Lte Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: lte
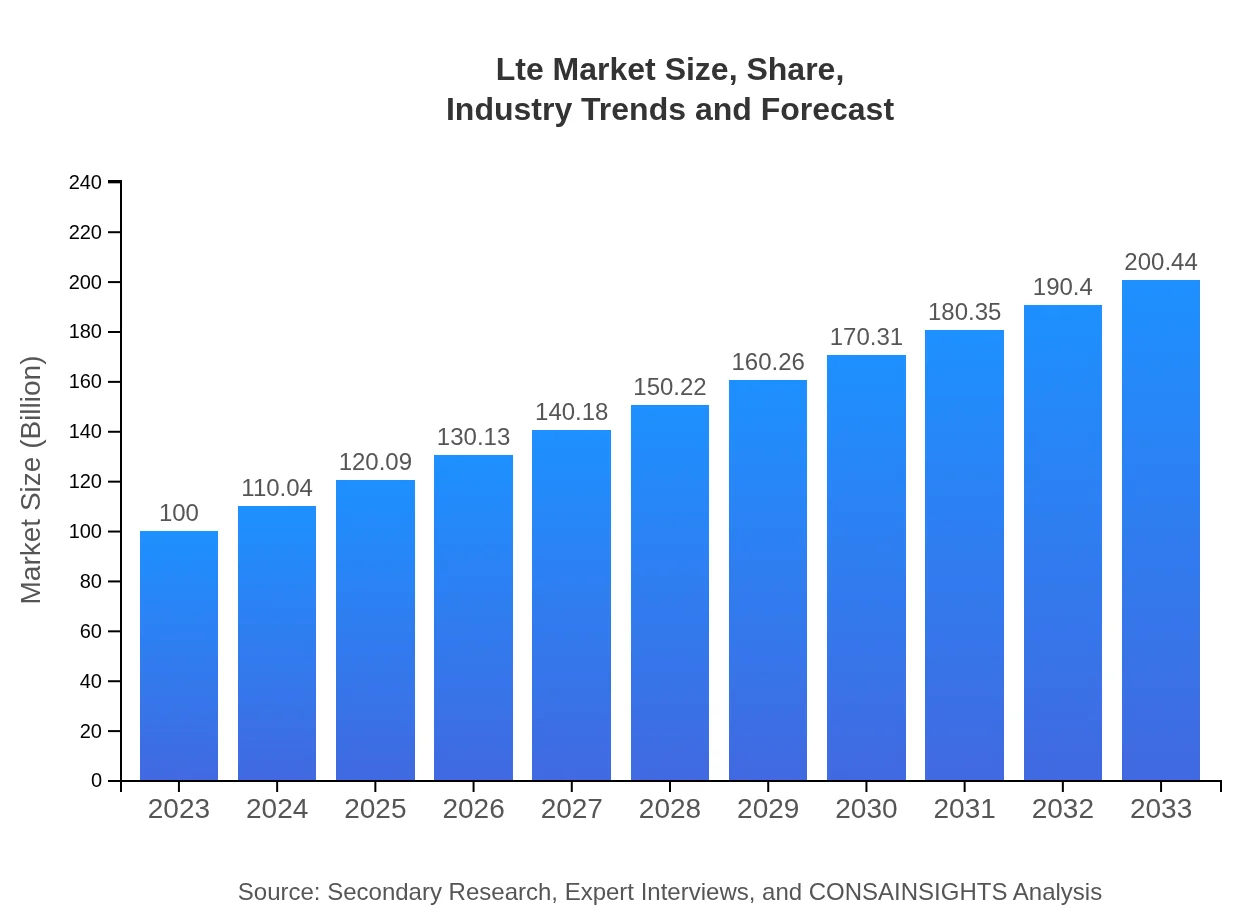
Lte Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an extensive analysis of the LTE market, covering aspects such as market size, growth trends, segmentation, and competitive landscape from 2023 to 2033. It also forecasts future developments and identifies key opportunities in the market.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $200.44 Billion |
| Top Companies | Ericsson , Nokia , Qualcomm , Huawei |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
LTE Market Overview
Customize Lte Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Lte market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Lte's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Lte
What is the Market Size & CAGR of LTE market in 2023?
LTE Industry Analysis
LTE Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
LTE Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Lte Market Report:
The European LTE market is anticipated to grow from $29 billion in 2023 to $58.13 billion by 2033. The regulatory framework and significant investments in advanced mobile systems across EU countries facilitate substantial LTE adoption.Asia Pacific Lte Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is expected to grow from $19.34 billion in 2023 to $38.77 billion by 2033. Increased smartphone penetration and significant investments in telecom infrastructure are the driving forces. Countries like India, China, and Japan are leading the adoption of LTE technologies, as service providers focus on expanding coverage in urban and rural areas.North America Lte Market Report:
North America, valued at $35.81 billion in 2023, is expected to rise to $71.78 billion by 2033. The U.S. leads in LTE adoption with robust infrastructure and high consumer demand for data services. The market is largely driven by competition among major players offering enhanced LTE services.South America Lte Market Report:
The LTE market in South America is projected to double from $5.99 billion in 2023 to $12.01 billion by 2033. Growing demand for mobile internet and government initiatives to improve connectivity are contributing to the market's positive trajectory. Major markets include Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Lte Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are witnessing a market expansion from $9.86 billion in 2023 to $19.76 billion by 2033. Mobile subscriber growth, especially in Africa, is fuelling this increase, as operators prioritize expanding wireless access in underserved regions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
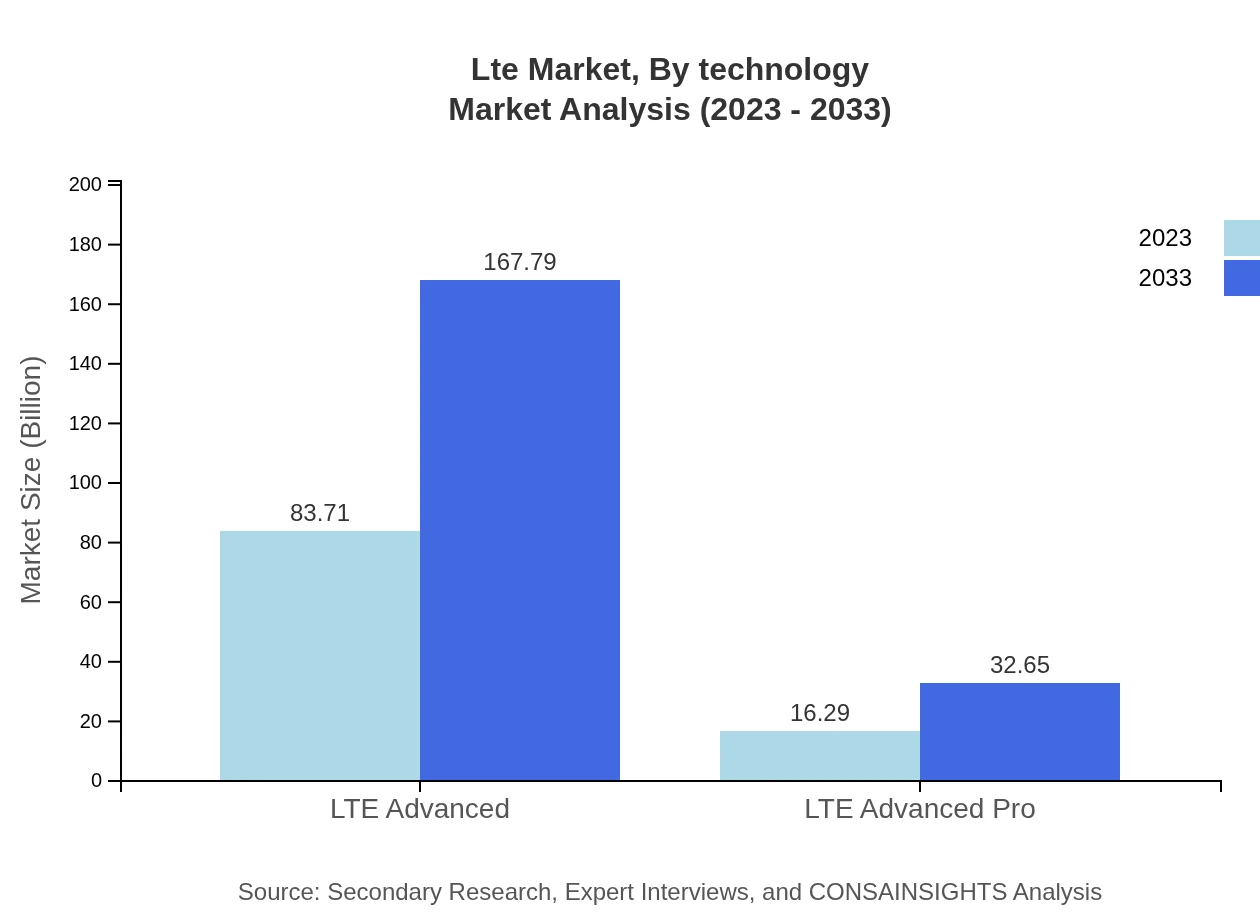
Lte Market Analysis By Technology
The LTE market, categorized by technology, highlights increasing adoption of LTE Advanced and Pro. LTE Advanced is crucial for operators seeking to enhance capacity and coverage, catering to the growing demand for high-speed data. LTE Pro, evolving into 5G, illustrates the subsequent phase of LTE development, enabling higher speeds and lower latency, critical for new applications.
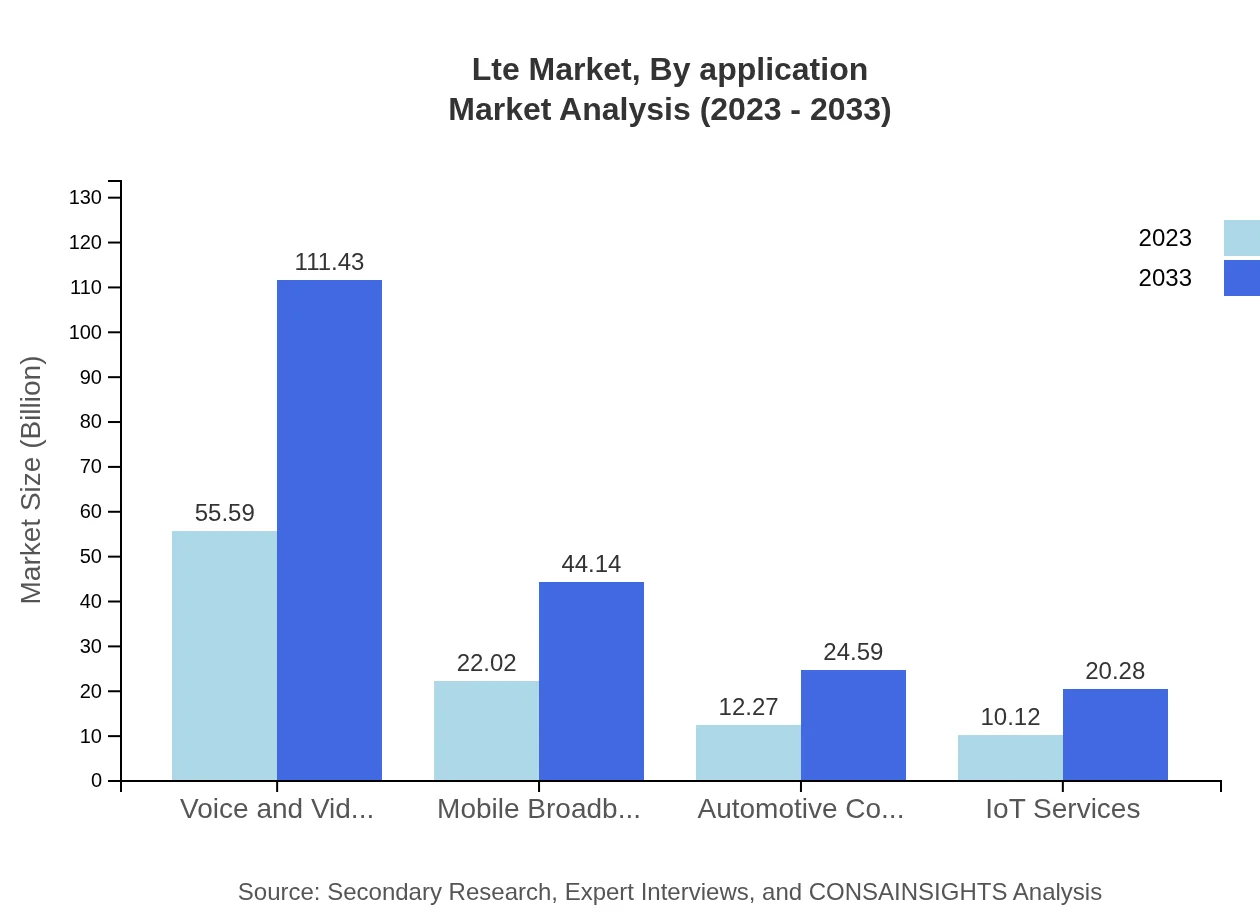
Lte Market Analysis By Application
Application-wise, mobile broadband encompasses the largest share of the LTE market, propelled by consumer demand for internet access on-the-go. Voice and video services continue to gain relevance with the rise of video conferencing and streaming platforms, while IoT services are emerging quickly, positioning LTE as a foundational technology for smart devices and applications.
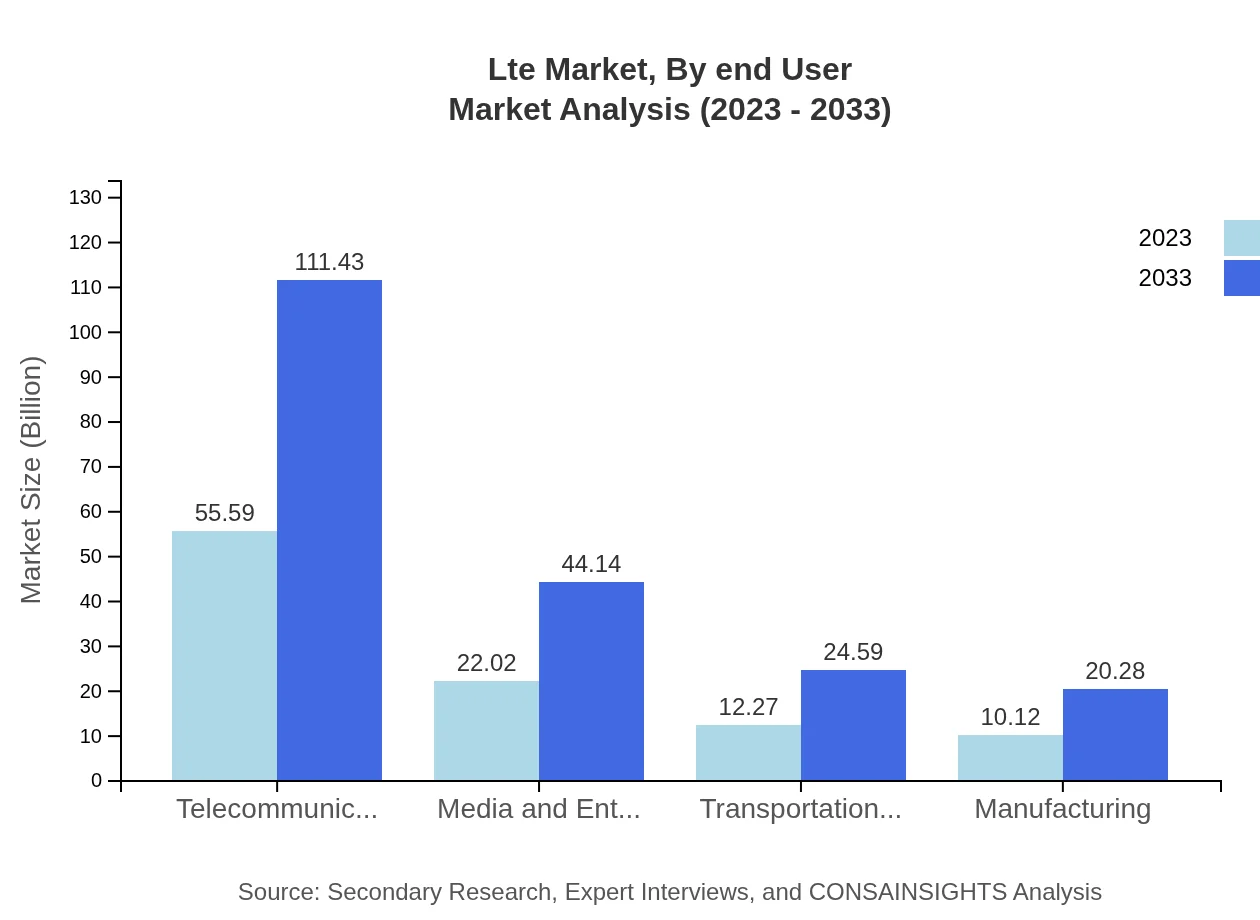
Lte Market Analysis By End User
End-user segmentation reveals telecommunications as the predominant sector in the LTE landscape, followed by media and entertainment, which relies on high-speed networks to deliver rich content. The growing prominence of industries like transportation and logistics reflects LTE's role in enabling real-time data analytics and operational efficiency.
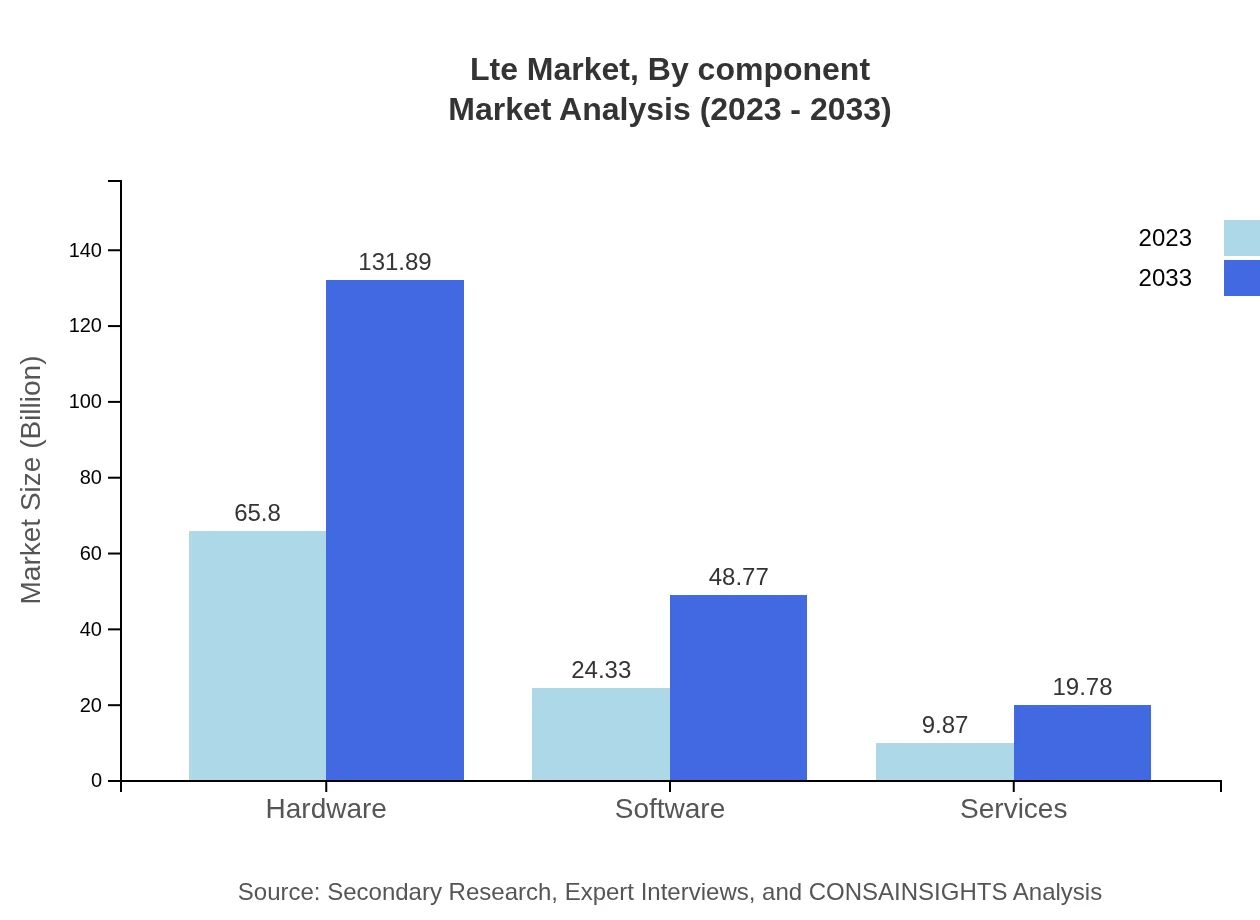
Lte Market Analysis By Component
In the LTE market, hardware dominates the component space, driven by infrastructure build and upgrade requirements. The software segment is also vital, particularly for network management tools, while services related to LTE deployment continue to play an essential role in ensuring quality and efficiency in network operations.
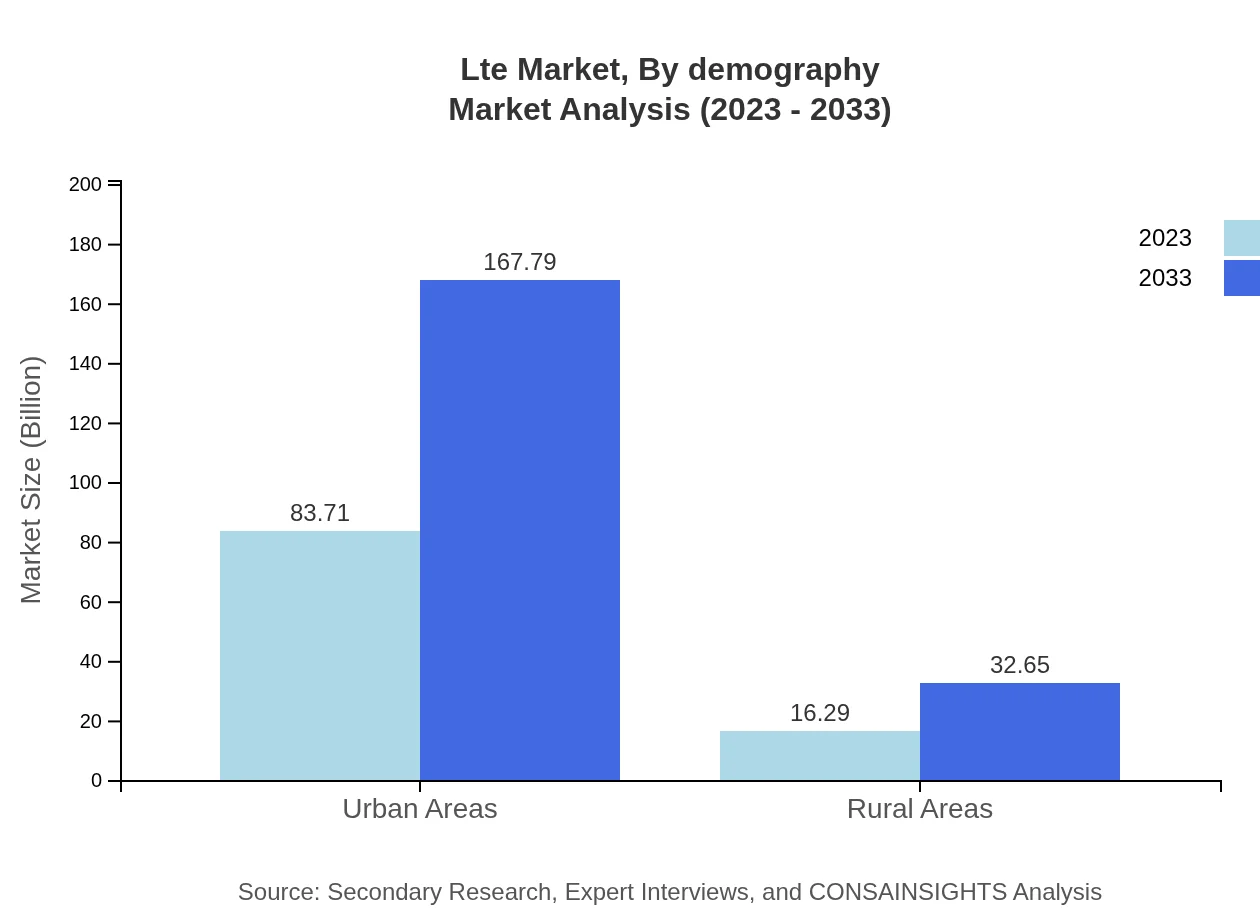
Lte Market Analysis By Demography
Demographically, urban areas exhibit significantly higher LTE usage due to better infrastructure, while rural deployment is gaining attention as service providers look to bridge the digital divide. The differences in usage patterns between these regions are crucial for shaping market strategies.
LTE Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in LTE Industry
Ericsson :
Ericsson is a leading telecommunications company focused on network infrastructure and services, known for its advancements in LTE technology and strong presence in 5G development.Nokia :
Nokia provides comprehensive solutions in mobile broadband networks and is recognized for its innovations in LTE infrastructure, enhancing connectivity across different markets.Qualcomm :
Qualcomm leads in semiconductor technology and has been pivotal in LTE evolution, providing essential chipsets that power mobile devices and advanced wireless communication.Huawei :
Huawei is a major player in telecommunications and ICT infrastructure, contributing significantly to LTE network deployments globally with innovative products.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of LTE?
The global LTE market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023, with a strong growth projection leading to an estimated market size of over $200 billion by 2033. This indicates a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 7%.
What are the key market players or companies in the LTE industry?
Key market players in the LTE industry include major telecommunications companies such as Ericsson, Nokia, and Huawei. Additionally, mobile operators like Verizon, AT&T, and China Mobile play significant roles, actively investing in expanding LTE infrastructure.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the LTE industry?
The growth of the LTE industry is primarily driven by the increasing demand for high-speed internet, the expansion of mobile broadband services, and the rise of IoT applications. Furthermore, advancements in smartphone technology and mobile applications significantly contribute to market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the LTE market?
Asia Pacific is currently the fastest-growing region in the LTE market, with a projected increase from $19.34 billion in 2023 to $38.77 billion by 2033. Europe and North America also show significant growth, particularly in urban areas.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the LTE industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the LTE industry. Clients can request detailed analysis based on unique parameters such as market segments, regional insights, and competitive landscape.
What deliverables can I expect from this LTE market research project?
Deliverables for the LTE market research project typically include detailed market reports, segmentation analysis, competitive landscape assessments, and growth forecasts. Additionally, clients receive actionable insights and strategic recommendations.
What are the market trends of LTE?
Current market trends in the LTE sector include increasing investment in 5G technology, the growth of mobile broadband applications, and the expansion of LTE-A technology. There are also rising consumer demands for high-speed internet services driving innovation.