Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: lab-automation-in-drug-discovery
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Lab Automation in Drug Discovery market, focusing on current trends, growth predictions, and competitive landscape from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
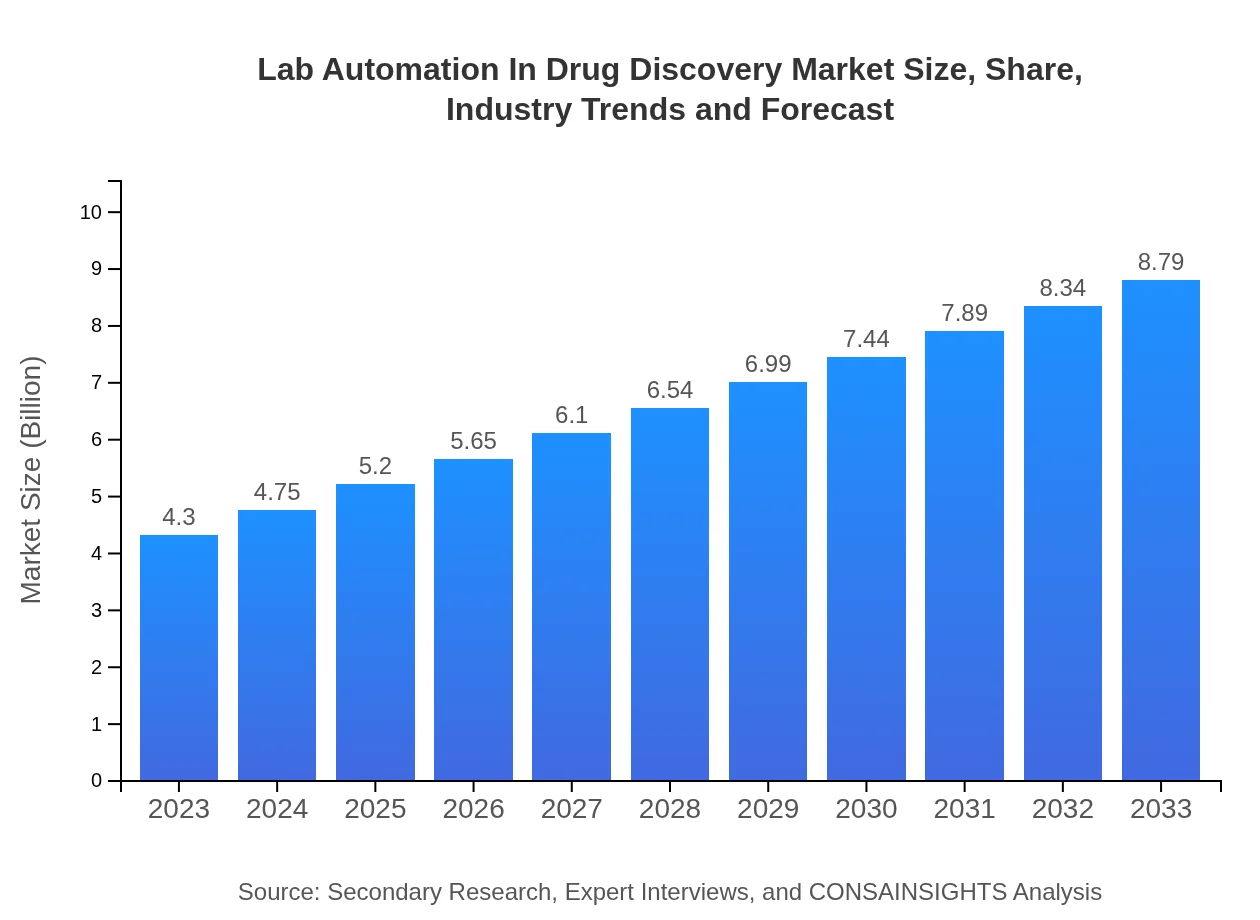
| 2023 Market Size | $4.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $8.79 Billion |
| Top Companies | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Abbott Laboratories, Agilent Technologies, PerkinElmer, Siemens Healthineers |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Overview
Customize Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Lab Automation In Drug Discovery market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Lab Automation In Drug Discovery's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Lab Automation In Drug Discovery
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Lab Automation In Drug Discovery market in 2023?
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Industry Analysis
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report:
In Europe, the market value was approximately $1.29 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach $2.63 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a well-established pharmaceutical industry and a strong emphasis on innovation and regulatory compliance.Asia Pacific Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific region's Lab Automation in Drug Discovery market is valued at approximately $0.78 billion and is expected to reach $1.60 billion by 2033. The increasing investment in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research in countries like China and India, along with government support for R&D initiatives, is driving this growth.North America Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report:
North America leads the Lab Automation in Drug Discovery market with a value of $1.60 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $3.26 billion by 2033. The US is a major contributor, with substantial investments from pharmaceutical companies towards R&D and emerging technologies.South America Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report:
The South America market, valued at $0.18 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $0.37 billion by 2033, driven largely by an increase in healthcare investments and growing pharmaceutical and biotech sectors, particularly in Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market, valued at $0.45 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to $0.92 billion by 2033, with increasing healthcare investment and initiatives aimed at strengthening the pharmaceutical infrastructure.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Analysis By Product
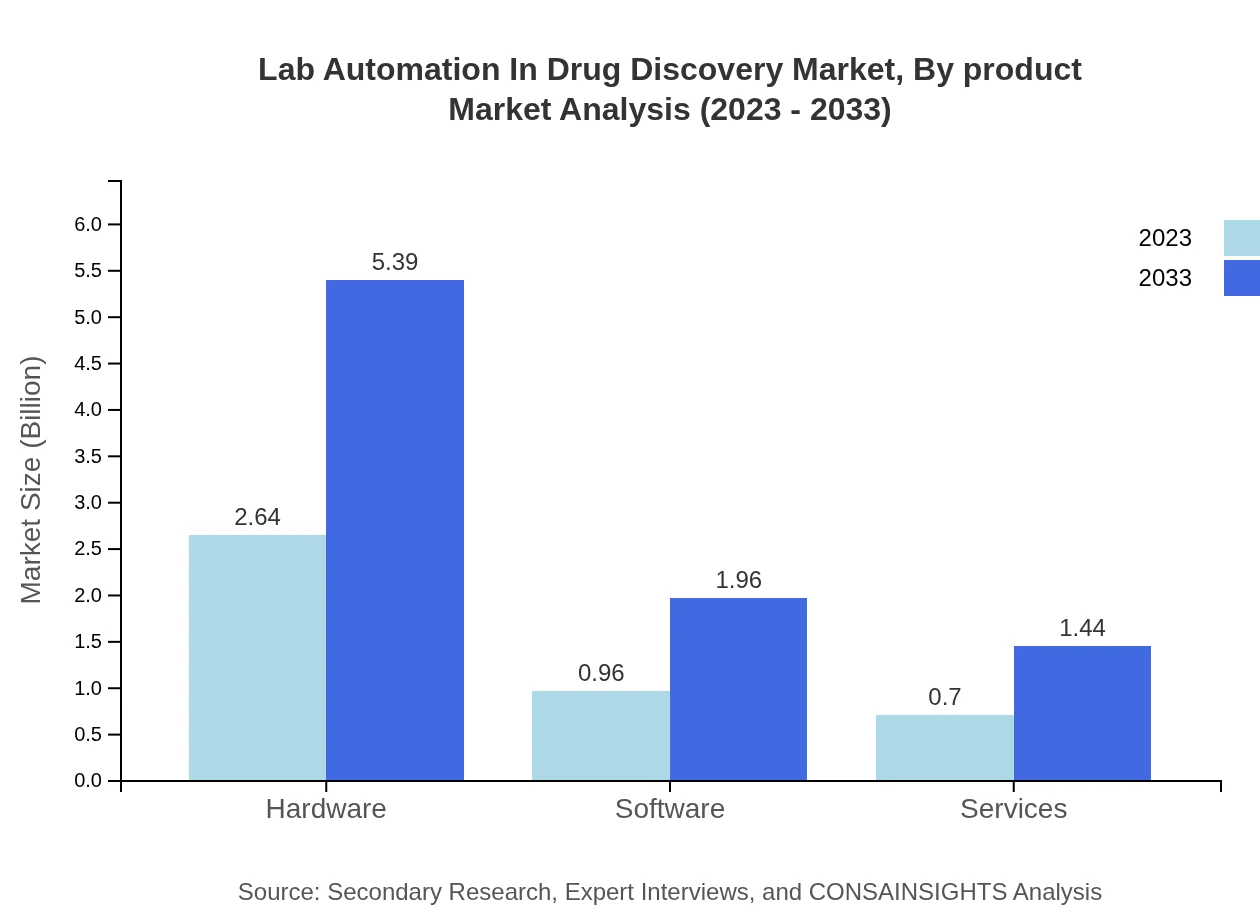
The Lab Automation in Drug Discovery market by product type is dominated by hardware, which accounts for a market size of $2.64 billion in 2023, expected to double to $5.39 billion by 2033, with a share of 61.37%. Software follows, with a market size of $0.96 billion in 2023 and projected growth to $1.96 billion by 2033, holding a 22.25% market share. Services segment stands at $0.70 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $1.44 billion, contributing 16.38%.
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Analysis By Application
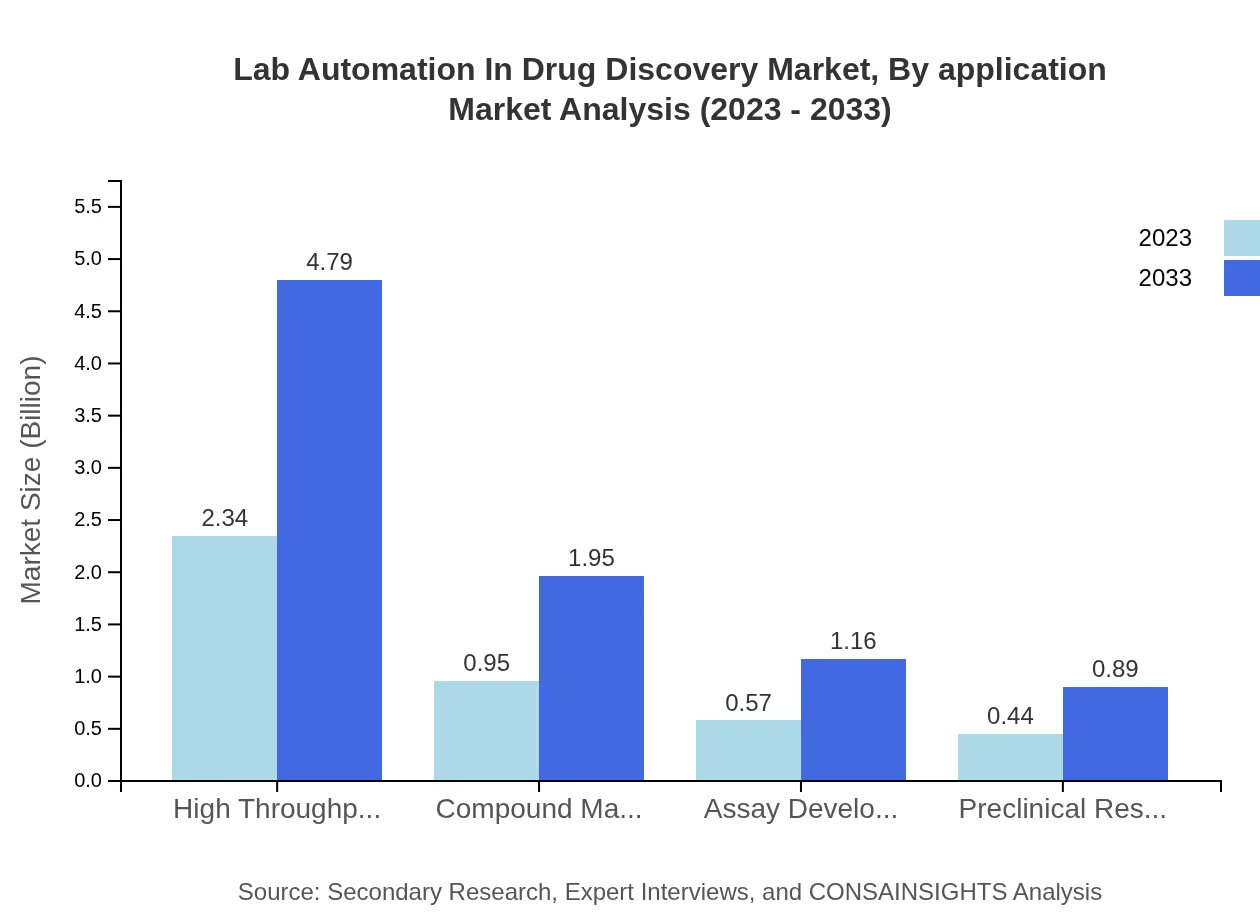
By application, the high-throughput screening segment is significant, with a market size of $2.34 billion in 2023, projected to rise to $4.79 billion by 2033, maintaining a share of 54.47%. Compound management and assay development also show substantial growth potential, with sizes of $0.95 billion and $0.57 billion in 2023, respectively.
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Analysis By End User
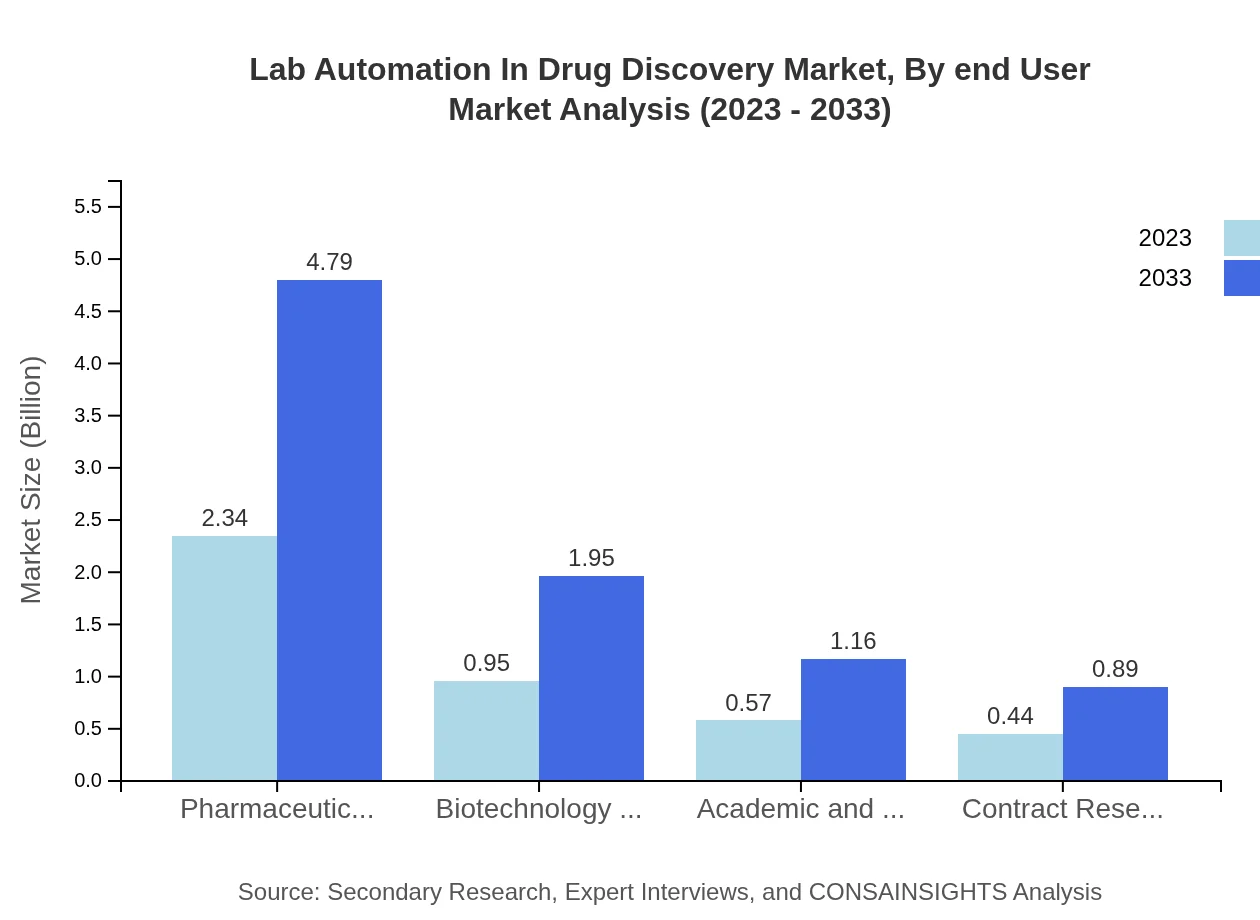
In terms of end-users, pharmaceutical companies dominate, accounting for a market size of $2.34 billion in 2023 and expected growth to $4.79 billion by 2033, representing a 54.47% share. Biotechnology firms contribute notably, with $0.95 billion in 2023 and projected growth to $1.95 billion, maintaining a 22.15% share.
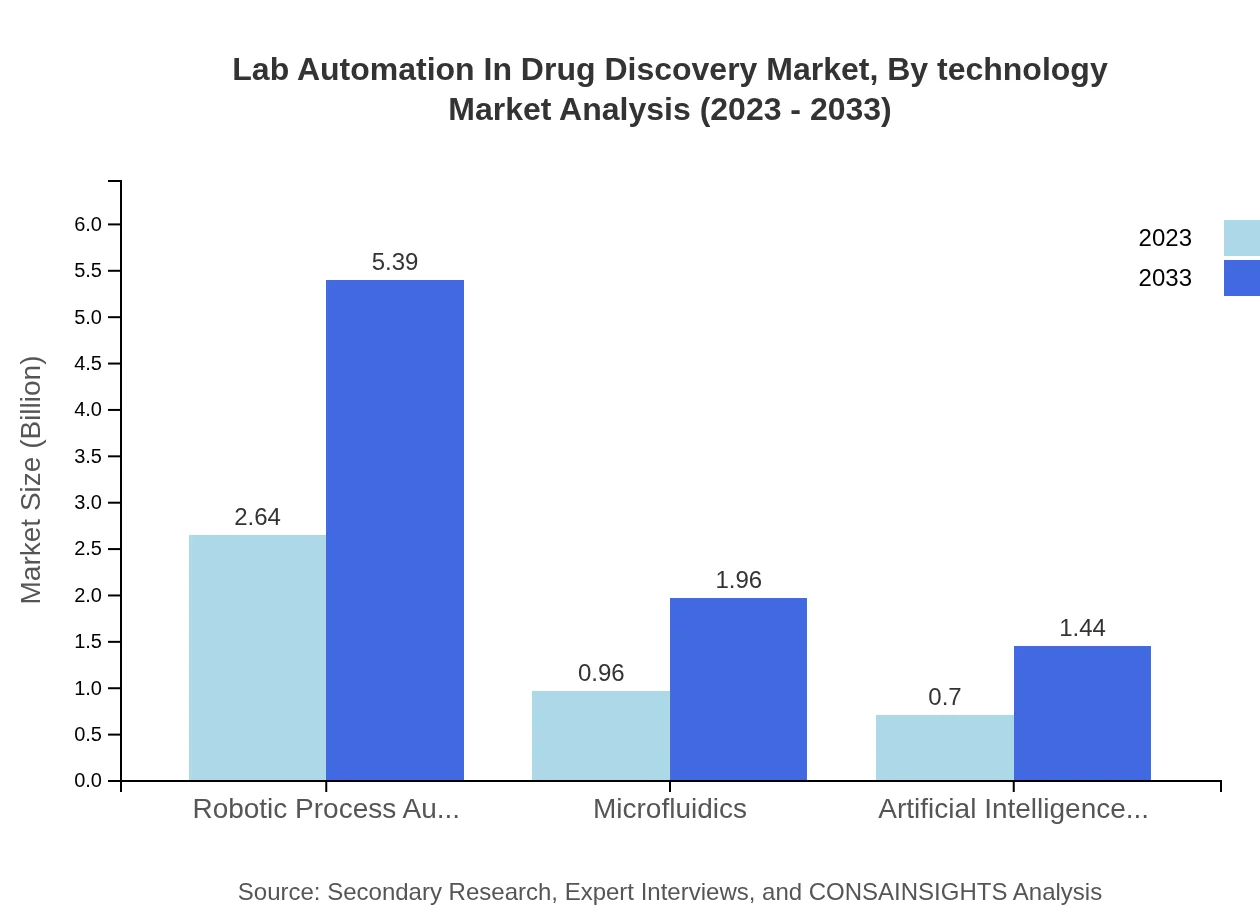
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment shows robust growth, particularly in robotic process automation, which generates a market size of $2.64 billion in 2023, expected to reach $5.39 billion by 2033, maintaining a 61.37% share. Advances in microfluidics and AI-enhanced automation also contribute to the technological landscape.
Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Lab Automation In Drug Discovery Industry
Thermo Fisher Scientific:
A leading global provider of analytical instruments, reagents, and software for laboratories involved in drug discovery, known for its innovation and research collaboration.Abbott Laboratories:
A healthcare company that develops measures and technologies to improve patient outcomes, including lab automation for drug discovery applications.Agilent Technologies:
Offers a broad range of lab automation solutions, particularly in life sciences, aiding laboratories in drug discovery and development processes.PerkinElmer:
Specializes in diagnostics and life science tools, providing integrated solutions for lab automation and drug discovery research.Siemens Healthineers:
A pioneer in healthcare technology, which contributes to laboratory automation through innovative tools that enhance drug detection and analysis.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of lab Automation In Drug Discovery?
The lab automation in drug discovery market is valued at approximately $4.3 billion as of 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% leading to significant growth over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in this lab Automation In Drug Discovery industry?
Key players in the lab automation in drug discovery market include major pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and contract research organizations (CROs) that invest in advanced technologies to enhance drug discovery processes.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the lab Automation In Drug Discovery industry?
Growth is driven by the increasing demand for faster drug development, technological advancements in robotics and AI, and the need for high-throughput screening and efficient compound management in research.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the lab Automation In Drug Discovery?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in lab automation for drug discovery, expanding from a market size of $1.60 billion in 2023 to approximately $3.26 billion by 2033.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the lab Automation In Drug Discovery industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs, allowing clients to gain precise insights into the lab automation in drug discovery sector.
What deliverables can I expect from this lab Automation In Drug Discovery market research project?
Expect detailed market analysis reports, forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, trend evaluations, and segment-specific data that cater to the lab automation in drug discovery industry.
What are the market trends of lab Automation In Drug Discovery?
Current trends include increasing integration of AI and machine learning, growth in high-throughput screening, automation of routine laboratory tasks, and emphasis on improving drug discovery efficiency.