Iot In Utilities Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: iot-in-utilities
Iot In Utilities Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the IoT in utilities market, covering current trends, challenges, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include market size, segmentation, regional analysis, and the impact of technology on this transformative space.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
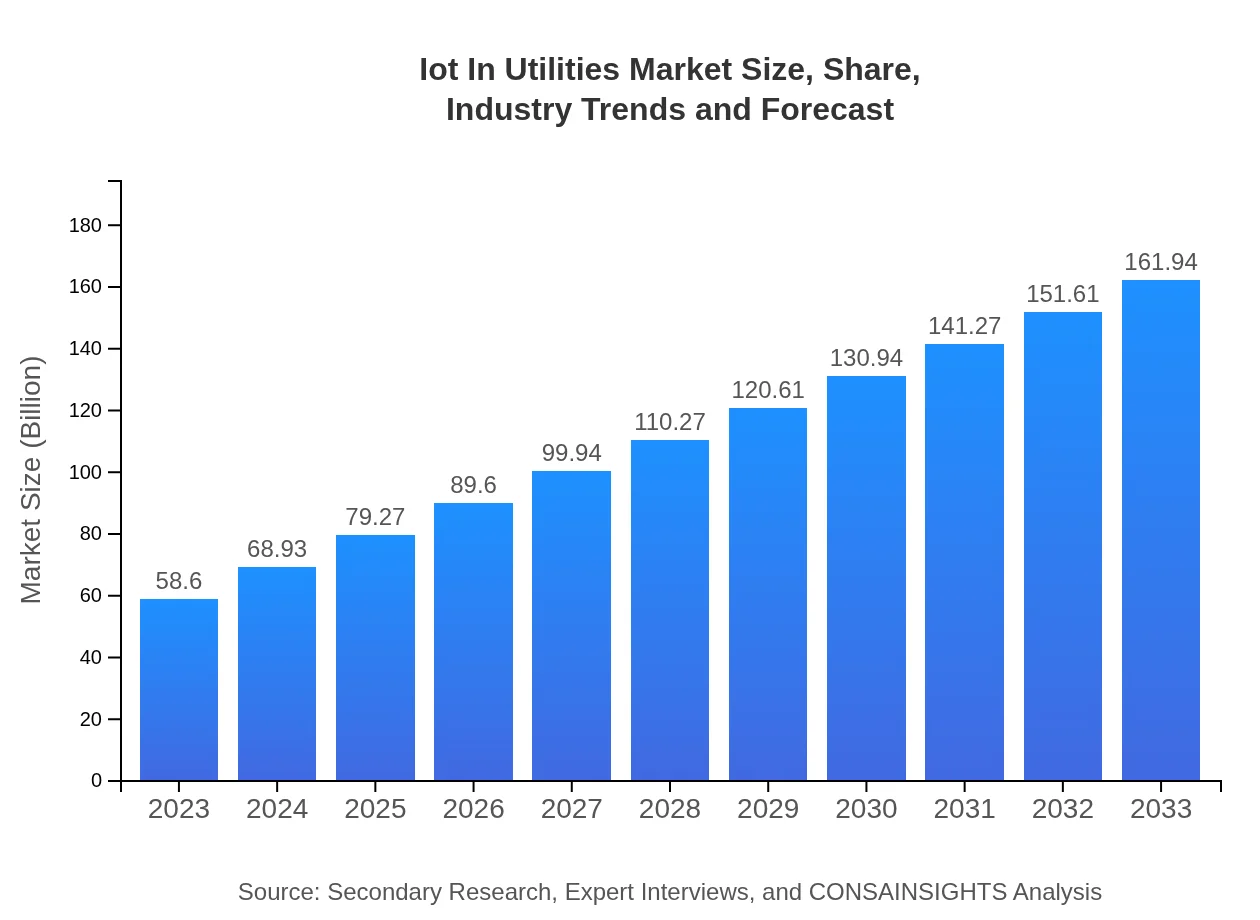
| 2023 Market Size | $58.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $161.94 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, Cisco Systems, IBM Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Iot In Utilities Market Overview
Customize Iot In Utilities Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Iot In Utilities market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Iot In Utilities's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Iot In Utilities
What is the Market Size & CAGR of IoT In Utilities market in 2023?
Iot In Utilities Industry Analysis
Iot In Utilities Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Iot In Utilities Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Iot In Utilities Market Report:
The European market is set to experience significant growth, increasing from $18.35 billion in 2023 to $50.70 billion by 2033. Strict regulatory frameworks and sustainability initiatives are encouraging utilities to adopt IoT solutions.Asia Pacific Iot In Utilities Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the IoT in utilities market is projected to grow from $10.13 billion in 2023 to $28.00 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization, government initiatives toward digital transformation, and the rising demand for efficient resource management.North America Iot In Utilities Market Report:
In North America, the market is forecasted to grow from $21.66 billion in 2023 to $59.87 billion by 2033. The presence of major technology companies and utilities investing heavily in IoT technologies underpins this impressive growth.South America Iot In Utilities Market Report:
The market in South America is expected to expand from $3.53 billion in 2023 to $9.77 billion by 2033. Key drivers include investments in smart technologies and the growing need for improved infrastructure to support population growth.Middle East & Africa Iot In Utilities Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is expected to grow from $4.92 billion in 2023 to $13.60 billion by 2033, aided by increasing investments in digital infrastructure and smart city projects.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
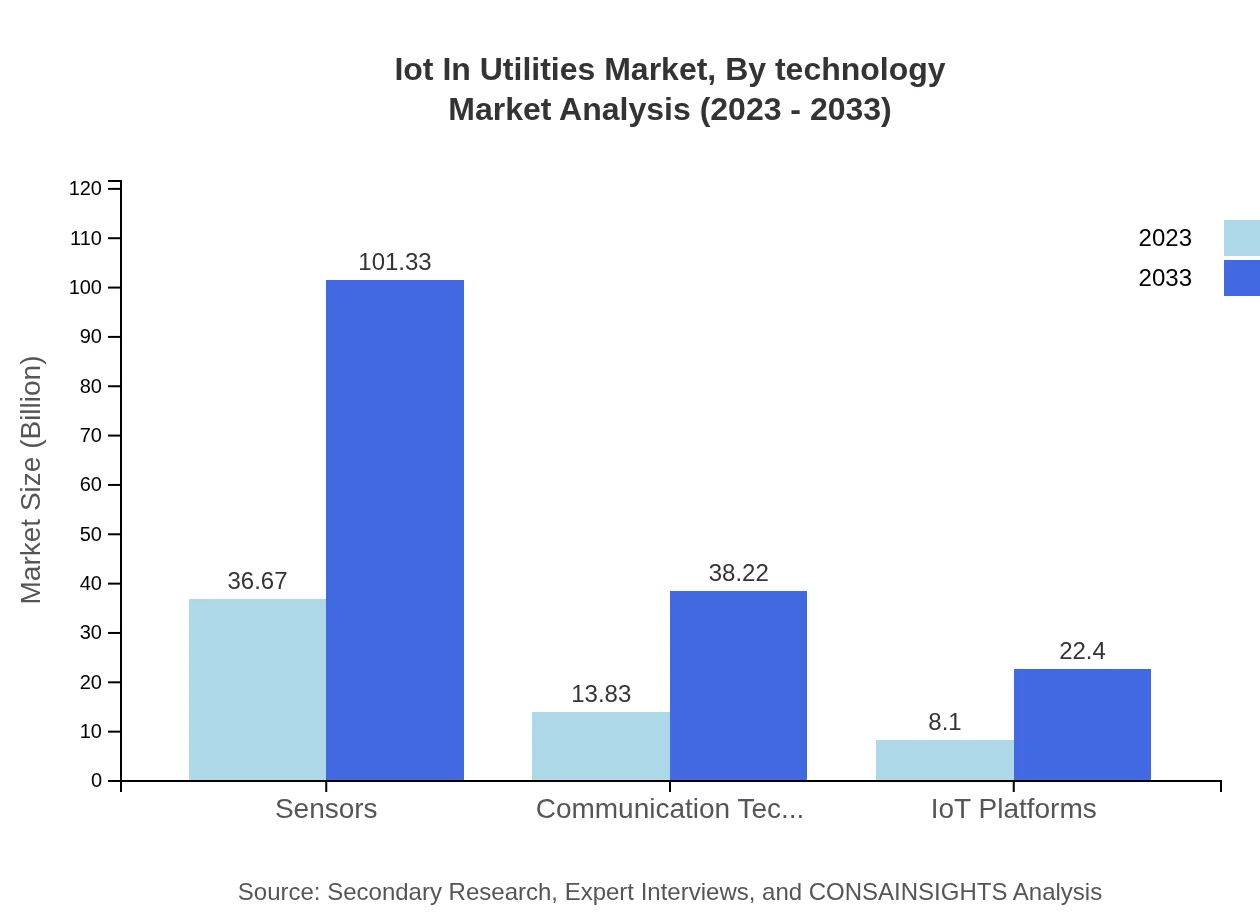
Iot In Utilities Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment includes sensors, communication technologies, and IoT platforms, which collectively enhance utility operations. Sensors play a critical role in data collection for utilities, contributing to a market size of $36.67 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $101.33 billion by 2033.
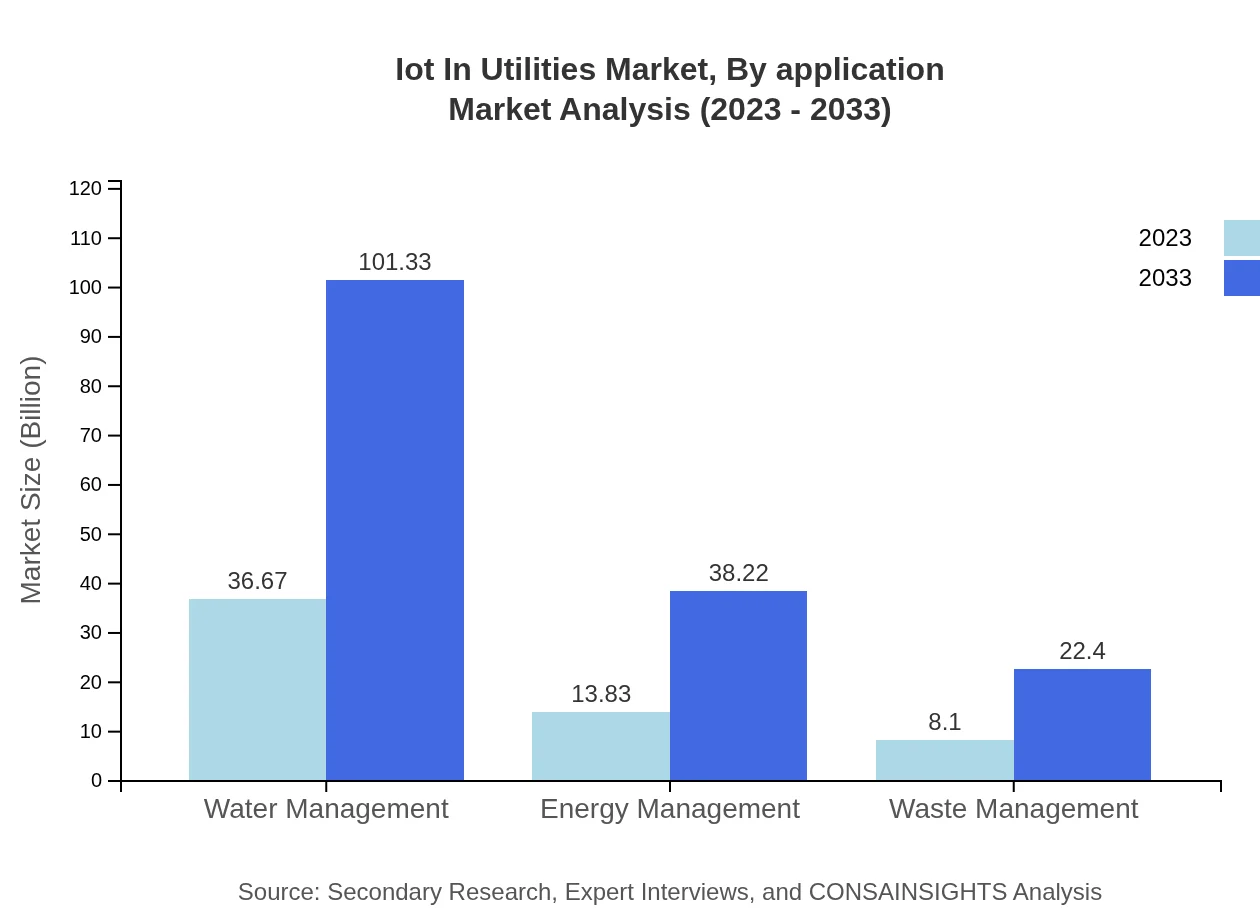
Iot In Utilities Market Analysis By Application
Applications such as water management and energy management are significant, with water management anticipated to grow from $36.67 billion in 2023 to $101.33 billion by 2033. This segment's importance lies in its role in addressing critical issues like water scarcity.
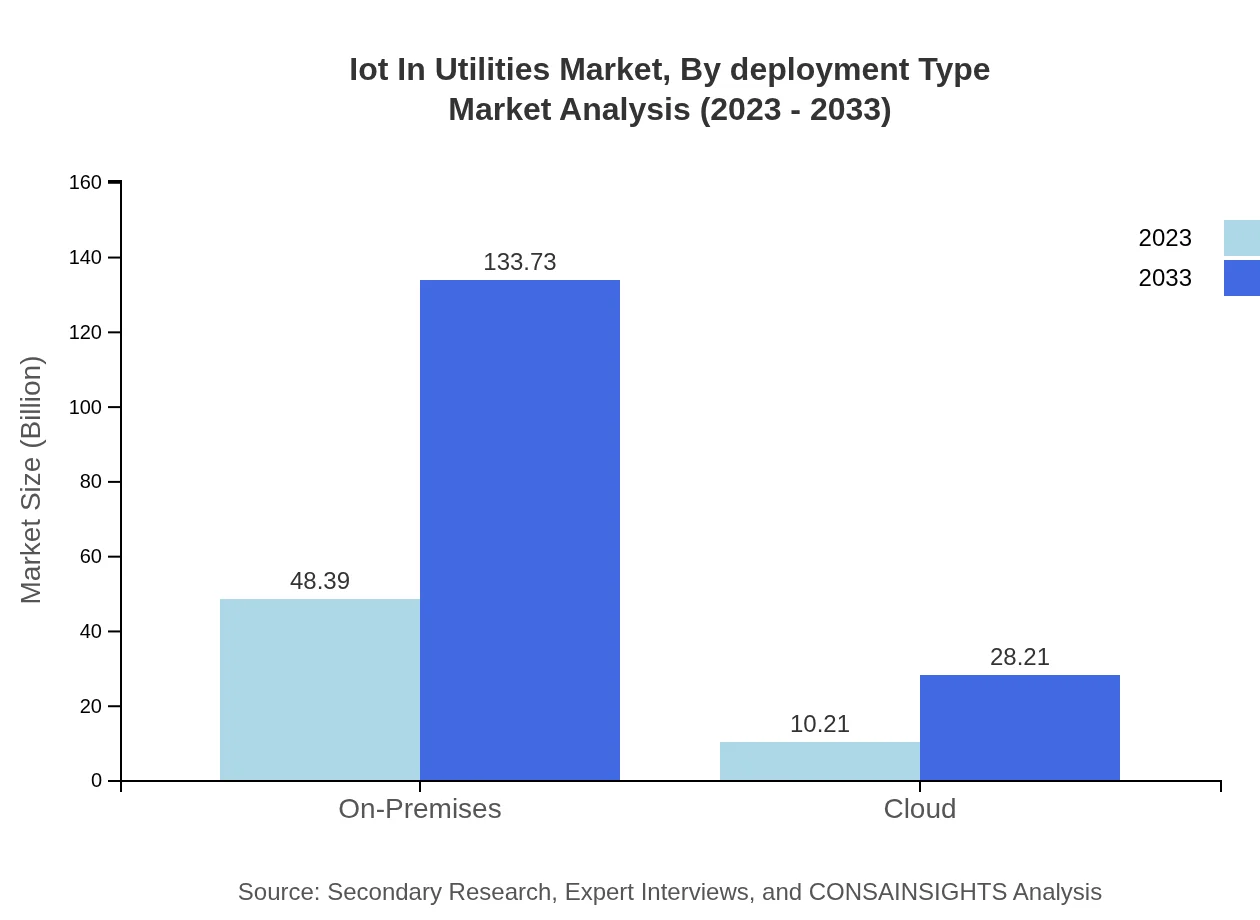
Iot In Utilities Market Analysis By Deployment Type
Deployment models, including on-premises and cloud solutions, reveal diverse strategies among utilities. The on-premises segment is massive, with a size of $48.39 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $133.73 billion by 2033.
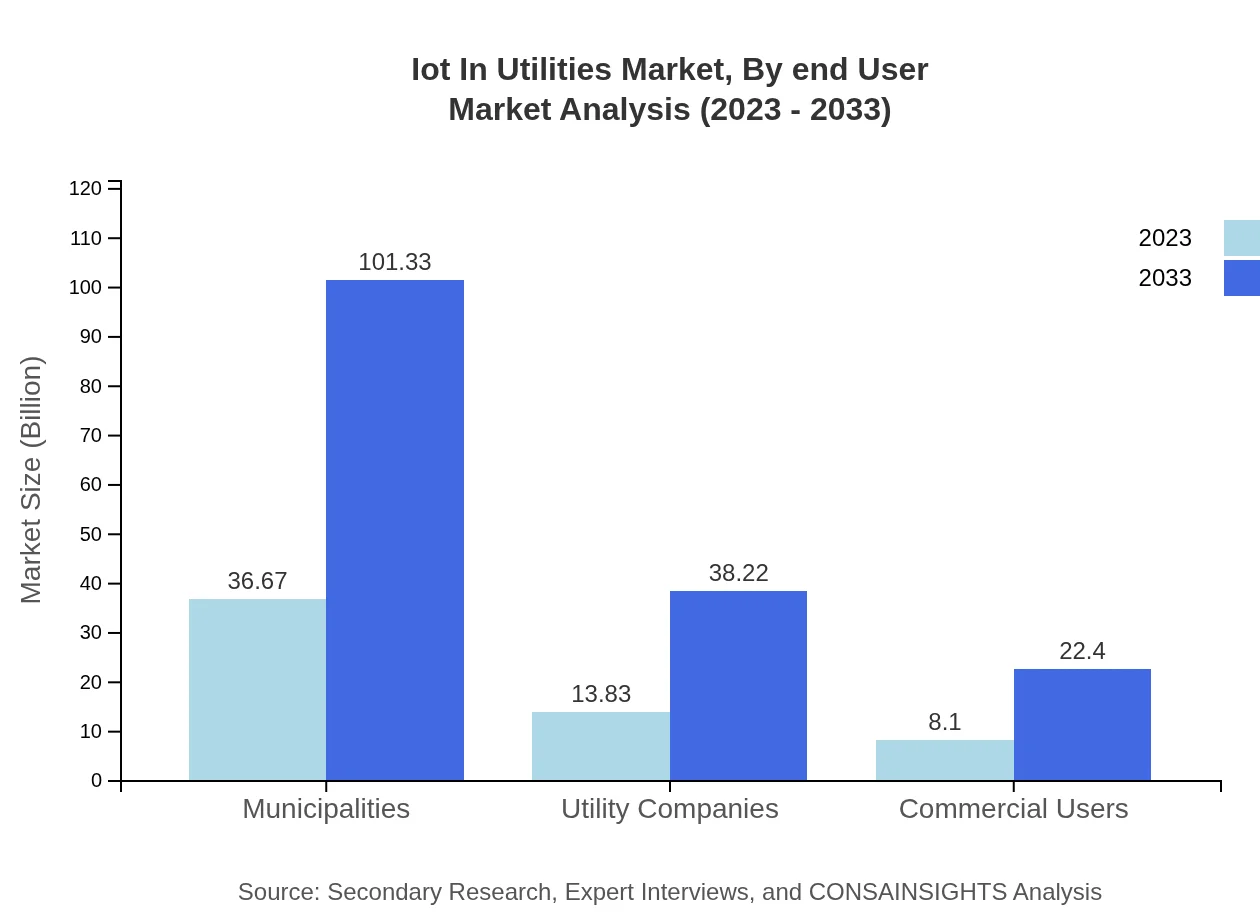
Iot In Utilities Market Analysis By End User
End-users are primarily divided into municipalities and utility companies. Municipalities dominate with a market presence of $36.67 billion in 2023, which is anticipated to expand to $101.33 billion by 2033.
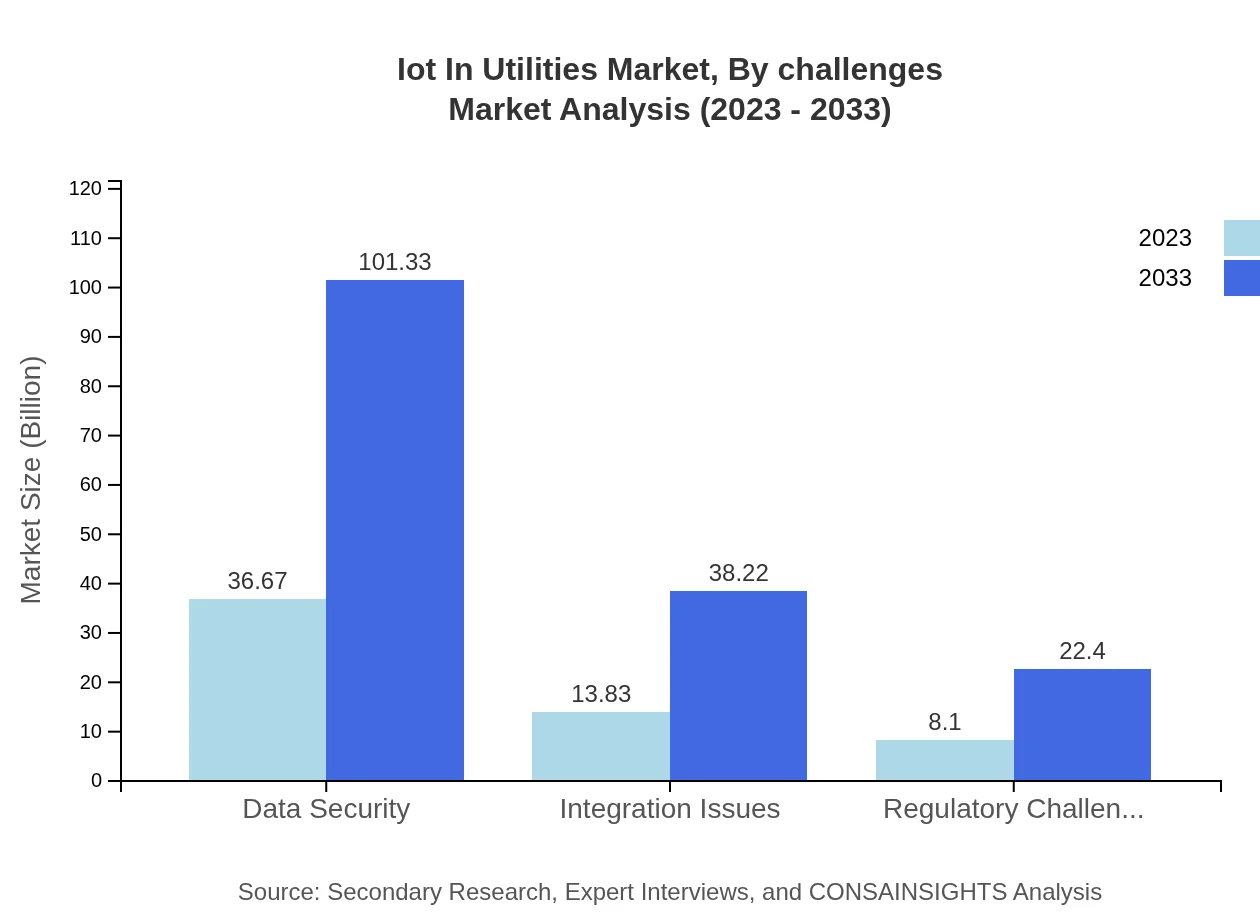
Iot In Utilities Market Analysis By Challenges
Challenges such as data security and regulatory hurdles are critical factors influencing market growth. Data security solutions, accumulating to $36.67 billion in 2023 and expanding to $101.33 billion by 2033, highlight the pressing need for robust security measures.
Iot In Utilities Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in IoT In Utilities Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a pioneer in industrial digitalization, providing advanced IoT solutions for utilities that enhance operational efficiency and reliability.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric specializes in digital transformation in energy management and automation solutions, focusing on sustainability and customer satisfaction in utility services.Cisco Systems:
Cisco provides robust networking and cybersecurity solutions essential for the deployment of IoT technologies in utilities, ensuring seamless connectivity and data protection.IBM Corporation:
IBM offers innovative IoT platforms and data analytics services that empower utilities to enhance their operational capabilities and make data-driven decisions.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of IoT in Utilities?
The IoT in Utilities market is valued at 58.6 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 10.3% leading to substantial growth by 2033. This growth represents a major evolution in utility sectors as they increasingly embrace IoT technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in the IoT in Utilities industry?
Key players in the IoT in Utilities industry include major utility companies and technology firms focusing on IoT solutions. These companies are at the forefront, driving innovation and providing integrated smart utility services across various regions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the IoT in Utilities industry?
Primary growth drivers for the IoT in Utilities industry include rising demand for smart technologies, enhanced operational efficiency, government regulations promoting sustainability, and innovation in IoT applications. These factors collectively push utility sectors to adopt IoT solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the IoT in Utilities?
The fastest-growing region in the IoT in Utilities market is North America, with a market size of 21.66 billion in 2023 expected to grow to 59.87 billion by 2033. This growth is buoyed by substantial infrastructure development and technology adoption.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the IoT in Utilities industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific requirements in the IoT in Utilities industry. This service ensures businesses can receive insights that directly relate to their market strategies and operational needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this IoT in Utilities market research project?
From the IoT in Utilities market research project, you can expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, segmentation insights, competitive landscape assessments, and future market projections, addressing both current and emerging trends.
What are the market trends of IoT in Utilities?
Current market trends in IoT in Utilities include increasing investment in automation, the shift towards higher data security measures, expansion of smart grid technologies, and a significant focus on regulatory compliance within the evolving utility landscape.