Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: low-gwp-refrigerants
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Low GWP Refrigerants industry, detailing market dynamics, segment analysis, regional insights, and future forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It aims to equip stakeholders with actionable insights and data for informed decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
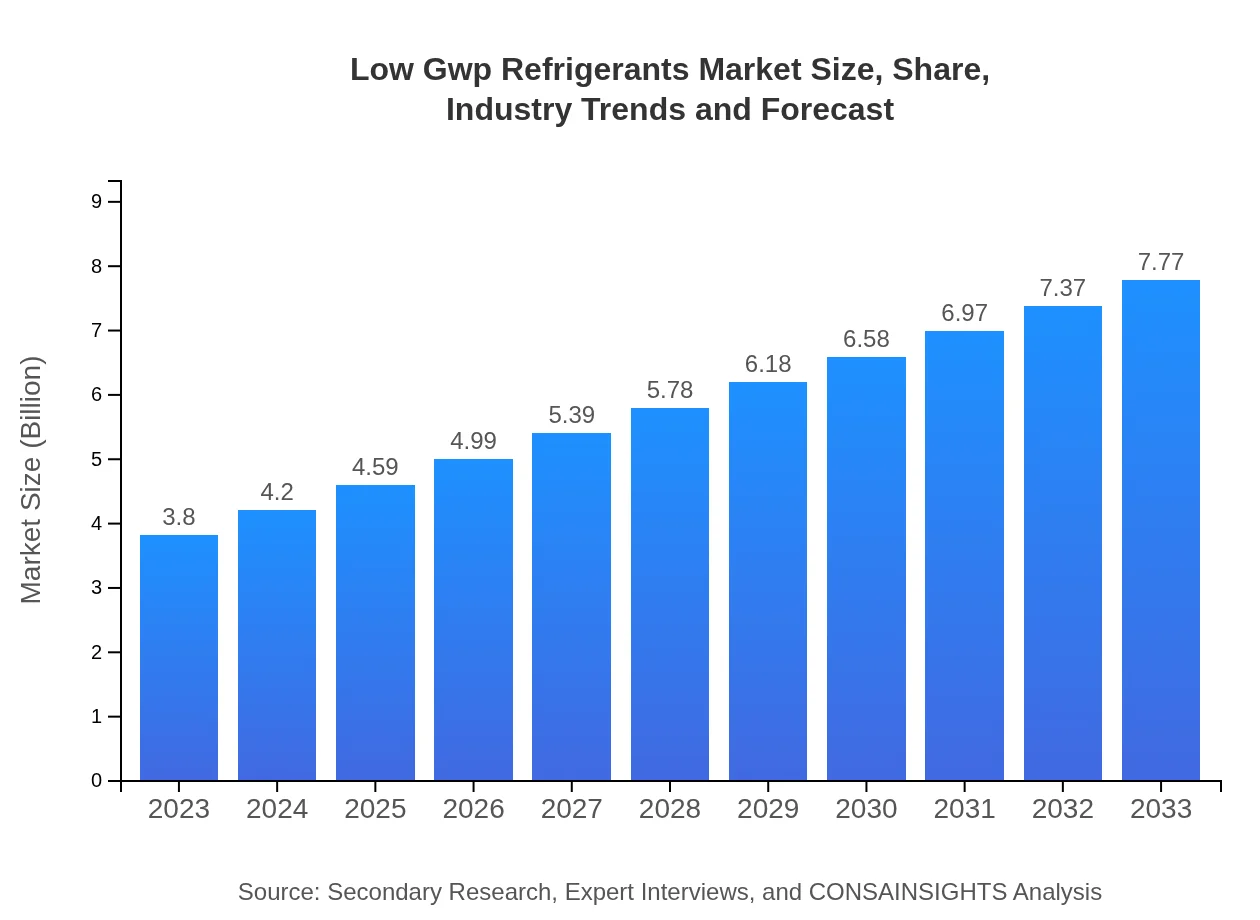
| 2023 Market Size | $3.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $7.77 Billion |
| Top Companies | Honeywell , Chemours, Daikin, Carrier |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Overview
Customize Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Low Gwp Refrigerants market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Low Gwp Refrigerants's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Low Gwp Refrigerants
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Low Gwp Refrigerants market in 2033?
Low Gwp Refrigerants Industry Analysis
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report:
Europe currently leads in the Low GWP Refrigerants market estimated at $1.37 billion in 2023, expected to reach $2.80 billion by 2033. Initiatives such as the European Union's F-Gas Regulation are pivotal in encouraging the adoption of low GWP refrigerants.Asia Pacific Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Low GWP Refrigerants market is expected to grow from $0.65 billion in 2023 to $1.33 billion by 2033, reflecting increasing industrialization and a push for compliance with environmental standards in countries like China and India.North America Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report:
North America is anticipated to see its market size grow from $1.24 billion in 2023 to $2.54 billion by 2033. The region's stringent regulations regarding refrigerants are driving the shift towards low GWP alternatives, especially in commercial and transport refrigeration.South America Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report:
The South America market is projected to expand from $0.36 billion in 2023 to $0.73 billion by 2033. This growth will be supported by rising investment in sustainable technologies and the need for efficient refrigeration systems in the food sector.Middle East & Africa Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is expected to grow from $0.18 billion in 2023 to $0.38 billion in 2033, driven by growing urbanization and the expanding refrigeration market across various sectors, notwithstanding infrastructural challenges.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Analysis By Type
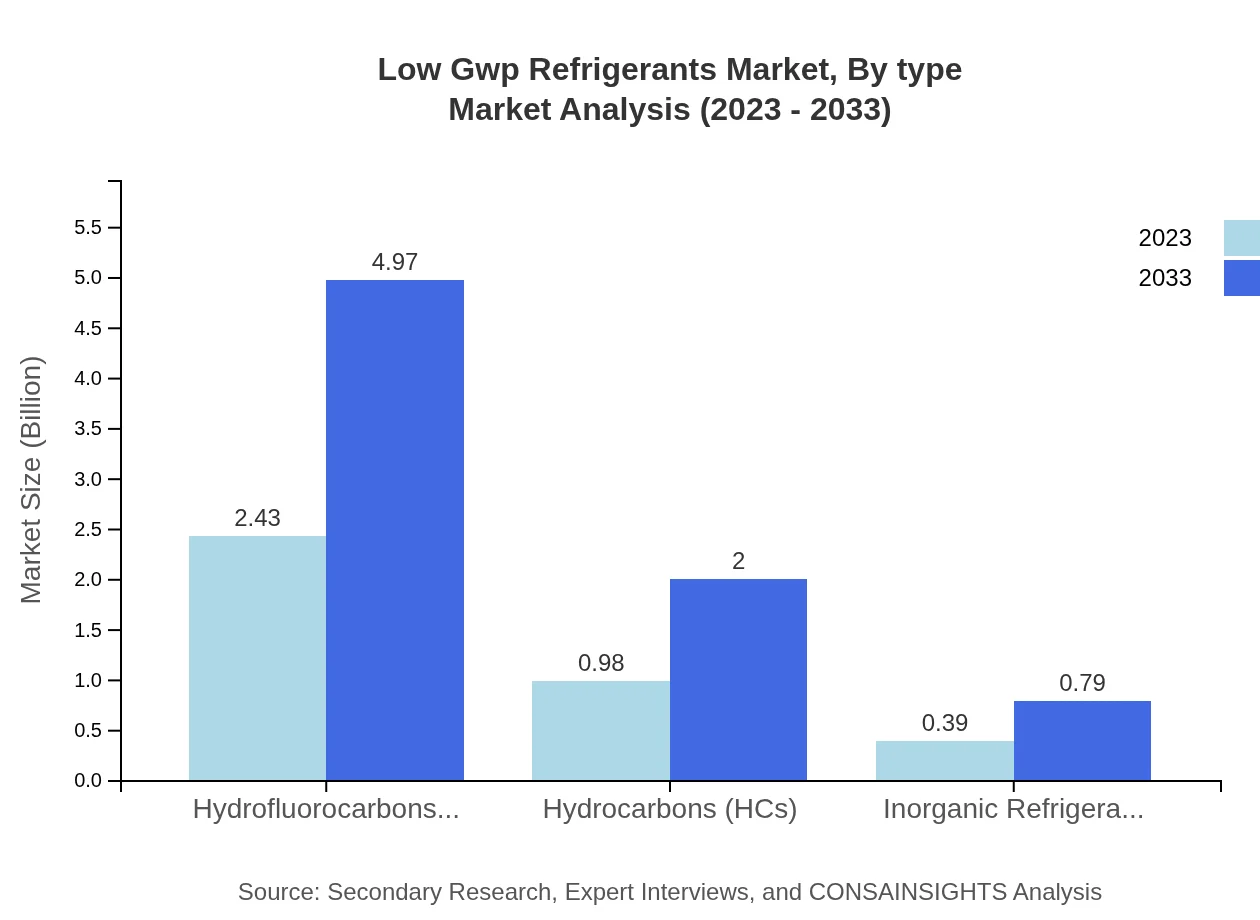
The Low GWP Refrigerants market, by type, is dominated by Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which account for a market size of $2.43 billion in 2023, with projections reaching $4.97 billion by 2033. Hydrocarbons (HCs) follow, with sizes of $0.98 billion in 2023 and anticipated growth to $2.00 billion by 2033. Inorganic Refrigerants, although smaller with market sizes of $0.39 billion in 2023 and expected $0.79 billion by 2033, present a growing opportunity as they are often seen as greener alternatives.
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Analysis By Application
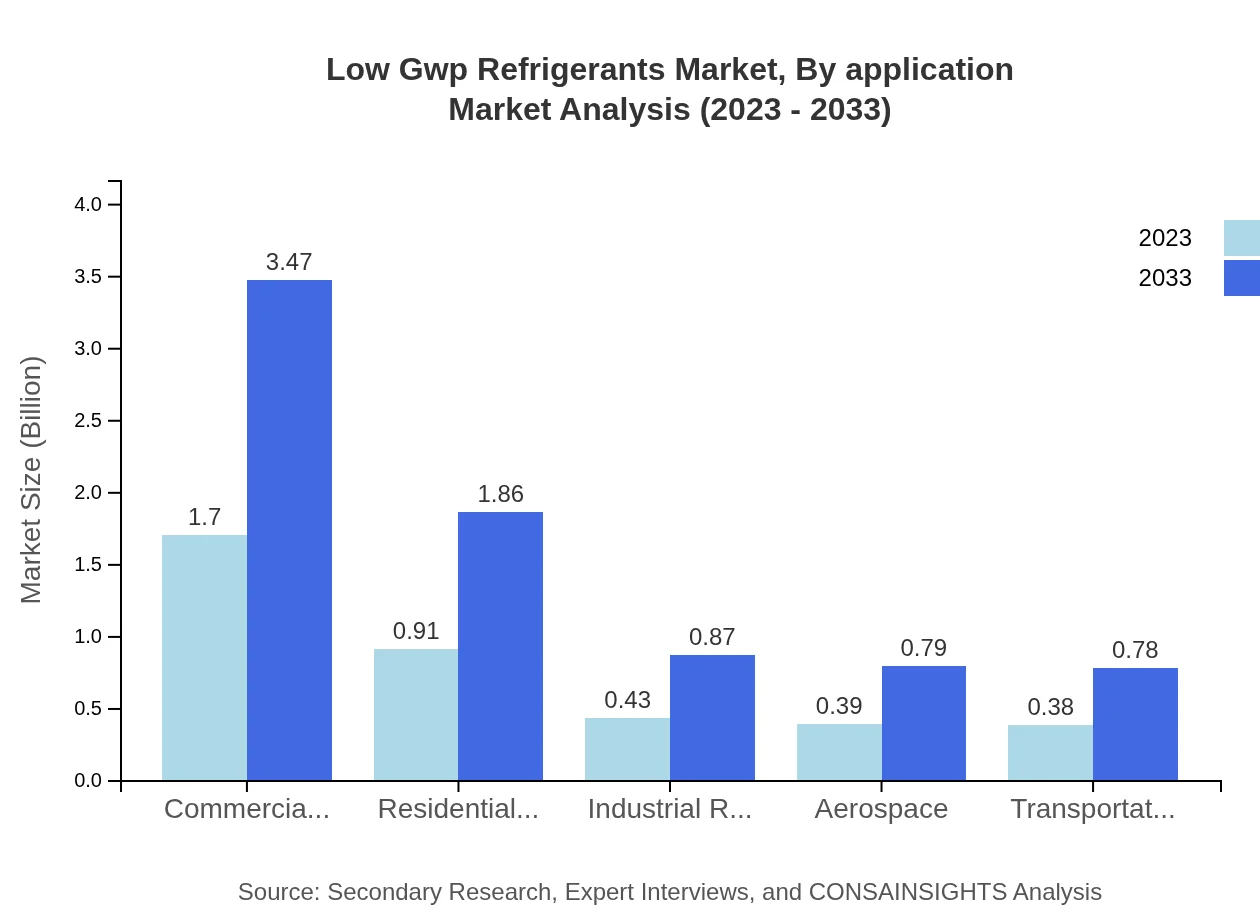
The application-based segmentation reveals that the Food & Beverage sector holds a significant share with a market size of $2.11 billion in 2023, expecting growth to $4.32 billion by 2033. Other leading applications include healthcare, commercial refrigeration, and residential refrigeration, indicating strong ongoing demand driven by the need for efficient temperature-controlled systems.
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Analysis By End User
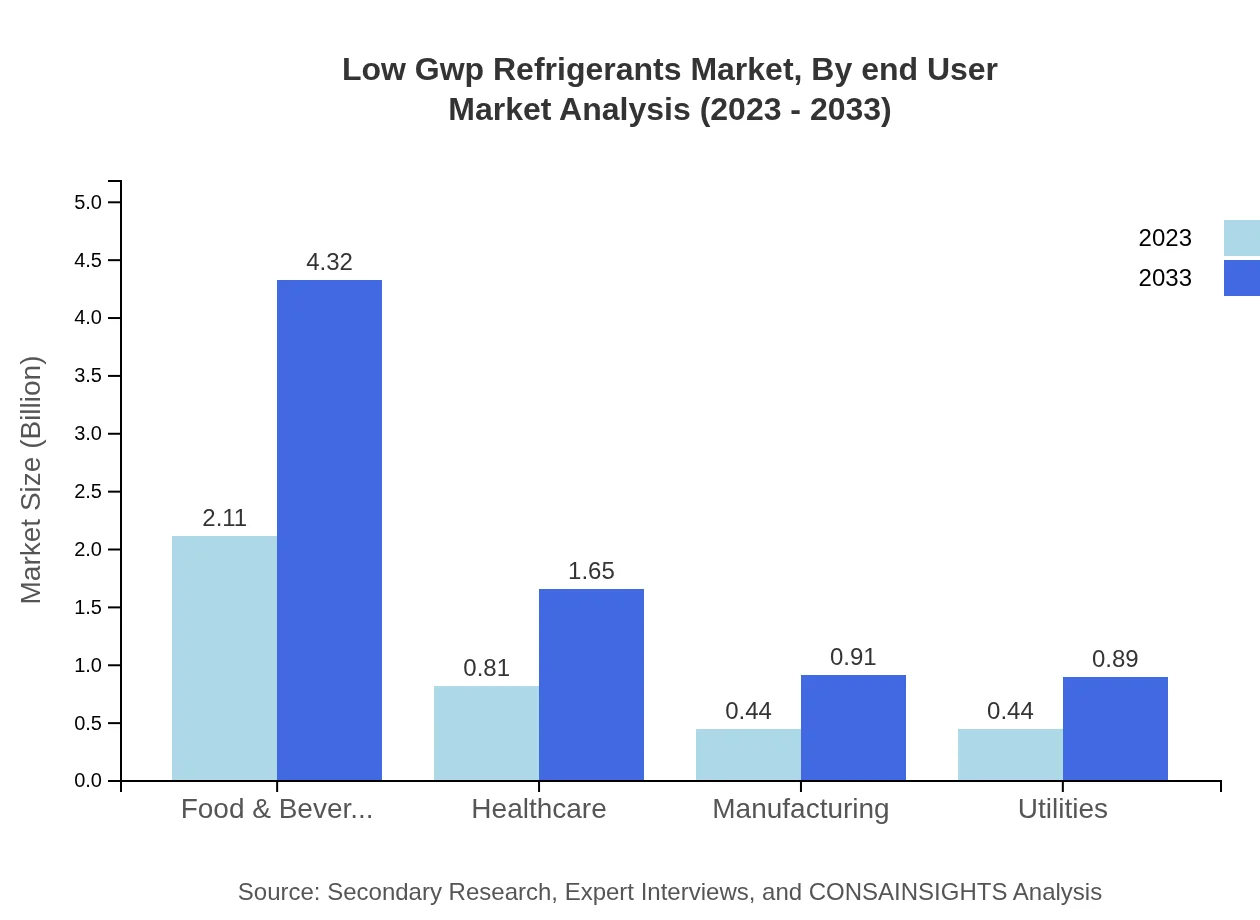
The end-user analysis underscores the importance of the commercial refrigeration industry, which accounted for $1.70 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $3.47 billion in 2033. Other significant end-users include manufacturing, healthcare, and utilities, each contributing to the overall shift towards environmentally friendly refrigerant options.
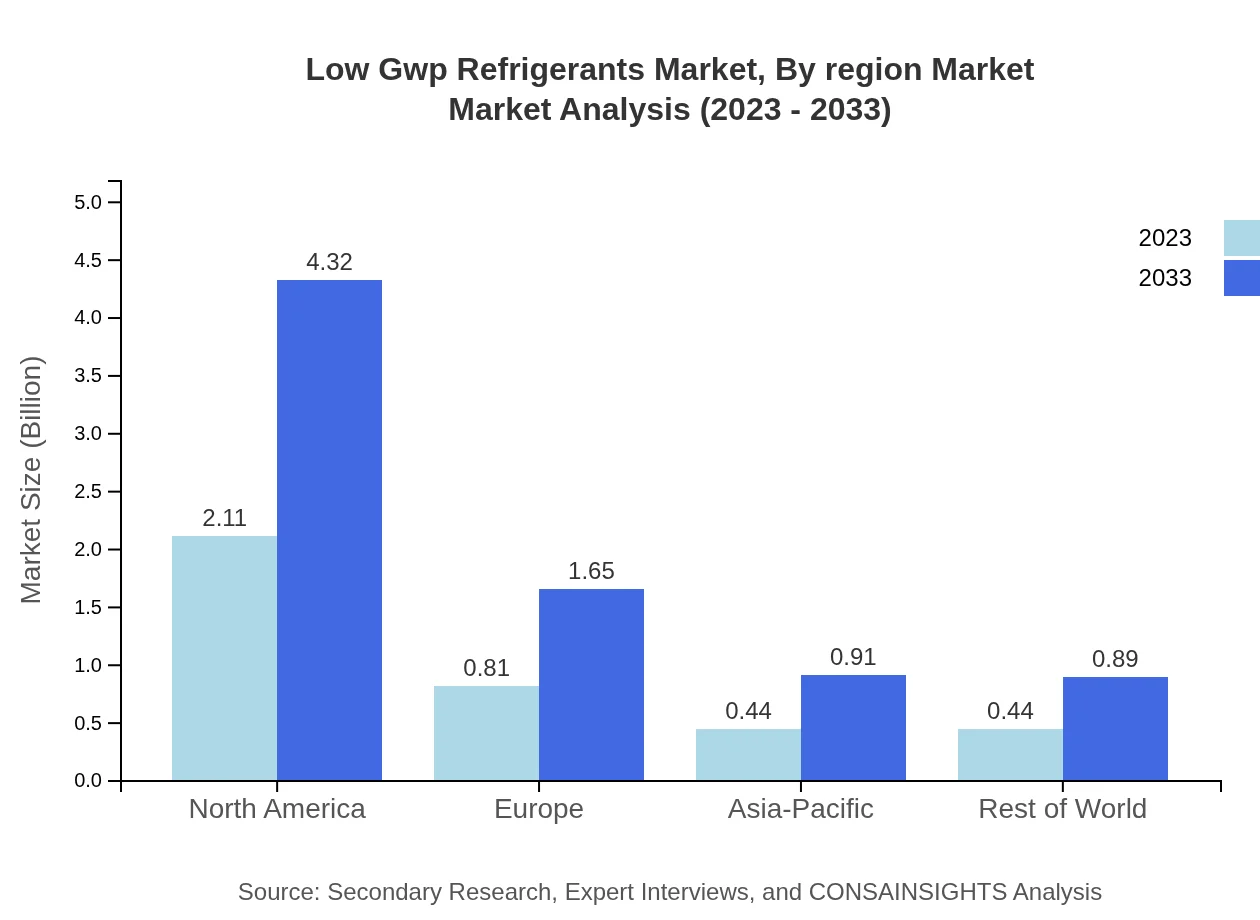
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Analysis By Region Market
Regionally, North America leads with a size of $2.11 billion in 2023, driven by regulatory pressures and technological advancements, while Europe follows closely with $0.81 billion in the same year. The Asia-Pacific and South America markets, although smaller, are witnessing rapid growth, reflecting increased compliance and investment in sustainability.
Low Gwp Refrigerants Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Low Gwp Refrigerants Industry
Honeywell :
Honeywell is a key player in developing sustainable refrigerant solutions, focusing on low GWP technologies to meet regulatory standards and customer needs.Chemours:
Chemours is recognized for its innovative refrigerant offerings, including hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), contributing significantly to the transition to low GWP alternatives.Daikin:
Daikin leads in HVAC and refrigeration technologies, continually advancing its product portfolio to incorporate environmentally friendly refrigerants.Carrier:
Carrier is notable for its range of refrigerants and systems optimized for energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of low-GWP refrigerants?
The global low-GWP refrigerants market is currently valued at approximately $3.8 billion with a projected CAGR of 7.2% leading to substantial growth over the next decade. This indicates a strong demand shift toward sustainable refrigerant options.
What are the key market players or companies in the low-GWP refrigerants industry?
Key players in the low-GWP refrigerants market include major manufacturers such as Honeywell International Inc., Chemours Company, and Daikin Industries, which are renowned for their innovation in developing eco-friendly refrigerants and solutions.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the low-GWP refrigerants industry?
The growth of the low-GWP refrigerants market is driven by stringent environmental regulations, increasing awareness of climate change, and the urgent need to transition from high-global warming potential gases to safer alternatives.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the low-GWP refrigerants?
Europe is currently the fastest-growing region in the low-GWP refrigerants market, projected to expand from $1.37 billion in 2023 to $2.80 billion by 2033, reflecting a robust CAGR as sustainability efforts intensify.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the low-GWP refrigerants industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to client needs in the low-GWP refrigerants industry, allowing businesses to gain specific insights and strategize effectively based on unique market requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this low-GWP refrigerants market research project?
Expect deliverables including in-depth market analysis reports, growth forecasts, competitive landscape insights, segmentation analysis, and regional market evaluations, providing a comprehensive overview of the low-GWP refrigerants market.
What are the market trends of low-GWP refrigerants?
Current trends in the low-GWP refrigerants market include increasing adoption of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which hold a market share of 63.99%, and notable growth in hydrocarbons, indicating a shift towards greener technologies in refrigeration.