Lead Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: lead
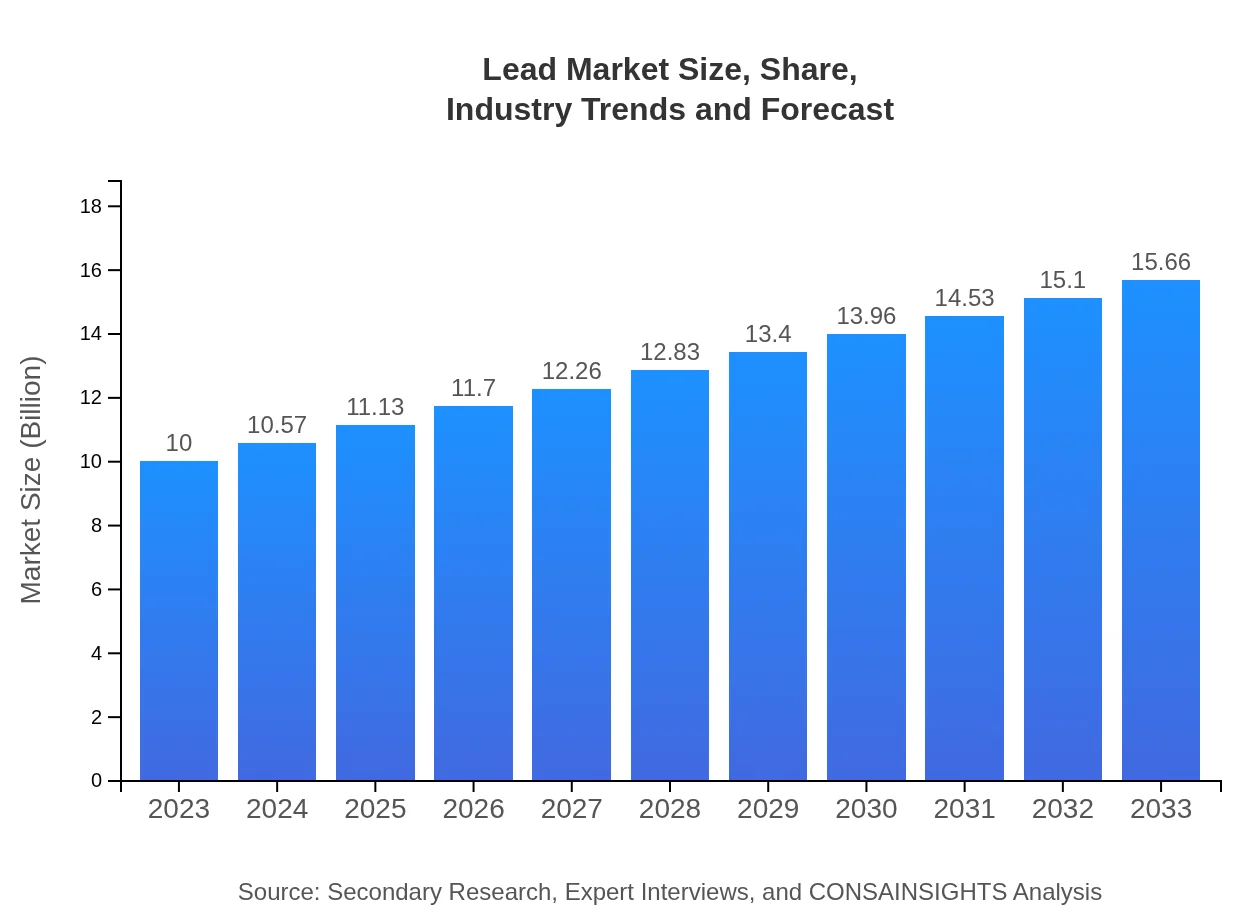
Lead Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Lead market from 2023 to 2033, focusing on key insights, trends, and data-driven forecasts. It covers market size, growth rates, and regional dynamics, highlighting significant trends and challenges in the Lead industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $15.66 Billion |
| Top Companies | Exide Technologies, Johnson Controls, Enersys, GS Yuasa Corporation |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Lead Market Overview
Customize Lead Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Lead market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Lead's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Lead
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Lead market in 2023?
Lead Industry Analysis
Lead Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Lead Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Lead Market Report:
Europe experiences significant market expansion from $2.61 billion in 2023 to $4.09 billion in 2033. Stringent environmental regulations are reshaping the market, pushing for recycling innovation while the automotive sector transitions to more eco-friendly solutions.Asia Pacific Lead Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Lead market is expected to grow from $2.04 billion in 2023 to $3.20 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increased industrial activities, a rise in automotive production, and the adoption of electric vehicles, which require lead-acid batteries and alloys.North America Lead Market Report:
North America is a key market for Lead, with expectations to increase from $3.76 billion in 2023 to $5.89 billion in 2033. Regulatory support for recycling and robust renewable energy initiatives bolster market uptake, as lead-acid batteries become central to energy storage solutions.South America Lead Market Report:
The South American Lead market witnesses moderate growth, expanding from $0.45 billion in 2023 to $0.71 billion in 2033. Increasing construction activities and the associated need for lead-based products contribute to this growth, despite slower industrial scaling in some areas.Middle East & Africa Lead Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Lead market is projected to grow from $1.14 billion in 2023 to $1.78 billion in 2033. The growth is largely attributed to mining activities, along with improving infrastructure, surge in power generation, and an uptick in automotive production.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
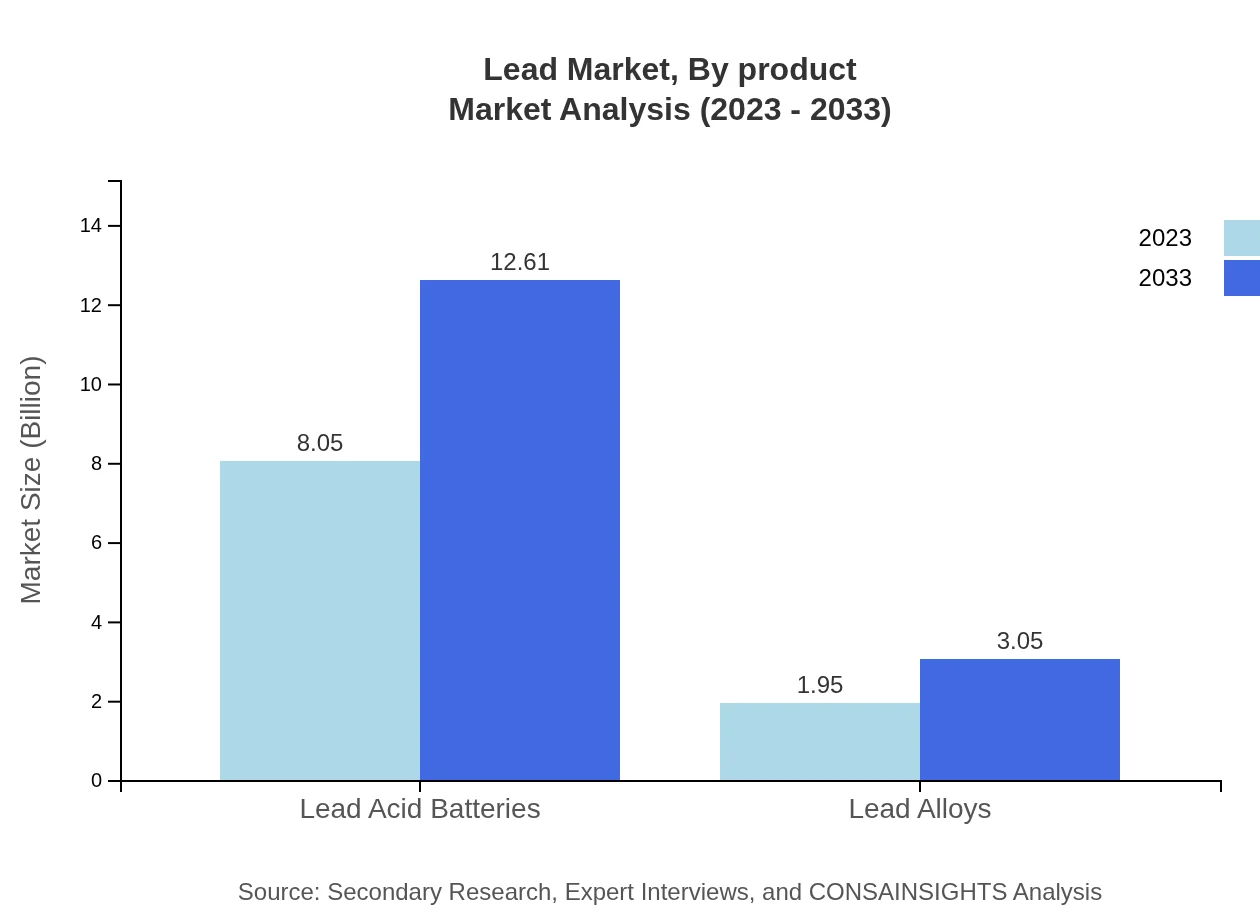
Lead Market Analysis By Product
The Lead market, segmented by product, shows lead-acid batteries leading with a market size of $8.05 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $12.61 billion by 2033. Lead alloys follow, starting at $1.95 billion and escalating to $3.05 billion over the same period. The lead-acid battery segment maintains an 80.54% share of the market, driven mainly by their reliability in energy storage.
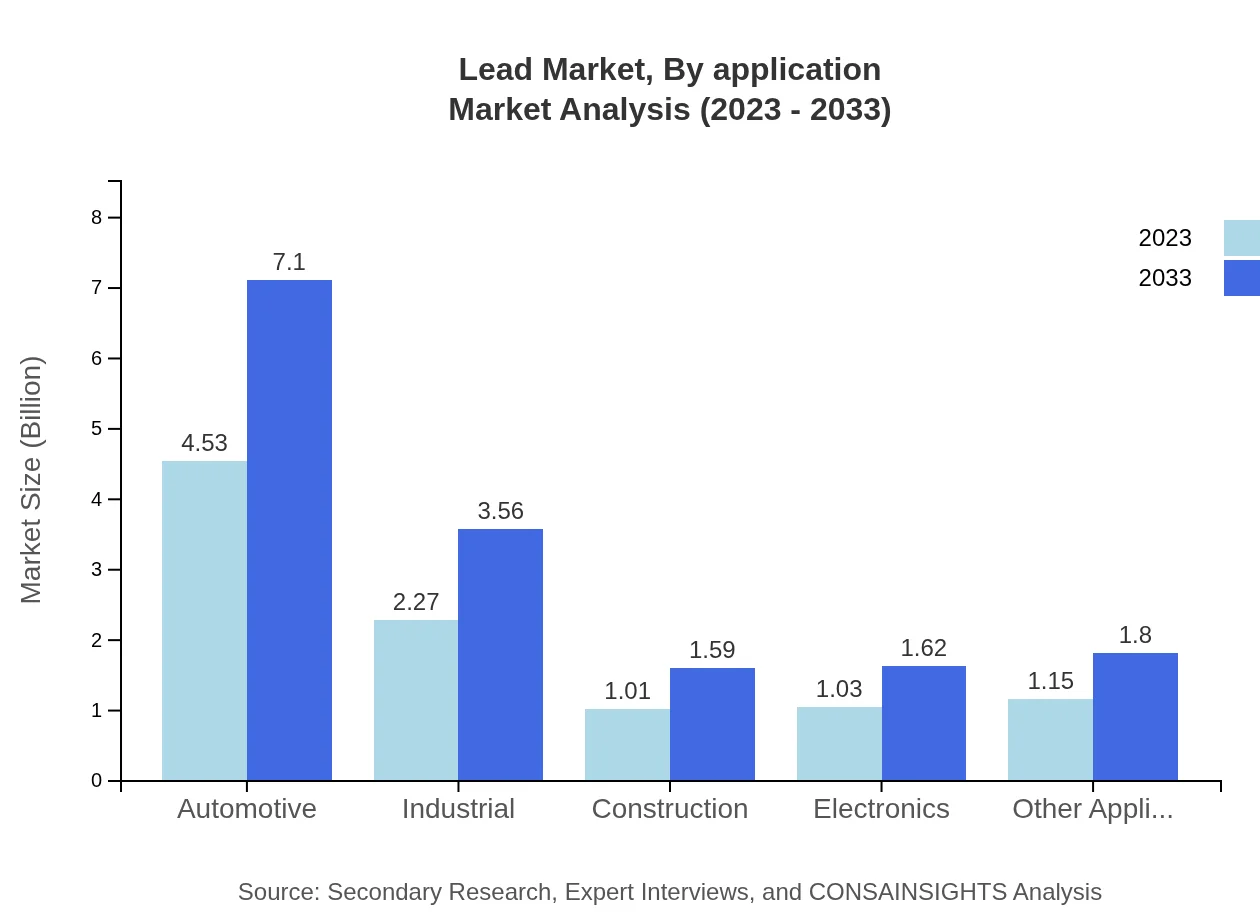
Lead Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the automotive industry holds a prominent share of 45.32% in 2023, with a projected growth from $4.53 billion to $7.10 billion by 2033. Power generation applications are also significant, with current market size at $2.27 billion growing to $3.56 billion. Telecommunications and construction applications, while smaller, also provide meaningful contributions.
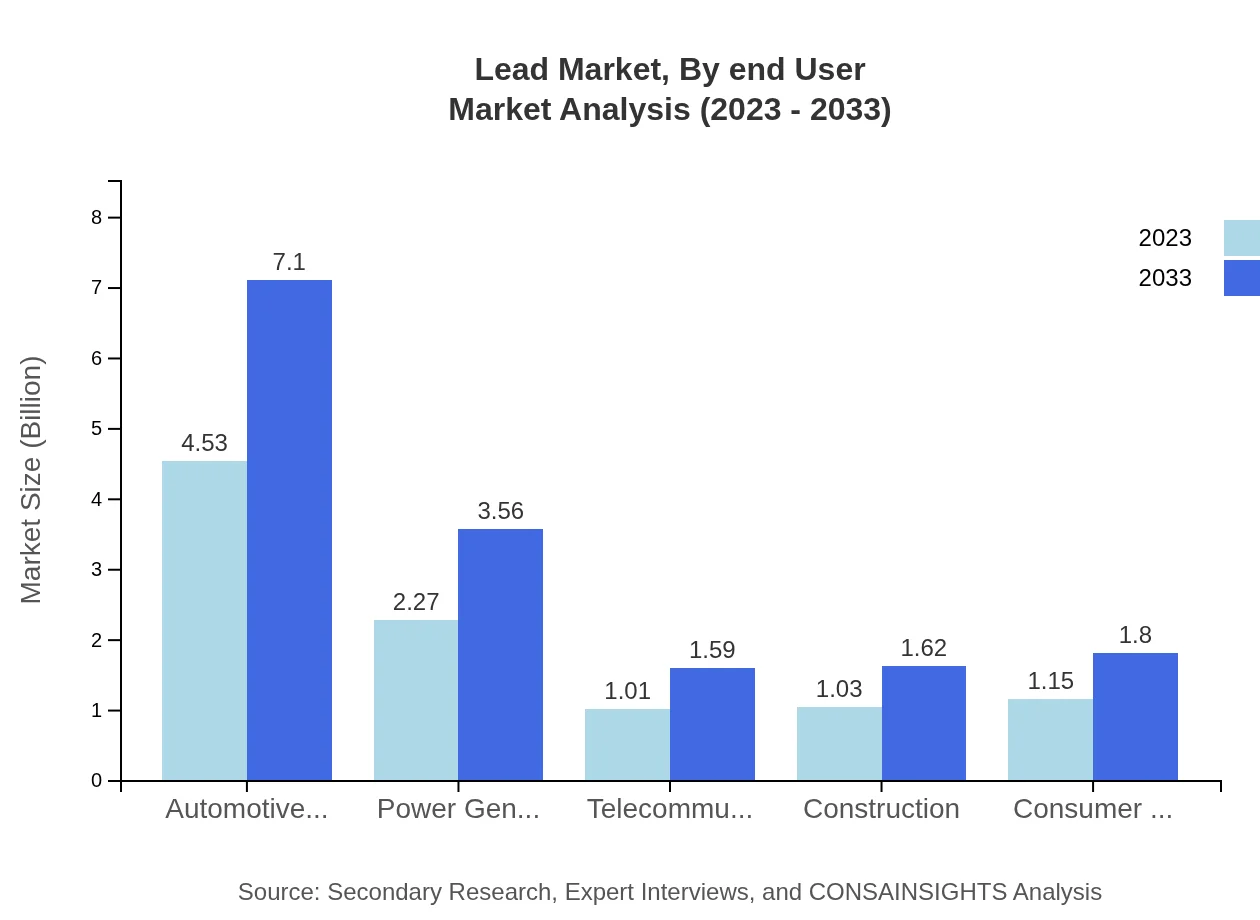
Lead Market Analysis By End User
The Lead market by end-user shows significant industrial utilization with a market size growing from $2.27 billion in 2023 to $3.56 billion by 2033, maintaining a 22.72% share. Automotive remains dominant, reflecting the critical dependency on lead-acid batteries for vehicle operations. Electronics and consumer segments also bolster the overall demand.
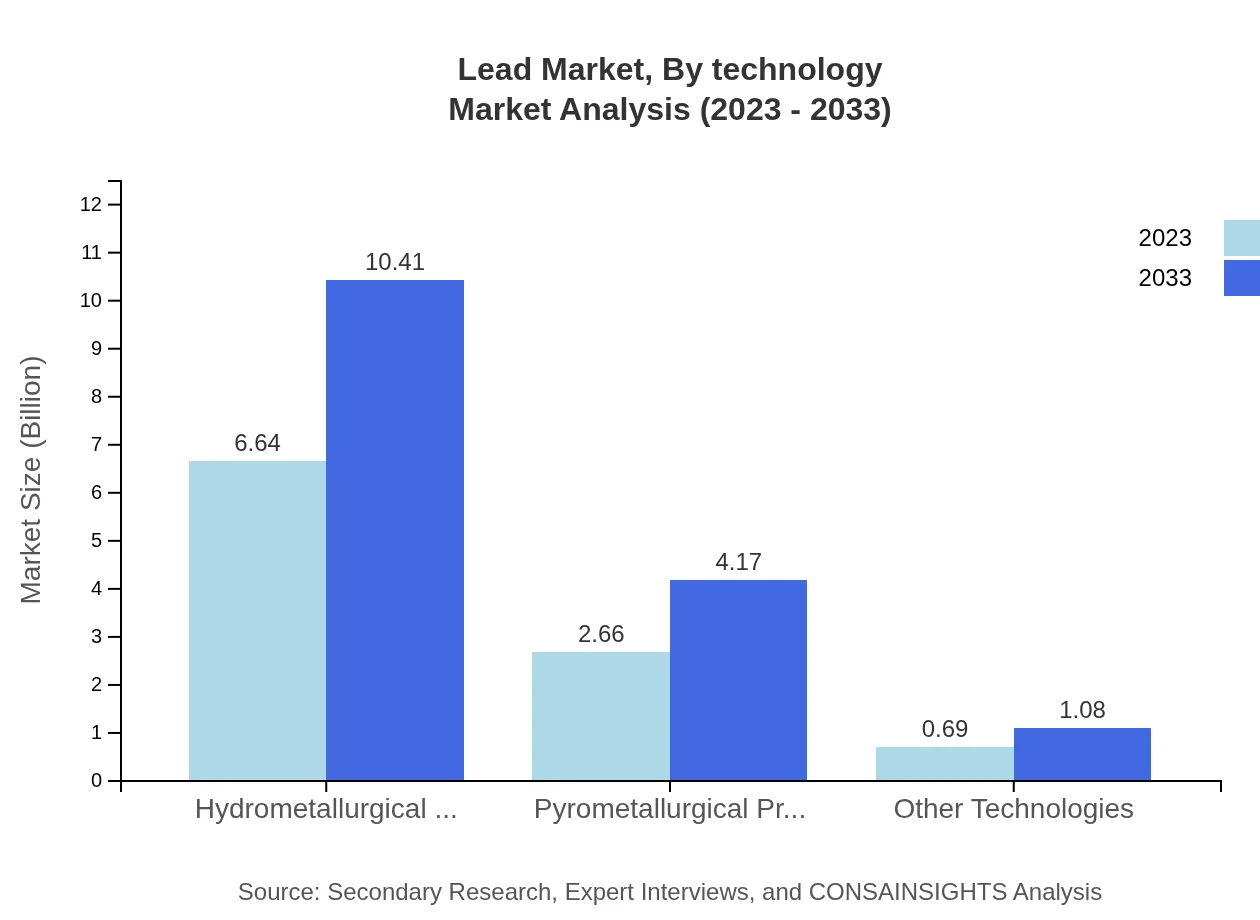
Lead Market Analysis By Technology
Technology influences the Lead market significantly. The hydrometallurgical process leads at $6.64 billion in 2023, growing to $10.41 billion by 2033, constituting 66.44% of the market. The pyrometallurgical process records a share of 26.64%, indicative of prevailing traditional extraction methods. Innovations in recycling technologies promise future market transformations.
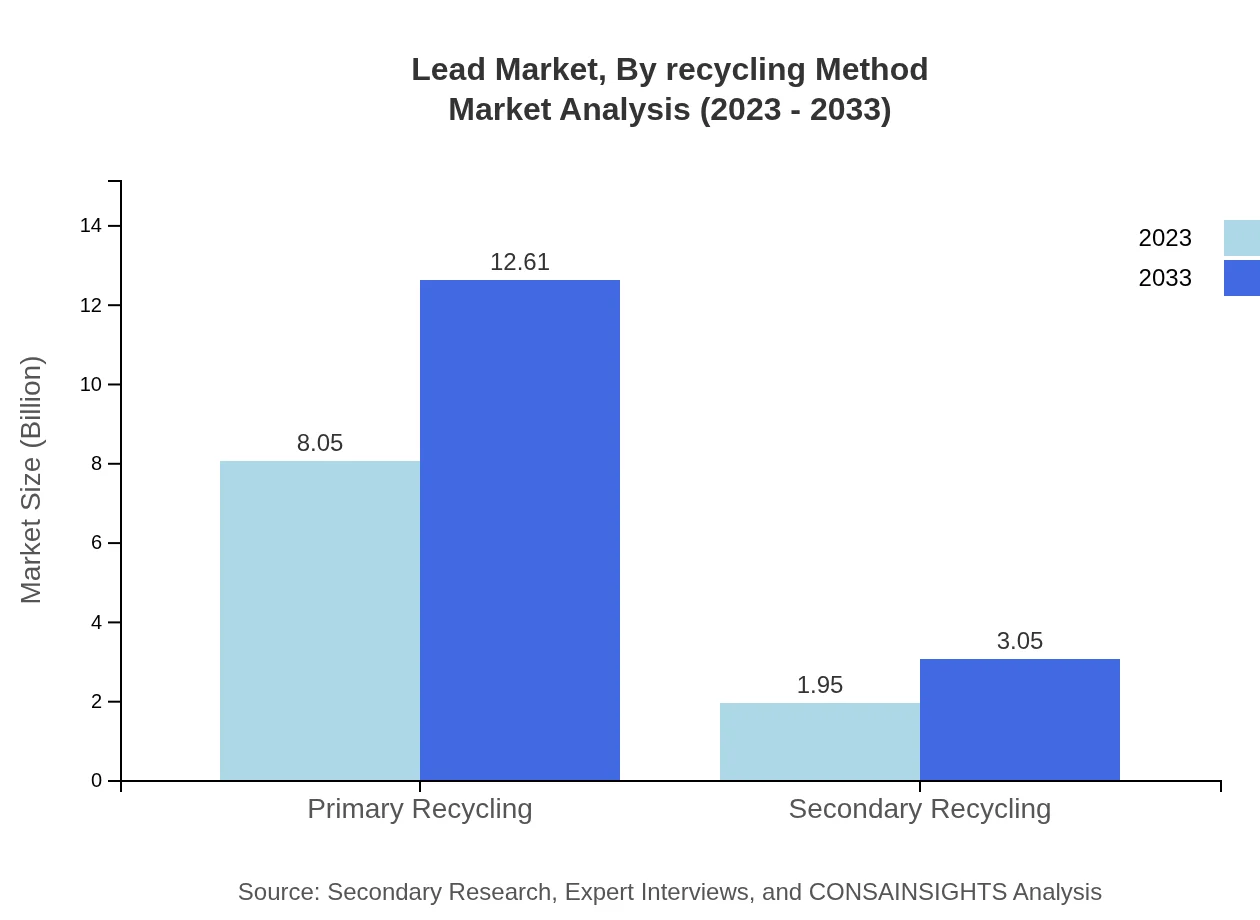
Lead Market Analysis By Recycling Method
In terms of recycling methods, primary recycling dominates with a staggering 80.54% market share, projected to grow from $8.05 billion to $12.61 billion by 2033. Secondary recycling, while smaller at 19.46%, presents an emerging opportunity for improved sustainability in Lead processing.
Lead Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Lead Industry
Exide Technologies:
Exide Technologies is a prominent player in the global lead-acid battery market, known for its innovative and sustainable battery solutions across various applications.Johnson Controls:
Johnson Controls is a leading manufacturer and supplier of automotive batteries and battery management solutions, focused on developing advanced energy storage technologies.Enersys:
Enersys operates as a global leader in stored energy solutions, providing batteries and associated equipment for industrial and commercial applications.GS Yuasa Corporation:
GS Yuasa Corporation specializes in a wide range of batteries, including lead-acid and lithium-ion technologies, contributing significantly to the automotive and industrial markets.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Lead?
The global lead market is projected to reach approximately $10 billion by 2033, with an annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5%. This growth reflects increasing applications in various sectors such as automotive and energy.
What are the key market players or companies in this Lead industry?
Key players in the lead market include prominent companies such as Doe Run Company, Nyrstar, and Teck Resources, which specialize in lead mining, smelting, and alloys.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Lead industry?
The lead industry is driven by rising demand in automotive batteries, construction, and technological advancements in recycling processes, alongside the growing need for sustainable energy solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Lead market?
The fastest-growing region in the lead market is projected to be North America, with the market expected to increase from $3.76 billion in 2023 to $5.89 billion by 2033, reflecting significant growth.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Lead industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific client needs in the lead industry, ensuring insights are relevant to individual market strategies and objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this Lead market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive market analysis reports, executive summaries, segment breakdowns, and actionable insights tailored to the lead industry's dynamics and trends.
What are the market trends of Lead?
Current market trends in the lead industry include an increasing focus on recycling lead, technological advancements in battery production, and the shift towards sustainable energy solutions in both automotive and industrial applications.