Kiwi Fruit Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: kiwi-fruit
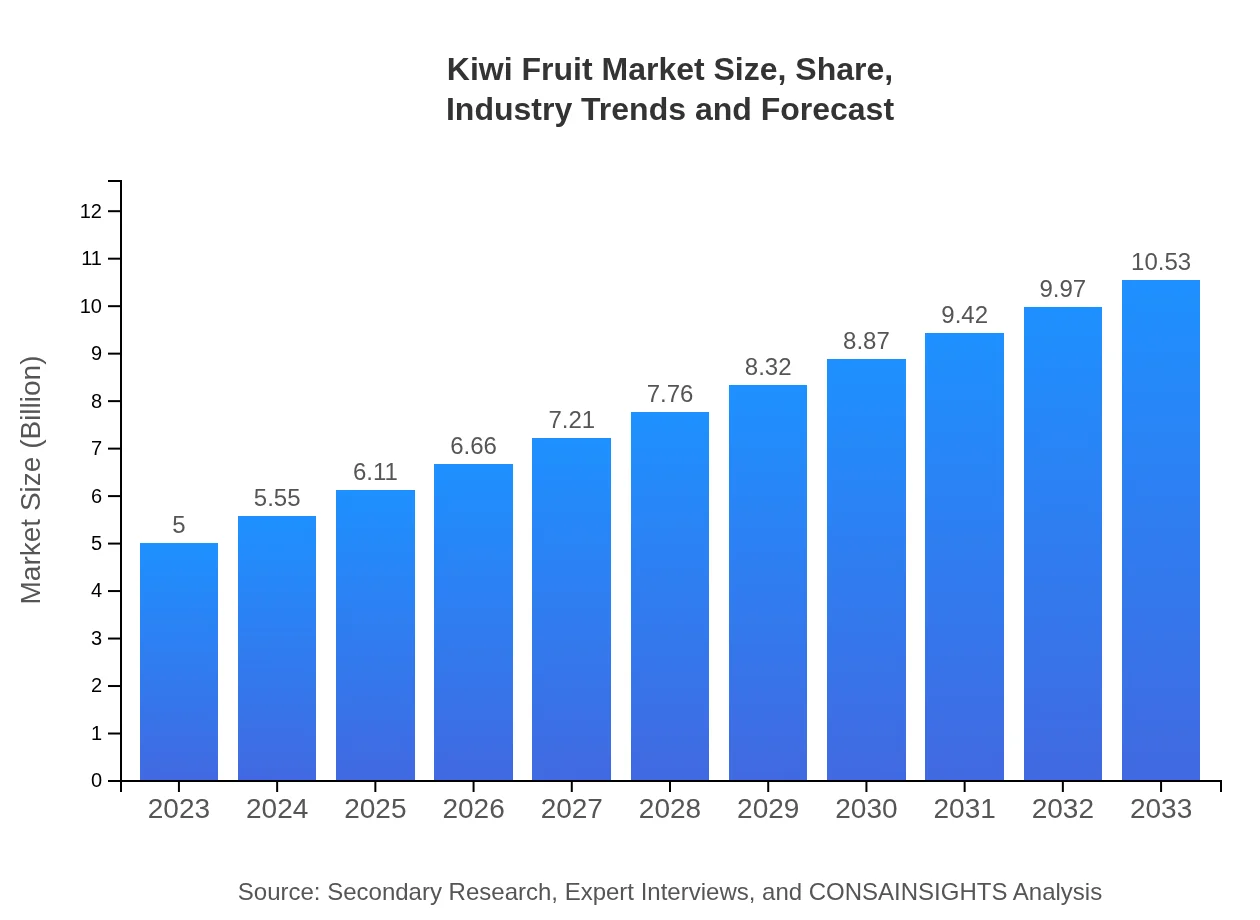
Kiwi Fruit Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an exhaustive analysis of the Kiwi Fruit market from 2023 to 2033, covering key insights on market size, growth trends, regional dynamics, competitive landscape, and segmentation. It offers data-driven forecasts and trends that help stakeholders make informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $5.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $10.53 Billion |
| Top Companies | Zespri International, Fresca Group, Playground Foods, Green Valley International |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Kiwi Fruit Market Overview
Customize Kiwi Fruit Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Kiwi Fruit market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Kiwi Fruit's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Kiwi Fruit
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Kiwi Fruit market in 2023?
Kiwi Fruit Industry Analysis
Kiwi Fruit Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
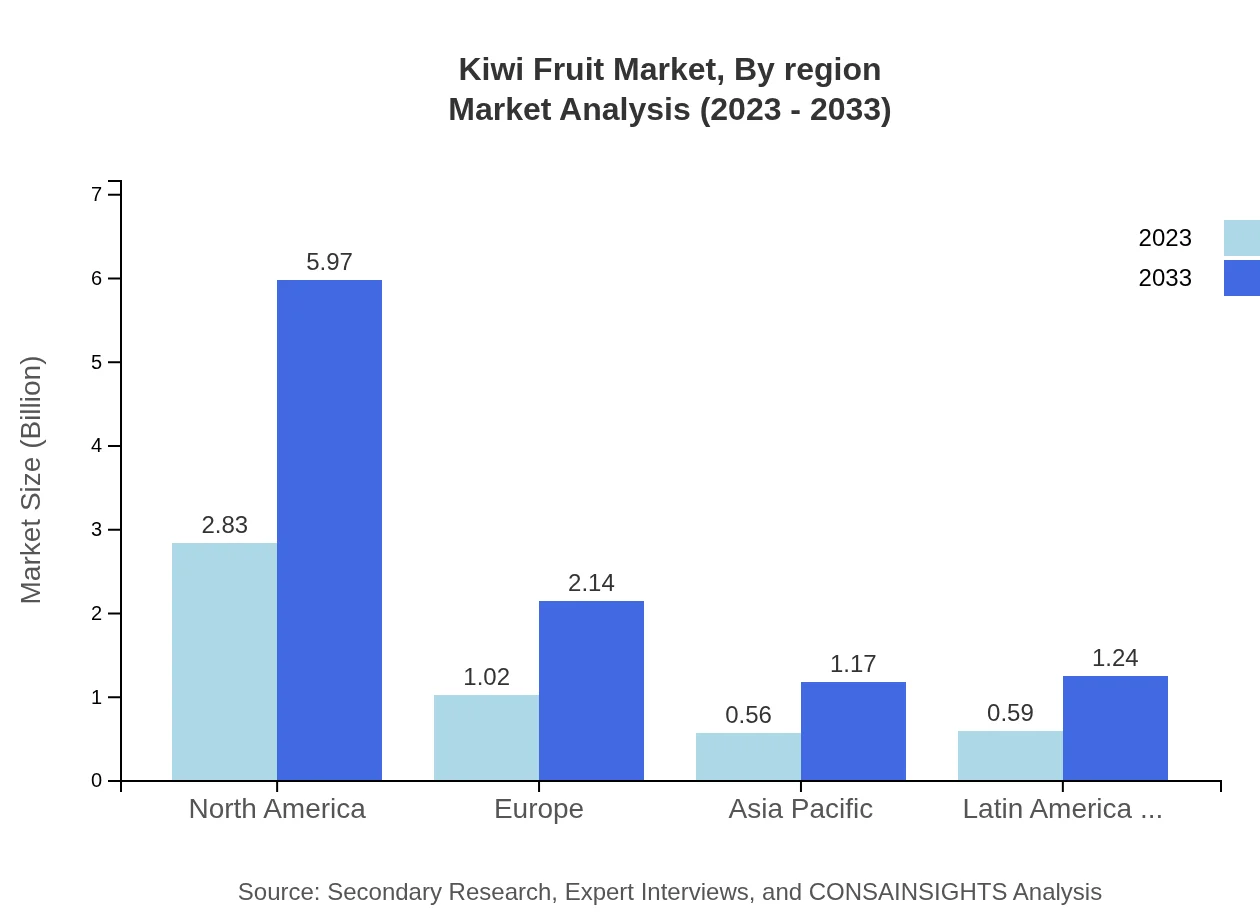
Kiwi Fruit Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Kiwi Fruit Market Report:
Europe's Kiwi Fruit market was valued at USD 1.61 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 3.38 billion by 2033. European consumers are increasingly favoring fresh and organic options, which is fueling market growth. Italy, Greece, and France are major producers, contributing significantly to the market.Asia Pacific Kiwi Fruit Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific Kiwi Fruit market was valued at approximately USD 0.95 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 1.99 billion by 2033. Factors driving this growth include increasing health awareness and a rising middle class, enhancing demand for imported fruits in countries like China and Japan. Additionally, countries like New Zealand and Australia are key players in Kiwi production.North America Kiwi Fruit Market Report:
The North American market for Kiwi Fruit, valued at USD 1.70 billion in 2023, is forecasted to achieve USD 3.58 billion by 2033. The growth is propelled by rising health-consciousness among consumers and increasing demand for organic products across the continent, particularly in the United States and Canada.South America Kiwi Fruit Market Report:
In South America, the Kiwi Fruit market was valued at USD 0.10 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 0.21 billion by 2033. The region's growth is attributed to favorable climatic conditions for Kiwi production and increasing domestic consumption as well as exports to North America.Middle East & Africa Kiwi Fruit Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's market for Kiwi Fruit was valued at USD 0.65 billion in 2023, with expectations to grow to USD 1.37 billion by 2033. Urbanization and an expanding middle class in countries such as South Africa and the UAE are encouraging the consumption of exotic fruits, including Kiwi.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
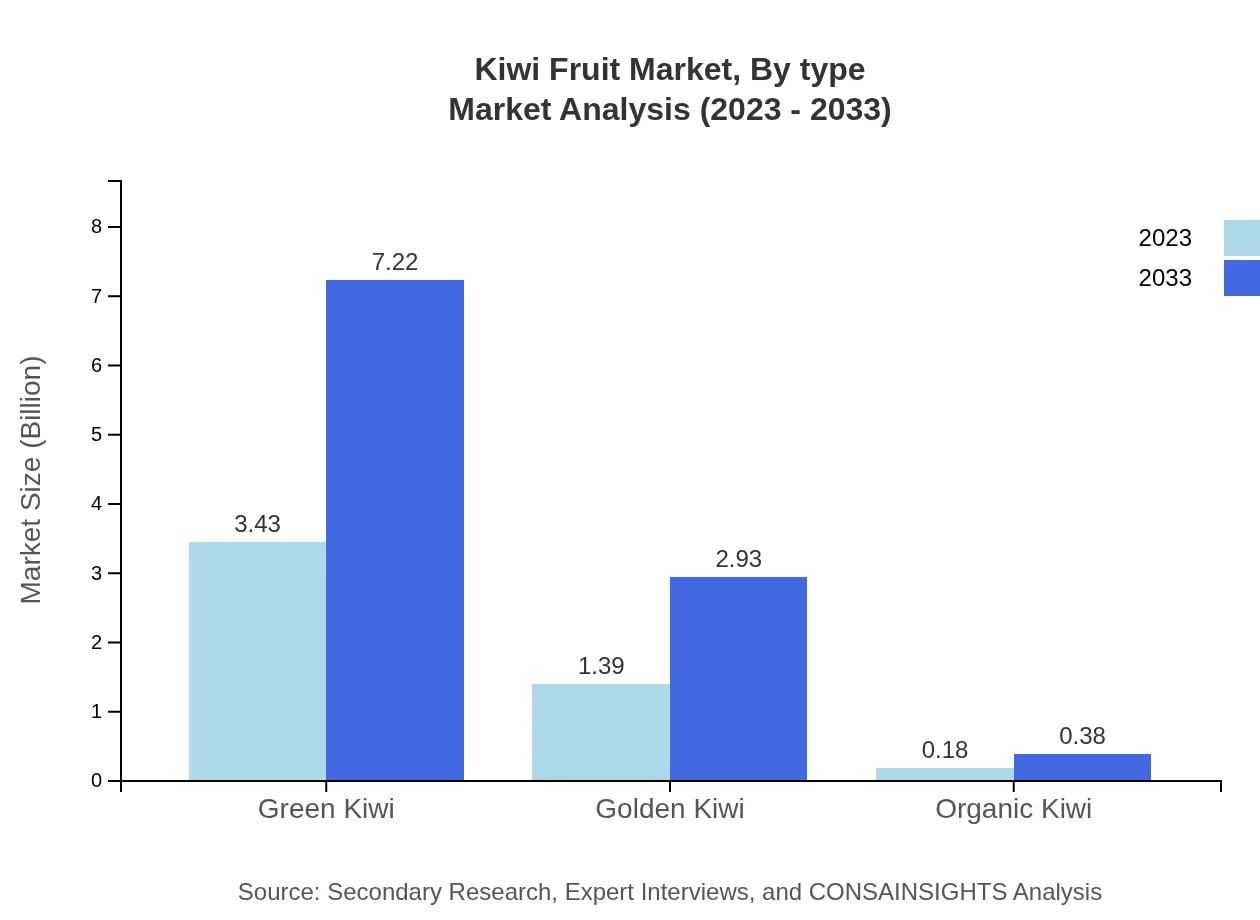
Kiwi Fruit Market Analysis By Type
The Kiwi Fruit market is segmented into Green Kiwi, Golden Kiwi, and Organic Kiwi. As of 2023, Green Kiwi is the dominant type, valued at USD 3.43 billion, and is projected to reach USD 7.22 billion by 2033, representing a significant market share of 68.6%. Golden Kiwi follows, starting from USD 1.39 billion in 2023 and increasing to USD 2.93 billion by 2033 (27.82% market share). Organic Kiwi, though smaller, is expected to grow from USD 0.18 billion to USD 0.38 billion, reflecting a steady rise in consumer demand for organic produce in health-conscious markets.
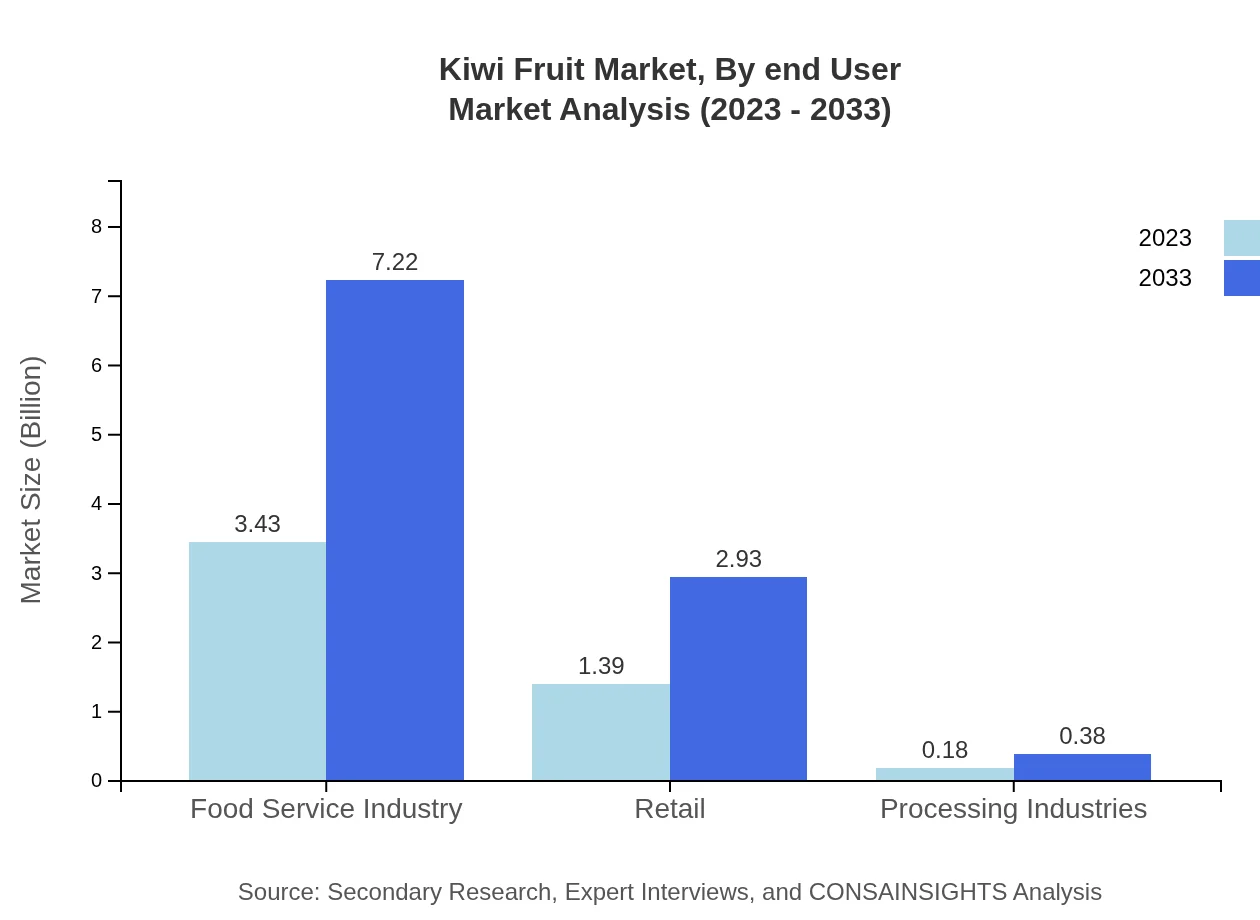
Kiwi Fruit Market Analysis By End User
The market is divided into Food Service, Retail, and Processing Industries. The Food Service industry holds a significant market share, evaluated at USD 3.43 billion in 2023, and is estimated to reach USD 7.22 billion by 2033. Retail follows with a market size of USD 1.39 billion, projecting growth to USD 2.93 billion by 2033, while Processing Industries contribute a smaller share, moving from USD 0.18 billion to USD 0.38 billion over the same period.
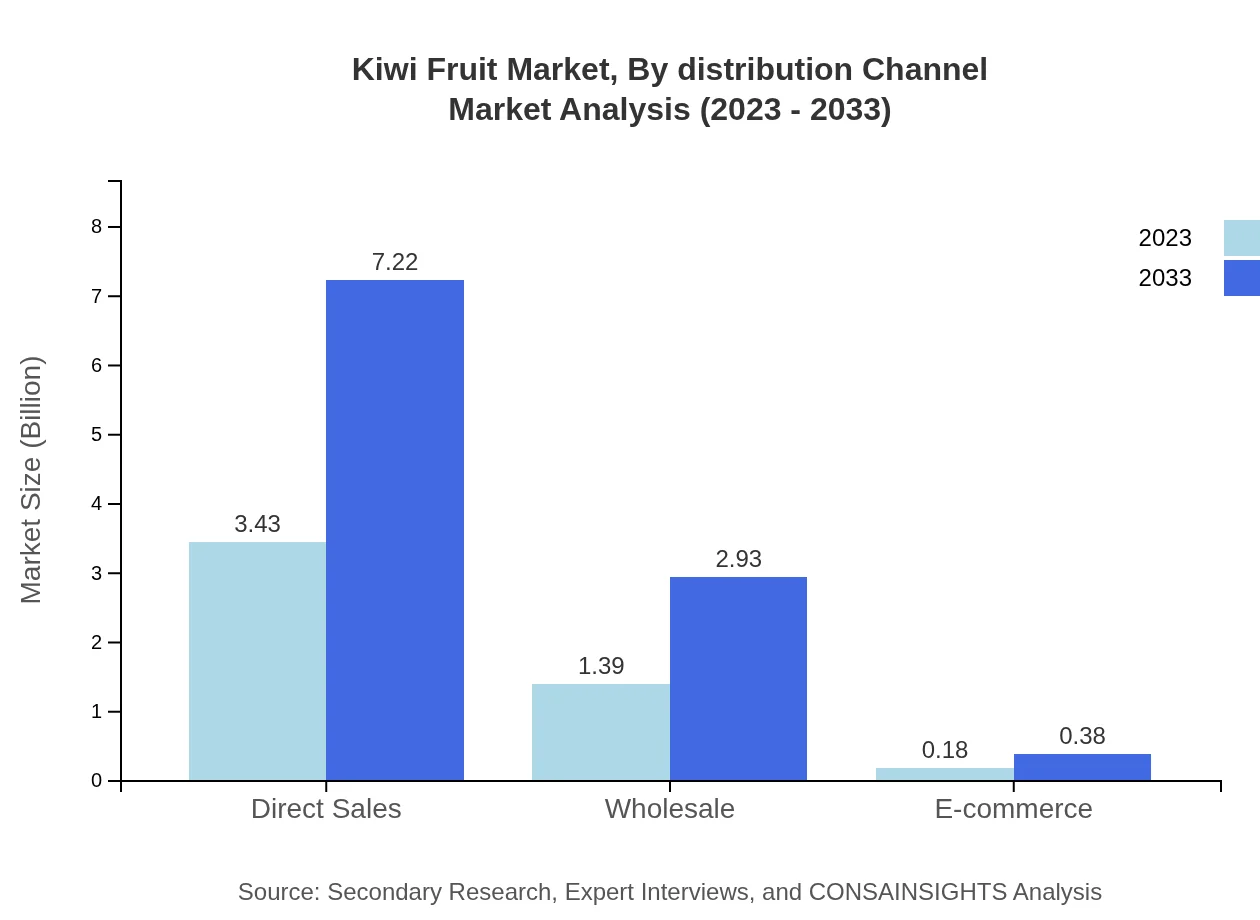
Kiwi Fruit Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Distribution channels for Kiwi Fruit include Direct Sales, Wholesale, E-commerce, and Retail. Direct Sales dominate the market, accounting for USD 3.43 billion in 2023, and forecasted to grow to USD 7.22 billion by 2033. Wholesale and Retail also represent significant avenues for sales, projected to rise from USD 1.39 billion to USD 2.93 billion over the same period. E-commerce is emerging, albeit slower, with a forecast growth from USD 0.18 billion to USD 0.38 billion as online shopping trends gain traction.
Kiwi Fruit Market Analysis By Region
Regional analysis shows strong performance in North America, closely followed by Europe and Asia Pacific. As the demand for healthy snacks grows, North America is expected to maintain its lead, whereas Europe is anticipated to increase presence in the organic segment and Asia Pacific witnesses heightened demand due to increasing disposable income.
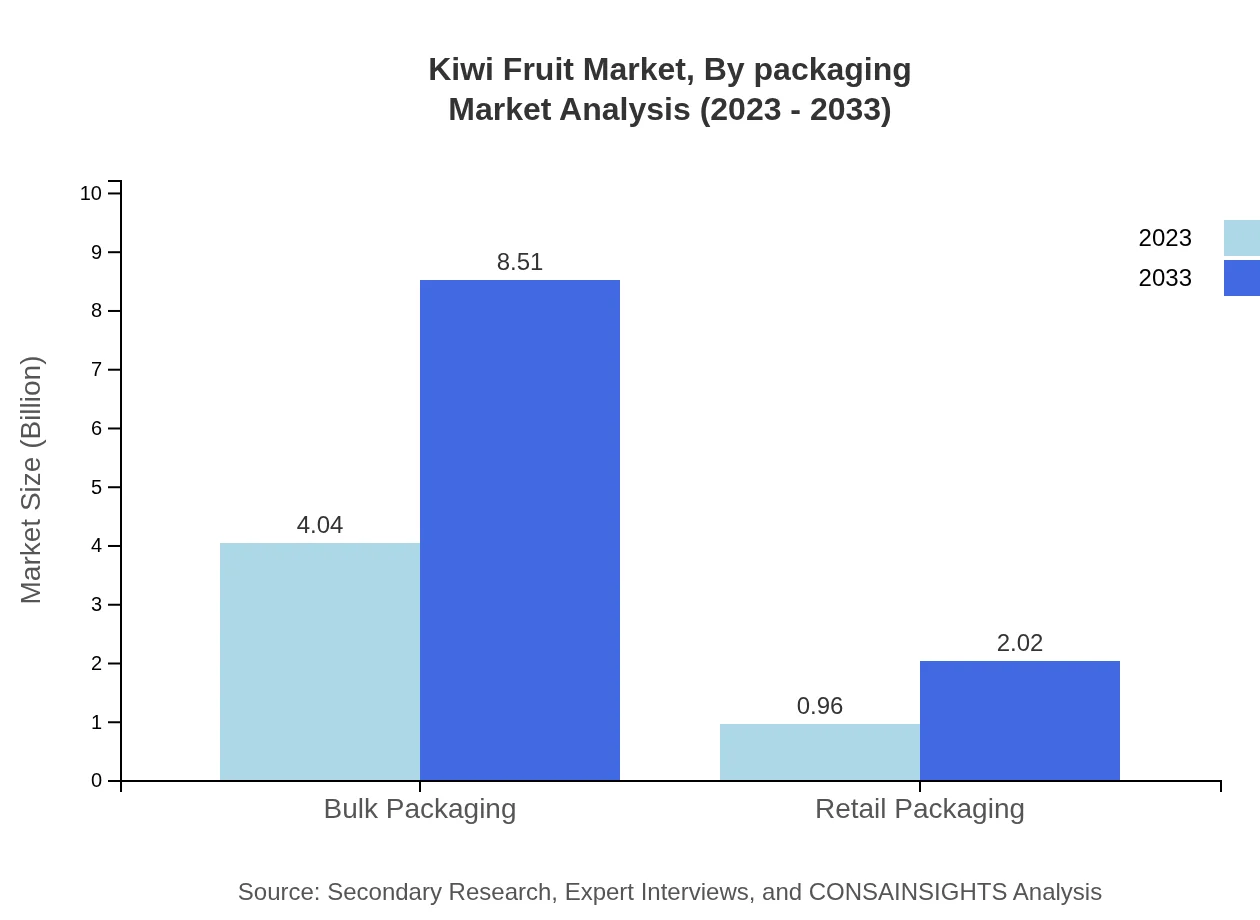
Kiwi Fruit Market Analysis By Packaging
Packaging types for Kiwi Fruit include Bulk Packaging and Retail Packaging. Bulk Packaging leads the market with USD 4.04 billion in 2023, set to rise to USD 8.51 billion by 2033, capturing an 80.84% market share. Retail Packaging holds a lesser share, starting at USD 0.96 billion and forecasted to increase to USD 2.02 billion, indicating growing interest in ready-to-consume Kiwi products.
Kiwi Fruit Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Kiwi Fruit Industry
Zespri International:
A leading kiwi marketer, Zespri is headquartered in New Zealand and is renowned for its premium quality kiwis, particularly the SunGold variety. The company focuses on sustainable practices and innovation in cultivation and exportation.Fresca Group:
This company is a major distributor of fresh fruits, specifically kiwi, in North America and is known for quality and service. Fresca Group prioritizes sustainability and local sourcing, relating closely to organic consumer preferences.Playground Foods:
Specializes in the production of organic kiwi products, including dried fruit snacks and purees aimed at health-conscious consumers, thereby expanding the kiwi market reach.Green Valley International:
Based in Italy, this company is a prominent exporter of kiwi, utilizing advanced agro-technological practices to improve yield and quality, enhancing the global supply chain.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Kiwi Fruit?
The global market size for kiwi fruit is projected to reach $5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.5%. This growth reflects increasing consumer demand for healthy and nutritious food options in conjunction with expanding agricultural practices.
What are the key market players or companies in the Kiwi Fruit industry?
Key players in the kiwi fruit market include Zespri International, California Kiwifruit Growers, and Horticultural Innovation Australia. These companies are known for their significant market share and influence in the production and distribution of kiwi fruit globally.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Kiwi Fruit industry?
The growth of the kiwi fruit industry is driven by increasing health consciousness among consumers, the popularity of kiwi as a superfood, and advancements in cultivation technologies that improve yield and sustainability.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Kiwi Fruit market?
The fastest-growing region in the kiwi fruit market is North America, projected to grow from $1.70 billion in 2023 to $3.58 billion by 2033. This growth is primarily fueled by rising health awareness and the increasing incorporation of kiwi in diets.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Kiwi Fruit industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the kiwi fruit industry to cater to specific client needs. This includes tailored insights on market trends, forecasts, and competitive analysis, empowering decision-makers.
What deliverables can I expect from this Kiwi Fruit market research project?
Deliverables from the kiwi fruit market research project include a comprehensive market analysis report, segmentation breakdown, competitive landscape assessment, and forecast data for various geographies and market segments.
What are the market trends of Kiwi Fruit?
Market trends for kiwi fruit include increased consumer preference for organic options, growth in health food sectors like food service and retail, and significant innovations in packaging methods aimed at enhancing shelf life and maintaining quality.