Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: marine-propulsion-engine
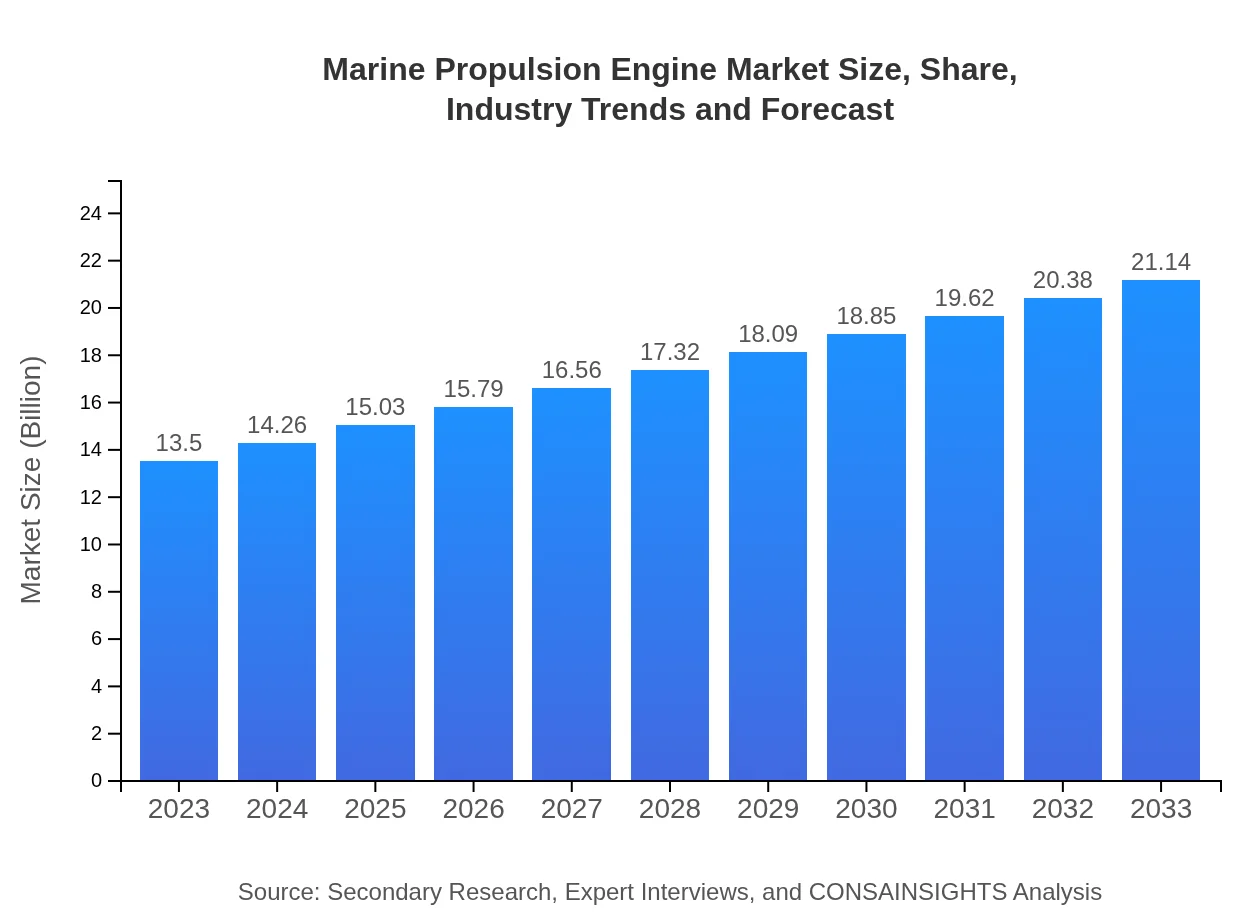
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report analyzes the Marine Propulsion Engine market from 2023 to 2033, providing insights on market trends, segments, and forecasts while assessing the impact of technological advancements and regulatory changes.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $13.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $21.14 Billion |
| Top Companies | Wärtsilä Corporation, MAN Energy Solutions, Rolls-Royce Holdings plc |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Overview
Customize Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Marine Propulsion Engine market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Marine Propulsion Engine's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Marine Propulsion Engine
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Marine Propulsion Engine market in 2033?
Marine Propulsion Engine Industry Analysis
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report:
Europe is a significant market for marine propulsion engines, estimated at $3.38 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $5.29 billion by 2033. The region is focused on strict environmental regulations promoting the transition to alternative fuels and technologies, with a notable emphasis on reducing carbon footprints.Asia Pacific Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is one of the largest markets for marine propulsion engines, valued at $2.68 billion in 2023 and projected to grow to $4.19 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing shipping activities, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, alongside a significant focus on developing eco-friendly engines.North America Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report:
North America has a robust marine engine market, projected to expand from $4.63 billion in 2023 to $7.26 billion by 2033. The US’s strong maritime economy, alongside federal regulations pushing for lower emissions, propels investment in sustainable propulsion technologies.South America Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report:
In South America, the market is smaller but growing, expected to rise from $1.14 billion in 2023 to $1.78 billion by 2033. The region's expanding fishing industry and investment in maritime infrastructure are driving demand.Middle East & Africa Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market, valued at $1.67 billion in 2023, is set to grow to $2.62 billion by 2033. Increased investments in naval capabilities and commercial shipping drive the demand for propulsion engines in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
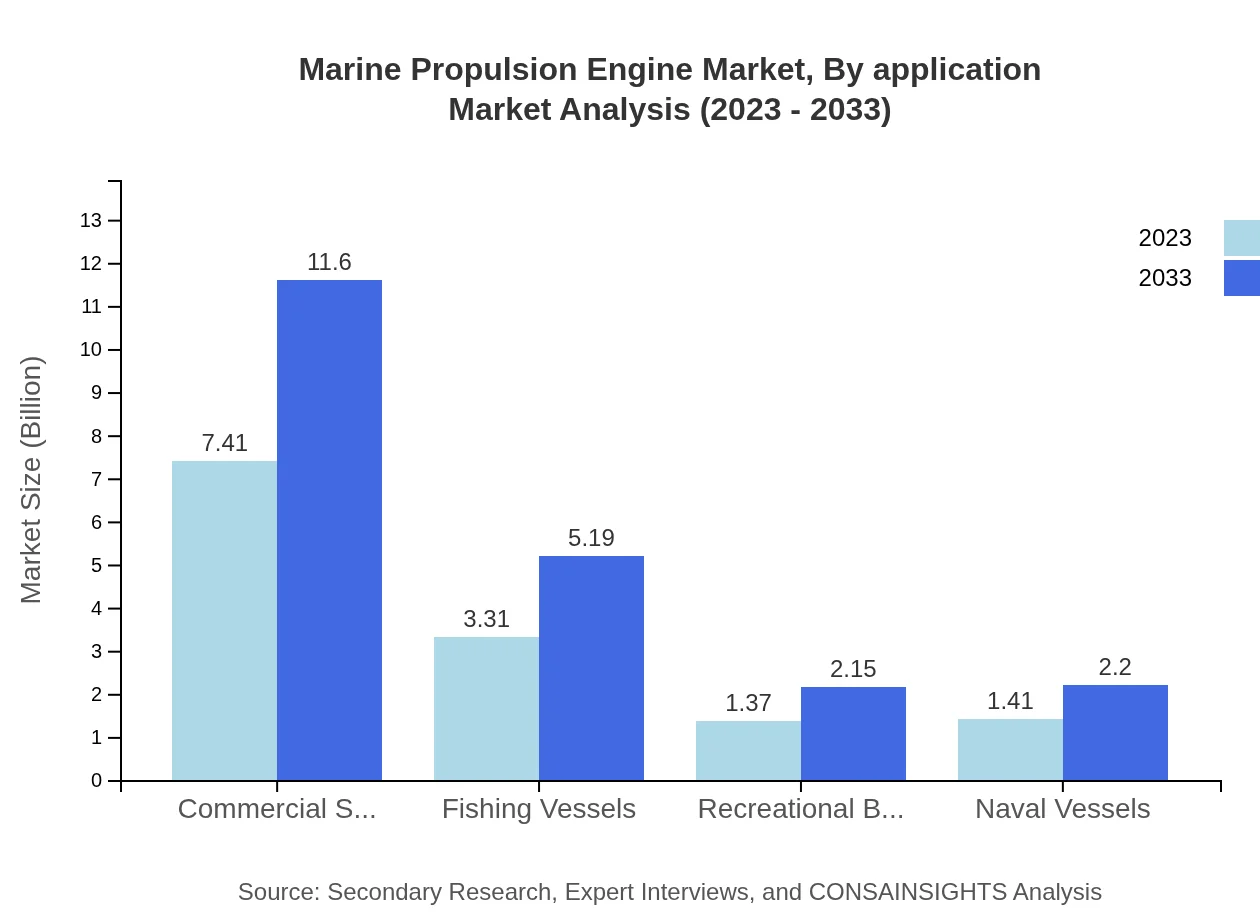
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Analysis By Application
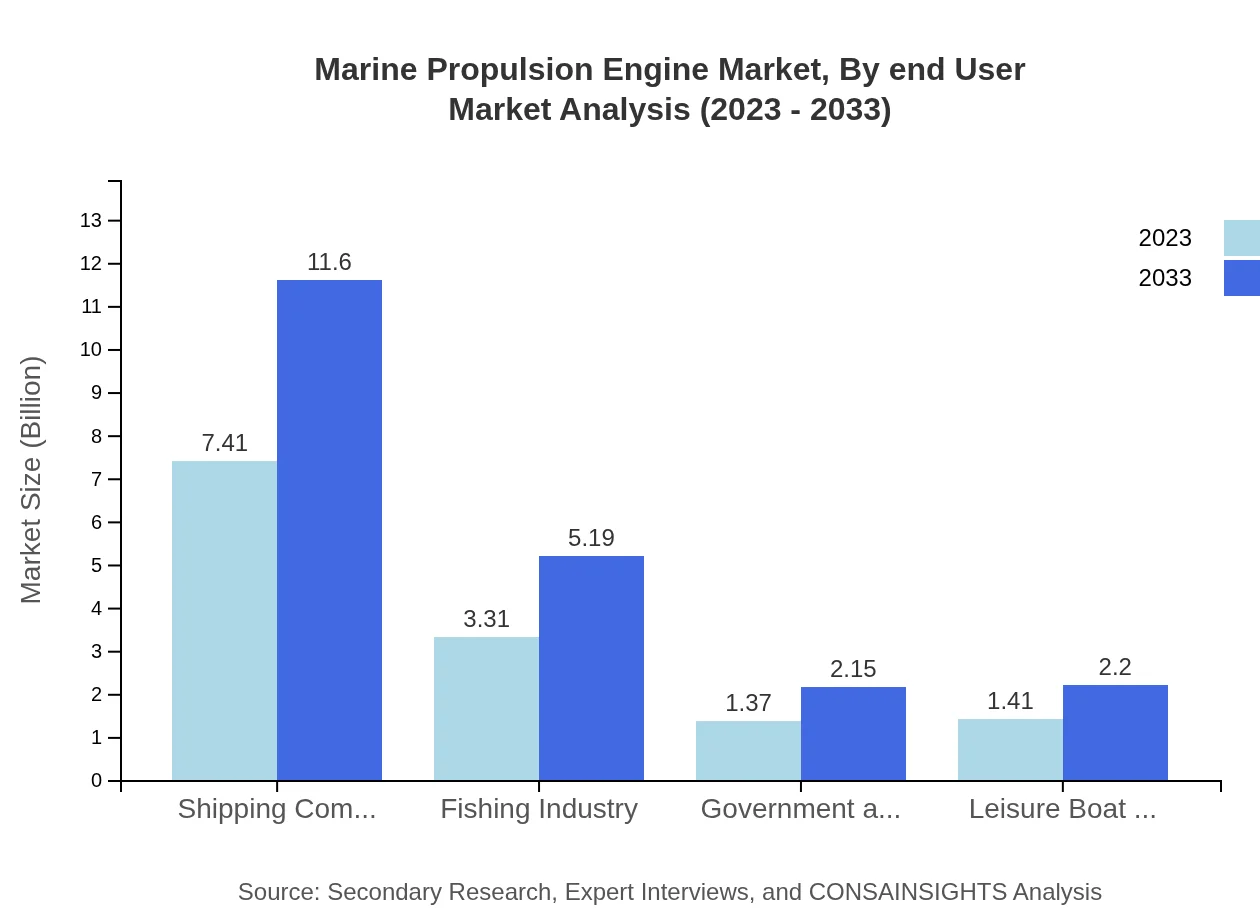
The application segment reveals that commercial shipping accounts for a majority share of the marine propulsion engine market, valued at $7.41 billion in 2023, growing to $11.60 billion by 2033, maintaining a 54.87% market share. The fishing industry also shows significant potential, growing from $3.31 billion in 2023 to $5.19 billion by 2033 (24.54% share). Government and military applications are expected to grow from $1.37 billion to $2.15 billion, while leisure boats anticipate growth from $1.41 billion to $2.20 billion.
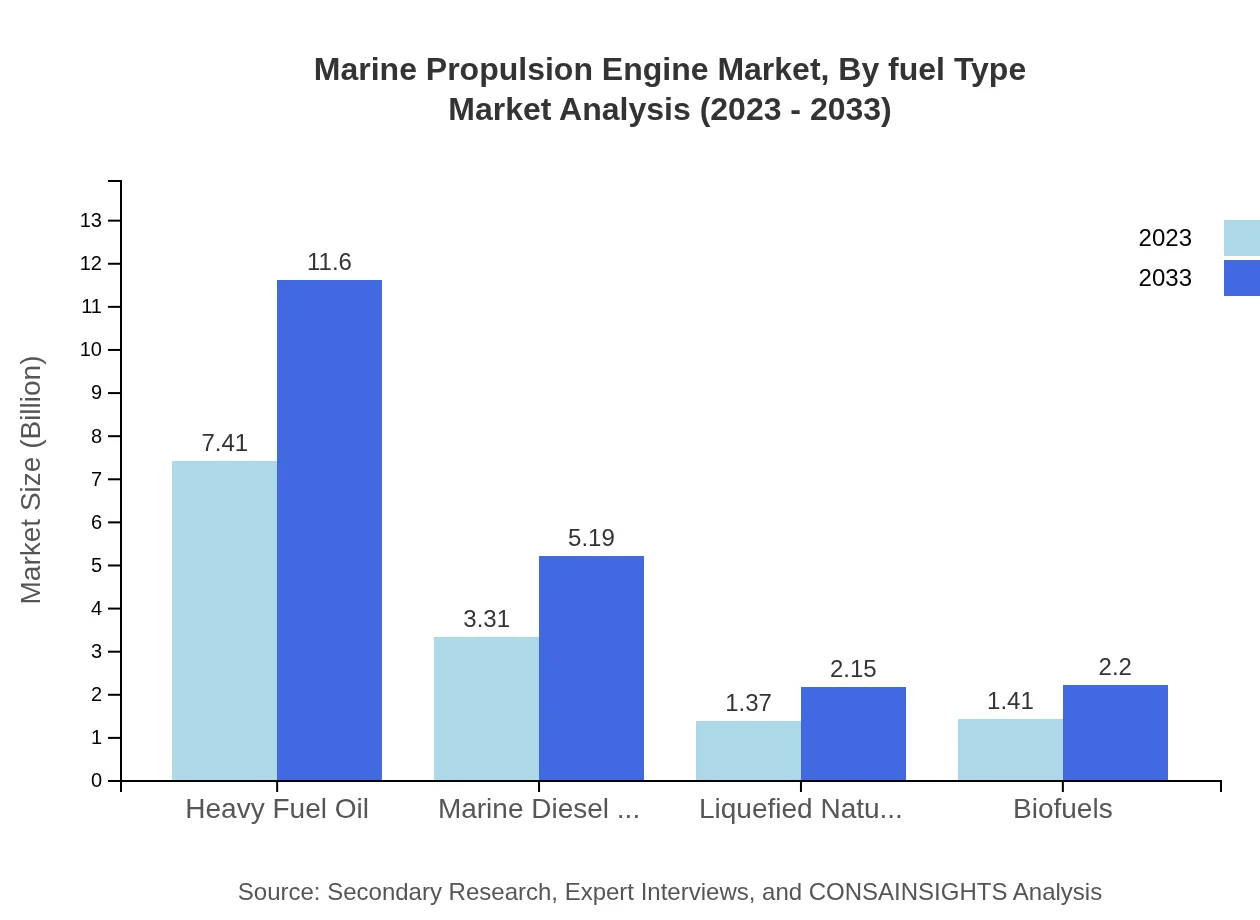
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Analysis By Fuel Type
Heavy fuel oil remains a dominant segment, estimated to hold a substantial share of 54.87% in 2023 and projected to grow accordingly. Marine diesel oil will follow, expanding from $3.31 billion to $5.19 billion. In contrast, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is gaining ground due to its environmental benefits, with growth anticipated from $1.37 billion to $2.15 billion by 2033, alongside biofuels gaining traction in the sector.
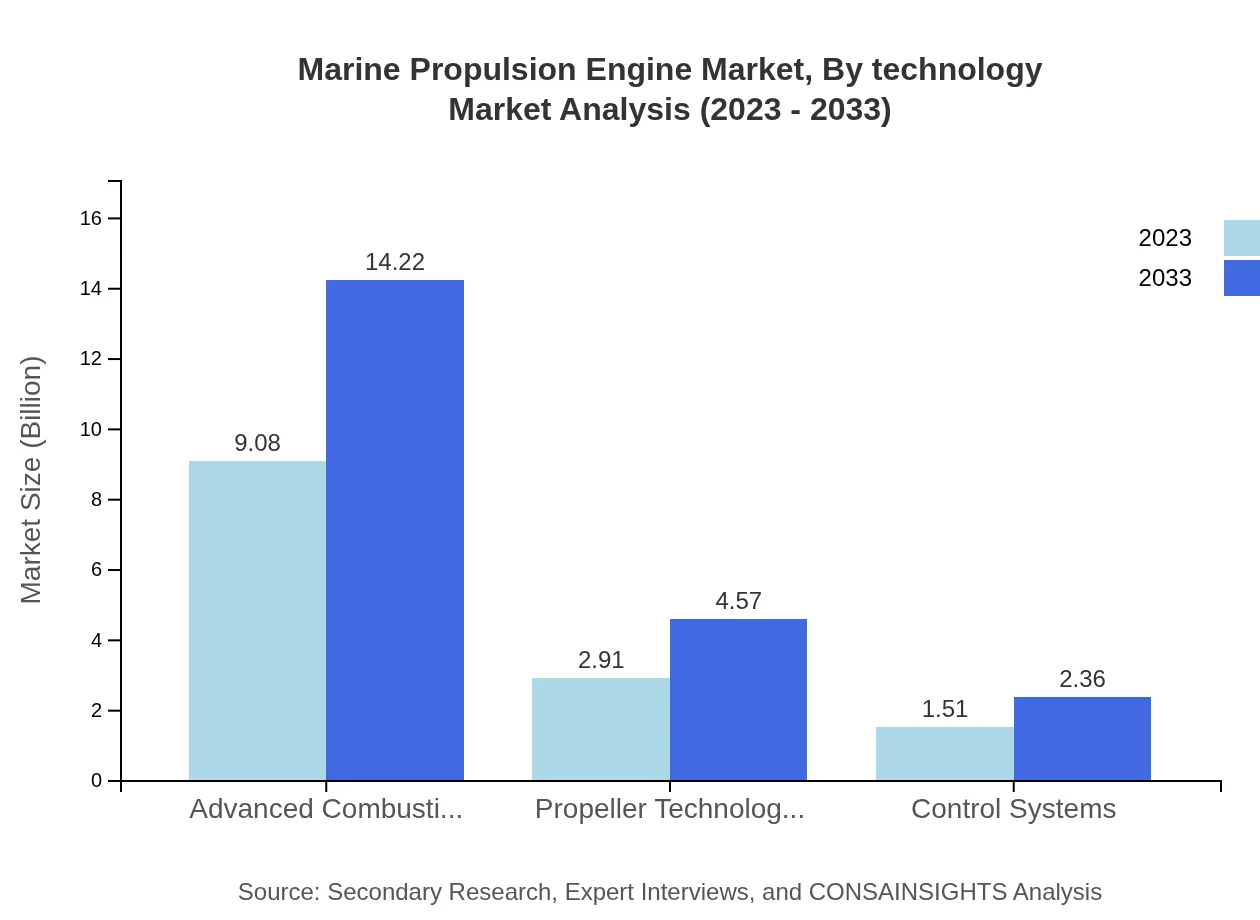
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements are transforming the marine propulsion landscape. Advanced combustion technologies represent a substantial market segment valued at $9.08 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $14.22 billion by 2033 (67.24% share). Electric propulsion systems and hybrid systems are becoming increasingly prevalent, with respective market sizes of $2.91 billion and $1.51 billion in 2023 growing significantly to address environmental impacts.
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Analysis By End User
End-users predominantly include commercial shipping and the fishing vessel sector. Commercial shipping holds a significant portion of the market, reflective of high demand for efficient and reliable propulsion. The fishing industry, although smaller, represents a vital segment fostering growth through advancements in engine technologies and performance.
Marine Propulsion Engine Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Marine Propulsion Engine Industry
Wärtsilä Corporation:
A leading global provider of marine propulsion solutions, Wärtsilä specializes in innovation and sustainability in engine technology, focusing on reducing environmental impact while enhancing performance.MAN Energy Solutions:
Known for their robust engineering capabilities, MAN Energy Solutions delivers a wide range of marine propulsion engines, emphasizing high efficiency and low emissions as part of their strategic goals.Rolls-Royce Holdings plc:
A prominent player in the marine propulsion market, Rolls-Royce is recognized for its advanced technologies in marine engines, contributing to the development of sustainable and flexible propulsion systems.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of marine Propulsion Engine?
The marine propulsion engine market is projected to reach a size of $13.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.5%. This growth signals significant expansion within the industry, driven by increased demand for advanced marine technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in the marine Propulsion Engine industry?
The marine propulsion engine industry consists of numerous key players, including leading manufacturers and innovators specializing in environments like shipping, fishing, and military, contributing to technological advancements and market growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the marine Propulsion Engine industry?
Driving factors for growth in the marine propulsion engine market include rising global trade, increasing demand for efficient marine vessels, advancements in propulsion technologies, and regulatory pressures for lower emissions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the marine Propulsion Engine market?
The fastest-growing region in the marine propulsion engine market is North America, projected to expand from $4.63 billion in 2023 to $7.26 billion by 2033, reflecting a strong focus on maritime industry advancements and innovation.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the marine Propulsion Engine industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data specifically for the marine propulsion engine industry, providing clients with insights and analysis based on their unique specifications, enabling informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this marine Propulsion Engine market research project?
In this marine propulsion engine market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth trends, competitive landscape, regional analysis, and insights into customer segments and technological advancements.
What are the market trends of marine Propulsion Engine?
Key trends in the marine propulsion engine market include a shift towards hybrid and electric propulsion systems, increasing adoption of advanced combustion technologies, and rising investments in sustainable and efficient marine operations.