Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: long-term-evolution-lte
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Long Term Evolution (LTE) market, covering market sizes, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include segment breakdowns, regional analyses, and key drivers shaping the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
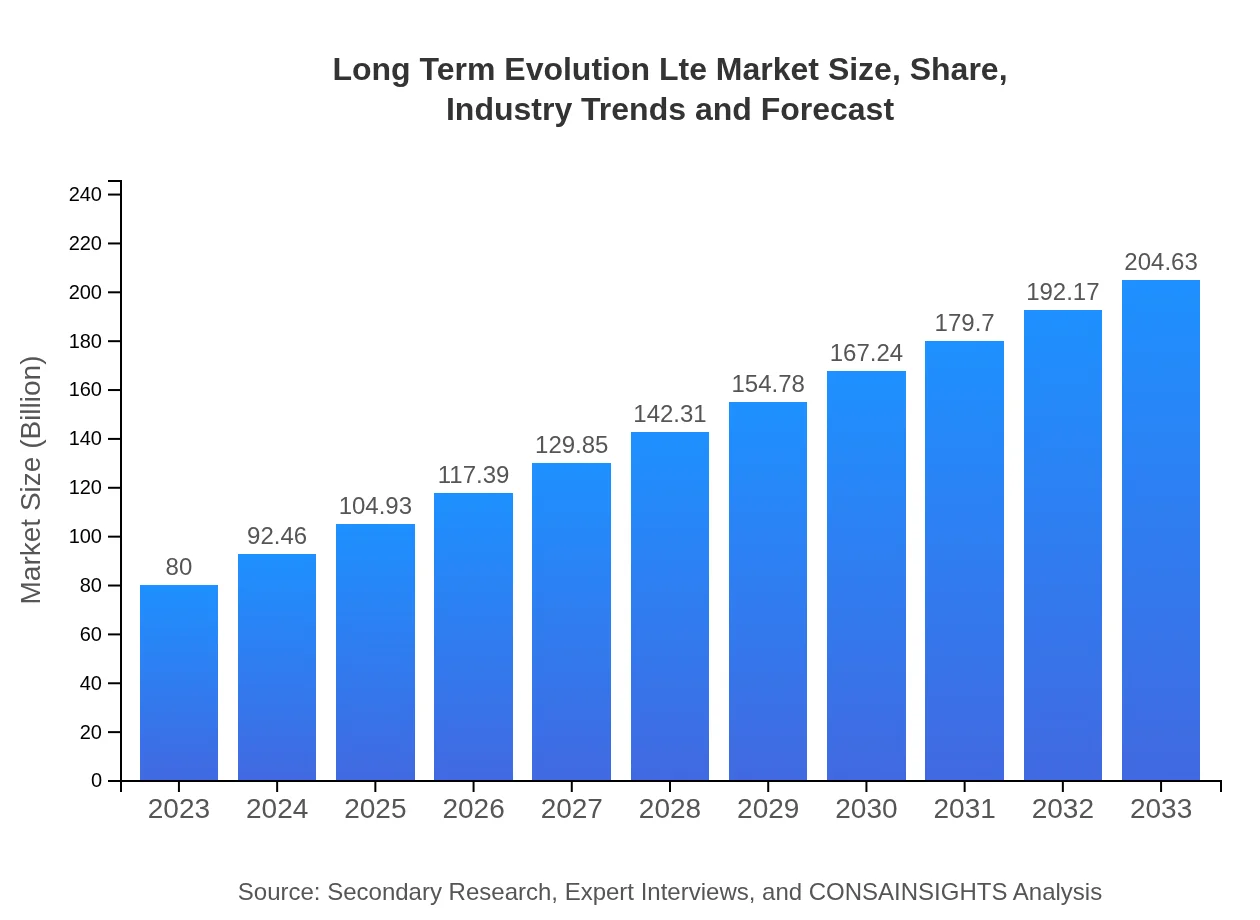
| 2023 Market Size | $80.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $204.63 Billion |
| Top Companies | Qualcomm , Ericsson , Nokia , Huawei |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Overview
Customize Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Long Term Evolution Lte market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Long Term Evolution Lte's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Long Term Evolution Lte
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Long Term Evolution Lte market in 2023 and 2033?
Long Term Evolution Lte Industry Analysis
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report:
In Europe, the LTE market is expected to grow from $26.45 billion in 2023 to $67.65 billion by 2033. Supported by favorable regulations and high consumer demand for mobile internet services, European telecom companies are continuously upgrading their LTE infrastructure, ensuring seamless connectivity.Asia Pacific Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the LTE market is expected to grow from $14.36 billion in 2023 to $36.73 billion in 2033. This growth is largely driven by the increasing smartphone penetration, rising demand for mobile data, and significant investments in network infrastructure by regional telecom operators. Additionally, initiatives from governments incentivizing technology adoption contribute to market growth.North America Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report:
North America is anticipated to see growth from $29.29 billion in 2023 to $74.91 billion in 2033. The region boasts high LTE penetration rates and robust investments from mobile operators in enhancing existing networks and exploring advanced solutions. The migration towards 5G technology also bolsters LTE usage as operators optimize current services.South America Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report:
The South American LTE market is projected to increase from $6.06 billion in 2023 to $15.49 billion by 2033. Growth drivers include expanding mobile network coverage, a growing middle class, and increasing internet accessibility. However, challenges related to regulatory frameworks and regional economic fluctuations may impact overall growth.Middle East & Africa Long Term Evolution Lte Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa LTE market is projected to grow from $3.85 billion in 2023 to $9.84 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by increasing mobile subscriptions and expansion of mobile networks in rural areas. However, economic disparities in the region present challenges that may hinder growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
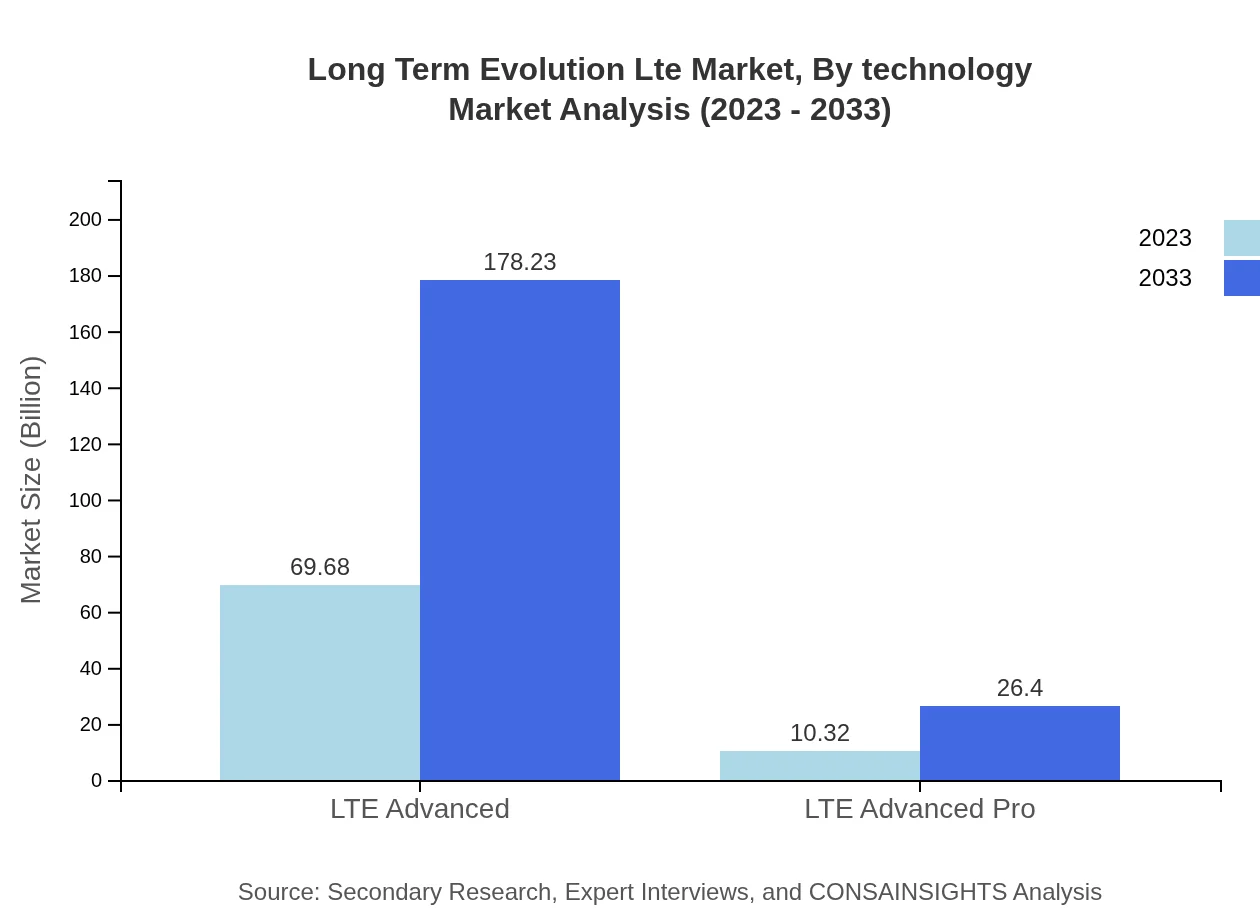
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Analysis By Technology
The LTE market is segmented into LTE Advanced, LTE Advanced Pro, and traditional LTE services. LTE Advanced is projected to dominate the market with sizes reaching $69.68 billion in 2023, growing to $178.23 billion in 2033, capturing 87.1% market share throughout the period. Meanwhile, LTE Advanced Pro, while smaller, showcases a strong growth potential from $10.32 billion to $26.40 billion, demonstrating the increasing demand for enhanced performance technologies.
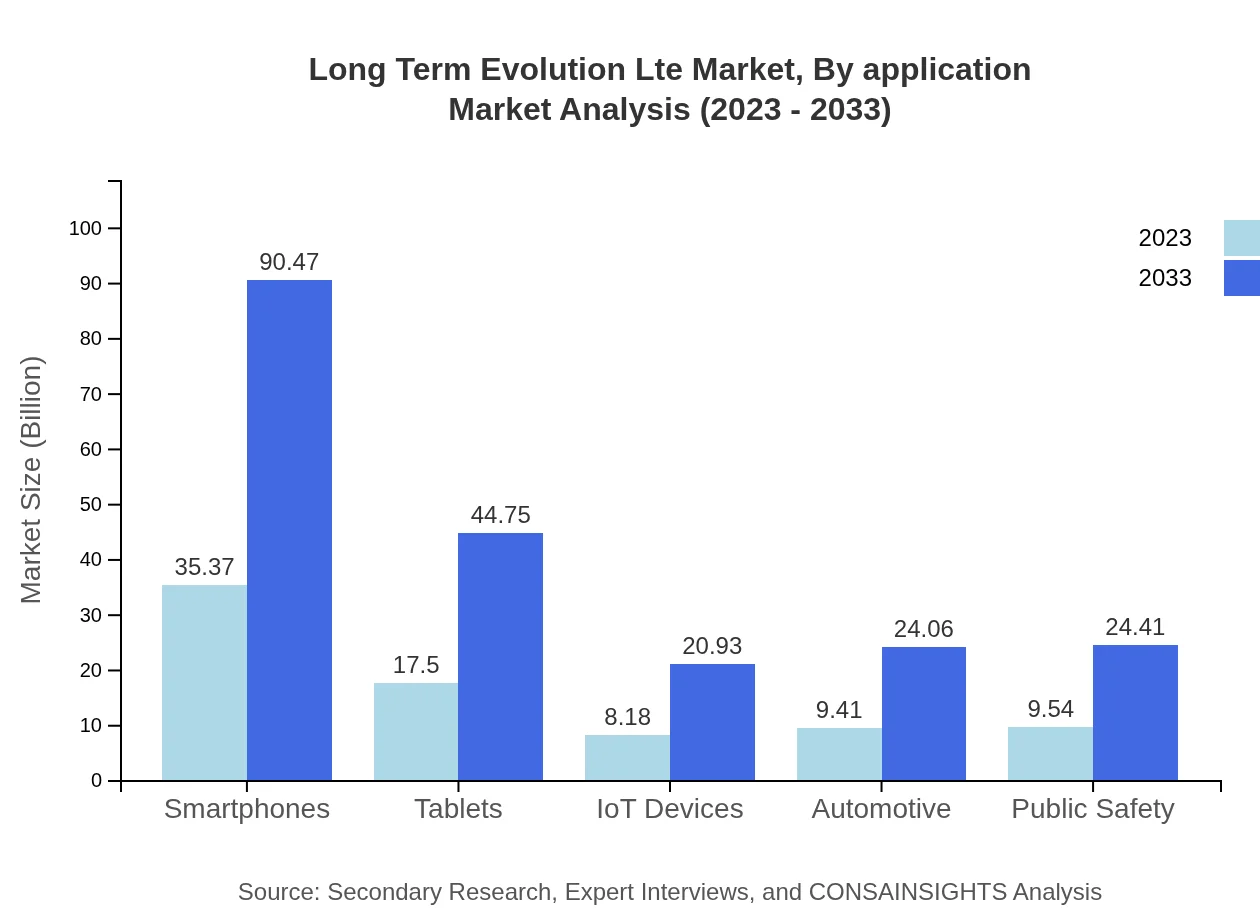
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Analysis By Application
Applications of LTE technology span various sectors including healthcare, automotive, public safety, and IoT. In 2023, the healthcare application size stands at $35.37 billion, anticipated to reach $90.47 billion by 2033, reflecting the critical need for reliable connectivity in medical services. The automotive sector is also witnessing significant growth due to the emergence of connected vehicles, forecasted to transition from $9.41 billion in 2023 to $24.06 billion by 2033.
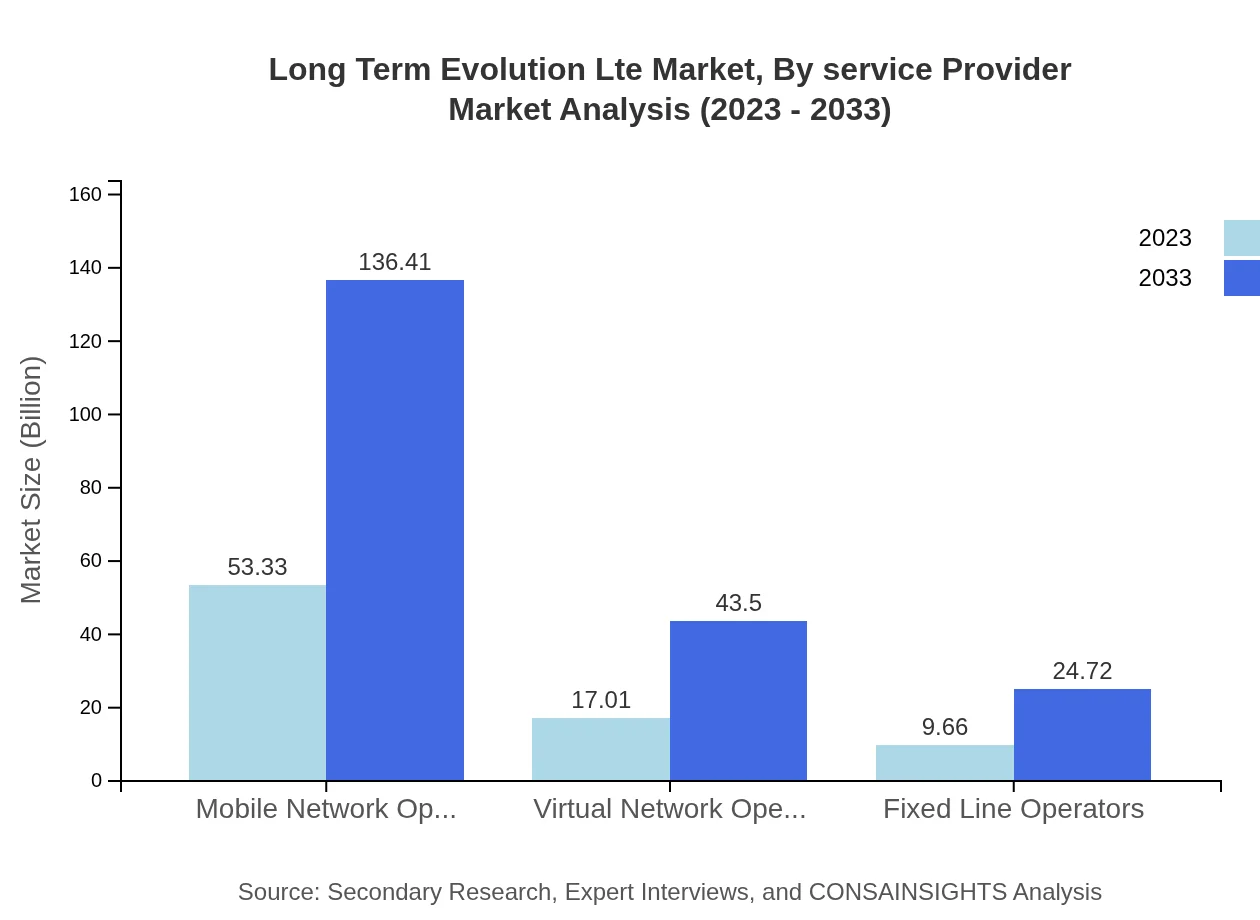
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Analysis By Service Provider
The LTE market is served by various types of providers, including mobile network operators, virtual network operators, and fixed-line operators. Mobile network operators dominate the segment, contributing $53.33 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $136.41 billion by 2033, holding steady at a market share of 66.66%. Virtual network operators also have a growing presence, expanding their offerings to meet diverse consumer needs.
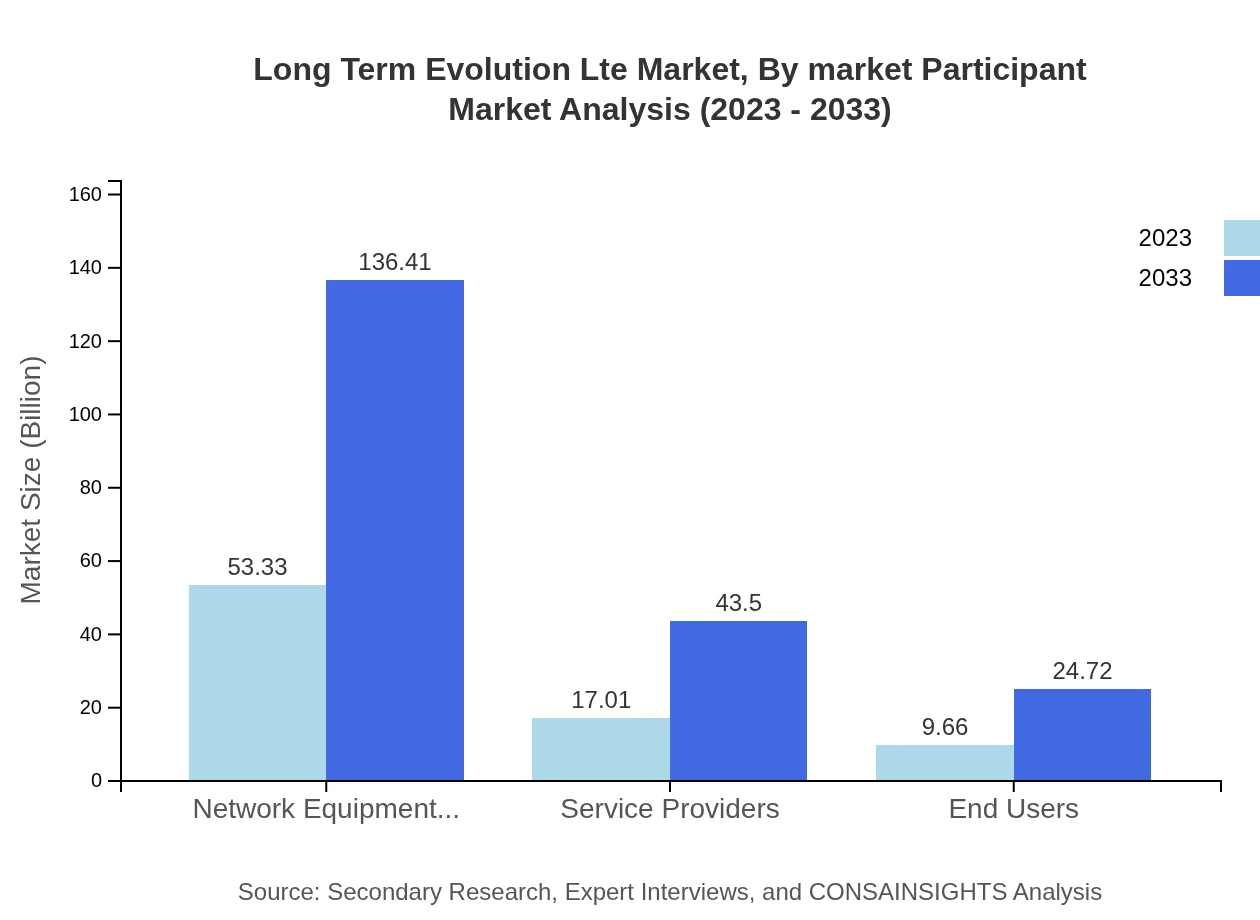
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Analysis By Market Participant
Market participation encompasses network equipment vendors, service providers, and end-users across industries. Network equipment vendors hold a conclusive share, growing from $53.33 billion in 2023 to $136.41 billion in 2033. The increasing demand for infrastructure and technological advancements is catalyzing growth across this participant segment.
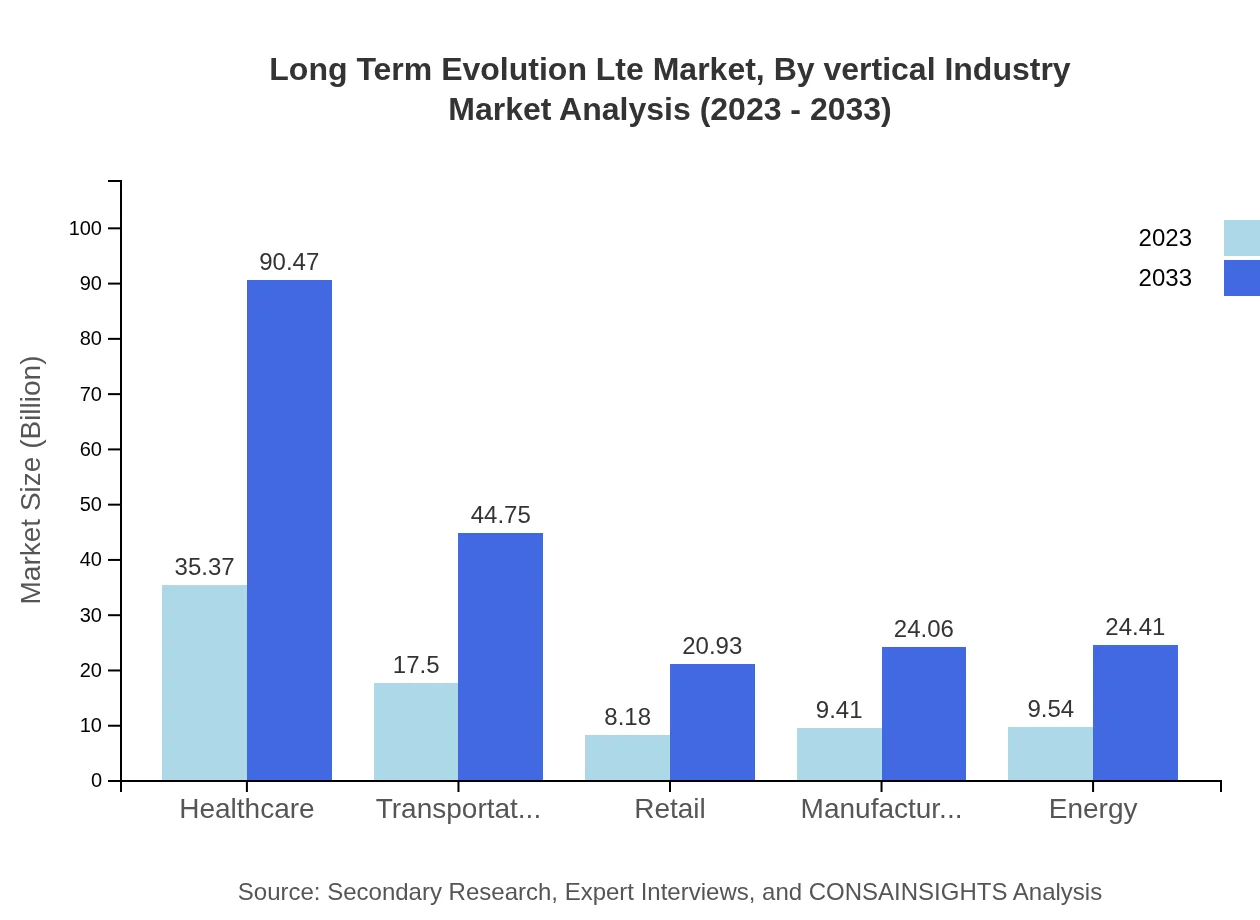
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Analysis By Vertical Industry
The vertical industry segment includes transportation, energy, retail, and manufacturing. The transportation sector's LTE utilization is growing as logistics companies leverage real-time data transmission, expected to jump from $17.50 billion in 2023 to $44.75 billion by 2033. The retail sector, too, is increasing LTE deployments to enhance consumer experience through better connectivity.
Long Term Evolution Lte Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Long Term Evolution Lte Industry
Qualcomm :
A leading technology company that specializes in wireless technology development, Qualcomm has pioneered critical advancements in LTE technology, providing key infrastructure for mobile connectivity.Ericsson :
Ericsson is a global leader in telecommunications equipment and services. Their strong focus on research and development has facilitated notable innovations in LTE technology.Nokia :
Nokia is recognized as a prominent player in the LTE market, providing comprehensive telecommunications solutions and services that enhance network efficiency and performance.Huawei :
Huawei is a global technology company that has significantly impacted the LTE landscape through its cutting-edge infrastructure and tech solutions, particularly in emerging markets.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Long Term Evolution (LTE)?
The Long Term Evolution (LTE) market size is projected to reach approximately $80 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.5%. This growth reflects the rising demand for high-speed data communication and mobile connectivity.
What are the key market players or companies in the LTE industry?
Key players in the LTE industry include major telecommunications companies such as Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile, alongside network equipment vendors like Ericsson, Nokia, and Huawei. These organizations are pivotal in driving LTE technology advancements.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the LTE industry?
The growth of the LTE industry is primarily driven by increasing mobile data usage, the rise of streaming services, advancements in IoT applications, and a growing demand for faster and more reliable mobile communication networks.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the LTE market?
North America emerges as the fastest-growing region for the LTE market, expected to grow from $29.29 billion in 2023 to $74.91 billion by 2033, driven by consumer technology adoption and extensive network infrastructure.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the LTE industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific research needs within the LTE industry. Clients can access detailed market insights and forecasts that align with their business objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this LTE market research project?
Deliverables from the LTE market research project include comprehensive reports on market trends, segment analysis, competitive landscape insights, regional data breakdowns, and future growth projections.
What are the market trends of Long Term Evolution (LTE)?
Current market trends in LTE include a shift towards LTE Advanced technologies, increasing integration with IoT devices, a proliferation of smartphones, and enhanced network capabilities to support higher data rates and reliability.