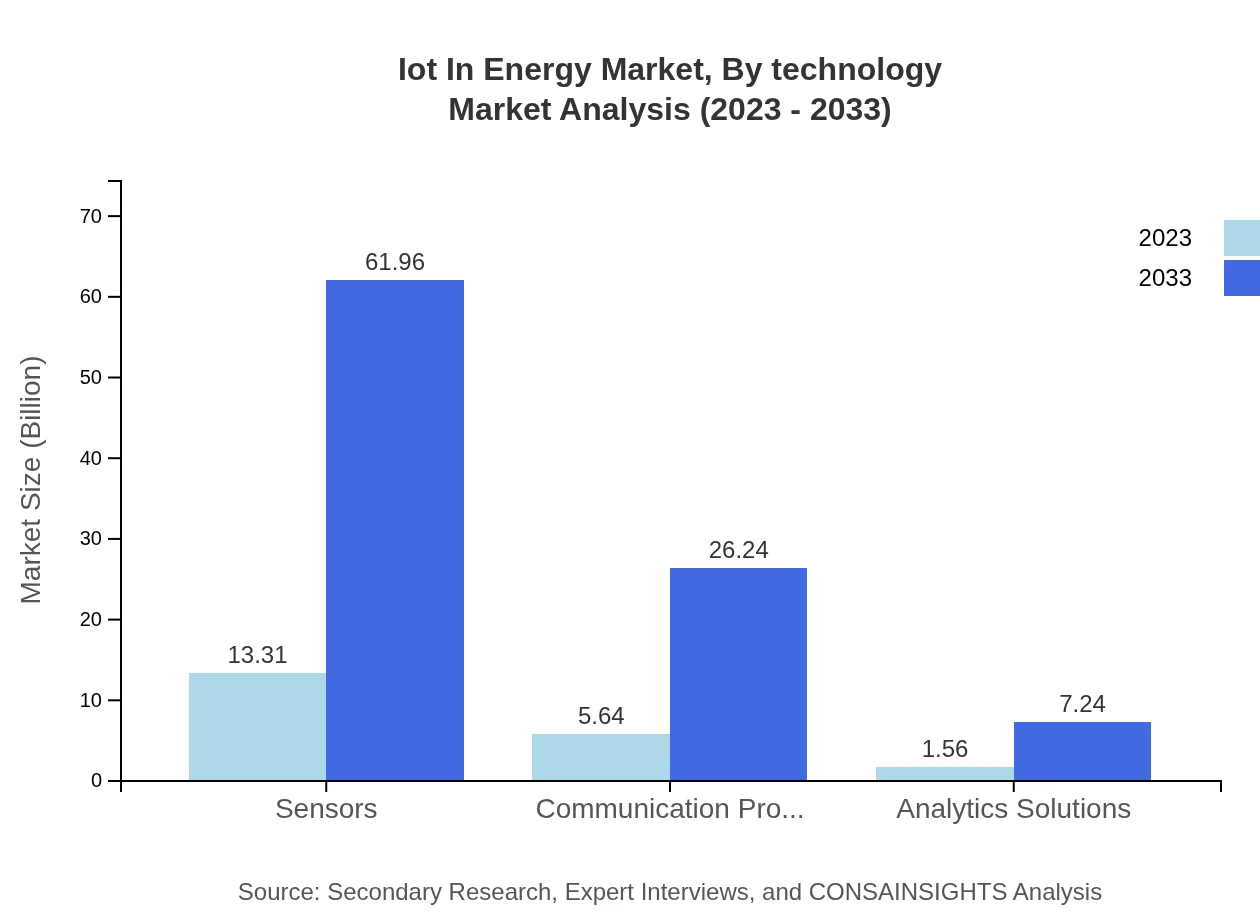
Iot In Energy Market Analysis By Technology
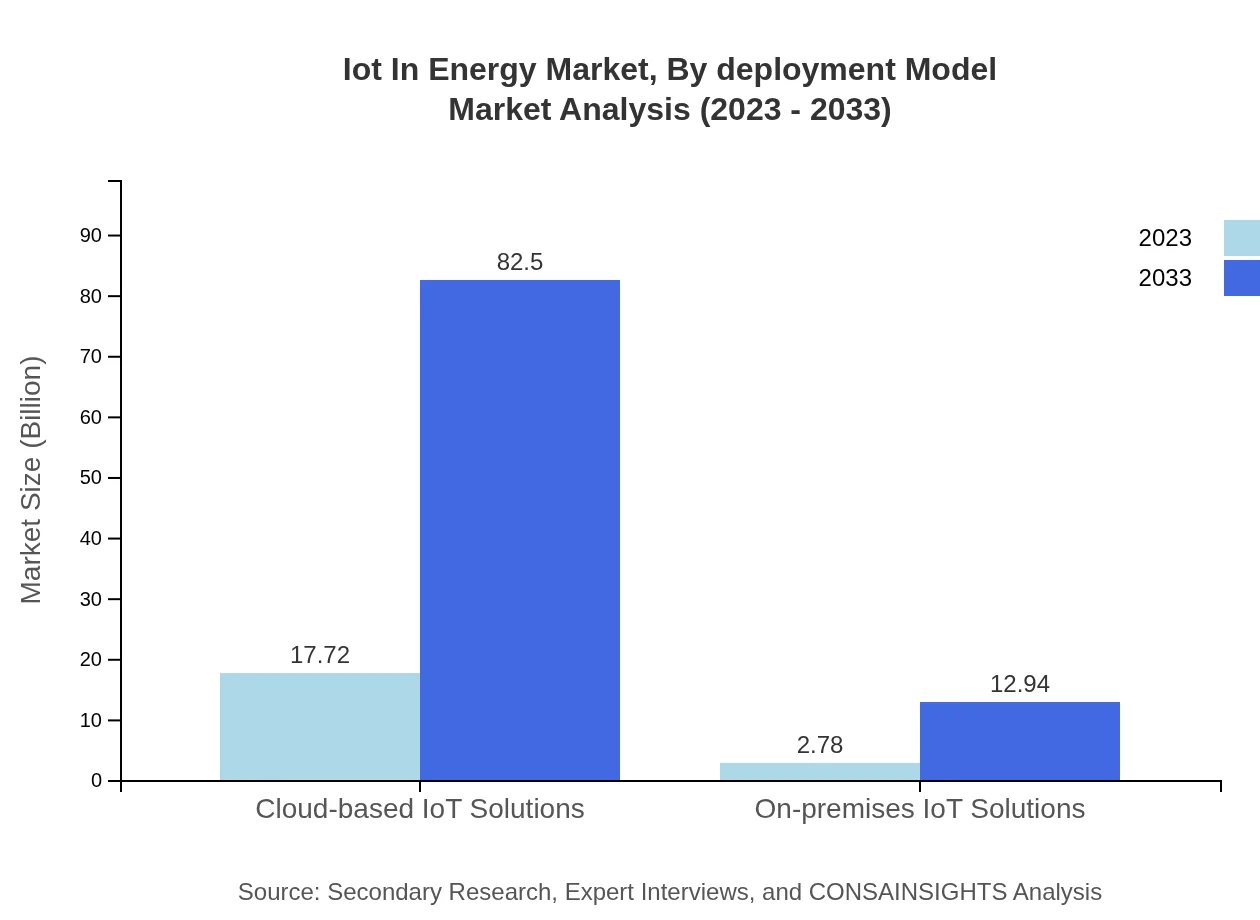
The IoT in Energy market is primarily segmented into Cloud-based IoT Solutions, On-premises IoT Solutions, Smart Grid Technologies, and Communications Protocols. Cloud-based solutions dominate the market, boasting a value of $17.72 billion in 2023, with a projection of $82.50 billion by 2033 driven by the scalability and flexibility they offer to utilities.
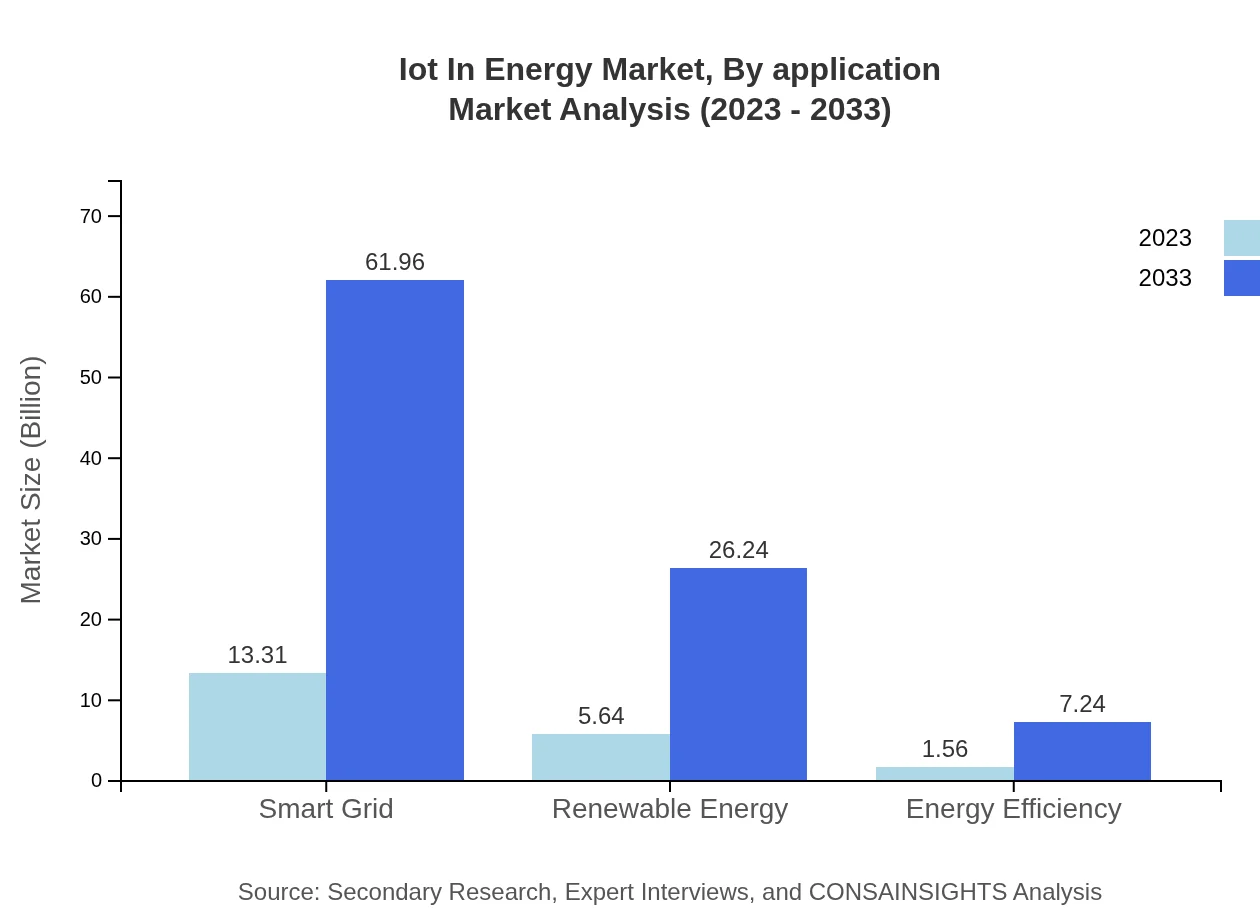
Iot In Energy Market Analysis By Application
The various applications of IoT in Energy include utility management, energy monitoring, equipment maintenance, and demand response. The utilities segment holds a major share, representing about 64.92% in 2023 and is expected to maintain its significance due to the continual need for enhancing operational efficiency.
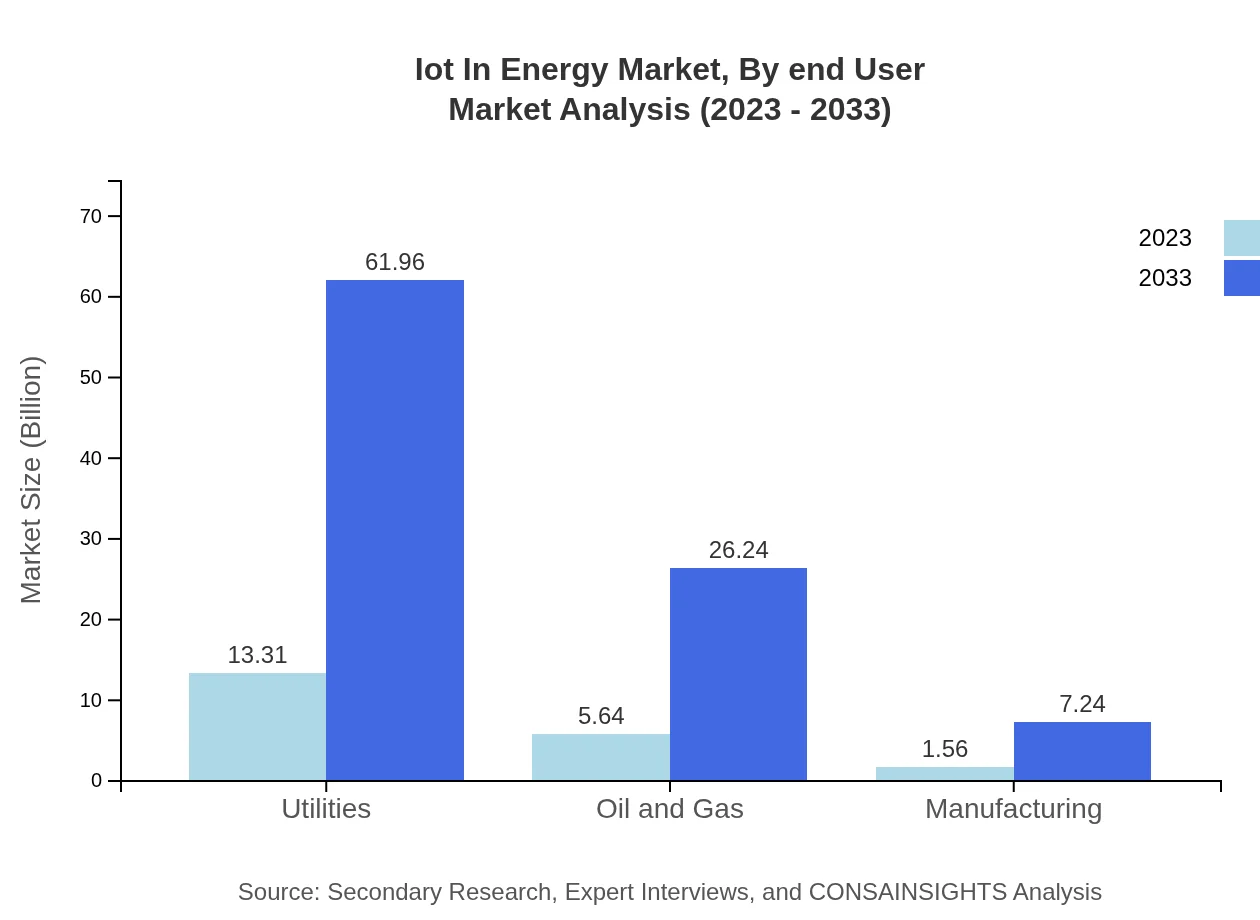
Iot In Energy Market Analysis By End User
End users of IoT in Energy span utilities, oil and gas, and manufacturing sectors. Utilities alone contributed approximately $13.31 billion in 2023, underscoring their pivotal role in adopting IoT solutions for energy management.
Iot In Energy Market Analysis By Deployment Model
In terms of deployment models, the market is categorized between Cloud-based and On-premises solutions. Cloud-based IoT solutions are projected to take a substantial lead in market share due to their extensive applicability and ease of implementation across various sub-sectors.
Iot In Energy Market Analysis By Region Application Technology
Regional analysis reflects diverse adoption rates of IoT technologies across the globe, with North America leading in cloud-based solutions implementation, while Europe focuses heavily on smart grid technology due to regulatory pressures.
IoT In Energy Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in IoT In Energy Industry
IBM:
IBM offers advanced IoT solutions that empower utilities to streamline operations, utilizing AI and analytics to enhance energy efficiency.Siemens :
Siemens provides industry-leading solutions in the IoT space, including smart grid technologies that optimize energy distribution networks.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric is a pioneer providing IoT-enabled energy management systems and solutions to improve operational efficiency in various industries.Cisco:
Cisco leverages its networking expertise to deliver secure and reliable IoT infrastructures designed specifically for the energy sector.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of IoT in Energy?
The IoT in Energy market was valued at approximately $20.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.8%, reaching around $20.5 billion by 2033. This growth illustrates the increasing integration of IoT technologies within the energy sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the IoT in Energy industry?
Key players in the IoT in Energy industry include major technology and energy firms such as Siemens, GE, Schneider Electric, and Cisco. These companies are pivotal in developing innovative solutions that harness IoT technology for enhanced energy management and efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the IoT in Energy industry?
Key factors driving the growth of the IoT in Energy industry include the increasing demand for energy efficiency, the rise of smart grid technologies, and the growing need for real-time data analytics in energy management. Additionally, government initiatives promoting renewable energy contribute significantly.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the IoT in Energy market?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the IoT in Energy market, with a projected market size of $39.90 billion by 2033, from $8.57 billion in 2023, highlighting significant growth driven by technological advancements and energy policy reforms.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the IoT in Energy industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client specifications in the IoT in Energy industry. This enables businesses to obtain targeted insights and analysis specific to their strategic needs and market opportunities.
What deliverables can I expect from this IoT in Energy market research project?
From an IoT in Energy market research project, you can expect detailed reports including market analysis, competitive landscape assessments, growth forecasts, and specific insights on key segments, helping stakeholders make informed decisions based on comprehensive data.
What are the market trends of IoT in Energy?
Current trends in the IoT in Energy market include the increased adoption of cloud-based IoT solutions, a focus on enhancing energy efficiency, and the integration of AI and big data analytics for improved energy management. These trends are reshaping how energy is monitored and controlled.