Micro Inverter Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: micro-inverter
Micro Inverter Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a detailed analysis of the Micro Inverter market, focusing on its size, growth projections, technology advancements, and regional insights from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
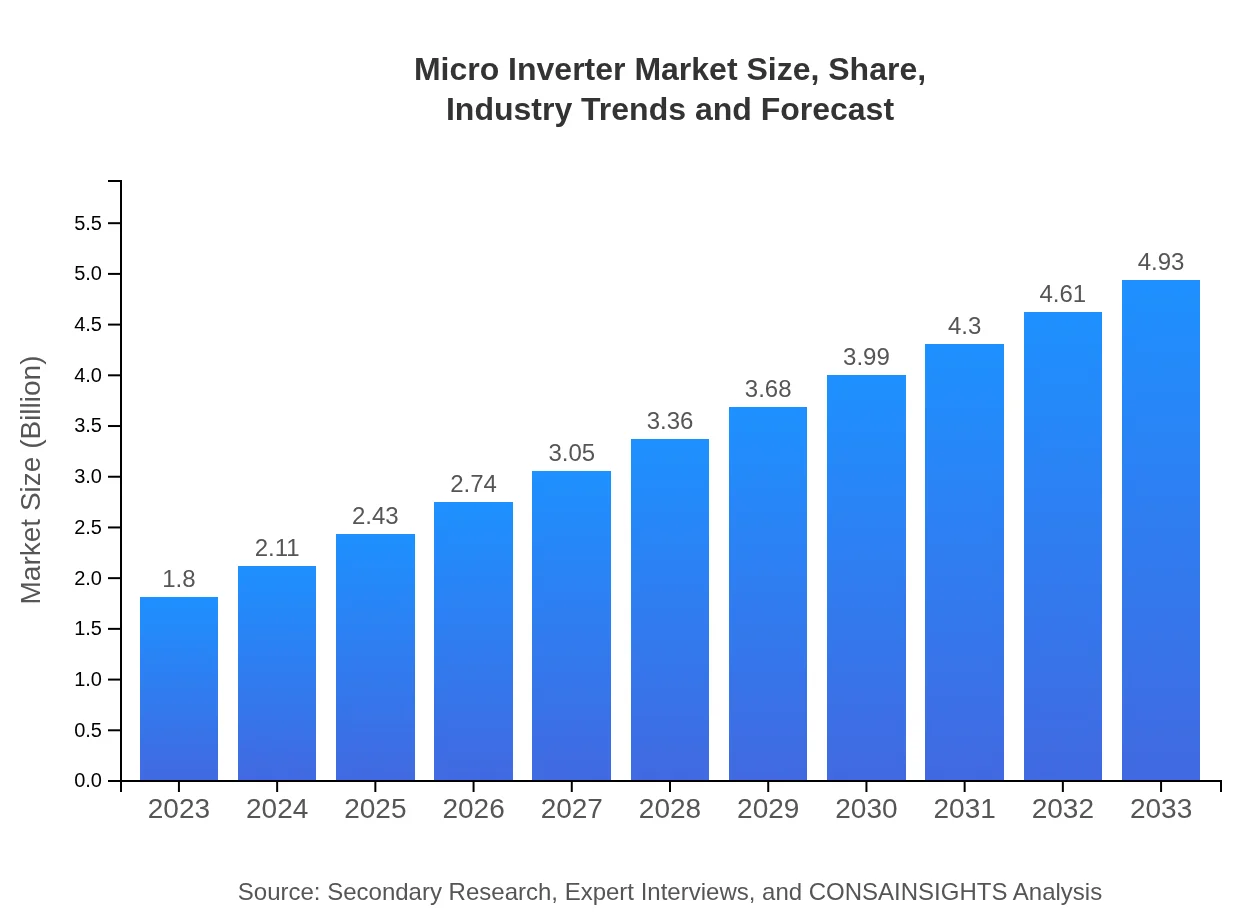
| 2023 Market Size | $1.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $4.93 Billion |
| Top Companies | Enphase Energy, SMA Solar Technology AG, Fronius International GmbH, SolarEdge Technologies |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Micro Inverter Market Overview
Customize Micro Inverter Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Micro Inverter market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Micro Inverter's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Micro Inverter
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Micro Inverter market in 2023?
Micro Inverter Industry Analysis
Micro Inverter Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Micro Inverter Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Micro Inverter Market Report:
Europe's micro inverter market, valued at 0.51 billion USD in 2023, is expected to reach 1.39 billion USD by 2033. The market's expansion is driven by the EU's aggressive targets for renewable energy generation and energy efficiency.Asia Pacific Micro Inverter Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region, valued at 0.35 billion USD in 2023 and projected to grow to 0.96 billion USD by 2033, is a key area for micro inverter deployments, driven by rapid urbanization and increased investment in solar infrastructure across countries like China and India.North America Micro Inverter Market Report:
North America is set to witness a significant rise in the micro inverter market, increasing from 0.59 billion USD in 2023 to 1.60 billion USD in 2033. Factors contributing to this increase include stringent regulatory mandates for renewable energy and growing residential solar installations.South America Micro Inverter Market Report:
In South America, the micro inverter market is expected to demonstrate growth from 0.12 billion USD in 2023 to 0.34 billion USD in 2033. The region's abundant solar resources and favorable governmental policies foster the adoption of solar technologies.Middle East & Africa Micro Inverter Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is experiencing growth in the micro inverter market, projected to increase from 0.23 billion USD in 2023 to 0.64 billion USD by 2033. Rising energy demands and efforts to diversify energy sources enhance the relevance of solar technologies in this region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
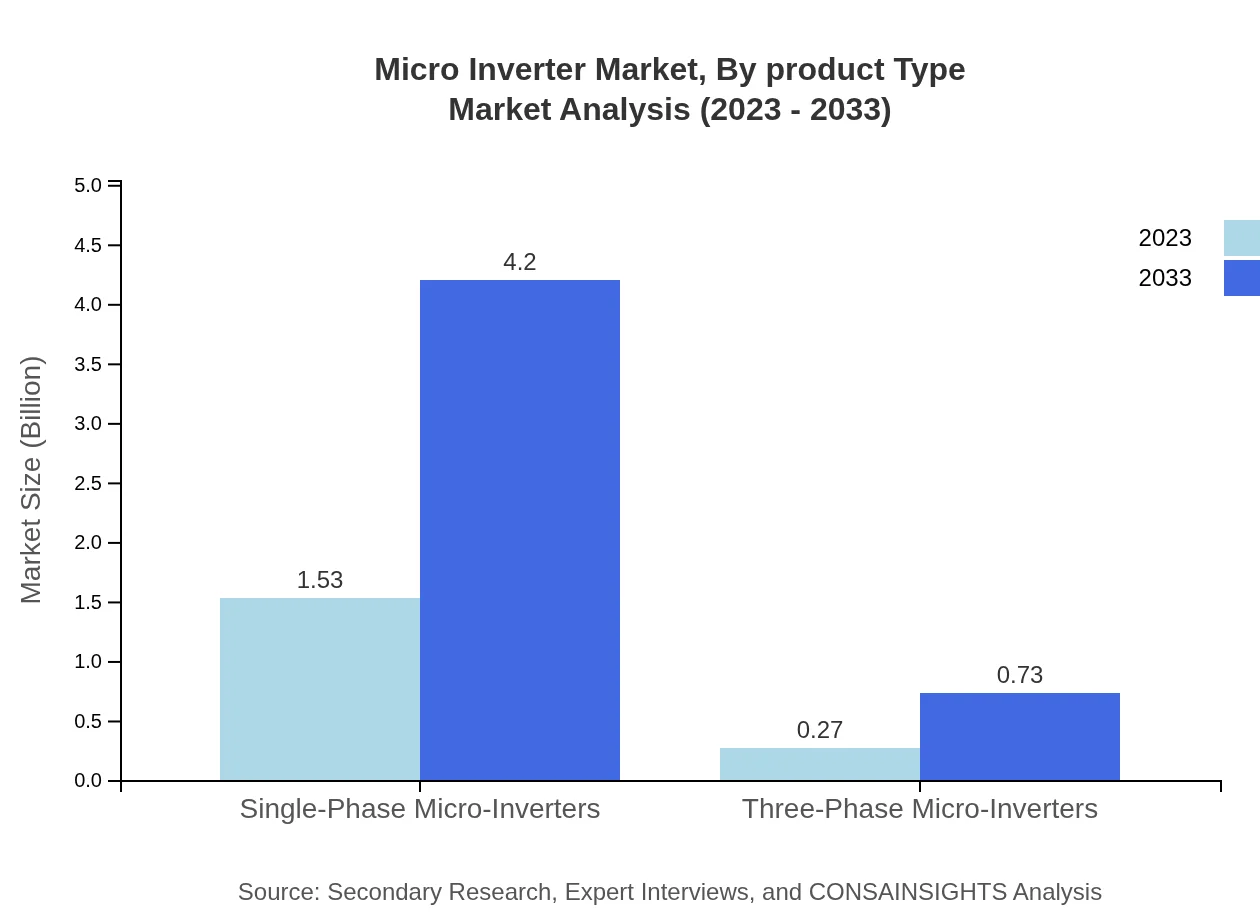
Micro Inverter Market Analysis By Product Type
In the Micro-Inverter market, single-phase micro-inverters dominate with a market size of 1.53 billion USD in 2023, expected to grow to 4.20 billion USD by 2033, representing 85.27% share. Three-phase systems, while less dominant, are also witnessing increasing adoption due to their applications in larger commercial solar installations.
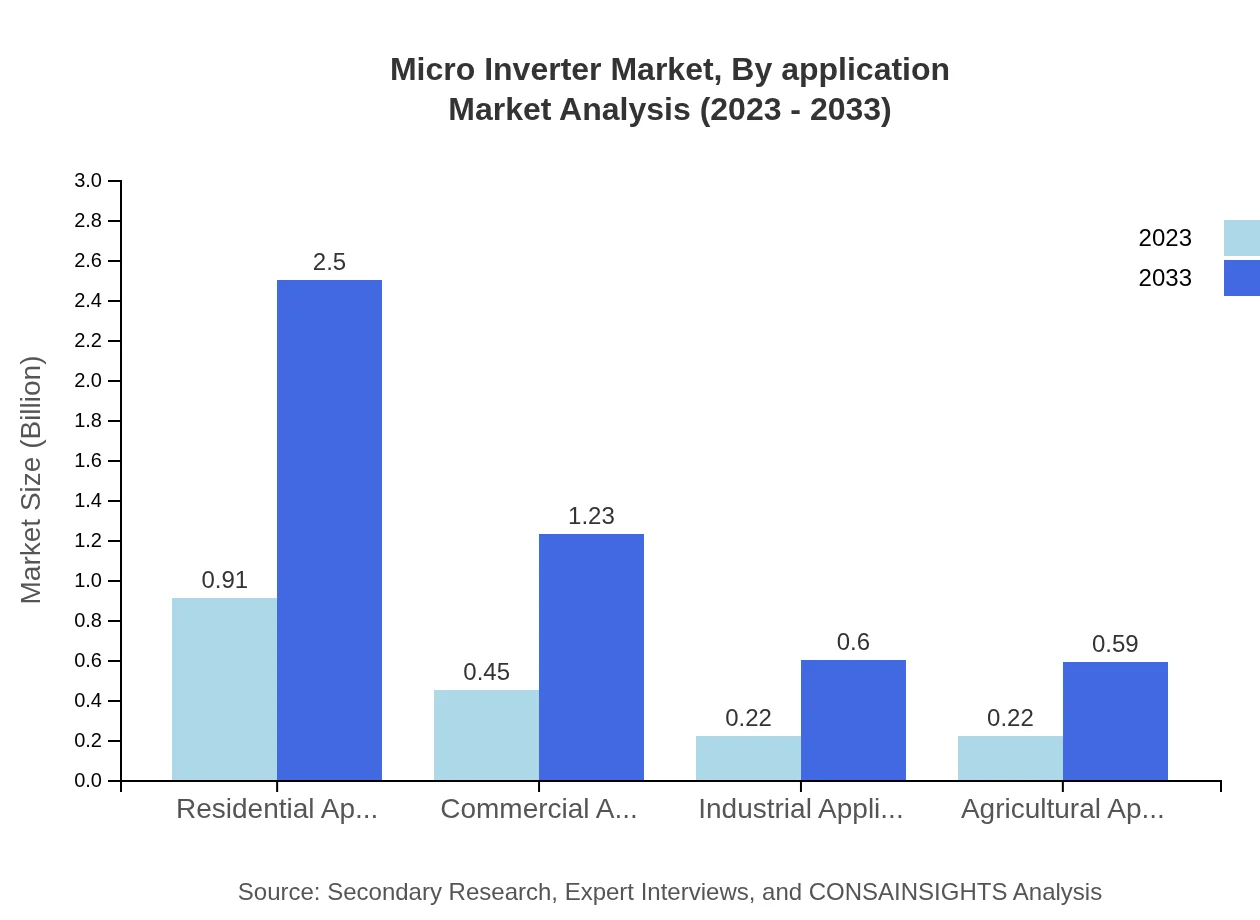
Micro Inverter Market Analysis By Application
Residential applications account for a significant portion of the market share, valued at 0.91 billion USD in 2023 and expected to reach 2.50 billion USD by 2033 (50.83% share). Commercial and industrial applications are also growing steadily, with robust projected growth due to rising energy needs in those sectors.
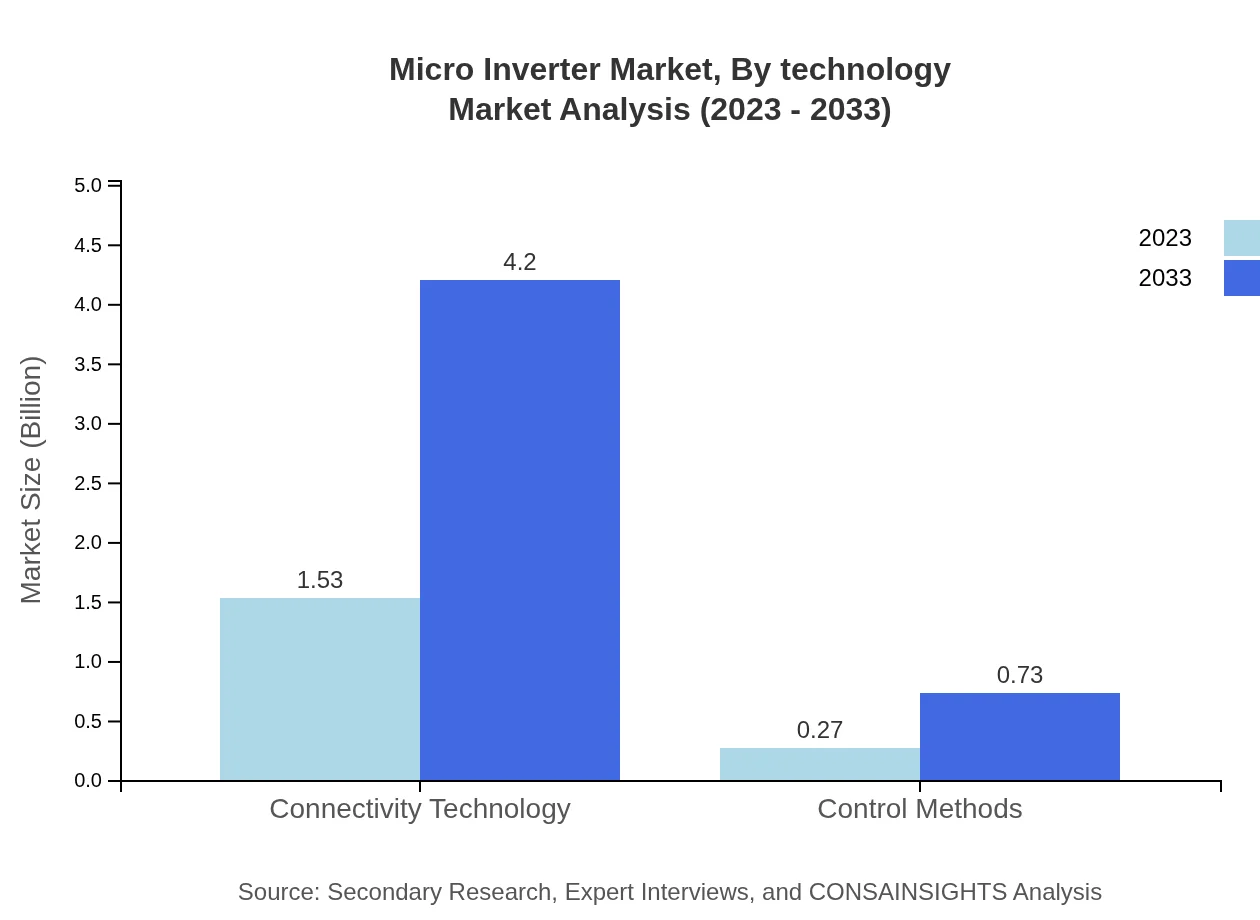
Micro Inverter Market Analysis By Technology
Connectivity technology is a key segment with a market size of 1.53 billion USD in 2023 and anticipated growth to 4.20 billion USD by 2033 (85.27% share), highlighting the importance of remote monitoring and control capabilities in micro inverter function.
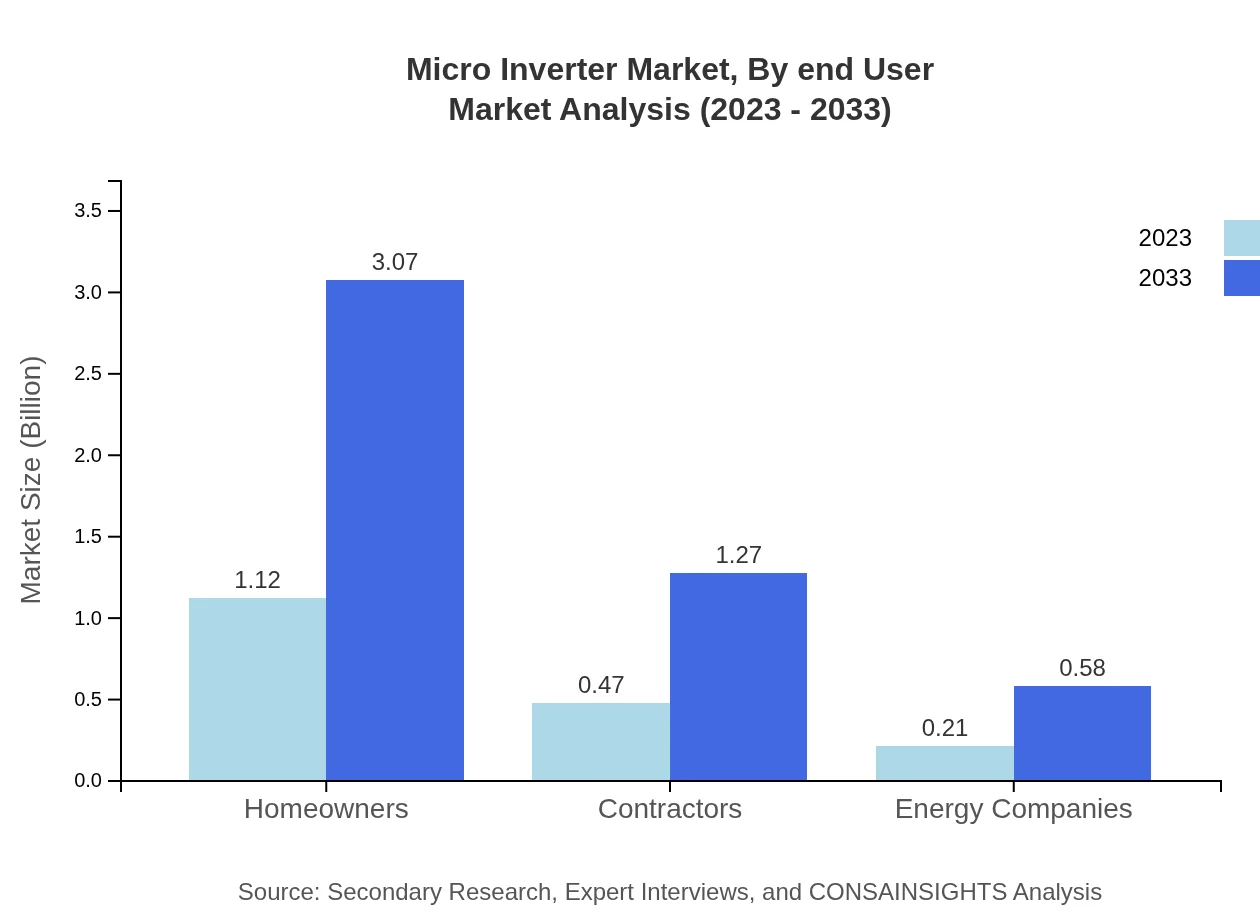
Micro Inverter Market Analysis By End User
The end-user distribution shows a strong inclination towards homeowners, capturing a market size of 1.12 billion USD in 2023 and expected to grow to 3.07 billion USD by 2033, reflecting a growing trend towards residential solar solutions.
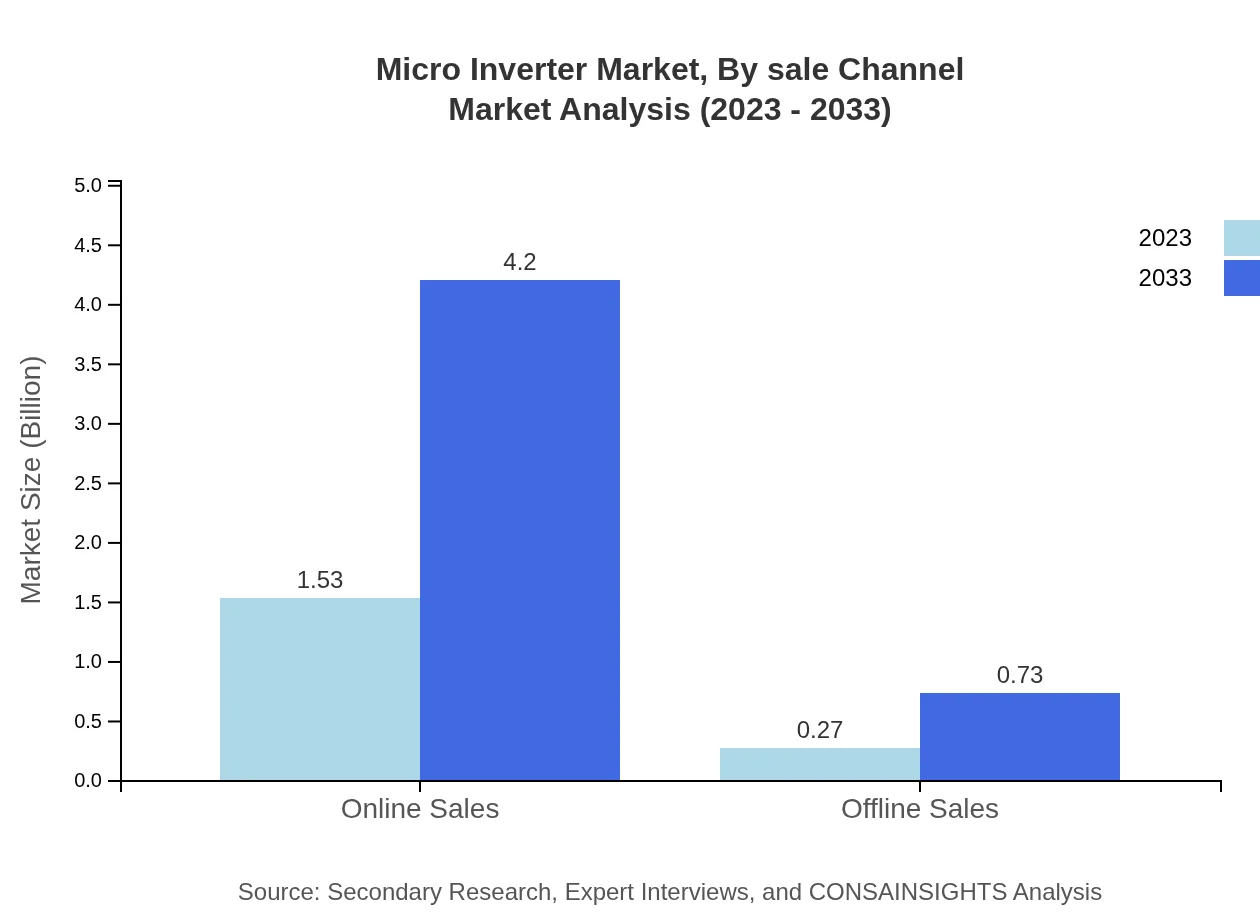
Micro Inverter Market Analysis By Sale Channel
Online sales dominate with a market size of 1.53 billion USD in 2023, expected to reach 4.20 billion USD by 2033, representing 85.27% of the market share. This shift towards online platforms underscores changing consumer purchasing behaviors and trends in the retail landscape.
Micro Inverter Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Micro Inverter Industry
Enphase Energy:
Enphase Energy is a leader in micro inverter technology, renowned for designing modern solar energy solutions that maximize energy production and performance monitoring.SMA Solar Technology AG:
SMA Solar Technology AG is a trusted name in the renewable energy market, offering a wide range of solar inverters, including innovative micro inverter solutions.Fronius International GmbH:
Fronius International is recognized for its cutting-edge solar technologies, including efficient micro inverters that cater to various market segments.SolarEdge Technologies:
SolarEdge Technologies leads the industry in providing optimized inverter solutions, enhancing energy efficiency and yield of solar installations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of micro Inverter?
The micro-inverter market is projected to reach approximately $1.8 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.2% during the period from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects increasing adoption of solar energy solutions globally.
What are the key market players or companies in this micro Inverter industry?
Key players in the micro-inverter industry include Enphase Energy, SolarEdge Technologies, and ABB, which are known for innovative solutions and strong distribution networks that drive market growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the micro Inverter industry?
Factors driving growth include the rising demand for renewable energy, government incentives for solar adoption, and advancements in micro-inverter technology that enhance efficiency and reliability.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the micro Inverter market?
North America is poised to be the fastest-growing region, projected to rise from $0.59 billion in 2023 to $1.60 billion by 2033, fueled by strong solar policy support and growing residential applications.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the micro Inverter industry?
Yes, Consainsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific inquiries within the micro-inverter industry, ensuring relevant insights for your strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this micro Inverter market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, trend identification, segmentation data, regional insights, and actionable recommendations to inform your investment and operational strategies.
What are the market trends of micro Inverter?
Current trends include increasing adoption of single-phase micro-inverters by homeowners, growth in online sales channels, and rising demand for connectivity and control technologies, shaping future developments.