Iot In Smart Cities Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: iot-in-smart-cities
Iot In Smart Cities Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the IoT in Smart Cities market, presenting forecasts and critical insights from 2023 to 2033, including market size, trends, and competitive landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
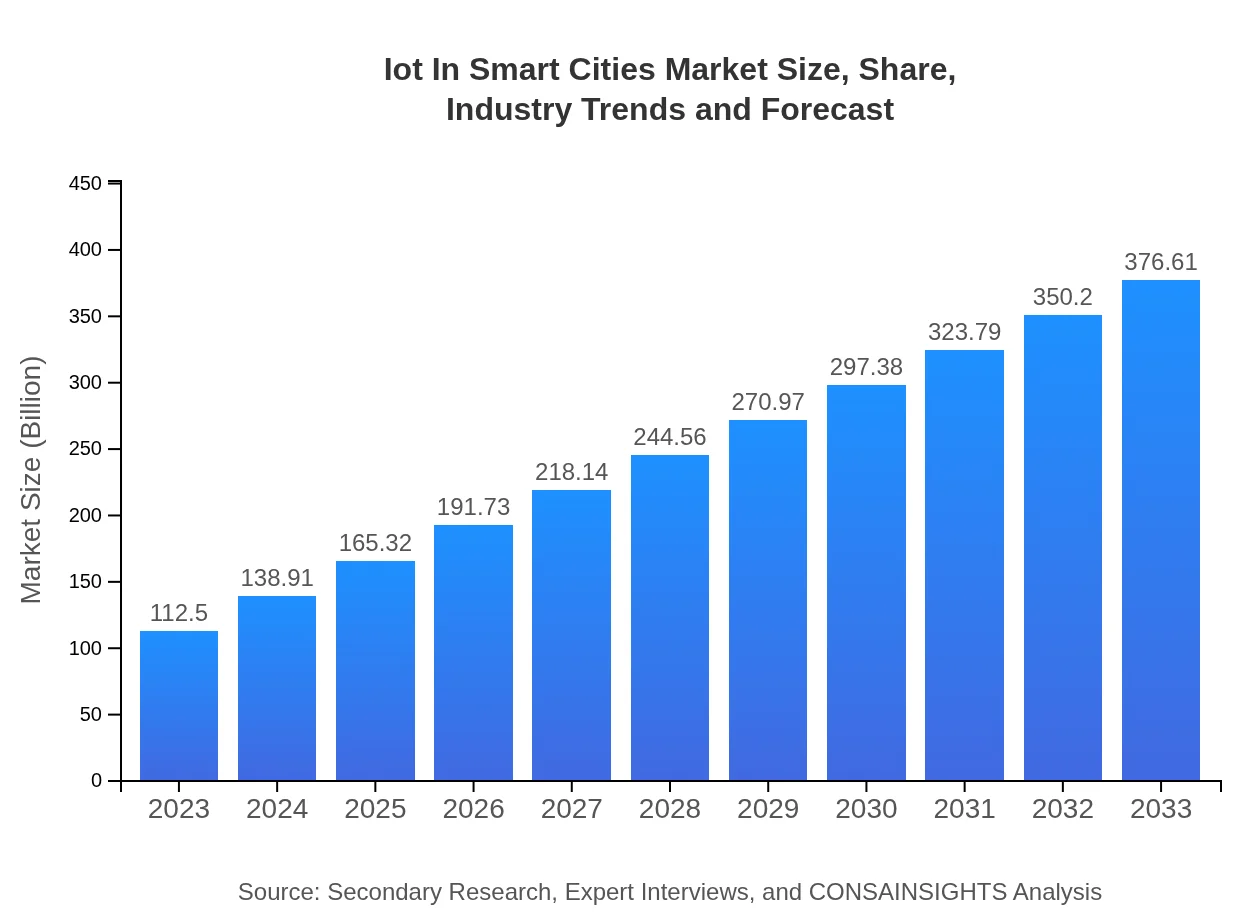
| 2023 Market Size | $112.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $376.61 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., IBM Corporation, Siemens AG, Schneider Electric |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Iot In Smart Cities Market Overview
Customize Iot In Smart Cities Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Iot In Smart Cities market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Iot In Smart Cities's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Iot In Smart Cities
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Iot In Smart Cities market in 2023 and 2033?
Iot In Smart Cities Industry Analysis
Iot In Smart Cities Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Iot In Smart Cities Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Iot In Smart Cities Market Report:
Europe's market size was $35.42 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $118.56 billion in 2033. The region is witnessing stringent regulatory frameworks advocating for smart cities, alongside robust public-private partnerships.Asia Pacific Iot In Smart Cities Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region held a market value of $19.08 billion in 2023, with a projected increase to $63.87 billion by 2033. The rapid urbanization in countries like China and India fuels the demand for smart city technologies as governments invest heavily in infrastructure development.North America Iot In Smart Cities Market Report:
North America is leading the IoT in Smart Cities market with a valuation of $42.14 billion in 2023 and an expected growth to $141.08 billion by 2033. Cities are investing in smart technologies to improve public safety, transport, and environmental sustainability.South America Iot In Smart Cities Market Report:
In South America, the IoT in Smart Cities market is set to grow from $0.35 billion in 2023 to $1.17 billion by 2033. While the market is currently small, emerging economies are beginning to adopt smart technologies to enhance urban resilience and citizen services.Middle East & Africa Iot In Smart Cities Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's market is anticipated to grow from $15.51 billion in 2023 to $51.93 billion by 2033. Notable investments in infrastructure projects and a focus on sustainability drive the adoption of IoT solutions in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
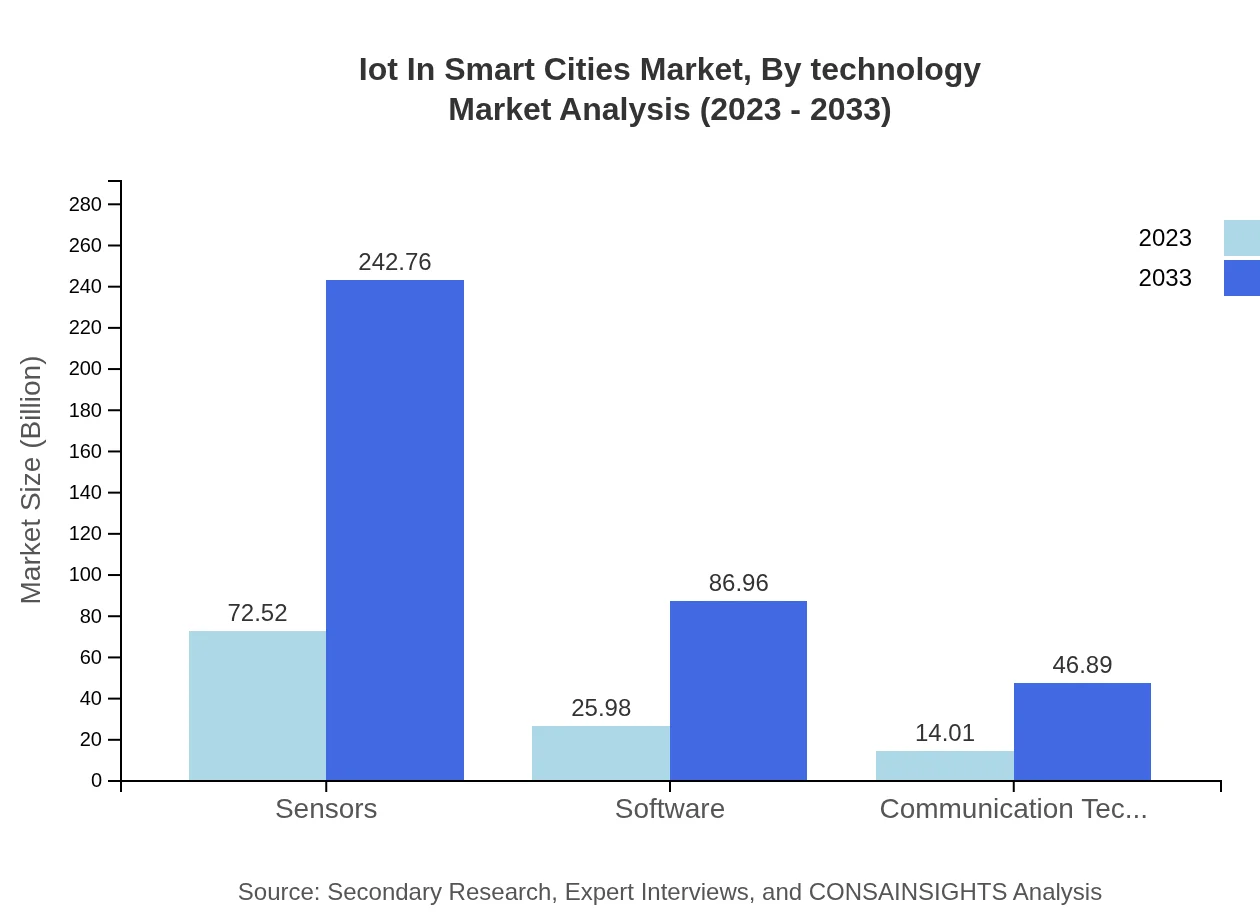
Iot In Smart Cities Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment comprised of sensors, cloud computing, and communication technologies plays a pivotal role in smart city infrastructures. In 2023, sensor technology alone accounts for a significant market share, estimated at $72.52 billion, with expectations to reach $242.76 billion by 2033 due to increasing sensor applications across various urban services.
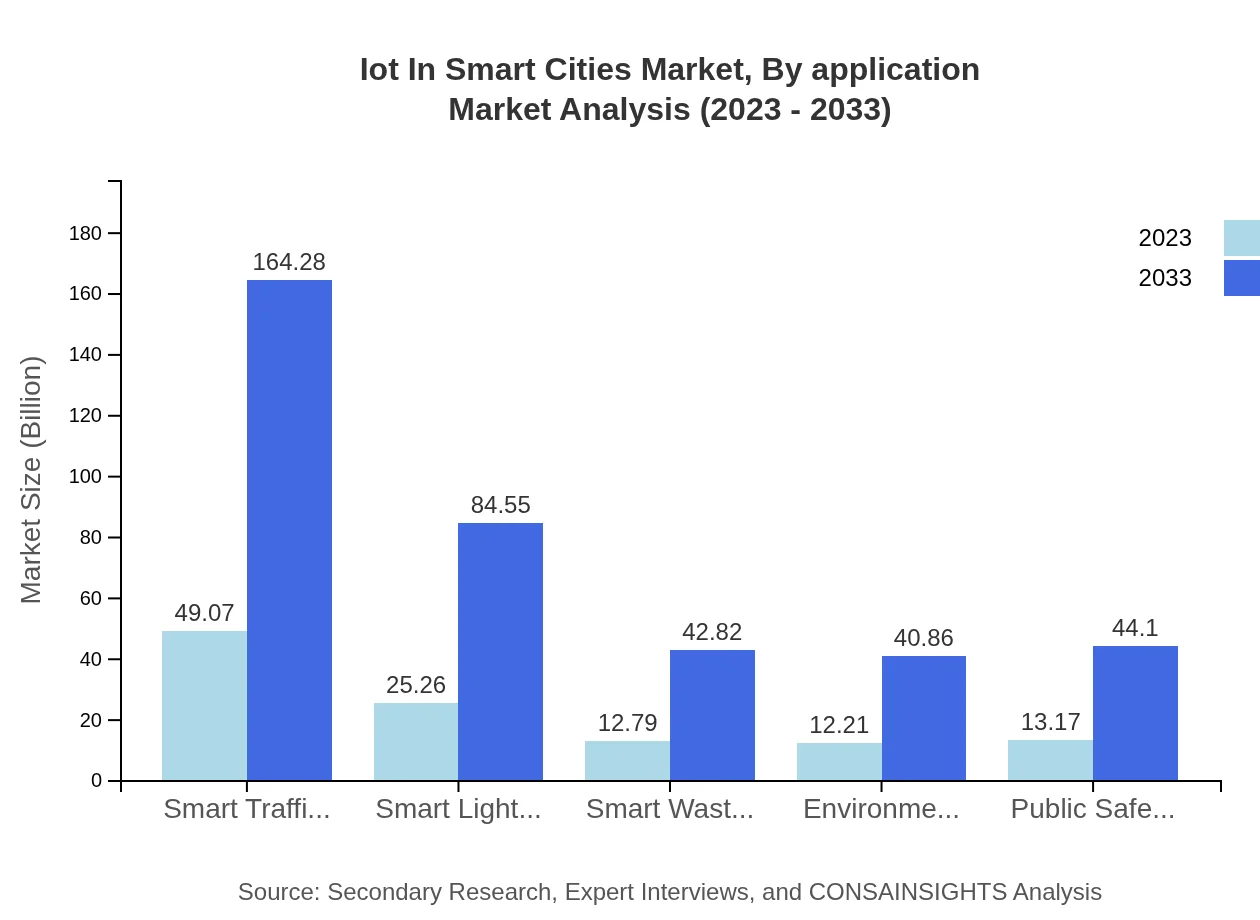
Iot In Smart Cities Market Analysis By Application
The application segment is diverse, covering critical areas such as smart traffic management, waste management, and public safety. The smart traffic management segment, valued at $49.07 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow significantly to $164.28 billion by 2033, driven by the need for efficient urban mobility solutions.
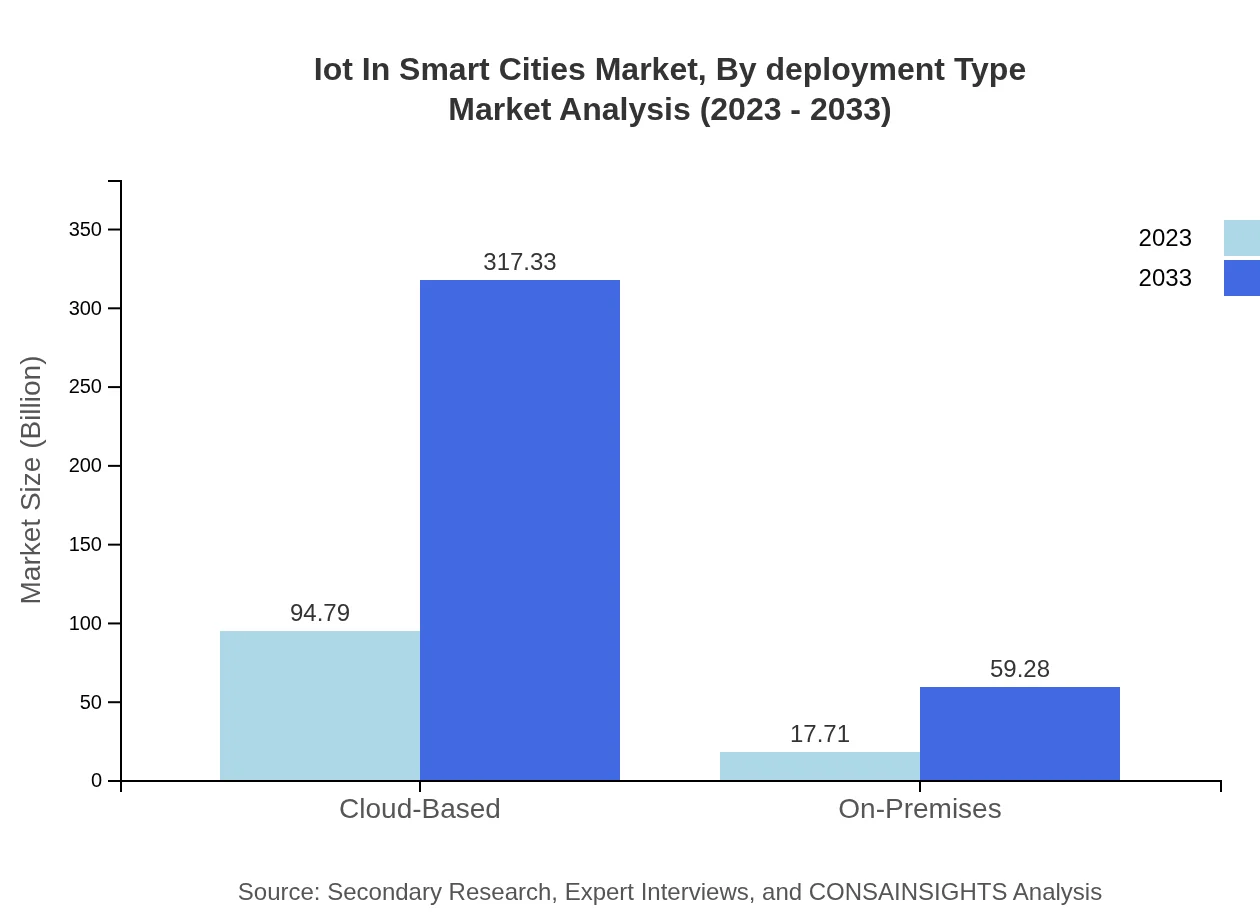
Iot In Smart Cities Market Analysis By Deployment Type
Deployment types include cloud-based and on-premises solutions. The cloud-based segment is expected to dominate the market, rising from $94.79 billion in 2023 to $317.33 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by the demand for scalable and flexible solutions in managing smart city systems.
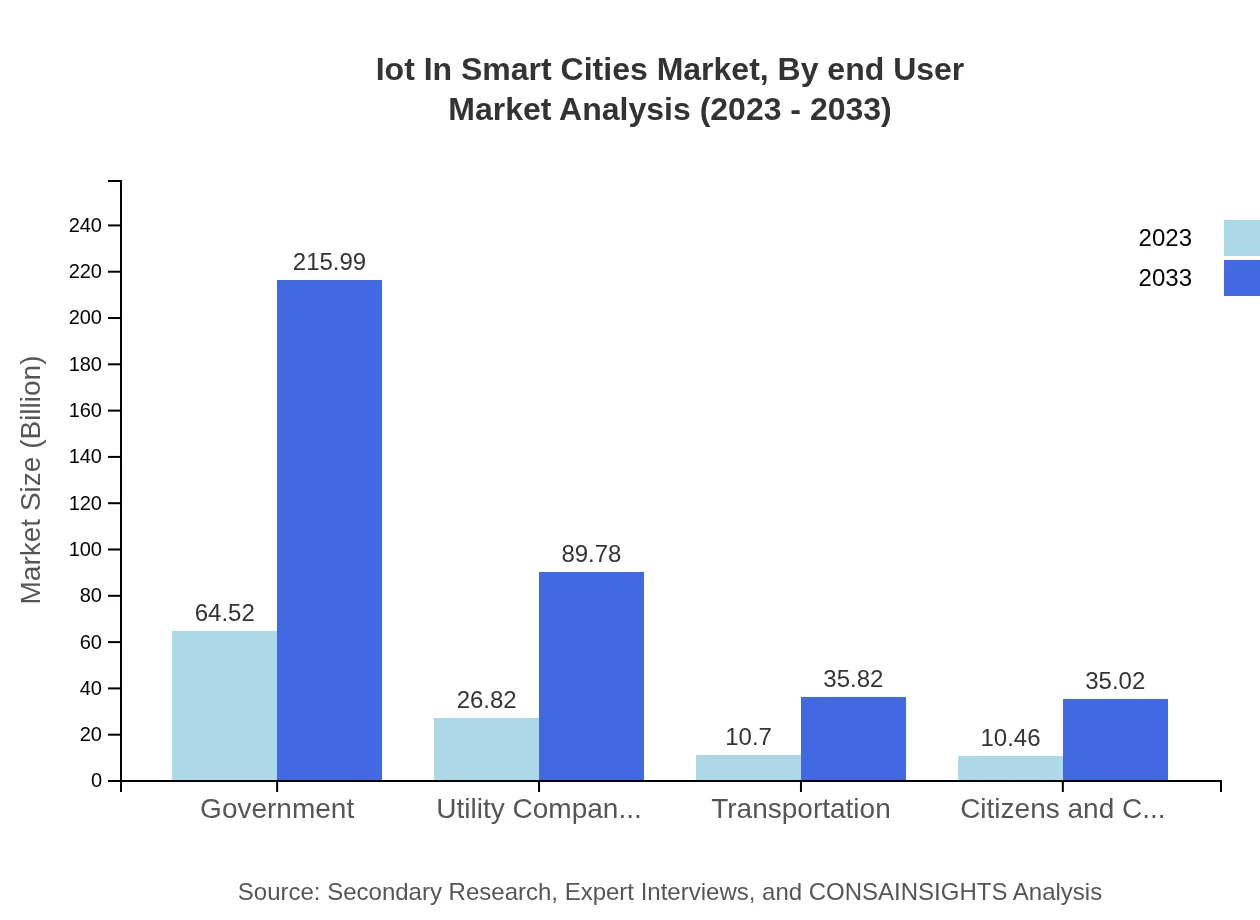
Iot In Smart Cities Market Analysis By End User
End-user segments such as government and utility companies play vital roles in influencing market dynamics. Government applications, projected to reach $215.99 billion by 2033 from $64.52 billion in 2023, highlight the critical focus on enhancing public services through IoT.
Iot In Smart Cities Market Analysis By Region
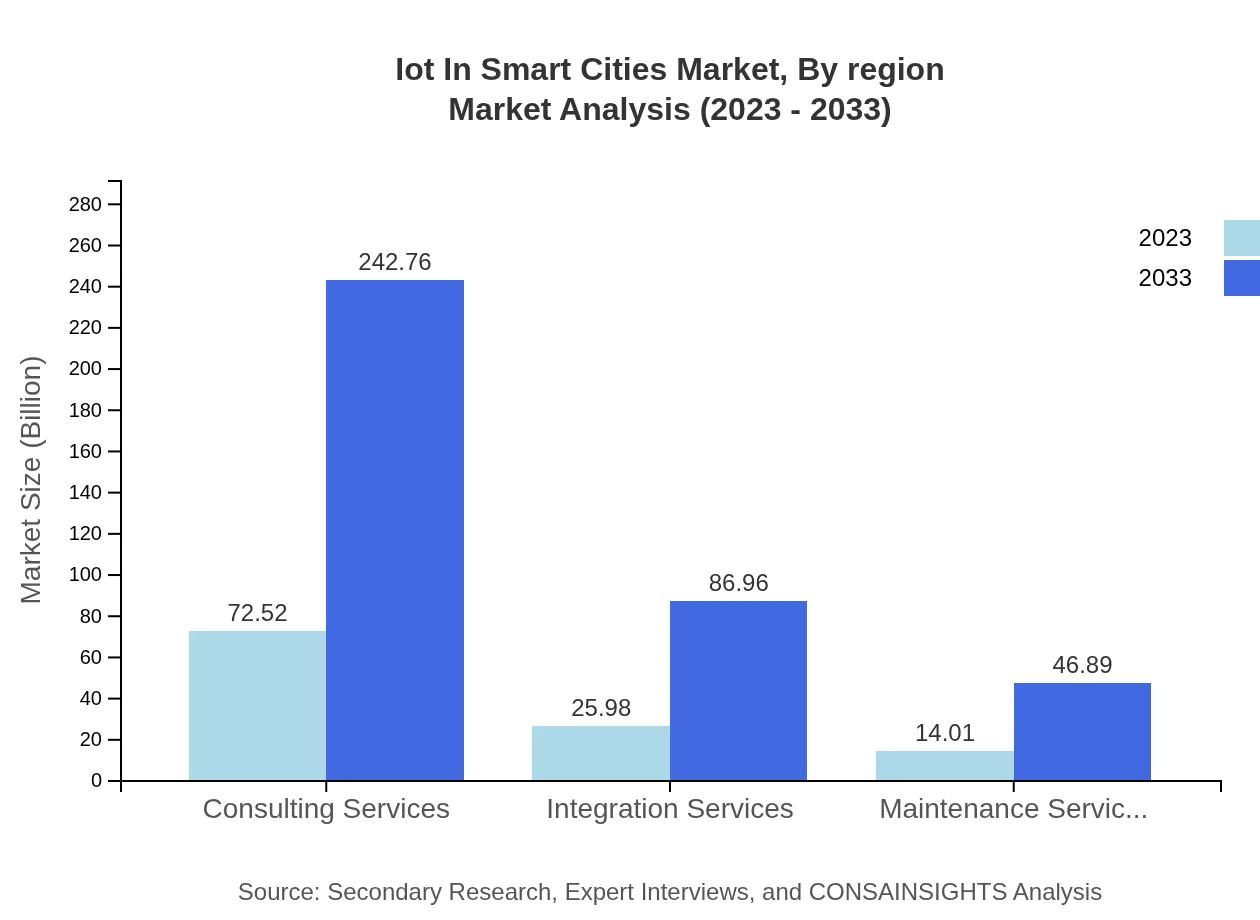
The services segment extends to consulting, integration, and maintenance services. Integration services, worth $25.98 billion in 2023, are anticipated to grow to $86.96 billion by 2033, demonstrating the essential nature of integrating new technologies into existing urban frameworks.
Iot In Smart Cities Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Iot In Smart Cities Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
Cisco is a leader in IT and networking, providing solutions that enable cities to enhance their operational efficiency through seamless connectivity in smart cities.IBM Corporation:
IBM offers a range of IoT solutions for smart cities, focusing on data analytics and cloud computing, helping urban centers to optimize their services through intelligent insights.Siemens AG:
Siemens is actively engaged in projects across smart infrastructure, energy efficiency, and digitalization, contributing extensively to the smart city ecosystem.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric provides integrated solutions for energy management and automation, playing a vital role in developing smart utilities and infrastructures.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of iot In Smart Cities?
The IoT in Smart Cities market size is projected to reach approximately $112.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.3% from 2023 to 2033. This growth indicates a significant expansion in applications and technologies that enhance urban living.
What are the key market players or companies in the iot In Smart Cities industry?
Key players in the IoT in Smart Cities industry include Cisco Systems, IBM, Siemens, General Electric, and Honeywell. These companies are at the forefront of developing innovative solutions that integrate IoT technologies into urban infrastructure, leading the way in this transformative sector.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the iot In Smart Cities industry?
The growth in the IoT in Smart Cities industry is primarily driven by the increasing urbanization across the globe, the need for efficient resource management, enhanced public safety, and improved quality of life. Additionally, advancements in IoT technologies and government initiatives further propel market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the iot In Smart Cities?
The fastest-growing region in the IoT in Smart Cities sector is North America, projected to grow from $42.14 billion in 2023 to $141.08 billion by 2033. Europe also shows significant growth, from $35.42 billion to $118.56 billion during the same period.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the iot In Smart Cities industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights does provide customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the IoT in Smart Cities industry. Clients can request detailed analysis specific to their requirements, ensuring that they receive valuable insights for informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this iot In Smart Cities market research project?
From the IoT in Smart Cities market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market size, growth forecasts, segmentation analysis, competitive landscape, regional insights, and trends. These deliverables offer actionable insights to support strategic planning.
What are the market trends of iot In Smart Cities?
Current trends in the IoT in Smart Cities market include the growing adoption of cloud-based solutions, increasing investment in smart infrastructure, and a focus on sustainable city planning. Additionally, advancements in AI and big data analytics are enhancing operational efficiency in urban environments.